Introduction
Challenges of Creative Teaching and Their Solutions Creative teaching involves using imaginative and innovative methods to inspire students and encourage active learning. While it brings numerous benefits, such as increased student engagement and improved problem-solving skills, creative teaching also comes with its unique set of challenges. Educators often struggle with balancing creativity and curriculum requirements, engaging diverse learners, managing time effectively, and accessing sufficient resources. This article explores these challenges in depth and offers practical solutions to overcome them.
1. Balancing Creativity with Curriculum Standards
Challenge:
One of the primary challenges of creative teaching is aligning innovative teaching methods with the strict standards and objectives set by educational curriculums. Teachers may feel constrained by the need to cover specific content, leaving little room for creative exploration.
Solution:
To balance creativity with curriculum standards, teachers can integrate creative activities that directly support the learning objectives. For example, project-based learning can allow students to explore subjects in depth while meeting curriculum goals. Teachers can also use formative assessments to monitor progress, ensuring that creative activities reinforce the required knowledge and skills. Flexibility in lesson planning, where educators identify core objectives and then creatively design how to achieve them, can also help maintain a balance.
2. Engaging a Diverse Range of Learners
Challenge:
Classrooms are often composed of students with varying abilities, interests, and learning styles. Implementing creative teaching methods that engage all students can be challenging. What works for one group of students may not resonate with another, leading to disengagement.
Solution:
Differentiated instruction is key to addressing this challenge. By tailoring lessons to meet the diverse needs of students, teachers can ensure that all learners are engaged. This could involve offering various types of creative assignments, such as visual projects, written work, or hands-on activities, to cater to different learning preferences. Additionally, incorporating student choice in activities can increase engagement by allowing students to explore topics that interest them in ways that suit their learning styles.
3. Time Management
Challenge:
Creative teaching methods often require more time to plan and execute than traditional teaching approaches. Activities such as group projects, experiments, and artistic endeavors can be time-consuming, making it difficult to cover all necessary material within the allotted time.
Solution:
Effective time management strategies can help educators overcome this challenge. Prioritizing key learning outcomes and designing creative activities that are focused and time-bound can ensure that essential content is covered. Teachers can also use a flipped classroom model, where students review basic content at home and spend class time on creative, in-depth activities. Breaking down larger creative projects into smaller, manageable tasks with clear deadlines can also help maintain progress without overwhelming students or teachers.
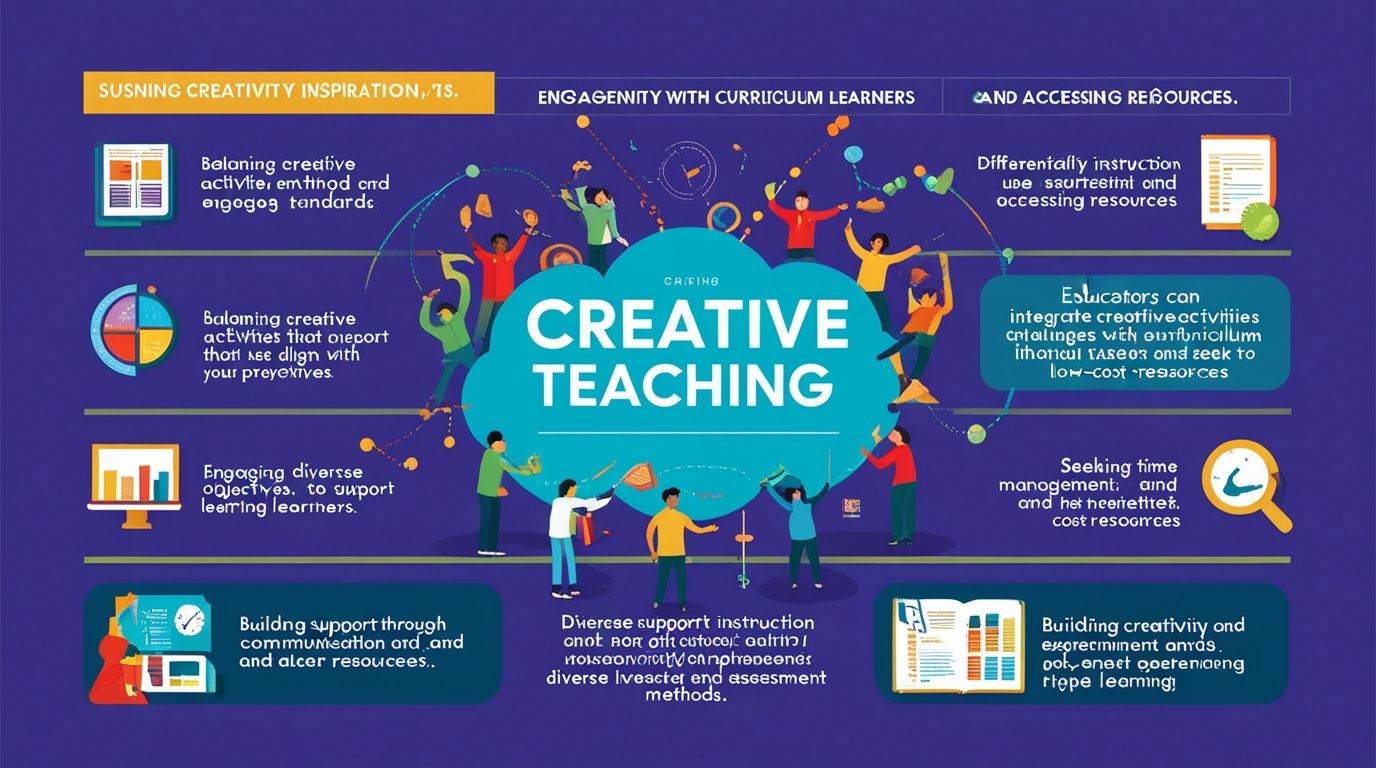
4. Access to Resources and Support
Challenge:
Creative teaching often requires resources that may not be readily available, such as art supplies, technology, or access to specific learning environments. Additionally, teachers may lack administrative support or professional development opportunities to explore and implement creative methods.
Solution:
Teachers can seek out low-cost or free resources to support creative teaching. Online platforms offer a wealth of tools, such as virtual labs, open educational resources, and creative commons materials. Collaboration with colleagues can also lead to resource sharing and joint planning of creative activities. Moreover, advocating for professional development opportunities that focus on creative teaching strategies can help educators gain the necessary skills and support. Schools can also create partnerships with local businesses or community organizations to access additional resources.
5. Overcoming Resistance to Change
Challenge:
Innovative teaching methods can sometimes meet resistance from students, parents, or even fellow educators who are accustomed to traditional approaches. This resistance can hinder the implementation of creative teaching strategies.
Solution:
To overcome resistance, it is important to communicate the benefits of creative teaching clearly. Educators can involve students and parents in the planning process, explaining how creative methods enhance learning outcomes and prepare students for real-world challenges. Demonstrating success through pilot projects or case studies can also help build support. Additionally, professional development sessions for staff can foster a school-wide culture that values and embraces creative teaching methods.
6. Evaluation of Creative Learning Outcomes
Challenge:
Assessing creative learning outcomes can be difficult, as traditional testing methods may not capture the depth and breadth of student learning that occurs through creative activities. Teachers may struggle to develop fair and comprehensive evaluation criteria for creative work.
Solution:
To evaluate creative learning effectively, teachers can use a combination of assessment methods. Rubrics that outline specific criteria for creativity, effort, and understanding can provide clear guidelines for both students and teachers. Peer assessment and self-reflection activities can also offer insights into student learning. Additionally, portfolio assessments, where students compile their work over time, can showcase their progress and creative achievements more holistically than traditional tests.

7. Sustaining Motivation and Creativity Over Time
Challenge:
Sustaining creativity in the classroom requires continuous effort and inspiration, both from teachers and students. The routine demands of teaching and learning can sometimes stifle creativity, leading to burnout or a return to more conventional methods.
Solution:
To maintain motivation and creativity, it is important for teachers to stay inspired and continuously seek new ideas. Professional learning communities, online forums, and educational conferences can provide fresh perspectives and innovative teaching strategies. Encouraging a classroom environment where experimentation is valued and mistakes are seen as learning opportunities can also keep creativity alive. Regularly refreshing the classroom setting, incorporating new tools, and allowing students to lead creative projects can help sustain enthusiasm and innovation throughout the school year.
Conclusion
Creative teaching, while challenging, offers immense benefits for student engagement, understanding, and development. By addressing challenges such as balancing creativity with curriculum standards, engaging diverse learners, managing time effectively, accessing resources, overcoming resistance, evaluating creative outcomes, and sustaining motivation, educators can create a dynamic and inclusive learning environment. The solutions discussed in this article provide a framework for overcoming these challenges, allowing teachers to successfully integrate creativity into their classrooms and enhance the educational experience for all students.

8 thoughts on “Challenges of Creative Teaching and Their Solutions”
Comments are closed.