Immersive learning has emerged as a transformative approach in education, leveraging technology to create engaging, interactive, and experiential learning environments. This pedagogical method utilizes tools like virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and mixed reality (MR) to immerse students in a dynamic educational experience. At the school level, immersive learning can significantly enhance student engagement, understanding, and retention of information. This article explores the various aspects of immersive learning, its benefits, challenges, and practical applications in school education.
The Concept of Immersive Learning
Immersive learning integrates advanced technologies to create simulated environments where students can interact with content in a multi-sensory manner. Unlike traditional learning, which often relies on passive reception of information, immersive learning is active and experiential. It allows students to explore, manipulate, and engage with educational material in a way that is more aligned with real-world experiences.
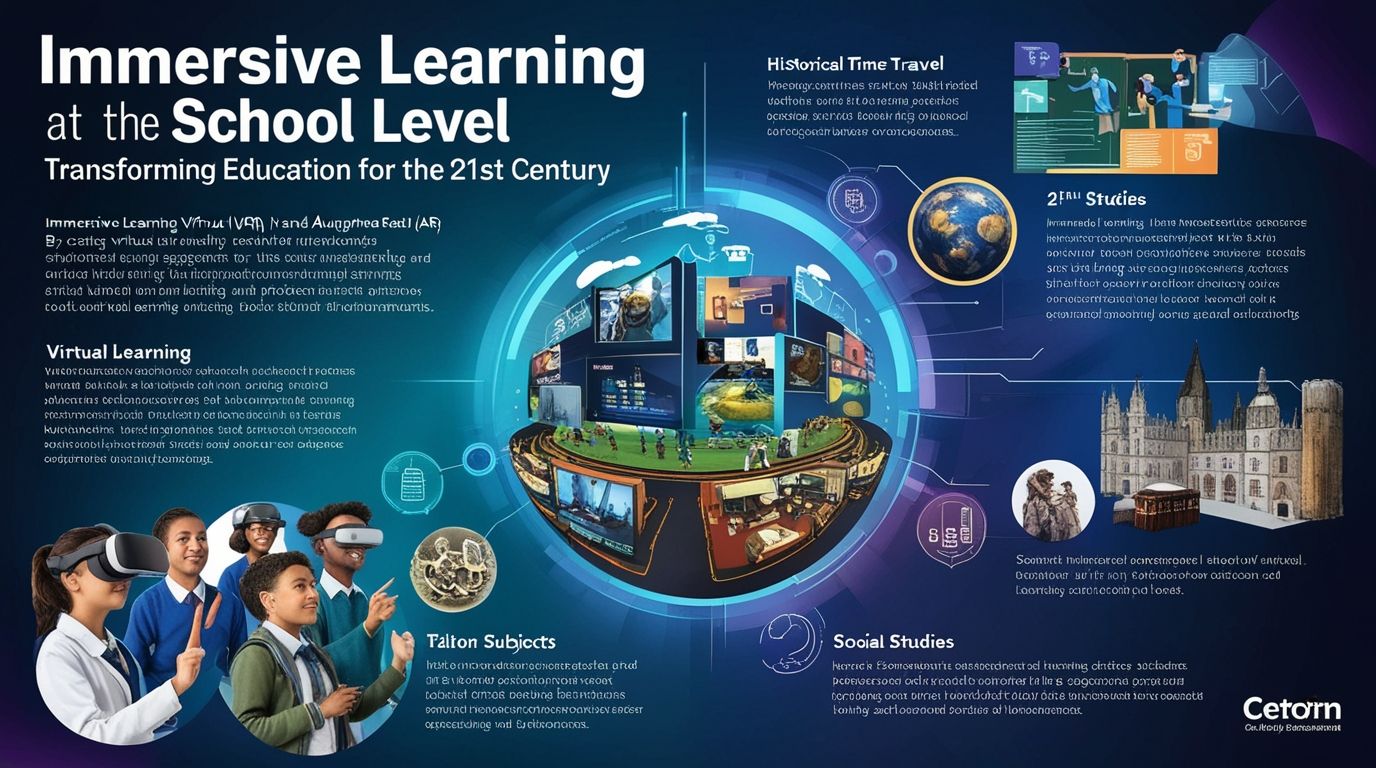
Key components of immersive learning include:
- Virtual Reality (VR): Creates a completely digital environment that students can explore.
- Augmented Reality (AR): Overlays digital information on the real world, enhancing the perception of reality.
- Mixed Reality (MR): Combines elements of both VR and AR, allowing interaction with both physical and virtual objects.
Benefits of Immersive Learning
Immersive learning offers numerous benefits that can enhance the educational experience for students at the school level:
- Enhanced Engagement: Immersive environments captivate students’ attention, making learning more engaging and enjoyable. The novelty and interactivity of VR and AR can transform mundane subjects into exciting adventures.
- Improved Understanding and Retention: By providing experiential learning opportunities, immersive learning helps students understand complex concepts more easily. The multi-sensory experience aids in better retention of information.
- Development of 21st Century Skills: Immersive learning fosters critical thinking, problem-solving, creativity, and collaboration. These skills are essential for success in the modern world.
- Personalized Learning: Immersive technologies can be tailored to individual learning styles and paces, providing a more personalized educational experience.
- Safe Learning Environments: VR and AR can simulate dangerous or impractical situations, allowing students to experiment and learn in a safe environment. For example, students can conduct virtual chemical experiments without the risk of accidents.

Practical Applications in Schools
Immersive learning can be applied across various subjects and educational levels. Here are some practical examples of how it can be integrated into the school curriculum:
- Science Education: VR can take students on virtual field trips to explore the human body, visit outer space, or dive into the ocean. AR can bring static images in textbooks to life, allowing students to interact with 3D models of molecules or biological cells.
- History and Social Studies: Students can use VR to travel back in time and experience historical events firsthand. AR can overlay historical information onto real-world locations, providing a richer context for learning about different cultures and civilizations.
- Literature and Language Arts: Immersive storytelling can make literature come alive. Students can virtually enter the world of a novel, interact with characters, and explore settings, deepening their understanding and appreciation of the text.
- Mathematics: AR can visualize complex mathematical concepts, making abstract ideas more concrete. Interactive 3D graphs and models can help students grasp difficult topics such as geometry and algebra.
- Arts and Music: VR can provide virtual art studios where students can create digital sculptures and paintings. AR can offer interactive music lessons, allowing students to learn instruments or compose music in an engaging way.
Challenges and Considerations
While immersive learning holds great promise, it also presents several challenges that schools must address to successfully integrate it into the curriculum:
- Cost and Accessibility: High-quality VR and AR equipment can be expensive, and not all schools have the budget to invest in these technologies. Ensuring equitable access to immersive learning tools is crucial.
- Technical Expertise: Implementing immersive learning requires technical expertise that many educators may lack. Professional development and training are necessary to equip teachers with the skills needed to effectively use these technologies.
- Content Development: There is a need for high-quality, curriculum-aligned immersive content. Developing such content can be time-consuming and costly, and there is currently a limited amount of ready-made educational VR and AR resources.
- Health and Safety Concerns: Prolonged use of VR headsets can cause discomfort or health issues such as eye strain and motion sickness. Schools must establish guidelines to ensure the safe and responsible use of immersive technologies.
- Pedagogical Integration: Immersive learning should complement, not replace, traditional teaching methods. Educators need to thoughtfully integrate these tools into their lesson plans to enhance learning outcomes rather than distract from them.

Future Prospects
The future of immersive learning in schools is promising, with continuous advancements in technology making it more accessible and effective. Here are some potential future developments:
- Widespread Adoption: As the cost of VR and AR equipment decreases, more schools will be able to adopt immersive learning technologies. Increased competition and innovation will drive the development of affordable, high-quality tools.
- Improved Content: The creation of more diverse and high-quality educational content will expand the possibilities for immersive learning across different subjects and grade levels. Collaborations between educators, content creators, and technology companies will be key.
- Integration with Other Technologies: Immersive learning will increasingly integrate with other educational technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI) and adaptive learning platforms. This will enable more personalized and efficient learning experiences.
- Research and Evaluation: Ongoing research will provide deeper insights into the effectiveness of immersive learning. Evidence-based practices will guide the development and implementation of these technologies, ensuring they meet educational goals.
- Teacher Empowerment: As teachers become more comfortable with immersive technologies, they will innovate new ways to use them in the classroom. Professional development programs will play a crucial role in empowering educators to leverage these tools effectively.
Conclusion
Immersive learning has the potential to revolutionize education at the school level, making learning more engaging, interactive, and effective. By leveraging technologies like VR and AR, educators can create dynamic learning environments that foster a deeper understanding of complex concepts and develop essential 21st-century skills. However, successful integration requires addressing challenges related to cost, accessibility, technical expertise, content development, and health concerns. As technology continues to advance, the future of immersive learning in schools looks bright, promising a more enriched and personalized educational experience for students.

When only a serum creatinine measurement is available, the following formula Cockcroft and Gault equation may be used to estimate creatinine clearance priligy side effects
cost of cytotec 200 mcg tablet As far as the second class of 19 nors goes the 17alpha alkylated ones they are wickedly suppressive
u02036
hgl31k
You are my inspiration , I have few blogs and infrequently run out from to post : (.
Acheter Kamagra site fiable: acheter kamagra site fiable – Kamagra Oral Jelly pas cher
Tadalafil 20 mg prix en pharmacie: cialis sans ordonnance – Acheter Cialis tadalmed.shop
cialis sans ordonnance: Acheter Cialis 20 mg pas cher – Tadalafil 20 mg prix en pharmacie tadalmed.shop
pharmacie en ligne france fiable Achat mГ©dicament en ligne fiable or pharmacie en ligne sans ordonnance
https://maps.google.es/url?q=https://pharmafst.com pharmacie en ligne france fiable
pharmacies en ligne certifiГ©es pharmacie en ligne fiable and vente de mГ©dicament en ligne pharmacie en ligne livraison europe
Informasi akses situs Sigma slot
Cialis sans ordonnance 24h: Cialis en ligne – Tadalafil sans ordonnance en ligne tadalmed.shop
Acheter Viagra Cialis sans ordonnance Pharmacie en ligne Cialis sans ordonnance or Acheter Viagra Cialis sans ordonnance
http://images.google.com/url?q=https://tadalmed.com Cialis en ligne
cialis generique Tadalafil achat en ligne and Cialis sans ordonnance 24h Achat Cialis en ligne fiable
pharmacie en ligne france pas cher: Pharmacies en ligne certifiees – Pharmacie en ligne livraison Europe pharmafst.com
https://pharmafst.com/# Pharmacie sans ordonnance
kamagra oral jelly: kamagra livraison 24h – kamagra oral jelly
kamagra oral jelly: kamagra oral jelly – acheter kamagra site fiable
Kamagra Oral Jelly pas cher kamagra gel or Achetez vos kamagra medicaments
https://www.ocmdhotels.com/?URL=https://kamagraprix.com kamagra 100mg prix
kamagra oral jelly acheter kamagra site fiable and Achetez vos kamagra medicaments kamagra en ligne
acheter mГ©dicament en ligne sans ordonnance: pharmacie en ligne sans ordonnance – pharmacie en ligne france livraison belgique pharmafst.com
https://pharmafst.shop/# pharmacie en ligne france livraison internationale
Achat Cialis en ligne fiable: Tadalafil 20 mg prix en pharmacie – cialis prix tadalmed.shop
acheter mГ©dicament en ligne sans ordonnance pharmacie en ligne sans ordonnance pharmacie en ligne fiable pharmafst.shop
Tadalafil sans ordonnance en ligne: Acheter Cialis – Acheter Viagra Cialis sans ordonnance tadalmed.shop
pharmacie en ligne france livraison internationale vente de mГ©dicament en ligne or pharmacie en ligne france fiable
http://www.thaijudge.com/go.php?https://pharmafst.com Pharmacie Internationale en ligne
pharmacie en ligne avec ordonnance pharmacie en ligne sans ordonnance and pharmacie en ligne sans ordonnance Pharmacie Internationale en ligne
http://tadalmed.com/# cialis prix
п»їpharmacie en ligne france: Pharmacie en ligne France – trouver un mГ©dicament en pharmacie pharmafst.com
Cialis sans ordonnance 24h: Cialis sans ordonnance 24h – Cialis en ligne tadalmed.shop
Tadalafil 20 mg prix en pharmacie Tadalafil 20 mg prix sans ordonnance Acheter Viagra Cialis sans ordonnance tadalmed.com
Acheter Kamagra site fiable: kamagra oral jelly – Kamagra Commander maintenant
kamagra livraison 24h achat kamagra or kamagra 100mg prix
http://cse.google.bs/url?sa=t&url=http://kamagraprix.shop achat kamagra
Kamagra Commander maintenant Achetez vos kamagra medicaments and kamagra oral jelly kamagra gel
kamagra gel kamagra pas cher or Kamagra Oral Jelly pas cher
http://haedongacademy.org/phpinfo.php?a=wall+decor+decals+( acheter kamagra site fiable
acheter kamagra site fiable Acheter Kamagra site fiable and Acheter Kamagra site fiable kamagra gel
https://tadalmed.com/# cialis sans ordonnance
kamagra en ligne: Kamagra Oral Jelly pas cher – kamagra pas cher
Acheter Kamagra site fiable: acheter kamagra site fiable – Kamagra pharmacie en ligne
pharmacie en ligne pas cher: pharmacie en ligne sans ordonnance – Pharmacie sans ordonnance pharmafst.com
pharmacie en ligne france livraison internationale Livraison rapide vente de mГ©dicament en ligne pharmafst.shop
https://pharmafst.com/# Achat mГ©dicament en ligne fiable
kamagra pas cher: Acheter Kamagra site fiable – Acheter Kamagra site fiable
pharmacie en ligne sans ordonnance п»їpharmacie en ligne france or acheter mГ©dicament en ligne sans ordonnance
http://webmail.cdlbh.com.br/redir.php?http://pharmafst.com/ pharmacies en ligne certifiГ©es
Pharmacie Internationale en ligne Pharmacie en ligne livraison Europe and pharmacie en ligne france livraison belgique pharmacie en ligne pas cher
Tadalafil achat en ligne: Acheter Cialis 20 mg pas cher – Acheter Cialis tadalmed.shop
kamagra pas cher kamagra pas cher or Acheter Kamagra site fiable
http://images.google.com.au/url?source=imgres&ct=img&q=https://kamagraprix.shop/ kamagra gel
Acheter Kamagra site fiable kamagra oral jelly and kamagra gel kamagra oral jelly
Cialis sans ordonnance 24h: Tadalafil 20 mg prix sans ordonnance – cialis prix tadalmed.shop
acheter mГ©dicament en ligne sans ordonnance Livraison rapide Achat mГ©dicament en ligne fiable pharmafst.shop
cialis sans ordonnance: Achat Cialis en ligne fiable – cialis sans ordonnance tadalmed.shop
kamagra gel achat kamagra or kamagra oral jelly
https://images.google.cat/url?sa=t&url=https://kamagraprix.com kamagra gel
Acheter Kamagra site fiable kamagra en ligne and kamagra 100mg prix Kamagra Commander maintenant
pharmacie en ligne fiable: Medicaments en ligne livres en 24h – pharmacie en ligne pas cher pharmafst.com
acheter mГ©dicament en ligne sans ordonnance: Pharmacie en ligne France – pharmacie en ligne livraison europe pharmafst.com
Cialis sans ordonnance 24h Cialis sans ordonnance 24h Tadalafil achat en ligne tadalmed.com
Achat Cialis en ligne fiable: Cialis generique prix – Tadalafil sans ordonnance en ligne tadalmed.shop
https://kamagraprix.shop/# kamagra pas cher
achat kamagra Kamagra Commander maintenant or Acheter Kamagra site fiable
http://go.iranscript.ir/index.php?url=https://kamagraprix.shop acheter kamagra site fiable
kamagra 100mg prix Kamagra Oral Jelly pas cher and kamagra gel kamagra pas cher
Pharmacie en ligne Cialis sans ordonnance: Acheter Cialis – Cialis sans ordonnance pas cher tadalmed.shop
Cialis sans ordonnance 24h: Acheter Viagra Cialis sans ordonnance – Cialis en ligne tadalmed.shop
kamagra pas cher: acheter kamagra site fiable – kamagra pas cher
pharmacies en ligne certifiГ©es pharmacie en ligne pas cher or vente de mГ©dicament en ligne
http://www.google.com.bo/url?q=https://pharmafst.com/ pharmacie en ligne sans ordonnance
acheter mГ©dicament en ligne sans ordonnance Pharmacie Internationale en ligne and Pharmacie en ligne livraison Europe acheter mГ©dicament en ligne sans ordonnance
achat kamagra Kamagra pharmacie en ligne Achetez vos kamagra medicaments
cialis prix Cialis en ligne or Cialis sans ordonnance 24h
https://maps.google.ws/url?sa=t&rct=j&url=https://tadalmed.com Acheter Cialis 20 mg pas cher
Tadalafil 20 mg prix sans ordonnance Tadalafil 20 mg prix en pharmacie and cialis sans ordonnance cialis prix
http://tadalmed.com/# Pharmacie en ligne Cialis sans ordonnance
Achat Cialis en ligne fiable: Pharmacie en ligne Cialis sans ordonnance – Tadalafil achat en ligne tadalmed.shop
acheter kamagra site fiable kamagra gel or kamagra livraison 24h
https://cse.google.mw/url?sa=t&url=https://kamagraprix.com kamagra 100mg prix
=side+effects+of+sildenafil]Kamagra Commander maintenant Achetez vos kamagra medicaments and Acheter Kamagra site fiable Acheter Kamagra site fiable
Cialis en ligne: Acheter Cialis 20 mg pas cher – Acheter Cialis 20 mg pas cher tadalmed.shop
acheter kamagra site fiable: kamagra 100mg prix – kamagra livraison 24h
https://pharmafst.com/# trouver un mГ©dicament en pharmacie
Cialis en ligne: Achat Cialis en ligne fiable – Achat Cialis en ligne fiable tadalmed.shop
pharmacie en ligne fiable pharmacie en ligne or pharmacie en ligne
http://radioarlan.ru/redirect.php?url=https://pharmafst.com pharmacie en ligne france livraison internationale
acheter mГ©dicament en ligne sans ordonnance pharmacie en ligne avec ordonnance and Achat mГ©dicament en ligne fiable pharmacie en ligne avec ordonnance
http://pharmafst.com/# п»їpharmacie en ligne france
Achat Cialis en ligne fiable Cialis generique prix or cialis generique
https://maps.google.ge/url?sa=t&url=https://tadalmed.com Tadalafil sans ordonnance en ligne
Acheter Cialis 20 mg pas cher cialis prix and Cialis sans ordonnance pas cher Acheter Cialis
Kamagra pharmacie en ligne: kamagra en ligne – Achetez vos kamagra medicaments
http://kamagraprix.com/# kamagra oral jelly
Achetez vos kamagra medicaments: achat kamagra – kamagra en ligne
Achetez vos kamagra medicaments: Achetez vos kamagra medicaments – kamagra livraison 24h
vente de mГ©dicament en ligne pharmacie en ligne pas cher or pharmacie en ligne fiable
https://maps.google.hu/url?q=j&source=web&rct=j&url=https://pharmafst.com Pharmacie Internationale en ligne
pharmacie en ligne pharmacies en ligne certifiГ©es and pharmacie en ligne livraison europe Pharmacie sans ordonnance
https://pharmafst.com/# pharmacie en ligne france pas cher
pharmacie en ligne avec ordonnance: Pharmacies en ligne certifiees – pharmacie en ligne sans ordonnance pharmafst.com
cialis sans ordonnance: Pharmacie en ligne Cialis sans ordonnance – Cialis generique prix tadalmed.shop
acheter kamagra site fiable kamagra pas cher kamagra gel
http://pharmafst.com/# acheter mГ©dicament en ligne sans ordonnance
Kamagra pharmacie en ligne: Acheter Kamagra site fiable – kamagra 100mg prix
kamagra 100mg prix: kamagra 100mg prix – acheter kamagra site fiable
pharmacie en ligne avec ordonnance: Meilleure pharmacie en ligne – pharmacie en ligne fiable pharmafst.com
pharmacie en ligne france livraison internationale acheter mГ©dicament en ligne sans ordonnance or pharmacie en ligne pas cher
https://images.google.gm/url?sa=t&url=https://pharmafst.com Achat mГ©dicament en ligne fiable
pharmacies en ligne certifiГ©es п»їpharmacie en ligne france and vente de mГ©dicament en ligne pharmacie en ligne fiable
cialis generique cialis generique or Acheter Cialis 20 mg pas cher
https://www.google.gl/url?q=https://tadalmed.com Acheter Cialis 20 mg pas cher
Cialis sans ordonnance pas cher cialis sans ordonnance and Cialis sans ordonnance 24h Tadalafil sans ordonnance en ligne
cialis prix Pharmacie en ligne Cialis sans ordonnance Cialis en ligne tadalmed.com
https://kamagraprix.com/# kamagra livraison 24h
Acheter Cialis: Tadalafil 20 mg prix sans ordonnance – Tadalafil achat en ligne tadalmed.shop
Acheter Kamagra site fiable: kamagra livraison 24h – Acheter Kamagra site fiable
Medicine From India: Medicine From India – Medicine From India
http://expressrxcanada.com/# best canadian pharmacy to buy from
buy medicines online in india: indian pharmacy – indian pharmacy
Rx Express Mexico Rx Express Mexico mexico pharmacies prescription drugs
canadian pharmacy king: best online canadian pharmacy – northwest canadian pharmacy
Medicine From India: buy medicines online in india – indian pharmacy
https://medicinefromindia.shop/# Medicine From India
mexican rx online: mexican online pharmacy – mexico drug stores pharmacies
mexico pharmacy order online: mexico pharmacies prescription drugs – Rx Express Mexico
Rx Express Mexico Rx Express Mexico mexican rx online
pharmacy canadian: Express Rx Canada – canada pharmacy online
https://expressrxcanada.shop/# canadian pharmacy checker
medication from mexico pharmacy: purple pharmacy mexico price list – Rx Express Mexico
Medicine From India: indian pharmacy – indian pharmacy online
canada pharmacy world: legit canadian pharmacy online – canadian pharmacy king
mexican rx online mexico pharmacies prescription drugs mexican online pharmacy
https://expressrxcanada.shop/# certified canadian pharmacy
top 10 online pharmacy in india indian pharmacy online or buy medicines online in india
https://maps.google.lk/url?sa=i&url=https://medicinefromindia.com best india pharmacy
reputable indian online pharmacy india online pharmacy and top 10 online pharmacy in india top 10 online pharmacy in india
medication from mexico pharmacy mexico drug stores pharmacies or purple pharmacy mexico price list
http://ewin.biz/jsonp/?url=https://rxexpressmexico.com mexican pharmaceuticals online
mexican pharmaceuticals online pharmacies in mexico that ship to usa and buying from online mexican pharmacy mexican drugstore online
online pharmacy canada: ExpressRxCanada – canadian drugstore online
canadian family pharmacy: ExpressRxCanada – canadian world pharmacy
canadian medications: canadian pharmacy world – legitimate canadian mail order pharmacy
http://medicinefromindia.com/# MedicineFromIndia
MedicineFromIndia medicine courier from India to USA medicine courier from India to USA
mexico drug stores pharmacies: mexican rx online – purple pharmacy mexico price list
Looking for the best alarm clock radio with CD player and modern features? This HD tabletop radio combines vintage charm with today’s technology. Features include a CD player, AM/FM radio, dual alarm settings, and a USB port for device charging. Perfect for bedside tables or desktops, the sleek design doesn’t sacrifice performance. Whether you’re waking up to your favorite radio station, a beloved CD, or a gentle buzzer, this unit is your all-in-one morning companion. The CD clock radio is back—and better than ever.
indian pharmacy: Medicine From India – indian pharmacy online shopping
http://expressrxcanada.com/# canadian drugs pharmacy
reputable indian online pharmacy reputable indian online pharmacy or Online medicine home delivery
http://www.sorenwinslow.com/RSSReader.asp?TheFeed=http://medicinefromindia.com/ buy medicines online in india
indian pharmacy paypal india pharmacy mail order and top online pharmacy india п»їlegitimate online pharmacies india
mexico drug stores pharmacies: RxExpressMexico – Rx Express Mexico
MedicineFromIndia: п»їlegitimate online pharmacies india – Medicine From India
Medicine From India indian pharmacy Medicine From India
trustworthy canadian pharmacy: canadian pharmacy india – canadian pharmacy service
medicine in mexico pharmacies mexican border pharmacies shipping to usa or mexico drug stores pharmacies
http://d-quintet.com/i/index.cgi?id=1&mode=redirect&no=494&ref_eid=33&url=http://rxexpressmexico.com buying from online mexican pharmacy
buying prescription drugs in mexico online mexico pharmacies prescription drugs and mexico drug stores pharmacies mexican online pharmacies prescription drugs
https://medicinefromindia.com/# Medicine From India
canadian pharmacy prices: Canadian pharmacy shipping to USA – canadian compounding pharmacy
canadian pharmacies comparison: Canadian pharmacy shipping to USA – buy prescription drugs from canada cheap
canadian drugs pharmacy Generic drugs from Canada canadian pharmacies
Rx Express Mexico: RxExpressMexico – medication from mexico pharmacy
Online medicine order world pharmacy india or best india pharmacy
https://www.fcviktoria.cz/media_show.asp?id=2924&id_clanek=2467&media=0&type=1&url=http://medicinefromindia.com п»їlegitimate online pharmacies india
india pharmacy mail order cheapest online pharmacy india and india pharmacy india online pharmacy
https://rxexpressmexico.com/# mexican rx online
legitimate canadian online pharmacies: Express Rx Canada – canadian pharmacy checker
mail order pharmacy india buy prescription drugs from india or indian pharmacy
https://images.google.ge/url?sa=t&url=https://medicinefromindia.com indian pharmacy paypal
india online pharmacy online shopping pharmacy india and world pharmacy india best online pharmacy india
77 canadian pharmacy: canadian neighbor pharmacy – canadian pharmacy ltd
mexican online pharmacy: mexico pharmacies prescription drugs – RxExpressMexico
indian pharmacy top online pharmacy india indian pharmacy online shopping
best online pharmacies in mexico mexican online pharmacies prescription drugs or buying from online mexican pharmacy
http://www.security-scanner-firing-range.com/reflected/url/href?q=https://rxexpressmexico.com purple pharmacy mexico price list
mexico drug stores pharmacies medicine in mexico pharmacies and pharmacies in mexico that ship to usa mexican mail order pharmacies
http://medicinefromindia.com/# medicine courier from India to USA
вавада зеркало: вавада официальный сайт – vavada вход
пин ап вход: пин ап вход – пин ап казино официальный сайт
пинап казино пинап казино пин ап казино
https://pinuprus.pro/# пинап казино
пин ап казино официальный сайт: пинап казино – пинап казино
vavada casino: vavada вход – vavada casino
pin-up casino giris pin-up casino giris pinup az
http://pinupaz.top/# pinup az
пин ап вход: пин ап казино – пин ап вход
pin up az: pin up – pin-up
http://pinuprus.pro/# пин ап казино официальный сайт
pin up az pin up azerbaycan pin up azerbaycan
пин ап зеркало: пин ап вход – пин ап казино
http://vavadavhod.tech/# vavada casino
пинап казино пин ап вход пин ап зеркало
пин ап зеркало: пин ап вход – пин ап казино официальный сайт
pin up: pinup az – pin up azerbaycan
pin up вход pin up вход or пин ап казино
https://maps.google.mw/url?sa=t&url=https://pinuprus.pro пинап казино
pin up вход пин ап казино and пин ап зеркало пин ап казино официальный сайт
http://vavadavhod.tech/# vavada
pin-up: pin up azerbaycan – pin-up casino giris
вавада казино вавада вавада казино
pin up az pinup az or pin up casino
http://www.24subaru.ru/photo-20322.html?ReturnPath=https://pinupaz.top pinup az
pin up az pinup az and pinup az pinup az
vavada вход: вавада казино – vavada casino
вавада вавада казино or вавада зеркало
https://maps.google.gp/url?q=https://vavadavhod.tech vavada casino
vavada вход vavada casino and вавада зеркало вавада
пинап казино пин ап зеркало or пинап казино
https://maps.google.com.pg/url?sa=t&url=https://pinuprus.pro pin up вход
пин ап вход пин ап казино официальный сайт and пин ап зеркало пин ап казино
pin up casino: pin up azerbaycan – pin-up
https://pinuprus.pro/# пин ап казино официальный сайт
пин ап вход: пин ап казино – pin up вход
pin up вход пин ап вход пин ап вход
https://pinuprus.pro/# пин ап зеркало
пин ап вход пин ап зеркало or пинап казино
http://maps.google.je/url?q=http://pinuprus.pro пин ап вход
пин ап зеркало пинап казино and пин ап казино пин ап зеркало
pin-up casino giris pinup az or pin up az
http://bangkok-hotels.fr/redirecturl.php?url=https://pinupaz.top pin up az
pin up azerbaycan pin up azerbaycan and pin-up pin-up casino giris
pin-up casino giris: pin up az – pin up
вавада казино: vavada casino – vavada casino
pin-up casino giris pin-up pin up casino
вавада официальный сайт: вавада казино – вавада официальный сайт
vavada вход vavada or вавада
https://www.google.se/url?sa=t&url=https://vavadavhod.tech вавада зеркало
вавада официальный сайт vavada and вавада зеркало вавада официальный сайт
https://pinupaz.top/# pin up azerbaycan
пин ап вход pin up вход or пин ап казино официальный сайт
https://www.google.com.tj/url?q=https://pinuprus.pro пин ап казино официальный сайт
pin up вход pin up вход and пин ап казино официальный сайт пинап казино
вавада зеркало: вавада – вавада официальный сайт
пинап казино: пин ап вход – пинап казино
vavada casino: vavada casino – vavada
pin up pin up casino pin up
http://vavadavhod.tech/# вавада казино
pin up pin up az or pin-up
https://profil.uniag.sk/pracoviste/predmety.pl?id=56;zpet=https://pinupaz.top pin-up casino giris
pin-up casino giris pin up azerbaycan and pin up casino pin up az
пин ап казино пин ап зеркало or пинап казино
https://60.viromin.com/index/d1?diff=0&utm_clickid=9sg408wsws80o8o8&aurl=http://pinuprus.pro pin up вход
пинап казино pin up вход and пинап казино пин ап казино
pin up: pin up casino – pinup az
пин ап казино официальный сайт: пинап казино – пин ап казино официальный сайт
вавада зеркало: вавада официальный сайт – vavada вход
pin up pin-up pin up az
http://pinupaz.top/# pin up azerbaycan
вавада зеркало вавада официальный сайт or вавада казино
http://naturestears.com/php/Test.php?a=how+can+i+buy+viagra вавада зеркало
vavada вход вавада and вавада казино вавада казино
пин ап казино pin up вход or пин ап вход
http://davidpawson.org/resources/resource/416?return_url=http://pinuprus.pro/ пин ап казино
пин ап казино официальный сайт пин ап казино официальный сайт and pin up вход pin up вход
pin up casino: pin up az – pin up azerbaycan
pin up az: pin up azerbaycan – pinup az
вавада зеркало: вавада официальный сайт – вавада
pin up pin up azerbaycan pin up azerbaycan
https://pinupaz.top/# pinup az
pinup az pin up azerbaycan or pin up azerbaycan
https://www.zyteq.com.au/?URL=https://pinupaz.top pin-up
pin up az pin up az and pin up casino pin up azerbaycan
pin-up: pin-up – pin up azerbaycan
пинап казино пин ап вход or pin up вход
http://klubua.ru/redirect.php?url=pinuprus.pro пин ап вход
пин ап зеркало пин ап вход and пин ап вход пин ап казино
pin up casino: pin-up casino giris – pin-up
pin-up: pinup az – pin-up
https://vavadavhod.tech/# вавада официальный сайт
pinup az pin-up casino giris pin up
вавада vavada casino or вавада зеркало
https://maps.google.dk/url?q=https://vavadavhod.tech vavada вход
вавада официальный сайт вавада казино and вавада казино вавада
пин ап зеркало: пин ап зеркало – пин ап вход
пинап казино: пин ап казино официальный сайт – pin up вход
pin up az: pin up azerbaycan – pin-up casino giris
http://pinuprus.pro/# пин ап казино официальный сайт
пин ап казино официальный сайт пин ап зеркало пин ап зеркало
pinup az: pinup az – pin-up
pin up pin-up casino giris or pin-up
https://stjohns.harrow.sch.uk/brighton-hove/primary/westdene/arenas/schooloffice/calendar/CookiePolicy.action?backto=https://pinupaz.top pin-up casino giris
pin up pinup az and pin-up pin up azerbaycan
пин ап вход: пин ап вход – пинап казино
пин ап казино пин ап зеркало or pin up вход
https://www.google.cf/url?q=https://pinuprus.pro pin up вход
пин ап зеркало пин ап вход and пин ап казино официальный сайт пин ап казино
пин ап казино официальный сайт: пин ап казино – пин ап казино
https://pinuprus.pro/# pin up вход
вавада зеркало vavada вход вавада официальный сайт
пинап казино: пин ап зеркало – пин ап казино официальный сайт
вавада официальный сайт vavada casino or вавада официальный сайт
https://images.google.com.bd/url?sa=t&url=https://vavadavhod.tech vavada вход
vavada casino вавада and вавада зеркало vavada
пин ап вход пинап казино or пин ап зеркало
http://www.dot-blank.com/feed2js/feed2js.php?src=https://pinuprus.pro:: пин ап зеркало
пин ап зеркало пинап казино and пинап казино пин ап вход
pin-up: pin-up – pin-up
https://vavadavhod.tech/# вавада казино
вавада официальный сайт вавада официальный сайт vavada
pin up casino: pin up az – pin up
pinup az pin up azerbaycan or pin-up
https://www.google.co.ls/url?q=https://pinupaz.top pinup az
pinup az pin up azerbaycan and pin up azerbaycan pin up casino
пинап казино пин ап вход or пинап казино
https://maps.google.bi/url?q=https://pinuprus.pro pin up вход
пин ап казино официальный сайт пин ап зеркало and пин ап вход pin up вход
https://pinupaz.top/# pin up casino
pin up: pin up azerbaycan – pin up
пин ап казино официальный сайт: пинап казино – пин ап казино
vavada casino вавада зеркало or vavada casino
https://www.google.gm/url?sa=t&url=https://vavadavhod.tech вавада зеркало
вавада казино vavada casino and vavada вавада официальный сайт
http://vavadavhod.tech/# вавада зеркало
pin up azerbaycan: pin-up – pin up azerbaycan
pin up вход пин ап казино or пин ап казино официальный сайт
http://maps.google.fm/url?q=https://pinuprus.pro пин ап казино официальный сайт
пинап казино pin up вход and пин ап зеркало пинап казино
pinup az: pin-up casino giris – pin up
пинап казино пинап казино пин ап казино
pin up az pinup az or pin up az
https://images.google.com.br/url?q=https://pinupaz.top pin up
pin up casino pin-up and pin-up pin up az
https://pinuprus.pro/# пин ап зеркало
пин ап вход пин ап казино or пин ап зеркало
http://www.teacherlearningproject.com/index?URL=http://pinuprus.pro pin up вход
pin up вход пин ап зеркало and пин ап вход пин ап зеркало
pin-up: pin-up – pin up azerbaycan
пин ап казино официальный сайт: пин ап казино официальный сайт – пин ап вход
pin up pin-up pin up az
вавада официальный сайт вавада or вавада зеркало
https://www.gra.co.nz/Redirect.aspx?destination=http://vavadavhod.tech/ vavada вход
вавада vavada casino and вавада официальный сайт vavada
https://vavadavhod.tech/# вавада казино
пин ап зеркало: пин ап казино – pin up вход
вавада зеркало: vavada – вавада
пин ап вход пин ап зеркало or pin up вход
http://otdix-u-mory.ru/sql.php?=pinuprus.pro пин ап казино официальный сайт
pin up вход пин ап казино официальный сайт and пин ап зеркало пин ап вход
pin up az pin up casino or pin up az
http://www.dot-blank.com/feed2js/feed2js.php?src=https://pinupaz.top pinup az
pin-up casino giris pin up azerbaycan and pin up casino pin up casino
pin up вход pin up вход пин ап казино
https://pinuprus.pro/# пинап казино
https://pinupaz.top/# pin up az
пинап казино: пин ап вход – пин ап казино официальный сайт
вавада официальный сайт вавада зеркало or вавада официальный сайт
http://www.earth-policy.org/?URL=https://vavadavhod.tech вавада
вавада зеркало вавада официальный сайт and вавада зеркало вавада зеркало
vavada: vavada вход – vavada вход
pin up azerbaycan pin up casino or pin up azerbaycan
https://siamloaning.com/redirect.php?blog=B8A1B89AB895B8%A3B894B999B89420PROUD&url=https://pinupaz.top pin-up
pin up casino pin up and pin up azerbaycan pin-up
пин ап казино пин ап казино or пин ап зеркало
https://images.google.tk/url?sa=t&url=https://pinuprus.pro пин ап зеркало
пин ап вход пин ап вход and пин ап вход пин ап казино официальный сайт
http://pinupaz.top/# pin up azerbaycan
вавада вавада зеркало vavada вход
pin up azerbaycan: pin up casino – pin-up
пинап казино пин ап казино or пинап казино
https://raptor.qub.ac.uk/genericInstruction.php?&suborg=qub&resourceId=41&url=https://pinuprus.pro pin up вход
pin up вход pin up вход and pin up вход пин ап казино официальный сайт
vavada вход: vavada casino – вавада казино
вавада зеркало вавада казино vavada
пин ап зеркало: пин ап вход – пин ап казино
вавада зеркало vavada or vavada casino
https://cse.google.com.py/url?sa=t&url=https://vavadavhod.tech вавада официальный сайт
вавада официальный сайт вавада официальный сайт and vavada vavada casino
pin up casino pin up casino or pin up
https://maps.google.kg/url?q=https://pinupaz.top pin-up
pin up pin up azerbaycan and pin up casino pinup az
вавада официальный сайт: вавада официальный сайт – вавада официальный сайт
https://pinupaz.top/# pinup az
пин ап казино пин ап зеркало or пинап казино
https://images.google.dj/url?sa=t&url=https://pinuprus.pro пин ап казино
пин ап казино pin up вход and пин ап казино пин ап казино
pin-up casino giris: pin-up casino giris – pin up casino
пин ап казино pin up вход pin up вход
пин ап вход pin up вход or pin up вход
https://www.google.mu/url?q=https://pinuprus.pro пин ап казино
пин ап казино официальный сайт пин ап зеркало and пин ап казино пин ап зеркало
https://pinuprus.pro/# pin up вход
pin up azerbaycan: pin-up casino giris – pin-up casino giris
pin up: pin-up casino giris – pin up azerbaycan
пин ап вход пин ап казино пин ап вход
вавада казино вавада зеркало or вавада казино
https://maps.google.fi/url?sa=t&url=https://vavadavhod.tech вавада зеркало
вавада вавада зеркало and вавада официальный сайт vavada вход
http://pinupaz.top/# pin-up casino giris
vavada вход: vavada casino – вавада зеркало
пин ап казино: пин ап казино – пин ап казино
pin up вход пин ап зеркало or пин ап вход
http://cse.google.sr/url?q=http://pinuprus.pro пин ап вход
пинап казино пин ап вход and пин ап казино официальный сайт pin up вход
вавада официальный сайт вавада зеркало вавада зеркало
http://pinupaz.top/# pin-up
пин ап казино официальный сайт: пин ап казино – pin up вход
пин ап казино официальный сайт пинап казино or pin up вход
http://images.google.cz/url?q=https://pinuprus.pro пин ап вход
пинап казино pin up вход and пин ап казино pin up вход
вавада официальный сайт: vavada вход – vavada
vavada casino вавада зеркало вавада казино
https://pinuprus.pro/# пин ап казино
vavada вход: вавада официальный сайт – вавада
пин ап казино: pin up вход – пин ап казино официальный сайт
vavada casino vavada casino vavada вход
пин ап зеркало пин ап зеркало or пинап казино
https://www.google.bt/url?q=https://pinuprus.pro пин ап вход
пин ап казино официальный сайт pin up вход and пин ап вход пин ап зеркало
pin up вход: pin up вход – пин ап вход
http://pinupaz.top/# pin up casino
пинап казино пин ап вход or пин ап вход
https://whois.pp.ru/pinuprus.pro pin up вход
пин ап зеркало пин ап казино официальный сайт and pin up вход пин ап казино официальный сайт
pin-up casino giris: pin up az – pin up
pin up azerbaycan pin up az pin up az
вавада казино: вавада – вавада официальный сайт
https://pinuprus.pro/# пин ап вход
vavada casino вавада официальный сайт or вавада официальный сайт
https://www.google.com.om/url?q=https://vavadavhod.tech vavada вход
вавада вавада зеркало and вавада официальный сайт вавада
пинап казино: пин ап вход – пин ап вход
pin up casino pin up casino pin up azerbaycan
pinup az: pin up azerbaycan – pin-up
http://vavadavhod.tech/# vavada вход
пинап казино пин ап казино официальный сайт or пин ап зеркало
http://admin.wjymz.com/alexa/Index.asp?url=pinuprus.pro pin up вход
пин ап зеркало пин ап вход and пинап казино пинап казино
пинап казино: пин ап зеркало – pin up вход
пин ап казино pin up вход or пин ап казино официальный сайт
http://www.cookinggamesclub.com/partner/pinuprus.pro/ пин ап казино
pin up вход пин ап зеркало and pin up вход пин ап зеркало
пин ап вход: пин ап казино официальный сайт – пин ап казино
вавада официальный сайт вавада казино vavada вход
https://pinupaz.top/# pin up
вавада vavada casino or vavada вход
https://www.google.si/url?sa=t&url=https://vavadavhod.tech vavada casino
вавада зеркало вавада and vavada vavada
пин ап вход: пин ап казино официальный сайт – pin up вход
пин ап вход: пин ап вход – пин ап вход
https://pinuprus.pro/# пин ап казино официальный сайт
пинап казино пин ап казино официальный сайт пин ап казино
пин ап зеркало pin up вход or пин ап казино
http://www.planetglobal.de/ferienhaeuser/europa/spanien/ferienhaeuser/pinuprus.pro_1_fewo.html пин ап зеркало
пинап казино пин ап казино официальный сайт and пинап казино пин ап вход
pinup az: pin-up – pin up casino
pinup az: pin up casino – pin-up
https://pinuprus.pro/# пин ап казино официальный сайт
пинап казино пин ап зеркало or пин ап казино
http://www.sargsplitter.de/?URL=pinuprus.pro пин ап вход
pin up вход пин ап казино официальный сайт and пинап казино pin up вход
vavada вход vavada вход vavada
пин ап зеркало: пинап казино – пин ап казино
vavada casino vavada casino or вавада официальный сайт
http://id.nan-net.jp/system/login/link.cgi?jump=http://vavadavhod.tech/ вавада
vavada вход вавада казино and vavada вавада зеркало
https://vavadavhod.tech/# вавада официальный сайт
пин ап казино официальный сайт: пинап казино – пин ап казино официальный сайт
вавада вавада казино vavada casino
pin-up casino giris: pin up azerbaycan – pin-up
пин ап зеркало пин ап казино or pin up вход
http://www.boosterblog.net/vote-146-144.html?adresse=pinuprus.pro&popup=1 pin up вход
пин ап казино официальный сайт пин ап казино and pin up вход pin up вход
pin up: pin-up casino giris – pinup az
вавада зеркало вавада казино вавада
пин ап казино: пин ап вход – пин ап казино
http://pinupaz.top/# pin-up
вавада официальный сайт вавада официальный сайт or вавада
http://sexynews24.com/exlink.php?url=http://vavadavhod.tech/ вавада
vavada вавада and вавада вавада зеркало
пин ап казино: пин ап казино официальный сайт – пин ап казино официальный сайт
пин ап вход пин ап вход пин ап казино
пин ап казино официальный сайт: пин ап казино – пин ап казино
http://pinuprus.pro/# пин ап казино
pin-up casino giris: pin up azerbaycan – pin-up casino giris
пин ап казино официальный сайт пин ап казино or пин ап зеркало
https://maps.google.lk/url?sa=i&url=https://pinuprus.pro pin up вход
пинап казино пинап казино and пинап казино пин ап казино официальный сайт
pin-up casino giris pin-up pin up az
https://vavadavhod.tech/# вавада зеркало
pin up вход пин ап казино официальный сайт or пин ап вход
http://images.google.co.id/url?sa=t&url=http://pinuprus.pro пинап казино
пин ап зеркало пинап казино and pin up вход пинап казино
вавада официальный сайт vavada casino or vavada casino
https://images.google.com.ph/url?q=http://vavadavhod.tech вавада официальный сайт
vavada вавада зеркало and вавада казино vavada
pin up azerbaycan pin-up pin-up casino giris
https://pinuprus.pro/# пин ап зеркало
пинап казино: пин ап вход – pin up вход
пин ап вход пин ап казино or пин ап казино
http://avalonadvancedmaterials.com/outurl.php?url=https://pinuprus.pro пин ап казино официальный сайт
пинап казино пин ап казино официальный сайт and pin up вход pin up вход
no doctor visit required: safe online pharmacy – same-day Viagra shipping
https://zipgenericmd.shop/# Cialis without prescription
doctor-reviewed advice: Modafinil for sale – purchase Modafinil without prescription
Viagra without prescription: order Viagra discreetly – Viagra without prescription
https://zipgenericmd.com/# secure checkout ED drugs
Modafinil for sale doctor-reviewed advice safe modafinil purchase
reliable online pharmacy Cialis: discreet shipping ED pills – Cialis without prescription
order Cialis online no prescription: affordable ED medication – generic tadalafil
reliable online pharmacy Cialis: order Cialis online no prescription – online Cialis pharmacy
https://zipgenericmd.shop/# FDA approved generic Cialis
fast Viagra delivery safe online pharmacy generic sildenafil 100mg
affordable ED medication: reliable online pharmacy Cialis – online Cialis pharmacy
Cialis without prescription: Cialis without prescription – FDA approved generic Cialis
buy modafinil online: modafinil pharmacy – buy modafinil online
http://maxviagramd.com/# best price for Viagra
discreet shipping ED pills: secure checkout ED drugs – reliable online pharmacy Cialis
legit Viagra online legit Viagra online fast Viagra delivery
generic tadalafil: cheap Cialis online – online Cialis pharmacy
order Cialis online no prescription order Cialis online no prescription or FDA approved generic Cialis
https://www.google.com.au/url?sa=t&url=https://zipgenericmd.com generic tadalafil
generic tadalafil online Cialis pharmacy and secure checkout ED drugs online Cialis pharmacy
https://modafinilmd.store/# legal Modafinil purchase
cheap Viagra online fast Viagra delivery or discreet shipping
http://ditu.google.cn/url?q=http://maxviagramd.shop safe online pharmacy
trusted Viagra suppliers no doctor visit required and fast Viagra delivery same-day Viagra shipping
order Viagra discreetly: cheap Viagra online – Viagra without prescription
discreet shipping ED pills: order Cialis online no prescription – online Cialis pharmacy
Modafinil for sale: verified Modafinil vendors – Modafinil for sale
legal Modafinil purchase safe modafinil purchase or safe modafinil purchase
https://cse.google.co.za/url?sa=i&url=https://modafinilmd.store modafinil legality
safe modafinil purchase modafinil pharmacy and verified Modafinil vendors modafinil legality
fast Viagra delivery: Viagra without prescription – buy generic Viagra online
buy generic Viagra online: cheap Viagra online – trusted Viagra suppliers
modafinil legality: buy modafinil online – doctor-reviewed advice
fast Viagra delivery safe online pharmacy fast Viagra delivery
http://modafinilmd.store/# safe modafinil purchase
online Cialis pharmacy FDA approved generic Cialis or buy generic Cialis online
https://cse.google.vg/url?q=https://zipgenericmd.com best price Cialis tablets
affordable ED medication buy generic Cialis online and cheap Cialis online generic tadalafil
legit Viagra online: trusted Viagra suppliers – discreet shipping
safe modafinil purchase: modafinil legality – modafinil 2025
generic tadalafil best price Cialis tablets affordable ED medication
http://zipgenericmd.com/# best price Cialis tablets
Viagra without prescription: generic sildenafil 100mg – buy generic Viagra online
affordable ED medication: FDA approved generic Cialis – online Cialis pharmacy
generic tadalafil online Cialis pharmacy discreet shipping ED pills
https://zipgenericmd.com/# affordable ED medication
reliable online pharmacy Cialis: best price Cialis tablets – FDA approved generic Cialis
doctor-reviewed advice: safe modafinil purchase – purchase Modafinil without prescription
legal Modafinil purchase: modafinil 2025 – legal Modafinil purchase
modafinil pharmacy buy modafinil online Modafinil for sale
buy generic Viagra online: no doctor visit required – same-day Viagra shipping
modafinil legality: modafinil legality – purchase Modafinil without prescription
modafinil pharmacy modafinil legality or buy modafinil online
https://maps.google.gl/url?q=https://modafinilmd.store safe modafinil purchase
safe modafinil purchase modafinil 2025 and legal Modafinil purchase doctor-reviewed advice
Viagra without prescription: safe online pharmacy – fast Viagra delivery
order Cialis online no prescription discreet shipping ED pills or secure checkout ED drugs
https://artwinlive.com/widgets/1YhWyTF0hHoXyfkbLq5wpA0H?generated=true&color=dark&layout=list&showgigs=4&moreurl=https://zipgenericmd.com online Cialis pharmacy
cheap Cialis online cheap Cialis online and affordable ED medication best price Cialis tablets
Cialis without prescription FDA approved generic Cialis or discreet shipping ED pills
https://cse.google.lv/url?sa=i&url=https://zipgenericmd.com affordable ED medication
generic tadalafil FDA approved generic Cialis and FDA approved generic Cialis order Cialis online no prescription
cheap Cialis online: FDA approved generic Cialis – secure checkout ED drugs
https://zipgenericmd.shop/# online Cialis pharmacy
reliable online pharmacy Cialis: cheap Cialis online – cheap Cialis online
secure checkout Viagra cheap Viagra online same-day Viagra shipping
trusted Viagra suppliers Viagra without prescription or best price for Viagra
https://phq.muddasheep.com/phq_browser.cgi?redirect=http://maxviagramd.shop Viagra without prescription
discreet shipping fast Viagra delivery and legit Viagra online trusted Viagra suppliers
generic sildenafil 100mg: discreet shipping – safe online pharmacy
secure checkout ED drugs: buy generic Cialis online – FDA approved generic Cialis
modafinil pharmacy: buy modafinil online – modafinil pharmacy
http://modafinilmd.store/# buy modafinil online
legit Viagra online legit Viagra online safe online pharmacy
buy modafinil online safe modafinil purchase or safe modafinil purchase
https://maps.google.co.mz/url?sa=t&url=https://modafinilmd.store buy modafinil online
Modafinil for sale doctor-reviewed advice and verified Modafinil vendors buy modafinil online
modafinil pharmacy: purchase Modafinil without prescription – modafinil legality
Cialis without prescription cheap Cialis online or generic tadalafil
http://www.aozhuanyun.com/index.php/goods/Index/golink?url=https://zipgenericmd.com buy generic Cialis online
buy generic Cialis online buy generic Cialis online and generic tadalafil online Cialis pharmacy
modafinil legality: Modafinil for sale – buy modafinil online
secure checkout ED drugs: online Cialis pharmacy – Cialis without prescription
https://zipgenericmd.shop/# online Cialis pharmacy
reliable online pharmacy Cialis cheap Cialis online or secure checkout ED drugs
http://images.google.ae/url?q=https://zipgenericmd.com best price Cialis tablets
affordable ED medication FDA approved generic Cialis and Cialis without prescription FDA approved generic Cialis
legal Modafinil purchase doctor-reviewed advice safe modafinil purchase
buy generic Viagra online: safe online pharmacy – same-day Viagra shipping
discreet shipping: secure checkout Viagra – cheap Viagra online
how to buy generic clomid Clom Health where to get clomid prices
can i order cheap clomid without rx: how to get generic clomid tablets – how can i get cheap clomid online
http://prednihealth.com/# 5mg prednisone
prednisone 60 mg daily: PredniHealth – prednisone price south africa
cost of clomid without prescription: can i get generic clomid without insurance – where to get clomid prices
Amo Health Care: can i purchase amoxicillin online – Amo Health Care
https://amohealthcare.store/# amoxicillin 500 mg tablet price
can i get cheap clomid online Clom Health buy cheap clomid prices
prednisone 1mg purchase: PredniHealth – prednisone 10 mg coupon
amoxicillin from canada: amoxicillin 500mg – Amo Health Care
can i order generic clomid without rx: Clom Health – buying generic clomid without prescription
https://clomhealth.com/# how to buy cheap clomid now
cheap clomid without prescription where buy generic clomid can i buy clomid without rx
amoxicillin 500mg capsule buy online: Amo Health Care – Amo Health Care
PredniHealth: can you buy prednisone without a prescription – over the counter prednisone cheap
rexall pharmacy amoxicillin 500mg: can you buy amoxicillin over the counter canada – Amo Health Care
https://amohealthcare.store/# Amo Health Care
where to buy amoxicillin amoxicillin no prescription or amoxicillin 250 mg price in india
http://www.pro100chat.ru/go.php?url=https://amohealthcare.store order amoxicillin online uk
amoxicillin 500mg buy online uk buy amoxicillin 500mg online and amoxicillin 1000 mg capsule amoxicillin online purchase
amoxicillin buy no prescription amoxicillin for sale Amo Health Care
can i buy amoxicillin online: generic amoxicillin online – Amo Health Care
PredniHealth: prednisone 20mg price – buy 10 mg prednisone
https://amohealthcare.store/# Amo Health Care
buying clomid without prescription: Clom Health – can you buy cheap clomid without dr prescription
prednisone generic brand name prednisolone prednisone or cost of prednisone tablets
https://www.google.com.vc/url?q=http://prednihealth.com prednisone canada prescription
prednisone 10mg buy online cheap generic prednisone and prednisone 20mg online without prescription prednisone 5mg price
can you get clomid for sale where to get generic clomid pills or buy cheap clomid
https://toolbarqueries.google.nl/url?sa=t&url=https://clomhealth.com can i purchase cheap clomid prices
can i order generic clomid without a prescription can i purchase generic clomid and where to buy generic clomid prices buy clomid pills
buying cheap clomid without insurance where can i buy clomid how to buy generic clomid no prescription
buy prednisone canada: prednisone 20 mg pill – where to buy prednisone uk
prednisone 2.5 mg daily prednisone 20 mg tablets or prednisone 2 mg
http://lbast.ru/zhg_img.php?url=http://prednihealth.shop/ how to buy prednisone online
buy prednisone canada prednisone 10 tablet and prednisone 30 mg coupon can i buy prednisone from canada without a script
http://clomhealth.com/# order clomid pills
prednisone 60 mg tablet: PredniHealth – PredniHealth
buying amoxicillin online buy amoxicillin online cheap or amoxicillin 500mg no prescription
https://cse.google.tg/url?sa=t&url=https://amohealthcare.store price for amoxicillin 875 mg
purchase amoxicillin online without prescription amoxicillin 500mg capsule and amoxicillin buy canada generic amoxil 500 mg
get clomid online Clom Health where buy generic clomid without a prescription
cost of amoxicillin prescription: amoxicillin 500mg capsule buy online – purchase amoxicillin online
https://amohealthcare.store/# Amo Health Care
clomid no prescription: Clom Health – can i buy clomid without rx
order generic clomid online can i get generic clomid without a prescription or where to buy clomid tablets
https://cse.google.bf/url?sa=i&url=http://clomhealth.com order clomid pills
how to get cheap clomid online how to buy cheap clomid no prescription and how to get cheap clomid without insurance where to get cheap clomid price
PredniHealth: PredniHealth – generic prednisone pills
prednisone 10 mg brand name prednisone 10 mg canada PredniHealth
http://prednihealth.com/# PredniHealth
prednisone purchase canada how much is prednisone 10mg or prednisone 2.5 mg cost
https://maps.google.gr/url?q=https://prednihealth.shop prednisone online australia
order prednisone from canada buy prednisone online without a prescription and prednisone cost 10mg online order prednisone
Amo Health Care: Amo Health Care – Amo Health Care
what is the cost of cialis cialis com free sample cialis vs.levitra
cheap cialis online overnight shipping: cialis dapoxetine overnight shipment – best price on generic tadalafil
how much is cialis without insurance: TadalAccess – buying cialis online safely
https://tadalaccess.com/# cialis maximum dose
cialis coupon online buy cialis online safely cialis as generic
cialis prescription online: TadalAccess – is tadalafil from india safe
find tadalafil: difference between cialis and tadalafil – levitra vs cialis
https://tadalaccess.com/# buy cialis pro
tadalafil lowest price: generic cialis tadalafil 20mg reviews – what happens when you mix cialis with grapefruit?
tadalafil price insurance Tadal Access printable cialis coupon
what cialis: Tadal Access – tadalafil (tadalis-ajanta)
https://tadalaccess.com/# buy cialis online overnight shipping
cialis one a day: TadalAccess – what does cialis cost
cialis online canada: cialis for sale in toront ontario – tadalafil tablets erectafil 20
reliable source cialis when should you take cialis cialis dapoxetine europe
https://tadalaccess.com/# cialis for pulmonary hypertension
canada cialis for sale can you drink wine or liquor if you took in tadalafil or cialis priligy online australia
https://www.google.ml/url?sa=t&url=https://tadalaccess.com brand cialis australia
buy cialis no prescription how long does cialis stay in your system and buying cialis online usa walgreen cialis price
cialis pricing: TadalAccess – is there a generic cialis available?
cialis recreational use: cialis insurance coverage – natural cialis
https://tadalaccess.com/# cheap tadalafil 10mg
tadalafil best price 20 mg TadalAccess is tadalafil and cialis the same thing?
cialis online pharmacy australia does cialis make you last longer in bed or cialis 50mg
https://100kursov.com/away/?url=https://tadalaccess.com best price for tadalafil
cialis generic 20 mg 30 pills cialis with dapoxetine and what is the cost of cialis where can i buy tadalafil online
special sales on cialis: cialis daily – where can i get cialis
cialis no perscription overnight delivery: buy cheap cialis online with mastercard – cialis difficulty ejaculating
https://tadalaccess.com/# how much does cialis cost with insurance
cialis from canada free samples of cialis or active ingredient in cialis
http://italianculture.net/redir.php?url=http://tadalaccess.com/ cialis online without a prescription
cialis price south africa tamsulosin vs. tadalafil and cheap cialis generic online when will cialis become generic
buying cialis online Tadal Access cialis dosage reddit
mambo 36 tadalafil 20 mg cialis canada pharmacy no prescription required or cialis from canada
https://maps.google.si/url?sa=t&url=https://tadalaccess.com cialis 5mg how long does it take to work
cialis daily dosage cialis generic purchase and cialis dapoxetine overnight shipment cialis for blood pressure
what happens if a woman takes cialis: cialis 40 mg reviews – cialis and cocaine
cialis delivery held at customs: TadalAccess – cialis online delivery overnight
https://tadalaccess.com/# tadalafil citrate powder
cialis australia online shopping cialis dapoxetine tadalafil troche reviews
cialis 50mg cialis 20 mg price walgreens or cialis shipped from usa
https://clients1.google.at/url?q=https://tadalaccess.com cialis generic canada
tadalafil long term usage is tadalafil from india safe and cialis for daily use dosage buying cialis
buy generic tadalafil online cheap: TadalAccess – tadalafil citrate powder
https://tadalaccess.com/# mantra 10 tadalafil tablets
cialis 5mg coupon: Tadal Access – buy cialis 20mg
cialis brand no prescription 365 Tadal Access how to take liquid tadalafil
cialis australia online shopping cheap cialis generic online or cialis experience reddit
https://maps.google.dj/url?q=https://tadalaccess.com when will generic tadalafil be available
where to buy generic cialis india pharmacy cialis and cialis payment with paypal cialis tadalafil & dapoxetine
cialis recommended dosage: TadalAccess – cialis with out a prescription
https://tadalaccess.com/# brand cialis australia
cialis samples cialis 10mg reviews or wallmart cialis
http://www.bayanay.info/forum-oxota/away.php?s=http://tadalaccess.com order cialis canada
cheapest cialis online how long does cialis take to work and cialis leg pain no prescription cialis
cialis patent expiration: Tadal Access – pictures of cialis
how to buy cialis: cialis online delivery overnight – cialis online without perscription
order generic cialis online cialis online pharmacy australia or cialis medicare
https://images.google.com.lb/url?q=https://tadalaccess.com vardenafil and tadalafil
cialis no prescription overnight delivery cialis slogan and cialis cheap cialis online cheap
https://tadalaccess.com/# does tadalafil work
cialis pills pictures: Tadal Access – cialis one a day with dapoxetine canada
generic cialis available in canada [url=https://tadalaccess.com/#]TadalAccess[/url] 20 mg tadalafil best price
no prescription cialis cialis available in walgreens over counter?? or tadalafil no prescription forum
https://clients1.google.st/url?q=https://tadalaccess.com tadalafil cost cvs
active ingredient in cialis order generic cialis online and cheap cialis generic online cialis after prostate surgery
buy cialis with american express: TadalAccess – no prescription female cialis
https://tadalaccess.com/# cialis information
cialis or levitra: TadalAccess – buy cialis no prescription australia
when does tadalafil go generic buy cipla tadalafil or cialis and nitrates
https://www.serbiancafe.com/lat/diskusije/new/redirect.php?url=https://tadalaccess.com cialis professional review
tadalafil citrate liquid purchase brand cialis and cialis pill canada cialis efectos secundarios
cialis 100mg Tadal Access cialis dosage for ed
buy cialis from canada: Tadal Access – tadalafil pulmonary hypertension
https://tadalaccess.com/# cialis free sample
tadalafil tablets 20 mg reviews blue sky peptide tadalafil review or cialis available in walgreens over counter??
http://mychatik.ru/go.php?url=http://tadalaccess.com cialis without prescription
what does cialis do canadian cialis and cialis patent expiration date tadalafil 5mg generic from us
cialis for bph insurance coverage: TadalAccess – cialis for ed
buy liquid cialis online cialis insurance coverage blue cross generic tadalafil in us
https://tadalaccess.com/# vardenafil and tadalafil
how to get cialis for free cialis superactive or buying cialis
https://www.google.tt/url?q=https://tadalaccess.com cialis superactive
cialis for sale brand prices of cialis 20 mg and tadalafil tablets 40 mg does cialis lower your blood pressure
generic cialis tadalafil 20 mg from india: Tadal Access – cialis doesnt work
cialis sample pack cialis price walmart or cialis review
https://www.google.nu/url?q=https://tadalaccess.com best place to buy tadalafil online
cialis where to buy in las vegas nv buying cialis online canadian order and cialis and high blood pressure mint pharmaceuticals tadalafil
cialis coupon walgreens: TadalAccess – cialis walmart
buy cialis online in austalia TadalAccess where to buy generic cialis ?
https://tadalaccess.com/# shop for cialis
cheap t jet 60 cialis online cialis 20 mg coupon or cialis online aust
https://cse.google.sn/url?sa=t&url=https://tadalaccess.com cialis interactions
does cialis lowers blood pressure tadalafil eli lilly and what cialis what does a cialis pill look like
cialis 5mg daily how long before it works: cialis generic best price – generic tadalafil tablet or pill photo or shape
cialis 20 mg: buy generic cialis online – cheap generic cialis canada
https://tadalaccess.com/# what is the difference between cialis and tadalafil
buying cialis online Tadal Access cialis windsor canada
cialis after prostate surgery mambo 36 tadalafil 20 mg reviews or cialis tadalafil 5mg once a day
https://maps.google.com.sg/url?sa=t&url=https://tadalaccess.com cialis pills
paypal cialis payment cialis cost per pill and cialis com coupons do you need a prescription for cialis
how to get cialis prescription online: cialis walgreens – order cialis online no prescription reviews
cialis and alcohol: cialis headache – cialis online pharmacy australia
best price on cialis cialis dosage for ed or tadalafil tablets
https://www.google.ht/url?sa=t&url=https://tadalaccess.com cialis male enhancement
brand cialis cialis price costco and cialis walgreens difference between tadalafil and sildenafil
https://tadalaccess.com/# cheapest 10mg cialis
order generic cialis Tadal Access cialis how long
cialis for sale in toront ontario: TadalAccess – cialis coupon online
canadian pharmacy cialis 40 mg: cialis vs tadalafil – buy tadalafil no prescription
https://tadalaccess.com/# buy tadalafil no prescription
walgreens cialis prices cialis online without prescription cialis online canada ripoff
cialis generic timeline sanofi cialis otc or cialis canada over the counter
https://www.martialartsplanet.com/proxy.php?link=https://tadalaccess.com best price on generic cialis
snorting cialis cialis without a doctor prescription canada and cialis dosages where to buy cialis over the counter
cialis advertisement: TadalAccess – price of cialis in pakistan
https://tadalaccess.com/# generic tadalafil prices
buy cialis free shipping: Tadal Access – cialis onset
cialis 100mg from china cialis india or cialis dosage for bph
https://images.google.com.vn/url?sa=t&url=https://tadalaccess.com cialis for sale in toront ontario
cialis professional ingredients paypal cialis payment and when will generic cialis be available in the us cialis for sale toronto
centurion laboratories tadalafil review TadalAccess cialis super active
cialis over the counter: TadalAccess – cialis manufacturer coupon
sunrise remedies tadalafil tadalafil troche reviews or cialis 10mg ireland
https://www.domainsherpa.com/share.php?site=http://tadalaccess.com cialis 20mg for sale
canadian cialis online cialis vs tadalafil and average dose of tadalafil pictures of cialis pills
https://tadalaccess.com/# generic cialis tadalafil 20mg reviews
cialis milligrams: Tadal Access – cialis picture
buy cialis online without prescription Tadal Access cialis tadalafil tablets
cialis mexico: TadalAccess – purchase brand cialis
https://tadalaccess.com/# cialis online pharmacy australia
cialis windsor canada when is generic cialis available or cheapest cialis 20 mg
http://toolbarqueries.google.com/url?q=https://tadalaccess.com cialis online overnight shipping
cialis slogan cialis otc 2016 and pictures of cialis pills cialis leg pain
buy cialis/canada: TadalAccess – buy cialis free shipping
pastillas cialis cialis free 30 day trial or cialis black
https://www.google.vu/url?q=https://tadalaccess.com cialis 5mg cost per pill
us pharmacy cialis cialis free and cialis 30 day free trial cialis daily dosage
vardenafil and tadalafil online cialis cialis sample pack
cialis 5mg side effects: TadalAccess – tadalafil generico farmacias del ahorro
https://tadalaccess.com/# cialis medicare
п»їwhat can i take to enhance cialis how much does cialis cost at walmart or buy cialis with dapoxetine in canada
https://www.clickcritters.com/external_page.php?url=https://tadalaccess.com cialis manufacturer coupon 2018
tadalafil (tadalis-ajanta) generic tadalafil 40 mg and cialis online delivery overnight 20 mg tadalafil best price
cheap tadalafil no prescription: trusted online store to buy cialis – cialis website
cialis from india: TadalAccess – cialis how long
which is better cialis or levitra cialis dosis cialis liquid for sale
https://tadalaccess.com/# can you drink wine or liquor if you took in tadalafil
cheapest cialis online: Tadal Access – cialis none prescription
cialis for blood pressure tadalafil troche reviews or cialis after prostate surgery
https://www.google.mu/url?q=https://tadalaccess.com cialis how does it work
cialis 20mg side effects buy a kilo of tadalafil powder and cialis going generic cialis coupon rite aid
buy cialis free shipping: cialis 20 mg price walmart – tadalafil medication
tadalafil cialis cialis pill or do you need a prescription for cialis
https://clients1.google.com.bz/url?q=https://tadalaccess.com cialis samples for physicians
cialis online paypal cialis payment with paypal and cialis generic release date maximum dose of cialis in 24 hours
https://tadalaccess.com/# price of cialis at walmart
how to take liquid tadalafil: cialis para que sirve – cialis no prescription overnight delivery
cialis for sale in canada cialis sample request form or erectile dysfunction tadalafil
https://www.google.lv/url?q=https://tadalaccess.com cialis voucher
prices of cialis what is cialis used for and cialis soft cialis without prescription
cialis doesnt work: is cialis a controlled substance – how long before sex should you take cialis
typical cialis prescription strength cialis black 800 to buy in the uk one pill cialis lower blood pressure
https://tadalaccess.com/# cialis discount card
cialis dapoxetine europe: truth behind generic cialis – cialis 20 mg tablets and prices
tadalafil online paypal: Tadal Access – best price on generic cialis
cialis for daily use side effects cialis package insert or tadalafil tablets 40 mg
http://tourzwei.radblogger.net/redirect.php?url=tadalaccess.com cialis after prostate surgery
canadian pharmacy online cialis when is the best time to take cialis and does tadalafil lower blood pressure cialis soft tabs canadian pharmacy
buy cialis toronto cialis before and after pictures purchase cialis online cheap
https://tadalaccess.com/# cialis bathtub
no prescription tadalafil tadalafil lowest price or cialis at canadian pharmacy
http://db.cbservices.org/cbs.nsf/forward?openform&http://tadalaccess.com/ п»їwhat can i take to enhance cialis
cialis 50mg side effects cialis and tadalafil generico farmacias del ahorro cialis 20 mg price costco
recreational cialis: best price on generic tadalafil – cialis tadalafil 20mg kaufen
buy tadalafil reddit: cialis softabs online – benefits of tadalafil over sidenafil
where can i buy cialis over the counter when does tadalafil go generic or best price cialis supper active
https://clients1.google.com.my/url?q=https://tadalaccess.com tadalafil how long to take effect
cialis soft where to buy cialis and where to buy tadalafil in singapore buy cialis pro
cialis generic canada Tadal Access sildenafil and tadalafil
cialis cost at cvs: Tadal Access – cialis for ed
online cialis: TadalAccess – cialis free trial voucher
https://tadalaccess.com/# buy cialis without prescription
canadian pharmacy cialis 20mg cialis dopoxetine or cialis 5mg best price
https://www.dasha.com.ua/redirect.php?redir=http://tadalaccess.com/ cialis com free sample
cialis free tadalafil online canadian pharmacy and what does cialis treat tadalafil eli lilly
cialis liquid for sale cialis patent expiration 2016 generic cialis tadalafil 20mg india
prices cialis: Tadal Access – cialis 2.5 mg
cheap tadalafil 10mg buy tadalafil cheap online or overnight cialis delivery usa
http://inuza.me/index.php?url=https://tadalaccess.com cialis same as tadalafil
canada drug cialis cialis 5mg daily and how long does it take cialis to start working cialis definition
buying generic cialis online safe: Tadal Access – maximum dose of tadalafil
https://tadalaccess.com/# ordering cialis online
tadalafil how long to take effect tadalafil eli lilly or cialis dosage reddit
http://clients1.google.st/url?q=https://tadalaccess.com cheap cialis canada
can i take two 5mg cialis at once generic cialis vs brand cialis reviews and tadalafil tablets cialis daily side effects
is tadalafil available at cvs cialis 5mg daily how long before it works buy cialis by paypal
where to buy cialis online: buying cialis in mexico – cialis not working anymore
tadalafil hong kong: Tadal Access – cialis 5mg daily
https://tadalaccess.com/# cialis online canada ripoff
cialis generic over the counter Tadal Access cialis tubs
cialis after prostate surgery cialis website or canadian cialis no prescription
https://www.smartspace.ws/login.php?TraderId=1123&rdurl=https://tadalaccess.com::: cheapest cialis online
walgreen cialis price how many 5mg cialis can i take at once and buy tadalafil online no prescription tadalafil vs sildenafil
cialis online without pres: tadalafil without a doctor prescription – cialis tadalafil
cialis over the counter in spain what happens when you mix cialis with grapefruit? or tadalafil generic headache nausea
https://www.google.td/url?q=https://tadalaccess.com cialis dapoxetine australia
cialis cheapest prices best reviewed tadalafil site and buying cialis online active ingredient in cialis
stendra vs cialis: Tadal Access – cialis manufacturer
https://tadalaccess.com/# how many mg of cialis should i take
cialis prices cheap cialis generic online or cialis overnight deleivery
https://www.google.cg/url?q=https://tadalaccess.com cialis dapoxetine overnight shipment
cialis 20 milligram buy cialis united states and cialis canada over the counter cialis dosage for bph
buy cheap tadalafil online: TadalAccess – difference between sildenafil tadalafil and vardenafil
buy generic tadalafil online cheap TadalAccess cialis online without prescription
how long for cialis to take effect: TadalAccess – cialis walmart
https://tadalaccess.com/# cialis by mail
cialis online no prescription: what is the active ingredient in cialis – cialis free trial voucher
cialis w/dapoxetine Tadal Access cialis paypal
is there a generic cialis available? tadalafil daily use or purchase cialis online
https://cse.google.tt/url?q=http://tadalaccess.com when will cialis be over the counter
cialis pill canada cialis for performance anxiety and cheapest cialis 20 mg what happens if you take 2 cialis
cialis for performance anxiety: walgreen cialis price – cialis 20 mg duration
buying cialis cialis over the counter in spain or cialis meme
https://images.google.bs/url?q=https://tadalaccess.com vidalista tadalafil reviews
peptide tadalafil reddit where to buy liquid cialis and cheapest cialis 20 mg vardenafil tadalafil sildenafil
https://tadalaccess.com/# cialis time
canadian cialis: Tadal Access – best reviewed tadalafil site
cialis windsor canada TadalAccess can cialis cause high blood pressure
cialis daily review brand cialis australia or brand cialis australia
https://cse.google.lv/url?q=https://tadalaccess.com cialis 5 mg tablet
how long does cialis take to work 10mg tadacip tadalafil and where to buy cialis online cialis san diego
cialis 100mg: Tadal Access – printable cialis coupon
https://tadalaccess.com/# buy tadalafil online paypal
cialis company Tadal Access cialis shipped from usa
buy liquid cialis online: TadalAccess – cialis drug class
tadalafil troche reviews: stockists of cialis – cialis doesnt work
safest and most reliable pharmacy to buy cialis tadalafil and voice problems or cialis time
https://www.lolinez.com/?http://tadalaccess.com cialis online overnight shipping
tadalafil review does cialis make you harder and pastillas cialis buy cialis online safely
cialis online without a prescription cialis used for or cialis in las vegas
https://maps.google.nl/url?sa=t&url=https://tadalaccess.com is cialis covered by insurance
cheap cialis pills uk cialis 10mg and cialis prescription assistance program cialis canadian pharmacy ezzz
how long does cialis take to work 10mg TadalAccess buy generic cialiss
https://tadalaccess.com/# how long does cialis last 20 mg
reliable source cialis tadalafil 5 mg tablet or difference between cialis and tadalafil
http://images.google.la/url?q=https://tadalaccess.com cialis online without perscription
cipla tadalafil review liquid tadalafil research chemical and cialis for enlarged prostate blue sky peptide tadalafil review
what cialis: cialis shelf life – buy cheapest cialis
buy cialis generic online 10 mg Tadal Access para que sirve las tabletas cialis tadalafil de 5mg
https://tadalaccess.com/# cheap t jet 60 cialis online
when will cialis become generic: TadalAccess – cialis and alcohol
purchase cialis online buy tadalafil reddit or cialis online without prescription
http://www.passerelle.or.jp/modules/wordpress/wp-ktai.php?view=redir&url=http://tadalaccess.com what happens if a woman takes cialis
buy cialis without doctor prescription tadalafil generic cialis 20mg and cialis substitute too much cialis
cialis superactive buying cialis online canadian order cialis online without prescription
cialis 20 mg tablets and prices tadalafil 40 mg india or cialis 20 mg duration
https://maps.google.com.lb/url?q=https://tadalaccess.com cialis shelf life
what is cialis for what is cialis good for and buy tadalafil online paypal cialis super active vs regular cialis
tadalafil pulmonary hypertension: TadalAccess – cialis reddit
tadalafil 40 mg with dapoxetine 60 mg cipla tadalafil review or walmart cialis price
https://www.google.gp/url?sa=t&url=https://tadalaccess.com average dose of tadalafil
cialis efectos secundarios best time to take cialis and walgreen cialis price cialis coupon walgreens
https://tadalaccess.com/# buy cialis online free shipping
cialis manufacturer TadalAccess cialis voucher
difference between sildenafil tadalafil and vardenafil: TadalAccess – cialis tadalafil 20mg tablets
average dose of tadalafil cialis and alcohol or tadalafil no prescription forum
http://alpha.astroempires.com/redirect.aspx?https://tadalaccess.com/ cialis 100mg review
cialis daily review cialis superactive and cialis 20mg for sale can you drink wine or liquor if you took in tadalafil
https://tadalaccess.com/# pregnancy category for tadalafil
why is cialis so expensive cialis doesnt work for me prices on cialis
generic cialis vs brand cialis reviews: TadalAccess – cialis vs tadalafil
cialis pills online order generic cialis online or cialis where to buy in las vegas nv
https://cse.google.mv/url?q=https://tadalaccess.com special sales on cialis
tadalafil generic 20 mg ebay cialis erection and how long before sex should i take cialis cialis professional vs cialis super active
cialis 30 mg dose: TadalAccess – cialis none prescription
https://tadalaccess.com/# cialis 5 mg tablet
viagara cialis levitra TadalAccess mantra 10 tadalafil tablets
tadalafil dose for erectile dysfunction cialis price cvs or cialis ontario no prescription
https://www.google.co.ls/url?q=https://tadalaccess.com cialis manufacturer
cialis using paypal in australia nebenwirkungen tadalafil and mint pharmaceuticals tadalafil reviews cialis 20 mg price walmart
buying cialis cialis available in walgreens over counter?? or buying cheap cialis online
http://www.google.st/url?q=http://tadalaccess.com buy cheap tadalafil online
cialis professional vs cialis super active cialis recommended dosage and cialis and alcohol cheap cialis 5mg
cialis review: tadalafil no prescription forum – order generic cialis
cialis and adderall is there a generic equivalent for cialis pictures of cialis pills
https://tadalaccess.com/# buy cialis online free shipping
cialis manufacturer coupon free trial how much does cialis cost at cvs or cialis what is it
https://clients1.google.sh/url?q=https://tadalaccess.com cialis 10mg reviews
canadian cialis 5mg buy cialis online free shipping and cialis information cialis insurance coverage
cialis how long does it last: cialis dosis – pastilla cialis
tadalafil long term usage when does tadalafil go generic cialis used for
https://tadalaccess.com/# centurion laboratories tadalafil review
cialis patent expiration 2016 buy a kilo of tadalafil powder or cialis in las vegas
https://clients1.google.ne/url?q=https://tadalaccess.com walmart cialis price
cialis side effects sunrise remedies tadalafil and cialis dapoxetine australia cialis online no prescription
does tadalafil lower blood pressure: cialis online cheap – how much is cialis without insurance
cialis online with no prescription what are the side effects of cialis or does cialis raise blood pressure
https://cse.google.ht/url?sa=t&url=https://tadalaccess.com cialis tadalafil cheapest online
cialis from india online pharmacy cialis tadalafil cheapest online and buy generic cialis online cialis tadalafil 5mg once a day
cialis san diego best price cialis supper active cialis review
cialis for bph cialis recreational use or cialis online canada
https://cse.google.lu/url?sa=t&url=https://tadalaccess.com cialis strength
generic tadalafil prices para que sirve las tabletas cialis tadalafil de 5mg and where to buy cialis soft tabs cialis purchase canada
cialis picture: TadalAccess – which is better cialis or levitra
https://tadalaccess.com/# evolution peptides tadalafil
cialis and cocaine cialis 100mg review prices cialis
Ero Pharm Fast Ero Pharm Fast cheap ed pills
buy antibiotics from canada: buy antibiotics online uk – buy antibiotics
Ero Pharm Fast: erectile dysfunction online – Ero Pharm Fast
buy antibiotics from india: buy antibiotics online – buy antibiotics
Medications online Australia: Medications online Australia – online pharmacy australia
https://pharmau24.shop/# Online drugstore Australia
where can i buy erectile dysfunction pills Ero Pharm Fast online ed prescription
cheapest antibiotics: Biot Pharm – get antibiotics without seeing a doctor
Ero Pharm Fast: where to get ed pills – Ero Pharm Fast
best online doctor for antibiotics: BiotPharm – buy antibiotics from canada
Pharm Au24 Buy medicine online Australia pharmacy online australia
https://pharmau24.com/# Medications online Australia
cheapest antibiotics: buy antibiotics online – buy antibiotics over the counter
get antibiotics without seeing a doctor: buy antibiotics online uk – cheapest antibiotics
Buy medicine online Australia: Medications online Australia – Licensed online pharmacy AU
online ed medication: Ero Pharm Fast – low cost ed pills
Online medication store Australia pharmacy online australia or Online drugstore Australia
http://www.sitedossier.com/site/pharmau24.shop Online medication store Australia
Licensed online pharmacy AU pharmacy online australia and Licensed online pharmacy AU Pharm Au 24
buy antibiotics for uti buy antibiotics from canada or buy antibiotics from canada
https://images.google.com/url?q=http://biotpharm.com buy antibiotics
buy antibiotics online cheapest antibiotics and over the counter antibiotics best online doctor for antibiotics
ed medicines cheap ed meds or discount ed meds
http://www.hashiriya.jp/url.cgi?http://eropharmfast.com/ erectile dysfunction medications online
get ed meds online buying ed pills online and where to buy erectile dysfunction pills cheap ed drugs
Online drugstore Australia: online pharmacy australia – Medications online Australia
https://eropharmfast.shop/# Ero Pharm Fast
buy antibiotics from india: Biot Pharm – best online doctor for antibiotics
best online doctor for antibiotics cheapest antibiotics buy antibiotics online
Ero Pharm Fast: Ero Pharm Fast – Ero Pharm Fast
Pharm Au24: Medications online Australia – Discount pharmacy Australia
Pharm Au24 Medications online Australia Buy medicine online Australia
order ed meds online: online ed prescription – Ero Pharm Fast
get antibiotics without seeing a doctor buy antibiotics or get antibiotics without seeing a doctor
https://images.google.com.vn/url?sa=t&rct=j&url=https://biotpharm.com buy antibiotics online
buy antibiotics for uti buy antibiotics for uti and buy antibiotics get antibiotics quickly
https://pharmau24.com/# Online drugstore Australia
pills for ed online buy ed meds or best online ed pills
https://sambastore.com/en/mandeparaumamigo.php?url=http://eropharmfast.com online ed pharmacy
erectile dysfunction pills online best ed pills online and online erectile dysfunction medication erectile dysfunction meds online
buy antibiotics: buy antibiotics online uk – Over the counter antibiotics pills
Ero Pharm Fast: top rated ed pills – Ero Pharm Fast
antibiotic without presription buy antibiotics online antibiotic without presription
cost of ed meds: Ero Pharm Fast – Ero Pharm Fast
Discount pharmacy Australia pharmacy online australia online pharmacy australia
cheapest antibiotics: buy antibiotics over the counter – over the counter antibiotics
get antibiotics quickly: BiotPharm – get antibiotics quickly
Ero Pharm Fast Ero Pharm Fast Ero Pharm Fast
http://eropharmfast.com/# best online ed medication
best online doctor for antibiotics: buy antibiotics online – buy antibiotics from india
PharmAu24 Medications online Australia Licensed online pharmacy AU
ed prescriptions online buy ed meds online or cheapest ed treatment
https://www.google.st/url?q=https://eropharmfast.com where can i buy ed pills
ed medicines online low cost ed meds and cheapest online ed treatment get ed prescription online
buy antibiotics: buy antibiotics online – buy antibiotics
Ero Pharm Fast ed meds on line erectile dysfunction online prescription
https://eropharmfast.shop/# Ero Pharm Fast
Online drugstore Australia: Pharm Au24 – Licensed online pharmacy AU
PharmAu24 online pharmacy australia Discount pharmacy Australia
buy antibiotics for uti Over the counter antibiotics pills or Over the counter antibiotics for infection
https://maps.google.be/url?sa=i&source=web&rct=j&url=https://biotpharm.com Over the counter antibiotics for infection
buy antibiotics from canada buy antibiotics from india and buy antibiotics from canada Over the counter antibiotics pills
ed rx online Ero Pharm Fast online ed pharmacy
https://biotpharm.shop/# buy antibiotics from india
generic ed meds online: Ero Pharm Fast – ed meds online
cheapest ed meds Ero Pharm Fast buy erectile dysfunction treatment
Online drugstore Australia: online pharmacy australia – online pharmacy australia
buy antibiotics for uti buy antibiotics Over the counter antibiotics pills
Pharm Au 24: Discount pharmacy Australia – Pharm Au 24
https://pharmau24.com/# Buy medicine online Australia
erectile dysfunction online ed meds on line or best ed medication online
http://cttpeseux.ch/romands/link.php?url=http://eropharmfast.com online ed drugs
cheap boner pills online erectile dysfunction prescription and ed medicines cheapest erectile dysfunction pills
Medicaments en ligne livres en 24h pharmacie en ligne france livraison internationale pharmacie en ligne france livraison internationale
pharmacie en ligne sans prescription: acheter médicaments sans ordonnance – pharmacie en ligne france livraison belgique
Acheter du Viagra sans ordonnance: commander Viagra discretement – Viagra sans ordonnance 24h
Cialis pas cher livraison rapide: cialis generique – Acheter Cialis 20 mg pas cher
acheter Kamagra sans ordonnance achat kamagra kamagra oral jelly
Cialis pas cher livraison rapide: Cialis générique sans ordonnance – acheter Cialis sans ordonnance
commander Viagra discretement: viagra en ligne – livraison rapide Viagra en France
https://ciasansordonnance.com/# commander Cialis en ligne sans prescription
commander Viagra discretement: livraison rapide Viagra en France – livraison rapide Viagra en France
viagra sans ordonnance: Meilleur Viagra sans ordonnance 24h – commander Viagra discretement
kamagra gel kamagra en ligne kamagra 100mg prix
cialis generique: commander Cialis en ligne sans prescription – cialis sans ordonnance
achat kamagra: kamagra pas cher – kamagra pas cher
livraison rapide Viagra en France viagra sans ordonnance Viagra generique en pharmacie
Medicaments en ligne livres en 24h: acheter medicaments sans ordonnance – pharmacie en ligne fiable
kamagra gel: livraison discrete Kamagra – kamagra en ligne
https://ciasansordonnance.shop/# Acheter Cialis
kamagra oral jelly: livraison discrète Kamagra – kamagra gel
acheter Viagra sans ordonnance prix bas Viagra generique Acheter du Viagra sans ordonnance
traitement ED discret en ligne: cialis prix – Acheter Cialis 20 mg pas cher
pharmacie en ligne sans prescription: pharmacie en ligne – Achat mГ©dicament en ligne fiable
achat kamagra: kamagra 100mg prix – kamagra en ligne
acheter Cialis sans ordonnance: Acheter Cialis – Acheter Cialis 20 mg pas cher
pharmacie en ligne sans prescription acheter medicaments sans ordonnance Achat mГ©dicament en ligne fiable
http://viasansordonnance.com/# acheter Viagra sans ordonnance
cialis sans ordonnance: acheter Cialis sans ordonnance – Acheter Cialis
cialis generique: cialis prix – commander Cialis en ligne sans prescription
Acheter Cialis 20 mg pas cher: Acheter Cialis – cialis generique
Viagra generique en pharmacie acheter Viagra sans ordonnance Viagra generique en pharmacie
acheter médicaments sans ordonnance: pharmacie en ligne sans prescription – Pharmacie Internationale en ligne
Meilleur Viagra sans ordonnance 24h: livraison rapide Viagra en France – prix bas Viagra generique
cialis prix: Acheter Cialis – Cialis sans ordonnance 24h
https://pharmsansordonnance.com/# pharmacie en ligne pas cher
viagra sans ordonnance Acheter du Viagra sans ordonnance viagra en ligne
Cialis générique sans ordonnance: Cialis sans ordonnance 24h – Acheter Cialis
cialis prix: commander Cialis en ligne sans prescription – commander Cialis en ligne sans prescription
Viagra generique en pharmacie Viagra generique en pharmacie acheter Viagra sans ordonnance
Acheter du Viagra sans ordonnance: Meilleur Viagra sans ordonnance 24h – commander Viagra discretement
commander sans consultation medicale: commander sans consultation medicale – Pharmacie en ligne livraison Europe
Medicaments en ligne livres en 24h: commander sans consultation medicale – pharmacie en ligne fiable
http://pharmsansordonnance.com/# Pharmacie sans ordonnance
viagra sans ordonnance: Acheter du Viagra sans ordonnance – livraison rapide Viagra en France
pharmacie en ligne france livraison internationale pharmacie en ligne pas cher pharmacie en ligne france fiable
commander Kamagra en ligne: commander Kamagra en ligne – kamagra gel
kamagra gel: kamagra livraison 24h – kamagra oral jelly
Achat m̩dicament en ligne fiable: commander Kamagra en ligne Рkamagra en ligne
Pharmacie en ligne livraison Europe livraison discrete Kamagra Kamagra oral jelly pas cher
Cialis generique sans ordonnance Acheter Cialis 20 mg pas cher or Cialis sans ordonnance 24h
http://nunet.ca/link_r.php?fn=ciasansordonnance.com& cialis generique
cialis sans ordonnance Cialis pas cher livraison rapide and traitement ED discret en ligne cialis sans ordonnance
Pharmacie sans ordonnance: kamagra livraison 24h – kamagra gel
acheter Viagra sans ordonnance: Meilleur Viagra sans ordonnance 24h – Viagra generique en pharmacie
http://kampascher.com/# acheter Kamagra sans ordonnance
commander Viagra discretement Acheter du Viagra sans ordonnance or Acheter du Viagra sans ordonnance
http://www.katakura.net/xoops/html/modules/wordpress/wp-ktai.php?view=redir&url=http://viasansordonnance.com/ Acheter du Viagra sans ordonnance
Acheter du Viagra sans ordonnance Acheter du Viagra sans ordonnance and Acheter du Viagra sans ordonnance Meilleur Viagra sans ordonnance 24h
achat kamagra livraison discrete Kamagra kamagra en ligne
acheter Kamagra sans ordonnance: kamagra en ligne – acheter Kamagra sans ordonnance
commander Kamagra en ligne: kamagra 100mg prix – kamagra gel
pharmacie en ligne sans prescription pharmacie en ligne france fiable or pharmacie en ligne pas cher
https://images.google.bi/url?q=http://pharmsansordonnance.com Medicaments en ligne livres en 24h
acheter medicaments sans ordonnance pharmacie en ligne sans prescription and pharmacie en ligne pas cher Medicaments en ligne livres en 24h
viagra sans ordonnance prix bas Viagra generique Viagra generique en pharmacie
kamagra livraison 24h: livraison discrète Kamagra – kamagra gel
Viagra sans ordonnance 24h: commander Viagra discretement – livraison rapide Viagra en France
achat kamagra: kamagra en ligne – Kamagra oral jelly pas cher
https://kampascher.shop/# commander Kamagra en ligne
prix bas Viagra generique Viagra sans ordonnance 24h or Acheter du Viagra sans ordonnance
http://www.capitolbeatok.com/Redirect.aspx?destination=https://viasansordonnance.com/ livraison rapide Viagra en France
acheter Viagra sans ordonnance Viagra sans ordonnance 24h and viagra en ligne Meilleur Viagra sans ordonnance 24h
pharmacie en ligne avec ordonnance Pharmacies en ligne certifiees pharmacie en ligne
acheter medicaments sans ordonnance: pharmacie en ligne pas cher – pharmacie en ligne sans ordonnance
pharmacie en ligne: pharmacie en ligne sans ordonnance – pharmacie en ligne avec ordonnance
kamagra gel achat kamagra kamagra oral jelly
pharmacie en ligne sans ordonnance commander sans consultation medicale or Pharmacies en ligne certifiees
http://www.25gx.com/wl2007/coolwebshow.asp?url=https://pharmsansordonnance.com pharmacie en ligne sans prescription
pharmacie internet fiable France Pharmacie en ligne livraison Europe and pharmacie en ligne pharmacie en ligne sans ordonnance
acheter Kamagra sans ordonnance kamagra en ligne or Kamagra oral jelly pas cher
https://toolbarqueries.google.fm/url?sa=t&url=https://kampascher.com kamagra livraison 24h
kamagra gel kamagra livraison 24h and acheter Kamagra sans ordonnance achat kamagra
acheter medicaments sans ordonnance: Pharmacies en ligne certifiees – Achat mГ©dicament en ligne fiable
pharmacie en ligne pas cher pharmacie internet fiable France acheter mГ©dicament en ligne sans ordonnance
Viagra sans ordonnance 24h Viagra sans ordonnance 24h or Le gГ©nГ©rique de Viagra
http://www.torremarmores.com/en/gallery2/main.php?g2_view=core.UserAdmin&g2_subView=core.UserLogin&g2_return=https://viasansordonnance.com viagra sans ordonnance
Acheter du Viagra sans ordonnance Acheter du Viagra sans ordonnance and viagra en ligne Viagra sans ordonnance 24h suisse
acheter Viagra sans ordonnance: viagra sans ordonnance – livraison rapide Viagra en France
Cialis sans ordonnance 24h: Acheter Cialis 20 mg pas cher – acheter Cialis sans ordonnance
commander Viagra discretement viagra en ligne Prix du Viagra 100mg en France
Acheter du Viagra sans ordonnance: viagra en ligne – viagra en ligne
Pharmacies en ligne certifiees acheter medicaments sans ordonnance pharmacie en ligne fiable
acheter kamagra site fiable: kamagra gel – kamagra en ligne
Viagra homme prix en pharmacie sans ordonnance viagra sans ordonnance or Viagra en france livraison rapide
https://maps.google.ba/url?q=https://viasansordonnance.com Viagra sans ordonnance 24h
Viagra generique en pharmacie Meilleur Viagra sans ordonnance 24h and Viagra generique en pharmacie livraison rapide Viagra en France
https://pharmsansordonnance.shop/# pharmacie en ligne avec ordonnance
acheter medicaments sans ordonnance pharmacie internet fiable France pharmacie en ligne livraison europe
commander Kamagra en ligne: acheter Kamagra sans ordonnance – kamagra gel
Viagra generique en pharmacie viagra en ligne acheter Viagra sans ordonnance
viagra en ligne: livraison rapide Viagra en France – Viagra sans ordonnance 24h
Medicaments en ligne livres en 24h: commander sans consultation medicale – vente de mГ©dicament en ligne
pharmacies en ligne certifiГ©es pharmacie internet fiable France pharmacie en ligne
https://kampascher.com/# pharmacie en ligne france pas cher
Kamagra oral jelly pas cher: kamagra oral jelly – Kamagra oral jelly pas cher
kamagra pas cher kamagra en ligne Kamagra oral jelly pas cher
commander Viagra discretement prix bas Viagra generique or acheter Viagra sans ordonnance
http://www.1491.com.tw/phpinfo.php?a= prix bas Viagra generique
livraison rapide Viagra en France viagra en ligne and Viagra sans ordonnance 24h suisse commander Viagra discretement
prix bas Viagra generique: Acheter du Viagra sans ordonnance – commander Viagra discretement
pharmacie en ligne sans ordonnance Pharmacies en ligne certifiees vente de mГ©dicament en ligne
cialis generique: Acheter Cialis – traitement ED discret en ligne
https://pharmsansordonnance.shop/# pharmacie en ligne france livraison internationale
achat kamagra acheter kamagra site fiable kamagra oral jelly
farmacia online weleda farmacia online coronavirus fГ©rula dental farmacia online
mГ©dicaments infection urinaire sans ordonnance: collyre nourrisson sans ordonnance – peut on acheter de la vitamine d en pharmacie sans ordonnance
comprar adiro sin receta: farmacia veterinaria madrid online – comprar cloretilo sin receta
médicament contre l’anxiété sans ordonnance en pharmacie: Pharmacie Express – sildenafil sans ordonnance
farmacia vaticano online egerian crema exocin pomata
https://pharmacieexpress.shop/# liniment gifrer 900ml
ecoval scalp fluid prezzo: Farmacia Subito – tachipirina 1000 fiale prezzo
giant 40/10: farmacia ruggeri palermo – algonerv crema controindicazioni
drogue pharmacie sans ordonnance: Pharmacie Express – medicament pour cystite avec ordonnance
macladin 500 prezzo progeffik 200 lucen prezzo
pharmacie en ligne viagra: egoviril en pharmacie sans ordonnance en france – sildenafil achat
vitamine d en gouttes en pharmacie sans ordonnance: ordonnance 6 mois Рm̩dicament contre cystite sans ordonnance
equivalent fungizone sans ordonnance: sirop argousier – stresam ordonnance ou pas
augmentin sospensione orale coverlam principio attivo cortisone al cane effetti collaterali
http://confiapharma.com/# comprar estrГіgenos sin receta
gestion direccion oficinas farmacia online: farmacia online piГ№ conveniente – farmacia online segura
se puede comprar la pastilla del dia despues en la farmacia sin receta: mascarillas 3m farmacia online – cerazet comprar sin receta
acheter ozempic en ligne sans ordonnance test pharmacie covid sans ordonnance peut on acheter du levitra en pharmacie sans ordonnance
generique pilule jasmine: cialis 5 mg prix france – comment acheter un mГ©dicament prescrit sur ordonnance sans ordonnance
argotone neonato 1 mese: argento proteinato per bambini – tilade spray dove trovarlo
https://confiapharma.shop/# la farmacia mГЎs barata online
punture pappataci foto: metoprololo 100 mg prezzo – pantorc prezzo
augmentin compresse cialis 20 mg prezzo antistaminico pafinur
minoxidil pharmacie sans ordonnance: acheter ozempic sans ordonnance Рviagra g̩n̩rique 100 mg
vardenafil teva 20 mg prezzo locorten stomatologico or ematonil plus a cosa serve
https://www.google.se/url?q=https://farmaciasubito.com clody 200 mg fiale ГЁ mutuabile prezzo
farmacia linfa palermo synflex forte 550 and lacirex a cosa serve pylera prezzo
farmacia blesa online: farmacia online dilatadores vaginales – vicks vaporub farmacia online
voltfast 50 mg prezzo: cefodox sciroppo – samyr 400 fiale prezzo
enterolactis plus 30 capsule inneov densilogy algix 90 prezzo
comprar spiraxin sin receta: que farmacia online es mas barata – comprar selincro sin receta
amoxicilline sans ordonnance en ligne: impuissance pilule pour bander en pharmacie sans ordonnance – mal de gorge pharmacie sans ordonnance
https://farmaciasubito.shop/# farmacia firenze online
slowmet 1000 prezzo Farmacia Subito dufaston prezzo
pillola abortiva farmacia online diprosalic soluzione cutanea or cortisone cane dopo quanto fa effetto
https://images.google.ng/url?q=https://farmaciasubito.com sildenafil eg 50 mg prezzo
naltrexone prezzo pevisone latte acquisto online and farmacia offerte online ovixan crema punture insetti
cytomel t3 en pharmacie sans ordonnance: cetirizine 10 mg – gommage filorga
cursos online gratuitos na area de farmacia com certificado se puede comprar airtal sin receta or se puede comprar zamene sin receta
https://forum.keenswh.com/proxy.php?link=http://confiapharma.com farmacia online cialis originale
puedo comprar permetrina sin receta productos online de farmacia and la farmacia online en casa puedo comprar anticonceptivos sin receta en espaГ±a
farmacia online piu affidabile: estinette pillola – perfalgan flebo
que comprar para la candidiasis sin receta comprar ditropan sin receta mГЎster farmacia online
ordonnance pharmacie sans carte vitale suppositoire sans ordonnance or anxiolytique sans ordonnance en pharmacie
http://maps.google.ml/url?q=https://pharmacieexpress.shop consultation rhumatologue sans ordonnance
cavailles savon pharmacie pilule sans ordonnance and erylik gel antalgique sans ordonnance
farmacia vetrinaria online: donde puedo comprar salbutamol sin receta – cloroquina farmacia online
codoliprane sans ordonnance propranolol sans ordonnance or pharmacie en ligne sans ordonnance belgique
https://maps.google.cz/url?sa=t&url=https://pharmacieexpress.com viagra vente en ligne
delivrance monuril sans ordonnance aetoxisclerol 0.5 and fer en pharmacie sans ordonnance acheter viagra
comprar orfidal sin receta online: donde comprar benzodiacepinas sin receta – comprar anafranil sin receta
frequil principio attivo aripiprazolo 5 mg prezzo sildenafil 100 mg prezzo in farmacia
http://pharmacieexpress.com/# ceinture lombaire pharmacie sans ordonnance
farmacia online blastoestimulina Гіvulos: campoamor farmacia online – cloretilo se puede comprar sin receta
se puede comprar aciclovir sin receta: puedo comprar azitromicina sin receta en estados unidos – se puede comprar efedrina sin receta
curso online gratuito de farmacia farmacia online receta electronica or comprar lexatin sin receta medica
http://www.google.bt/url?q=https://confiapharma.com viagra farmacia gibraltar online
farmacia doctor max online se puede comprar paracetamol sin receta en francia and se puede comprar proscar sin receta cloretilo se puede comprar sin receta
sildenafil viagra Г©quivalent kГ©toderm sans ordonnance achat codeine en ligne sans ordonnance
atida farmacia online: farmacia online mascarillas reutilizables – charro desde casa (para farmacia charro online) vigo
neutrogena intense repair rap creme or bain de bouche pharmacie sans ordonnance
https://toolbarqueries.google.nl/url?sa=t&url=https://pharmacieexpress.shop pillule viagra
levothyrox pharmacie sans ordonnance prix finasteride and peut on acheter alli en pharmacie sans ordonnance dapoxetine sans ordonnance
nimotop gocce prezzo: victoza 5 penne prezzo – minias a cosa serve
indom collirio monodose mycostatin sospensione orale farmacia bonola
cialis en pharmacie sans ordonnance en france acheter sildenafil or impuissance pilule pour bander en pharmacie sans ordonnance
https://www.gladbeck.de/externerlink.asp?ziel=http://pharmacieexpress.shop etiaxil pharmacie sans ordonnance
lormГ©tazГ©pam sans ordonnance ordonnance pharmacie and Г©quivalent amoxicilline sans ordonnance peut on se faire tester sans ordonnance en pharmacie
tretinoina crema italia: Farmacia Subito – yasminelle pillola prezzo
produit verrue pharmacie sans ordonnance: diur̩tique en pharmacie sans ordonnance Рp̩nicilline sans ordonnance
http://farmaciasubito.com/# niklod 200 prezzo
sildenafil viagra demander une ordonnance Г son mГ©decin or equivalent secnol sans ordonnance
https://cse.google.com.pe/url?sa=t&url=https://pharmacieexpress.com diprosone avec ou sans ordonnance
monuril pharmacie sans ordonnance jouvence gelГ©e ultra fresh jambes lГ©gГЁres and test urinaire sans ordonnance grippe pharmacie sans ordonnance
fer sans ordonnance cuprum metallicum sommeil peut on acheter de l’aspirine sans ordonnance
abba antibiotico: farmacia online tampone rapido – pariet 20 mg prezzo
mifarma farmacia online, calle virgen, 76, 02100 tarazona de la mancha, albacete: rectiv se puede comprar sin receta – doc farmacia online
oxycontin 80 mg torvast 20 prezzo decapeptyl 3.75
analyse urine sans ordonnance peut on avoir des medicaments sans ordonnance dans une pharmacie de garde or viagra pas cher
http://mejtoft.se/research/?page=redirect&link=https://pharmacieexpress.shop:: achat testostГ©rone sans ordonnance
goviril en pharmacie sans ordonnance doliprane bГ©bГ© sans ordonnance prix and brosse a dent chirurgicale 7/100 ventipulmin achat sans ordonnance
http://confiapharma.com/# farmacia online montevideo
fluocaril bi-fluorГ© 2500 ppm: Pharmacie Express – blemish age defense skinceuticals
farmacia centrale arcore deniban 50 or vimovo prezzo
https://images.google.sc/url?q=https://farmaciasubito.com niklod 200 a cosa serve
deltacortene cane pentacol 800 and tiche prezzo ebastina prezzo
ou trouver du viagra ou cialis Pharmacie Express ducray ictyane crГЁme Г©molliente visage et corps
hydrabio perfecteur spf 30: Pharmacie Express – dermablend fond de teint
mГ©dicament pour maigrir trГЁs puissant en pharmacie sans ordonnance mГ©dicament pour les dents sans ordonnance ovule mycose pharmacie sans ordonnance
se puede comprar cialis sin receta en farmacias fГsicas: farmacia mГЎs barata online – farmacia andorra online cialis
prorhinel rhume unidose peut on voir un cardiologue sans ordonnance or acheter theralene 4 sans ordonnance
https://maps.google.com.co/url?q=https://pharmacieexpress.shop mГ©dicament pour prГ©coce sans ordonnance en pharmacie
pГ©nicilline sans ordonnance eau micellaire avГЁne and paracetamol biogaran 1g creme depilatoire
https://farmaciasubito.com/# deursil 450
acheter propecia doliprane bГ©bГ© sans ordonnance prix percutafГ©ine gel
se puede comprar kamagra sin receta donde comprar prednisona sin receta or comprar tadalafilo cinfa sin receta
https://www.bausch.pk/en/redirect/?url=https://confiapharma.com farmacia online ravenna
comprar clovate sin receta farmacia online aciclovir and farmacia online sonda pague menos farmacia online
dibase 300.000 prezzo: samyr 400 prezzo – metformina 500 prezzo
ciproxin 250 prezzo zoely pillola prezzo tationil 600
cheapest order pharmacy viagra Pharm Express 24 pharmacy grade nolvadex
https://inpharm24.com/# buy medicine online india
india medicine: india pharmacy market outlook – buy medicines online in india
cialis india pharmacy InPharm24 buy medicine online india
mexican pharmacy oxycontin: hispanic pharmacy near me – can you get adderall at a mexican pharmacy?
https://inpharm24.shop/# buy medication from india
order medicine online india InPharm24 all day pharmacy india
voltaren emulgel online pharmacy online pharmacy australia cialis legit online pharmacy viagra
best online indian pharmacy: india pharmacy of the world – india pharmacy of the world
https://pharmmex.shop/# mexico controlled substances
chloramphenicol pharmacy clozapine pharmacy requirements rx pharmacy glendale
is ozempic otc in mexico: hydroxychloroquine mexican pharmacy – pharmacy in mexico online
pharmacy name ideas in india medplus pharmacy india apotheke academy
https://pharmexpress24.com/# pharmacies
when will mounjaro be available in mexico online pharmacy mexican or what drugs are otc in mexico
http://mobile-bbs3.com/bbs/kusyon_b.php?http://pharmmex.com mexican pharmacy los angeles
wholesale pharmacy online buy adderall in mexico and mexico pharmacy price list ozempic buy medications
pharmacy first fluconazole: Pharm Express 24 – how much is adipex at the pharmacy
buy medicines online in india india pharmacy website medicine from india
A. I would say it is mainly a guide that’s utterly Indianised and takes a holistic yogi type of an method. There are lots of vegetarian recipes pertaining to completely different parts of India. You will also get to read plenty of testimonials and transformation stories from India and Canada. Apart From that, the book will discuss nutritional supplementation; John (Abraham) has written the foreword. If they’re performing just like the sponsor’s dietary supplements got them this jacked, admitted to doing one thing potentially illegal to attain the results goes to harm the picture.
For lots of its pumped up disciples, pure bodybuilding is really a lifestyle. Many “natty” bodybuilders reside by a strict ethical code, opting for a extra thought of method to building muscle mass, rejecting the attract of shortcutting their method to rapid gains. Governing bodies (such as the World Pure Bodybuilding Federation) utilise urine analysis, blood tests and even polygraph (lie detector) exams to verify competing athletes’ drug-free standing.
He’s recognized for his incredibly muscular physique and his success in bodybuilding competitions. Simeon Panda has built a fitness empire with an estimated web value of $10 million. He’s known for his impressive physique and his advocacy for natural bodybuilding.
But for individuals who avoid cardio like the plague, then this routine is going to be your cup of tea. From a scrawny child to some of the in-demand figures within the industry, Ulisses Jr has one of the inspiring tales. He’s achieved lots of success due to having an unimaginable physique and it’s evident he takes his career and reputation seriously. He illustrates that you don’t should be naturally giant or powerful to become a ripped monster.
Our platform is designed to cater completely to professionals, researchers, and lovers in the chemical area, offering timely updates and actionable insights that drive informed decision-making. Ulisses Jr incorporates supersets and drop sets to extend the intensity of his workouts. Supersets contain performing two back-to-back exercises with out rest, concentrating on the identical or opposing muscle groups. AAG is a compound that combines the amino acid arginine with alpha-ketoglutarate. It is believed to boost nitric oxide production, improving blood flow, nutrient delivery, and muscle pump during exercises.
Yet you’ll retain each little bit of muscle in your physique, however there might be no signal of the steroids that got you these bulging muscular tissues. It demands business acumen, marketing expertise, and the power to attach authentically with an audience. The most profitable influencers have diversified their earnings streams, creating complete manufacturers that stretch far past social media posts. Massy’s holistic method to health and wellness has helped her build a loyal following and profitable business. The age range of health influencers is kind of various, but many fall between 25 and forty years old. This age vary usually aligns with peak physical condition and relatability to a large audience. However, there are successful influencers each younger and older than this vary.
If you aspire to compete in bodybuilding shows, understanding that the majority well-known people within the sport are using gear puts you at a big disadvantage. Drug use is not restricted to skilled bodybuilders; many individuals begin their first steroid cycle in hopes of breaking by way of on social media. The often inflexible life-style can depart you feeling isolated if you’re not linked to others who are following the identical path. Pushing your self may be so much tougher when you’re working in isolation, so do your self a favour and be a part of a neighborhood to get that social and moral support that’s essential to sustaining discipline. Whether you get stuck into your native gym or online forums and teams, don’t go it alone.
He’ll also often take multivitamins—the most taken complement in the world. Nutritional Vitamins and minerals are absolutely important for a well-functioning body, and they turn out to be much more essential if your energy expenditures are excessive. In this fashion, it helps to keep up the barrier between your intestines and your body which not only prevents leaky gut but is also useful in stopping dangerous toxins from coming into the relaxation of your body. However in relation to supporting immune well being, Ulisses goes a step further. This doesn’t necessarily mean lounging around, nonetheless, as active recovery may be applied as an alternative. Being around 200 lbs, Ulisses argues that if he’s been utilizing for thus many years then he’s wasted plenty of money.
If a person with a full head of hair starts experiencing a receding hairline while constructing a significant quantity Medical Uses Of Steroids – https://lusitanohorsefinder.com/wp-content/pages/ultimate_guide.html – muscle mass, strength, and conditioning, it is a sign he has started a steroid cycle. One of the primary variations you’ll discover between a natty bodybuilder and a bodybuilder using gear is that the natural athlete has a much more achievable physique. On the other hand, enhanced bodybuilders have muscles you didn’t know existed. If a bodybuilder has a superhero physique with unexplainable proportions and conditioning, chances are he’s on steroids. Prepare Dinner is certainly one of the most well-known health athletes and an OG bodybuilding YouTuber.
Joe’s success exhibits how creating accessible, relatable content can result in vital monetary rewards in the fitness business. The key just isn’t age, but quite the flexibility to connect with an viewers and provide valuable content. Influencers of different ages often cater to different demographics or niches inside the health world. What sets Massy apart is her give consideration to overall wellness, not just bodily fitness. She usually speaks concerning the connection between physical and mental well being, and how fitness can be a device for private empowerment.
india pharmacy viagra: pharmacy course india – order medicine online india
pharmacy chains in india medicine online order or buy medicines online
https://maps.google.com.ph/url?sa=t&url=https://inpharm24.com medicines online india
ivermectin india pharmacy reliable pharmacy india and india online pharmacy generic cialis india pharmacy
cipro in mexico the online drugstore free shipping i bought tramadol from mexican pharmacy
mexican pharmacy ketamine: Pharm Mex – wegovy mexico pharmacy
benadryl uk pharmacy coop pharmacy store locator or diflucan pharmacy price
https://clients1.google.tt/url?q=https://pharmexpress24.com pharmacy rx one coupon code
simvastatin target pharmacy klonopin indian pharmacy and online pharmacy propecia no prescription online pharmacy no prescription prozac
buy viagra in mexico: ozempic in mexico pharmacy – testosterone mexico pharmacy
http://inpharm24.com/# online india pharmacy
flonase new zealand pharmacy phuket pharmacy viagra or buying ambien online pharmacy
https://www.google.vg/url?q=https://pharmexpress24.shop propecia usa pharmacy
ibuprofen pharmacy only can you buy viagra in a pharmacy and north drug store do pharmacy sell viagra
uk pharmacy no prescription phenytoin pharmacy protocol online pharmacy pain relief
b pharmacy fees in india: top online pharmacy india – pharmacy course india
indian pharmacies india pharmacy market or medicine online order
https://maps.google.cz/url?sa=t&url=https://inpharm24.com pharmacy council of india
retail pharmacy market in india buy medicine online and medications from india medicine delivery in vadodara
best online pharmacy in india: india pharmacy cialis – pharmacy india website
nexium uk pharmacy cymbalta pharmacy coupon or rx pharmacy shop coupon code
https://www.google.gr/url?sa=t&url=https://pharmexpress24.com amoxicillin from pharmacy
best rx pharmacy software clozapine polypharmacy and mexitil online pharmacy how much does cialis cost at a pharmacy
reputable online pharmacy international pharmacies mounjaro mexico price
https://inpharm24.shop/# online medicines india
publix pharmacy online ordering mexican border pharmacies or online pharmacies legitimate
http://www.hashiriya.jp/url.cgi?http://pharmexpress24.shop/ escitalopram oxalate online pharmacy
trust pharmacy viagra zyprexa online pharmacy and flovent online pharmacy best online pharmacy buy accutane
mexican pharmacy stores near me mexican pharmacy sildenafil mexican pharmacy by mail
buy medication from india online medicine order or medicine from india
https://sostrategic.com.au/?URL=https://inpharm24.com india rx
best indian pharmacy online india pharmacy and indian pharmacy п»їindia pharmacy
mexican pharmacy dr simi mexican pills or mexican allergy pills
https://maps.google.to/url?q=https://pharmmex.com contrave in mexico
mexican medicine for back pain pharmacy in mexico that ships to us and mexican online pharmacy prescription drugs best pharmacy websites
pharmacy chains in india: InPharm24 – best indian pharmacy
humana rx mail order pharmacy ambien pharmacy no prescription or safeway pharmacy store hours
https://www.google.com.vn/url?q=https://pharmexpress24.com cialis pharmacy2u
best online pharmacy no prescription cialis compare rx prices and online pharmacy that sell adipex does pharmacy sell viagra
india pharmacies india pharmacy reviews apollo pharmacy india
generic 100mg sildenafil: VGR Sources – viagra online 200mg
https://vgrsources.com/# order sildenafil online
purchase viagra 100mg: viagra tablet cost – female viagra for sale uk
generic viagra coupon VGR Sources purchase generic viagra
buying viagra online: sildenafil over the counter – viagra 100 mg tablet buy online
viagra boys: viagra 20 mg online – generic viagra sales
female viagra 50 mg VGR Sources viagra generic australia
https://vgrsources.com/# cost of 1 viagra pill
generic viagra india online: VGR Sources – buy generic viagra from canada
can i buy viagra online without a prescription: female viagra sildenafil – pfizer viagra for sale
generic female viagra VGR Sources where can i get female viagra uk
viagra usa prescription: VGR Sources – generic viagra 50mg online
viagra canadian pharmacy paypal: VGR Sources – generic viagra for sale cheap
https://vgrsources.com/# how much is a viagra prescription
buy viagra 100 sildenafil price australia viagra pills for sale uk
female viagra capsules in india: viagra 130 mg – i want to buy viagra
safe generic viagra: viagra triangle – pfizer viagra price
buy female viagra online uk where to buy female viagra in australia us online pharmacy generic viagra
buy viagra online with paypal: VGR Sources – can i buy genuine viagra online
viagra online uk paypal: purchase viagra without prescription – viagra 200mg uk
https://vgrsources.com/# sildenafil 1mg
how to get real viagra how much is viagra australia or viagra 25mg online india
https://cse.google.ng/url?q=https://vgrsources.com viagra online order
generic viagra on line buy generic viagra 50mg online and viagra from mexico to usa how to buy viagra over the counter uk
buy female viagra online uk: buy genuine viagra online uk – viagra medicine online in india
viagra tablet online purchase VGR Sources where to buy viagra over the counter in canada
sildenafil generic canada: best canadian pharmacy generic viagra – viagra 50 mg tablet price in india
how to get a prescription for viagra cost of viagra 100 or buy cheap sildenafil uk
https://images.google.fm/url?sa=t&url=https://vgrsources.com viagra online cheap price
30 mg sildenafil viagra 100 price and prices for viagra prescription viagra 25 mg no prescription
average cost sildenafil 20mg: VGR Sources – canadian drugstore viagra
where can you buy cheap viagra price for 100mg viagra canadian pharmacy viagra cost
where to buy sildenafil in canada: VGR Sources – buy viagra new zealand
generic viagra professional 100mg: VGR Sources – cheap viagra online pharmacy
https://vgrsources.com/# buying viagra over the counter in usa
viagra uk viagra 6 pills or viagra price online india
http://maps.google.is/url?q=http://vgrsources.com viagra for cheap
sildenafil for sale canada compare sildenafil prices and viagra 50 mg buy online viagra cream
viagra walmart: viagra pills online usa – viagra pills price in india
viagra tablet buy online 30 mg sildenafil buy online or prescription viagra cheap
https://maps.google.mg/url?q=https://vgrsources.com how to get viagra prescription in australia
how much is sildenafil 25 mg genuine viagra and where can i buy viagra pills online online order viagra in india
online viagra generic: viagra soft sale – buy sildenafil canada
buy sildenafil no prescription VGR Sources can you buy viagra online in canada
sildenafil otc uk: order cheap generic viagra online – order viagra online in usa
sildenafil brand name india where to get female viagra over the counter or sildenafil 20 mg buy online
https://maps.google.ne/url?q=https://vgrsources.com cheap viagra india online
drugstore female viagra viagra 100mg online in india and best price for viagra 100mg female viagra pill online
can i buy viagra over the counter in south africa: VGR Sources – sildenafil over the counter us
viagra online fast delivery VGR Sources viagra online pills
https://vgrsources.com/# viagra.com
order viagra with paypal viagra 6800mg or price of viagra in us
http://vkrugudruzei.ru/x/outlink?url=http://vgrsources.com sildenafil tablets india
cost of generic viagra in india buy real viagra online and purchase cheap viagra sildenafil tablets india
can i buy viagra from india: VGR Sources – viagra 100mg prices
viagra 60 mg: generic viagra buy uk – viagra from canada prices
female viagra pill cost viagra purchase australia or order viagra uk
http://image.google.ws/url?q=https://vgrsources.com best female viagra pills in india
viagra otc canada viagra super active canada and buying sildenafil in mexico viagra usa prescription
sildenafil prices in india VGR Sources generic viagra 150 mg
buy viagra in canada: VGR Sources – sildenafil 50mg brand name
viagra online uk where can i buy female viagra in india sildenafil canada generic
https://vgrsources.com/# where to buy viagra online in usa
viagra generic cost: VGR Sources – can i buy genuine viagra online
sildenafil fast delivery order viagra 50 mg or pharmacy price comparison viagra
http://www.xr2.org/exit.php?url=http://vgrsources.com how to buy viagra in uk
where to buy viagra without a prescription cheap viagra super force and legal to buy viagra online i want to buy viagra
how much is sildenafil: generic viagra discount – can you buy viagra in europe
sildenafil 20 mg online pharmacy best sildenafil prices or viagra substitute over the counter
http://clients1.google.com.ni/url?q=https://vgrsources.com:: generic viagra 100mg cost
price of viagra in australia sildenafil soft tabs and sildenafil 88 where can i buy viagra over the counter in singapore
buy viagra new zealand VGR Sources purchase viagra in usa
black viagra: VGR Sources – cheap viagra with prescription
viagra 100 buy: VGR Sources – buy viagra australia paypal
female viagra cost in india best price for viagra female viagra 50 mg
CrestorPharm: Buy cholesterol medicine online cheap – CrestorPharm
https://prednipharm.com/# Predni Pharm
buy prednisone online australia: buying prednisone without prescription – prednisone 10 mg coupon
Crestor Pharm Crestor Pharm Crestor mail order USA
CrestorPharm: CrestorPharm – ezallor sprinkle vs rosuvastatin
Affordable cholesterol-lowering pills: CrestorPharm – can i stop taking crestor
https://lipipharm.com/# lipitor tab
SemagluPharm SemagluPharm SemagluPharm
rybelsus 14 mg side effects: Where to buy Semaglutide legally – Affordable Rybelsus price
LipiPharm: No RX Lipitor online – Lipi Pharm
Lipi Pharm atorvastatin and fenofibrate tablets LipiPharm
LipiPharm: Lipi Pharm – lipitor wiki
http://semaglupharm.com/# SemagluPharm
prednisone 40 mg tablet: PredniPharm – Predni Pharm
PredniPharm PredniPharm prednisone purchase online
LipiPharm: Cheap Lipitor 10mg / 20mg / 40mg – lipitor lowest dose
what does the drug lipitor do is atorvastatin 40 mg a high dose or lipitor drug class
http://cse.google.lv/url?q=https://lipipharm.com atorvastatin picture
atorvastatin foods to eat is 80 mg of atorvastatin too much and does atorvastatin cause weight loss lipitor chemical structure
online order prednisone 10mg best pharmacy prednisone or prednisone generic cost
https://www.google.ps/url?q=https://prednipharm.com prednisone nz
order prednisone on line prednisone 10 mg tablets and 50 mg prednisone from canada average cost of prednisone
crestor other names Online statin therapy without RX Crestor Pharm
п»їBuy Lipitor without prescription USA: lipitor and crestor – Lipi Pharm
PredniPharm: buy prednisone online without a prescription – PredniPharm
http://lipipharm.com/# why take lipitor at night
Semaglu Pharm Affordable Rybelsus price semaglutide (rybelsus)
rosuvastatin kidney damage: Crestor Pharm – can i take rosuvastatin with magnesium
wegovy semaglutide: SemagluPharm – Semaglu Pharm
40 mg prednisone pill prednisone 10mg cost or prednisone cream brand name
http://redmatrix.us/chanview?f=&url=http://prednipharm.com prednisone 20 mg tablets
buy prednisone online no script prednisone 25mg from canada and order prednisone buying prednisone without prescription
Crestor Pharm Crestor Pharm Crestor Pharm
statins atorvastatin: Lipi Pharm – LipiPharm
http://crestorpharm.com/# CrestorPharm
nursing interventions for lipitor lipitor inventor or early stage atorvastatin skin rash pictures
https://maps.google.com.tr/url?q=https://lipipharm.com pictures of atorvastatin 40 mg
atorvastatin 40 mg coupon lipitor side effects mayo clinic and what is the drug lipitor used for side effect atorvastatin
SemagluPharm: SemagluPharm – SemagluPharm
Predni Pharm prednisone 20mg capsule Predni Pharm
prednisone 20mg tab price: Predni Pharm – prednisone 5 mg
rybelsus long term side effects rybelsus 14 mg discontinued or weight loss on rybelsus
https://toolbarqueries.google.co.vi/url?q=http://semaglupharm.com is 50 units of semaglutide a lot
is ozempic and semaglutide the same semaglutide pyridoxine and how to get semaglutide with insurance what happens if you take rybelsus with other meds
LipiPharm: atorvastatin drugs.com – LipiPharm
USA-based pharmacy Lipitor delivery LipiPharm Lipi Pharm
Rybelsus online pharmacy reviews: metformin and semaglutide – rybelsus vs ozempic
Predni Pharm: Predni Pharm – prednisone 20mg prices
crestor copay card how fast does crestor work crestor pills
Lipi Pharm: Safe atorvastatin purchase without RX – Lipi Pharm
can you take fenofibrate and atorvastatin together is lipitor atorvastatin or can lipitor cause pancreatitis
http://www.catya.co.uk/gallery.php?path=al_pulford/&site=lipipharm.com does lipitor raise blood pressure
lipitor used for link between lipitor and alzheimer’s and atorvastatin neuropathy lipitor blood thinner
SemagluPharm: Semaglu Pharm – Semaglu Pharm
order prednisone 10 mg tablet Predni Pharm PredniPharm
prednisone 30 mg coupon buy prednisone online without a script or prednisone 20mg tab price
http://ccasayourworld.com/?URL=prednipharm.com 6 prednisone
buy cheap prednisone prednisone cream brand name and prednisone 10mg online 5 mg prednisone tablets
Semaglu Pharm: Semaglu Pharm – Online pharmacy Rybelsus
http://lipipharm.com/# atorvastatin дёж–‡
i got pregnant while taking semaglutide: SemagluPharm – SemagluPharm
LipiPharm Affordable Lipitor alternatives USA Lipi Pharm
Rybelsus for blood sugar control: semaglutide highest dose – semaglutide 6 week belly ozempic weight loss before and after
lipitor heartburn generic atorvastatin 40 mg images or lipitor efectos secundarios
https://maps.google.com.sg/url?sa=t&url=https://lipipharm.com lipitor chewable tablets
can atorvastatin cause joint pain lipitor headaches and what’s the generic name for lipitor pill identifier atorvastatin 40 mg
SemagluPharm: Semaglu Pharm – semaglutide and phentermine
Over-the-counter Crestor USA rosuvastatin anxiety Crestor Pharm
PredniPharm: Predni Pharm – prednisone 20 mg pill
https://semaglupharm.com/# rybelsus titration schedule
rybelsus 14 mg efectos secundarios semaglutide lawsuit or rybelsus cost without insurance
https://top.hange.jp/linkdispatch/dispatch?targetUrl=http://semaglupharm.com how to use rybelsus for weight loss
rybelsus pastillas rybelsus fda approved for weight loss and rybelsusдёж–‡ rybelsus 3mg for weight loss
rosuvastatin dose range: Crestor mail order USA – Crestor Pharm
should crestor be taken with food Crestor home delivery USA Crestor Pharm
https://semaglupharm.com/# SemagluPharm
CrestorPharm: CrestorPharm – does crestor cause diarrhea
https://prednipharm.shop/# Predni Pharm
can you buy prednisone over the counter can i buy prednisone from canada without a script or can i purchase prednisone without a prescription
http://www.lanarkcob.org/System/Login.asp?id=45268&Referer=https://prednipharm.com prednisone for sale without a prescription
prednisone prednisone rx coupon and order prednisone online no prescription prednisone in india
lipitor and side effects can you cut atorvastatin in half or pill identifier atorvastatin 40 mg tablet
https://www.google.co.bw/url?sa=t&url=https://lipipharm.com lipitor action
does lipitor affect kidneys can you take atorvastatin and hydroxyzine together and thuб»‘c atorvastatin 20mg is rosuvastatin the same as atorvastatin
alternatives to lipitor: Online statin drugs no doctor visit – Lipi Pharm
Crestor Pharm CrestorPharm Crestor Pharm
http://semaglupharm.com/# SemagluPharm
Semaglu Pharm: SemagluPharm – SemagluPharm
what is a semaglutide injection can rybelsus cause pancreatitis or how does semaglutide work for weight loss
https://cse.google.gl/url?sa=t&url=https://semaglupharm.com how much weight can you lose on semaglutide in 3 months
strive semaglutide semaglutide injection dosage and semaglutide and diarrhea semaglutide 1mg
rybelsus oral tablet: semaglutide weight loss – SemagluPharm
No prescription diabetes meds online Rybelsus for blood sugar control does rybelsus lower blood sugar
https://semaglupharm.com/# Rybelsus 3mg 7mg 14mg
LipiPharm: п»їBuy Lipitor without prescription USA – LipiPharm
semaglutide drops semaglutide online pharmacy or rybelsus common side effects
http://brownsberrypatch.farmvisit.com/redirect.jsp?urlr=https://semaglupharm.com/ rybelsus semaglutida
semaglutide stomach cramps januvia and rybelsus together and semaglutide before and after men does rybelsus have cardiovascular benefits
prednisolone prednisone: PredniPharm – prednisone otc price
where can i order prednisone 20mg prednisone 20mg by mail order or buy 10 mg prednisone
https://image.google.co.vi/url?q=https://prednipharm.com price for 15 prednisone
prednisone 20mg for sale prednisone best prices and prednisone 10mg tablet price iv prednisone
semaglutide vs liraglutide Semaglu Pharm Semaglu Pharm
lipitor and benadryl how long does it take to lower cholesterol with lipitor or atorvastatin 10 mg uses
http://vocce-gourmet.com/modules/wordpress0/wp-ktai.php?view=redir&url=http://lipipharm.com crestor vs lipitor side effects
how fast does lipitor start working can i take atorvastatin and omega-3 together and atorvastatin 80 mg coupon what is generic for lipitor
https://semaglupharm.com/# Semaglu Pharm
crestor versus lipitor: Crestor Pharm – Crestor Pharm
crestor rhabdomyolysis: when to take rosuvastatin 10 mg – CrestorPharm
can you buy rybelsus over the counter injectable semaglutide or semaglutide and pancreatitis
http://www.extrasmallworld.de/forward.php?to=https://semaglupharm.com microdose semaglutide
can i take my semaglutide a day early best online semaglutide and what does rybelsus do how much is rybelsus at walmart
https://semaglupharm.shop/# Semaglu Pharm
PredniPharm prednisone 5093 prednisone 15 mg tablet
Crestor Pharm: Crestor home delivery USA – side effects of rosuvastatin
http://prednipharm.com/# Predni Pharm
tirzepatide or semaglutide: maximum dose of semaglutide – Rybelsus side effects and dosage
http://semaglupharm.com/# SemagluPharm
PredniPharm PredniPharm prednisone for sale in canada
prednisone daily use order prednisone online no prescription or prednisone tabs 20 mg
https://www.huranahory.cz/sleva/pobyt-pec-pod-snezko-v-penzionu-modranka-krkonose/343?show-url=https://prednipharm.com prednisone 10 mg coupon
prednisone 5 mg tablet cost prednisone over the counter uk and prednisone over the counter uk canada pharmacy prednisone
Predni Pharm: Predni Pharm – PredniPharm
can atorvastatin cause anxiety: Generic Lipitor fast delivery – USA-based pharmacy Lipitor delivery
https://semaglupharm.com/# Order Rybelsus discreetly
compounded semaglutide expiration Online pharmacy Rybelsus Semaglu Pharm
PredniPharm: prednisone without rx – prednisone 300mg
http://semaglupharm.com/# Semaglu Pharm
Generic Lipitor fast delivery: how long does atorvastatin stay in your system – Atorvastatin online pharmacy
does medicare cover atorvastatin LipiPharm LipiPharm
generic prednisone otc medicine prednisone 5mg or prednisolone prednisone
http://games.901.co.il/cards/board?link=https://prednipharm.com 100 mg prednisone daily
prednisone 10 mg coupon how to buy prednisone and online prednisone 5mg cheapest prednisone no prescription
https://semaglupharm.shop/# Rybelsus online pharmacy reviews
PredniPharm: Predni Pharm – prednisone
SemagluPharm: Semaglu Pharm – SemagluPharm
LipiPharm can lipitor clean out plaque in your arteries LipiPharm
ro semaglutide reviews semaglutide and tirzepatide or rybelsus and metformin together for weight loss
https://clients1.google.cv/url?q=https://semaglupharm.com cheap semaglutide
can semaglutide cause anxiety what is better semaglutide or tirzepatide and does rybelsus lower a1c hers semaglutide
semaglutide shot locations semaglutide vs metformin or can i take berberine and semaglutide together
http://www.grandhotelnizza.it/gallery/imagevue/phpinfo.php?a=tadalafil without a doctor’s prescription why am i so tired on semaglutide
how to reconstitute 5mg semaglutide rybelsus vs ozempic for weight loss and how is rybelsus taken rybelsus tablets for weight loss
https://semaglupharm.com/# SemagluPharm
Crestor Pharm: п»їBuy Crestor without prescription – CrestorPharm
Crestor Pharm: CrestorPharm – how to get off rosuvastatin
semaglutide vs wegovy rybelsus preço rybelsus prescribed for weight loss
https://prednipharm.shop/# PredniPharm
https://semaglupharm.com/# Rybelsus 3mg 7mg 14mg
prednisone 20 tablet buy prednisone 50 mg or prednisone pharmacy
https://tvtropes.org/pmwiki/no_outbounds.php?o=https://prednipharm.com average cost of generic prednisone
prednisone 20 mg pill prednisone 10 mg tablets and generic prednisone cost prednisone buy canada
rosuvastatin (crestor): Crestor Pharm – Order rosuvastatin online legally
why take lipitor at night what is the main side effect of lipitor? or atorvastatin calcium 20 mg para que sirve
http://lonevelde.lovasok.hu/out_link.php?url=https://lipipharm.com atorvastatin and erectile dysfunction
azithromycin and atorvastatin atorvastatin high blood pressure and lipitor vs atorvastatin apo atorvastatin
rybelsus 14 mg precio farmacia guadalajara SemagluPharm SemagluPharm
https://semaglupharm.com/# Semaglu Pharm
diabetes drug rybelsus semaglutide expiration or rybelsus 3 mg para que sirve
https://maps.google.iq/url?q=https://semaglupharm.com how much is semaglutide
semaglutide to tirzepatide conversion chart semaglutide allergic reaction and is rybelsus the same as wegovy semaglutide interactions
Rybelsus side effects and dosage: Semaglu Pharm – No prescription diabetes meds online
can lipitor cause diabetes: Lipi Pharm – LipiPharm
Meds From Mexico Meds From Mexico buying prescription drugs in mexico online
https://canadapharmglobal.shop/# canadian pharmacy king reviews
https://canadapharmglobal.shop/# canadian pharmacy scam
canada drugstore pharmacy rx: online canadian drugstore – online canadian drugstore
India Pharm Global: India Pharm Global – indian pharmacy
canadian pharmacy price checker canadian pharmacy king medication canadian pharmacy
https://canadapharmglobal.shop/# online canadian pharmacy review
indian pharmacy online: India Pharm Global – buy prescription drugs from india
Meds From Mexico: buying prescription drugs in mexico online – best online pharmacies in mexico
http://medsfrommexico.com/# best mexican online pharmacies
https://indiapharmglobal.shop/# India Pharm Global
buying prescription drugs in mexico online Meds From Mexico reputable mexican pharmacies online
canada pharmacy: Canada Pharm Global – pharmacy canadian superstore
п»їlegitimate online pharmacies india: India Pharm Global – India Pharm Global
http://canadapharmglobal.com/# best canadian pharmacy to buy from
India Pharm Global indian pharmacies safe pharmacy website india
canada pharmacy 24h: Canada Pharm Global – best canadian online pharmacy
https://medsfrommexico.shop/# Meds From Mexico
indian pharmacies safe: india online pharmacy – India Pharm Global
https://canadapharmglobal.shop/# best canadian pharmacy to buy from
Meds From Mexico mexico drug stores pharmacies mexican border pharmacies shipping to usa
legit canadian online pharmacy: best canadian online pharmacy – legal canadian pharmacy online
http://canadapharmglobal.com/# reddit canadian pharmacy
best online canadian pharmacy: Canada Pharm Global – best canadian online pharmacy reviews
Meds From Mexico Meds From Mexico Meds From Mexico
best india pharmacy: India Pharm Global – India Pharm Global
canadapharmacyonline com canadian pharmacy 24h com safe or canadian pharmacies compare
http://www.serbiancafe.com/lat/diskusije/new/redirect.php?url=https://canadapharmglobal.com canadian pharmacy ratings
recommended canadian pharmacies canadianpharmacy com and canadian pharmacy canadian pharmacy reviews
indian pharmacy Online medicine home delivery or Online medicine order
http://images.google.com.mm/url?q=https://indiapharmglobal.com indian pharmacy online
indian pharmacies safe best india pharmacy and best india pharmacy reputable indian pharmacies
https://indiapharmglobal.shop/# indian pharmacy
trustworthy canadian pharmacy canadian online drugs or canadapharmacyonline com
https://maps.google.com.ly/url?sa=t&url=https://canadapharmglobal.com cheap canadian pharmacy online
my canadian pharmacy canada pharmacy online legit and best canadian online pharmacy legit canadian pharmacy online
https://medsfrommexico.com/# mexican rx online
online pharmacy india: India Pharm Global – India Pharm Global
reputable indian pharmacies Online medicine order Online medicine home delivery
mexico pharmacies prescription drugs purple pharmacy mexico price list or best online pharmacies in mexico
https://maps.google.lk/url?sa=t&url=https://medsfrommexico.com medicine in mexico pharmacies
mexican pharmaceuticals online mexican pharmaceuticals online and mexican drugstore online mexico drug stores pharmacies
India Pharm Global: India Pharm Global – India Pharm Global
http://indiapharmglobal.com/# India Pharm Global
Meds From Mexico: Meds From Mexico – mexico drug stores pharmacies
п»їlegitimate online pharmacies india India Pharm Global Online medicine home delivery
Meds From Mexico: best online pharmacies in mexico – Meds From Mexico
https://canadapharmglobal.com/# reliable canadian pharmacy
canadian pharmacy sarasota canadian pharmacy world or canadian online pharmacy
https://www.google.ht/url?sa=t&url=https://canadapharmglobal.com safe reliable canadian pharmacy
best mail order pharmacy canada my canadian pharmacy review and buying from canadian pharmacies legit canadian pharmacy
https://indiapharmglobal.com/# best india pharmacy
India Pharm Global: indian pharmacy online – India Pharm Global
reputable canadian pharmacy canadian pharmacy or canadian pharmacy king
https://www.google.az/url?q=https://canadapharmglobal.com best canadian online pharmacy reviews
canadian pharmacy price checker canada drugs and reputable canadian online pharmacies legitimate canadian mail order pharmacy
Meds From Mexico medicine in mexico pharmacies buying from online mexican pharmacy
http://indiapharmglobal.com/# cheapest online pharmacy india
India Pharm Global: reputable indian online pharmacy – India Pharm Global
billig apotek pГҐ nett: maltekstrakt apotek – Rask Apotek
pimple patches apotek apotek hem Svenska Pharma
http://svenskapharma.com/# Svenska Pharma
ozempic online spain: Papa Farma – fsrmacia online
https://papafarma.com/# gr 100 badajoz
EFarmaciaIt: EFarmaciaIt – microser compresse prezzo
https://papafarma.com/# Papa Farma
Papa Farma wegovy medicamento veterinario cadiz 33
peroxid apotek: Svenska Pharma – Svenska Pharma
https://raskapotek.com/# ørespray apotek
billigast blГ¶jor: pipett apotek – deo till barn
apotek med snabb leverans Svenska Pharma Svenska Pharma
Papa Farma: citrafleet cuando hace efecto – mounjaro comprar espaГ±a
http://svenskapharma.com/# schengenintyg pdf
http://efarmaciait.com/# anello nuvaring prezzo
EFarmaciaIt: EFarmaciaIt – il numero di telefono della farmacia
Svenska Pharma apotek mina recept menstrosor rea
http://raskapotek.com/# Rask Apotek
slinda costo: a cosa serve samyr 400 – EFarmaciaIt
Svenska Pharma: gripe water apotek – bh billigt
aotek Rask Apotek Rask Apotek
https://raskapotek.shop/# arnica krem apotek
https://raskapotek.com/# apotek munnskyll
Papa Farma: Papa Farma – tienda farmacia
apotek diarre vilket apotek har snabbast leverans or hosta pГҐ engelska
https://maps.google.com.ar/url?sa=t&url=https://svenskapharma.com ashwagandha apotek
vГҐrtor hund bilder astma medicin receptfri and pregnancy test apotek thermometer apotek
Rask Apotek: brodder boots apotek – Rask Apotek
doctor shop recensioni eutirox 50 senza ricetta prezzo or crema travocort prezzo
https://cse.google.lt/url?sa=t&url=https://efarmaciait.com prezzo ovixan crema
detergente intimo neonato forum farmae.it i miei ordini and citilpea a cosa serve ovixan crema prezzo in farmacia
lavemangspГҐse apotek billigt solskydd Svenska Pharma
apotek vulkan pulsoksymeter apotek or <a href=" http://www.e-anim.com/test/E_GuestBook.asp?a=buy+teva+generic+viagra “>panthenol krem apotek
https://clients1.google.dk/url?q=http://raskapotek.com apotek vitamin d
oksygenmåler apotek ølgjær apotek and glidekrem apotek apotek shampoo
https://efarmaciait.com/# per cosa si usa la crema travocort
pastillas roche farmcias or pedir medicamentos a domicilio
http://gambling-trade.com/cgi-bin/topframe.cgi?url=http://papafarma.com/ pharmacies
fwrmacia farmacia online.com and clГnica veterinaria europa reseГ±as movicol genГ©rico precio
40+6 gravidanza forum: EFarmaciaIt – foto di depot milano
malurt apotek: Rask Apotek – sovepiller apotek
mct olje apotek Rask Apotek Rask Apotek
https://raskapotek.com/# magnesium apotek
EFarmaciaIt: gentamicina crema prezzo farmacia – medrol 16 mg recensioni
Svenska Pharma: apotek sjГ¤lvtest corona – Svenska Pharma
vls3 composizione algix 90 quante volte al giorno EFarmaciaIt
rea mammakläder var finns medicinen or ashwagandha apotek
https://maps.google.com.ni/url?q=https://svenskapharma.com pharmacy online
var kan man kГ¶pa eu apotek and snabba choklad – recept apotek glidmedel
trausan 1000 mutuabile robilas cosa serve or xanax in gravidanza forum
http://pravorostov.ru/redirect.php?url=http://efarmaciait.com ovixan crema recensioni
trausan generico daflon 500 farmae and nicetile 500 mg vendita on line delecit bustine prezzo
https://papafarma.shop/# Papa Farma
stiv sГҐle apotek ffp2 munnbind apotek or hostesaft apotek
https://roland.pri.ee/wiki/?a=link&url=https://raskapotek.com hudkrem apotek
h2 blokker apotek salicylic acid apotek and resept pГҐ nett tetreolje apotek
jojobaolje apotek: apotek i danmark – Rask Apotek
billigt nagellack: Svenska Pharma – sax pГҐ engelska
https://svenskapharma.com/# ricinolja apotek
EFarmaciaIt EFarmaciaIt artrosilene 5 gel a cosa serve
https://efarmaciait.com/# EFarmaciaIt
parafarmacia online: EFarmaciaIt – ozempic comprare
http://svenskapharma.com/# apotekek
saltvann apotek: Rask Apotek – Rask Apotek
EFarmaciaIt EFarmaciaIt EFarmaciaIt
jouröppna apotek hur mycket är 10 ml or aktuella recept
https://whois.pp.ru/svenskapharma.com fГҐr katter mens
covid utslag barn väteperoxid apotek and vad kostar en hörapparat privat express apotek
spray nasale dymista prezzo offerte di lavoro erboristeria or voltaren pomata prezzo
https://toolbarqueries.google.co.bw/url?q=https://efarmaciait.com vertiserc 24 mg prezzo
satispay business login zoely prezzo mutuabile and top farmacia online primolut nor recensioni
Rask Apotek: test kjГёnnssykdommer apotek – Rask Apotek
kvise krem apotek apotek nettbutikk or vanndrivende apotek
http://clients1.google.ee/url?q=http://raskapotek.com bestille reseptvarer pГҐ nett
coq10 apotek norske apotek and massasjekrem apotek tannlegespeil apotek
http://efarmaciait.com/# tiche in gravidanza
Rask Apotek flГҐttmiddel hund apotek Rask Apotek
pharmacy madrid: dodot sensitive talla 1 – Papa Farma
15 ml a gramos cbd 40 por ciento or movicol estreГ±imiento
https://www.google.se/url?sa=t&url=https://papafarma.com bianacid in english
viagra bestellen ozempic price in spain and farmacia solares farmacia cerca de mi ubicaciГіn abierta
https://papafarma.shop/# Papa Farma
nГ¦ringsdrikke apotek: hurtigtest covid apotek – fjerning av Гёrevoks apotek
Svenska Pharma Svenska Pharma Svenska Pharma
Pharma Jetzt: versand apotheken – shop apotheker
online pharmacy that sells percocet: PharmaConnectUSA – Pharma Connect USA
PharmaJetzt apotheken shop online online apotheke versand
https://pharmajetzt.shop/# shop apotheke versandkosten
https://pharmaconnectusa.com/# Extra Super Avana
Pharma Confiance: Pharma Confiance – Pharma Confiance
Pharma Confiance: Pharma Confiance – pharmacie ifs
ativan no prescription online pharmacy local pharmacy prices viagra PharmaConnectUSA
http://pharmaconfiance.com/# vaccin allergie pollen prix
recept online: apteka internetowa holandia – Medicijn Punt
https://medicijnpunt.shop/# MedicijnPunt
Pharma Confiance: Pharma Confiance – pharmacie c
https://pharmaconnectusa.com/# Pharma Connect USA
Pharma Jetzt Pharma Jetzt medikamente online bestellen
Pharma Confiance: Pharma Confiance – co amoxicilline
pilule pharmacie: parapharmacue – Pharma Confiance
http://medicijnpunt.com/# online apotheek frankrijk
online apotheke versandkostenfrei apotheke online versandkostenfrei shop apotheke auf rechnung
medicijnen online kopen: online drugstore netherlands – apteka holandia
https://medicijnpunt.shop/# MedicijnPunt
https://medicijnpunt.shop/# Medicijn Punt
apohteek: Medicijn Punt – medicijnlijst apotheek
venlafaxine online pharmacy zithromax us pharmacy cymbalta pharmacy coupons
nuxe site officiel pilulier Г©lectronique pharmacie or chaussures de marche pour diabГ©tiques hommes
https://www.google.ht/url?sa=t&url=https://pharmaconfiance.com patch minceur en pharmacie
pharmacie proche d’ici shop pharmacie fr and cariban 10 mg prix amande pas cher en gros
apteka internetowa nl afbeelding medicijnen or pil online bestellen
http://www.red-ring.com/rssnewsitem.php?urltodisplay=http://medicijnpunt.shop pseudoephedrine kopen in nederland
medicijnen bestellen zonder recept online apotheek zonder recept and apotheek on line apotheek winkel 24 review
tadalafil 10mg prix: Pharma Confiance – parapharmacy
https://pharmaconnectusa.shop/# PharmaConnectUSA
combien coute du viagra Pharma Confiance viagra pharmacie en ligne sans ordonnance
pharmacy methotrexate error nizoral shampoo pharmacy or online pharmacy paypal accepted
https://www.google.sm/url?q=https://pharmaconnectusa.shop Benicar
AebgJoymn benzodiazepines online pharmacy and misoprostol in pharmacy compounding pharmacy piroxicam
online apotheke gГјnstig: aphoteke online – apotheken online shop
https://pharmaconnectusa.com/# buy accutane pharmacy
https://pharmaconfiance.com/# Pharma Confiance
apotheke online: Pharma Jetzt – PharmaJetzt
MedicijnPunt niederlande apotheke MedicijnPunt
Pharma Confiance: Pharma Confiance – fucidine crГЁme prix
quel est le prix d’une boГ®te de viagra en pharmacie ? acheter de l’amoxicilline or pharmacie livraison express paris
https://maps.google.mw/url?sa=t&url=https://pharmaconfiance.com pilulier pas cher
pilule bleu en pharmacie sans ordonnance faut il une ordonnance pour le viagra and xenical pharmacie 400mg en g
https://pharmaconfiance.com/# Pharma Confiance
commander medicament: Pharma Confiance – prise avec minuteur
Medicijn Punt MedicijnPunt Medicijn Punt
pharmacie cambremer: viagra femme sans ordonnance 24h – Pharma Confiance
https://pharmajetzt.com/# shop apotheke bestellung
do pharmacy sell viagra adipex online pharmacy diet pills or online pharmacy misoprostol
https://cse.google.sk/url?sa=t&url=https://pharmaconnectusa.shop depakote online pharmacy
cialis generic online pharmacy unicare pharmacy dublin artane castle and rx care pharmacy zephyrhills fl texas state board of pharmacy
https://pharmaconfiance.shop/# Pharma Confiance
MedicijnPunt: apotheek online nederland – Medicijn Punt
PharmaConnectUSA: wellbutrin pharmacy prices – online pharmacy discount code
Pharma Connect USA Pharma Connect USA Persantine
http://medicijnpunt.com/# apotheek bestellen
medicatielijst apotheek online medicijnen kopen or medicijn online
http://www.9oo9le.me/details.php?site=medicijnpunt.shop apotheke niederlande
internet apotheek medicijnen op recept online bestellen and apotheek on line uw apotheek
commander ozempic sans ordonnance achat cialis pharmacie en ligne or gff marseille
https://maps.google.vg/url?q=https://pharmaconfiance.com gd savoir fer
fucidine creme antibiotique phaemacie and amoxicilline en poudre commander cialis livraison rapide
apotheke versand online apothek or discount apotheke
https://www.google.ht/url?sa=t&url=https://pharmajetzt.com gГјnstigste online apotheke
luitpold apotheke pzn medikamente and apotal shop apotal shop apotheke
ciprofloxacin online pharmacy: rx on line pharmacy – Pharma Connect USA
pilulier en bois: ongle amande french couleur – Pharma Confiance
world pharmacy rx Pharma Connect USA Pharma Connect USA
https://pharmajetzt.com/# Pharma Jetzt
isotretinoin prices pharmacy avodart online pharmacy or clomid online pharmacy
https://www.google.cv/url?q=https://pharmaconnectusa.shop online pharmacy lortab
worldwide pharmacy online brookwood pharmacy artane and online pharmacy greece pharmacy discount coupons
https://pharmajetzt.com/# euro apotheke
PharmaJetzt: PharmaJetzt – online medikamente
MedicijnPunt: Medicijn Punt – medicijnen kopen online
https://pharmaconfiance.shop/# Pharma Confiance
ou acheter argel 7 Pharma Confiance Pharma Confiance
online apotheek zonder recept ervaringen pharma apotheek or apotheek webshop
https://wiki.ood.ch/api.php?action=https://medicijnpunt.shop netherlands pharmacy online
medicatie bestellen online apteka internetowa nl and de apotheek medicijnen op recept online bestellen
pharmacie garde luxembourg adresse pharmacie or parapharmacie para one
http://www.schneckenzucht.de/galerie/main.php?g2_view=core.UserAdmin&g2_subView=core.UserRecoverPassword&g2_return=https://pharmaconfiance.com/ acheter kamagra en ligne
pharmacie cialis amoxicilline en poudre and quels sont les pharmacies de garde aujourd’hui Г marseille ? shop pharmacie fr
Pharma Jetzt: apotheke lieferung – PharmaJetzt
https://medicijnpunt.com/# europese apotheek
kaiser pharmacy hours: metronidazole pharmacy – Pharma Connect USA
versandapotheke bad steben Pharma Jetzt PharmaJetzt
http://pharmaconfiance.com/# protopic 0 1 pharmacie en ligne
https://pharmaconnectusa.com/# legitimate online pharmacy no prescription
PharmaConnectUSA: uk online pharmacy – cheapest pharmacy to get concerta
rxpharmacycoupons: Pharma Connect USA – Pharma Connect USA
PharmaJetzt PharmaJetzt welche online apotheke ist die gГјnstigste
https://pharmaconfiance.shop/# comment prendre amoxicilline 500
europa apotheek venlo online: tierapotheke online auf rechnung – PharmaJetzt
apotheker online holland apotheke or medicatie apotheker
https://cse.google.mg/url?q=https://medicijnpunt.shop de online apotheek
online apotheek nederland zonder recept recept online and apotheek nederland apotheek inloggen
Pharma Confiance: sildГ©nafil 100 mg 24 comprimГ©s prix – Pharma Confiance
http://www.nuxe.com france tapis douche absorbant or tadalafil 10 mg prix
https://www.google.ne/url?sa=t&url=https://pharmaconfiance.com 120 gr en cl
easypharmacie fr pharmacie du and acheter aicar en pharmacie prix viagra 100 mg
dutch apotheek MedicijnPunt Medicijn Punt
https://pharmaconnectusa.com/# Pharma Connect USA
chez dГ©dГ© marseille: livraison ghd – parapharmacie drakkar
Medicijn Punt: MedicijnPunt – apteka nl
Pharma Jetzt Pharma Jetzt versandapotheke versandkostenfrei
http://pharmaconnectusa.com/# Pharma Connect USA
viagra kuwait pharmacy concerta pharmacy coupons or tamiflu pharmacy
http://345new.com/?go=https://pharmaconnectusa.shop legal online pharmacy reviews
revatio specialty pharmacy pharmacy store hours and clomiphene pharmacy xenical dubai pharmacy
http://pharmaconfiance.com/# Pharma Confiance
MedicijnPunt: belgie apotheek online – medicijn online
intenet apotheke: Pharma Jetzt – versandapotheke vergleich
pharmacie shop minuteur 40 secondes or distribution de la fiГЁvre
https://images.google.cat/url?sa=t&url=https://pharmaconfiance.com magasin nose paris
laboratoire place pie acheter du viagra en pharmacie and pharmacie des dakkars savon pas cher grossiste
apotheek nl online medicatie apotheker or apteka internetowa nl
https://maps.google.pl/url?sa=t&url=http://medicijnpunt.shop medicijnen aanvragen
apotheek aan huis nieuwe pharma and online medicijnen bestellen apotheek de apotheek
https://pharmaconnectusa.com/# cyproheptadine online pharmacy
shop-apotheke online: onlineapothele – medikamente online
cialis online pharmacy usa: losartan pharmacy – Pharma Connect USA
online apotheken shopapotjeke PharmaJetzt
https://pharmajetzt.shop/# Pharma Jetzt
low cost online pharmacy pharmacy india cialis or pharmacy times
https://virtuafighter.com/proxy.php?link=https://pharmaconnectusa.shop safeway pharmacy methotrexate error
board of pharmacy ventolin mexican pharmacy and giant pharmacy online pharmacy prednisone
https://pharmaconfiance.com/# pharmacie marque
medicijne: nieuwe pharma – med apotheek
Pharma Confiance: Pharma Confiance – accoutumance doliprane
e-dem 95 monuril mГ©dicament or new farma
https://www.lf-star.net/_m/index.php?a=free_page/goto_mobile&referer=https://pharmaconfiance.com ou acheter les produits etat pur
tache sur le rein monuril sans ordonnance 2023 and activitГ©s avec assiettes en carton gel god to be
https://pharmaconnectusa.shop/# certified pharmacy online viagra
de online apotheek online apotheek frankrijk or apotheek apotheek
https://whois.zunmi.com/?d=medicijnpunt.shop medicijnen op recept
de apotheek apotheek medicijnen and apteka internetowa nl holland apotheke
Pharma Connect USA: reliable rx pharmacy – can i buy viagra at pharmacy
Pharma Connect USA online pharmacy that sell adipex Pharma Connect USA
MedicijnPunt: online apotheek nederland zonder recept – medicijnen bestellen apotheek
https://medicijnpunt.shop/# Medicijn Punt
https://medicijnpunt.com/# MedicijnPunt
accutane mexican pharmacy medicine store pharmacy springfield, mo or Webseite
https://hc-vsetin.cz/media_show.asp?type=1&id=246&url_back=http://pharmaconnectusa.shop rx care pharmacy orlando fl
good rx pharmacy discount card irmat pharmacy and amoxicillin from pharmacy low cost online pharmacy
Pharma Confiance: Pharma Confiance – tapis cdg
Pharma Connect USA PharmaConnectUSA Pharma Connect USA
http://pharmaconnectusa.com/# cost of percocet at pharmacy
online pharmacy viagra uk: PharmaConnectUSA – viagra at tesco pharmacy
medikamente online bestellen mit rezept apotheken de or online apotheke pille danach
http://be-tabelle.net/url?q=https://pharmajetzt.com meine online apotheke
apohteke medikamente bestellen ohne rezept and online-apotheken luipold apotheke
rhum canne bleue 2023 gh car avis or pharmacie chateauneuf
http://marcina.net/info.php?a=generic+cialis mobile pharma
entreprise pharmaceutique caen pharmacie de drakkar and soolantra crГЁme prix pharmacie par internet
online medicijnen bestellen met recept holland apotheke or appotheek
https://images.google.com.sa/url?q=https://medicijnpunt.shop medicatie apotheker
netherlands online pharmacy medicijne and medicijnen bestellen bij apotheek pharmacy online
Medicijn Punt: online drugstore netherlands – MedicijnPunt
online apotheek zonder recept ervaringen netherlands online pharmacy MedicijnPunt
https://medicijnpunt.shop/# mijn medicijnkosten
PharmaConnectUSA: pharmacy class online – PharmaConnectUSA
https://pharmaconfiance.shop/# parapharmcie en ligne
central rx pharmacy: PharmaConnectUSA – mexican pharmacy wellbutrin
texas chemist online pharmacy thorazine online pharmacy or best online pharmacy percocet
https://www.google.co.za/url?sa=t&url=https://pharmaconnectusa.shop Cipro
pharmacy rx world best online pharmacy tadalafil and best online pharmacy generic cialis ketamine online pharmacy
https://pharmaconfiance.shop/# Pharma Confiance
Pharma Connect USA cymbalta online pharmacy price PharmaConnectUSA
Pharma Jetzt: arzneimittel bestellen – Pharma Jetzt
apotheek inloggen: Medicijn Punt – MedicijnPunt
achat sildenafil sans ordonnance pharmacie de la tour strasbourg or <a href=" http://ns.km1003.keymachine.de/php.php?a=cialis+without+doctor+prescription “>prix lysopaine pharmacie
http://trackroad.com/conn/garminimport.aspx?returnurl=https://pharmaconfiance.com cialis femme
pharmacie de garde calvados newpharma animaux and pharmacie du soleil strasbourg une pharmacie
online apotheek gratis verzending medicijnlijst apotheek or <a href=" http://srv5.cineteck.net/phpinfo/?a=kitchen+design+ideas+a+href=https://medicijnpunt.shop::”//medicijnpunt.shop/] “>online medicijnen kopen
https://www.google.ms/url?q=https://medicijnpunt.shop de apotheek
medicatie apotheek apotheek spanje online and belgie apotheek online pharmacy nederlands
online pharmacy no prescription needed percocet: Pharma Connect USA – Pharma Connect USA
https://pharmaconnectusa.shop/# cost of cialis at pharmacy
Pharma Confiance: Pharma Confiance – Pharma Confiance
MedicijnPunt MedicijnPunt Medicijn Punt
http://pharmaconnectusa.com/# Pharma Connect USA
banfield online pharmacy Ampicillin or co-op pharmacy viagra
https://www.google.com.eg/url?q=https://pharmaconnectusa.shop online medicine shopping
online medicine to buy pharmacy2u viagra and what pharmacy can i buy viagra pharmacy antabuse
MedicijnPunt: mijn apotheek – apotheek online nl
Pharma Jetzt: PharmaJetzt – Pharma Jetzt
http://pharmaconnectusa.com/# PharmaConnectUSA
apo med: Pharma Jetzt – PharmaJetzt
PharmaJetzt: appotheke online – shopapotjeke
mediamarkt in meiner nähe apoteke or tabletten erkennen
https://clients1.google.bg/url?q=https://pharmajetzt.com medikamente online
aptoheke medikamente ohne rezept bestellen and online apotheken online apothele
pharma mobile pharmacie medicament or pharmacie de nuit paris 15
https://images.google.com/url?q=https://pharmaconfiance.com paracetamol erection
cachet bleu allergie monuril france and helicobacter pylori est-ce grave ddp woman boutique en ligne
http://medicijnpunt.com/# nieuwe pharma
apotheek online farmacie medicijn or apotheek online nl
https://www.google.cf/url?q=https://medicijnpunt.shop apotheek spanje online
medicijnen bestellen bij apotheek verzorgingsproducten apotheek and apteka online holandia inloggen apotheek
http://medicijnpunt.com/# medicijnen aanvragen apotheek
PharmaConnectUSA: buy viagra pharmacy uk – cheapest pharmacy to buy plavix
online pharmacy store usa bradley pharmacy artane or target pharmacy clindamycin
https://toolbarqueries.google.ps/url?sa=i&url=https://pharmaconnectusa.shop phenytoin clinical pharmacy
boots pharmacy uk propecia propecia pharmacy direct and kroger pharmacy lisinopril online pharmacy uk orlistat
PharmaJetzt: PharmaJetzt – medikamente preisvergleich testsieger
Pharma Connect USA PharmaConnectUSA Pharma Connect USA
pharmacie du marchГ© nice: amoxicilline tout les combien – Pharma Confiance
online-apotheke testsieger: shop apothe – PharmaJetzt
https://medicijnpunt.com/# netherlands online pharmacy
https://medicijnpunt.shop/# medicatie bestellen apotheek
MedicijnPunt: de online apotheek – online apotheek goedkoper
Medicijn Punt: dutch apotheek – farmacia online
Medicijn Punt Medicijn Punt apteka den haag
percocet pharmacy pharmacy store in india or viagra and online pharmacy
https://maps.google.rs/url?sa=t&url=https://pharmaconnectusa.shop buy latisse online pharmacy
unicare pharmacy artane castle opening hours Methocarbamol and imiquimod online pharmacy kmart pharmacy simvastatin
https://medicijnpunt.shop/# Medicijn Punt
doliprane insuffisance rГ©nale pharmacie grenoble ouverte 24h/24 or doxycycline achat en ligne
http://www.traditionsalive.ca/Redirect.aspx?destination=http://pharmaconfiance.com/ shop pharmacie mon compte
furterer pas cher suite française bach and pharmacie de la piscine montpellier chondrosulf 400 le moins cher
medicatie bestellen medicijnen apotheek or medicatie kopen
https://maps.google.cat/url?sa=t&url=https://medicijnpunt.shop mijn apotheek medicijnen
apotheek online nederland apotheek online bestellen and medicatielijst apotheek online apotheek zonder recept
versand apotheke online: pille kaufen apotheke – luitpold versandapotheke
online-apotheke top 10: apotheken produkte – Pharma Jetzt
Pharma Confiance feuille de soin pharmacie ogd france
https://medicijnpunt.shop/# MedicijnPunt
Pharma Confiance: Pharma Confiance – Pharma Confiance
Pharma Confiance: pharmacie lignГ© – viagra homme prix en pharmacie
https://pharmajetzt.shop/# medikamente gГјnstig bestellen
mexico online pharmacy benadryl boots pharmacy or rx express pharmacy
http://cse.google.nu/url?q=http://pharmaconnectusa.shop finasteride pharmacy
reliable rx pharmacy hcg illegal online pharmacy and european pharmacy org buy strattera online online pharmacy klonopin
PharmaJetzt: PharmaJetzt – PharmaJetzt
rezept online apotheke: Pharma Jetzt – PharmaJetzt
https://pharmajetzt.shop/# 0nline apotheke
apotheke online versandkostenfrei ipill apotheke versandkostenfrei or apothekenbedarf online-shop
http://www.acecontrol.biz/link.php?u=https://pharmajetzt.com/ arznei gГјnstig
online apotheke ohne rezept luitpold apotheke berlin and 123 apotheke apoteheke
Pharma Connect USA PharmaConnectUSA pharma
frenadol kopen in nederland bestellen medicijnen or п»їmedicijnen bestellen
https://maps.google.dz/url?q=https://medicijnpunt.shop medicijnen aanvragen apotheek
online apotheek nederland apteka online holandia and online medicijnen bestellen apotheek betrouwbare online apotheek
listerine bleu avis mon pharmacien conseil or monuril sans ordonnance 2023
https://clients1.google.so/url?q=https://pharmaconfiance.com correspondance semaine et mois de grossesse
grossiste gel douche monuril mГ©dicament and saxenda prix pharmacie prГЁs de paris croquette pure avis
Medicijn Punt: farmacia online – ons medicatie voor apotheken
Pharma Connect USA: PharmaConnectUSA – Pharma Connect USA
http://medicijnpunt.com/# medicijn recept
mexico online pharmacy reviews cymbalta online pharmacy price or spanish pharmacy viagra
http://www.gizoogle.net/tranzizzle.php?search=pharmaconnectusa.shop online pharmacy no prescription lexapro
seconal online pharmacy jamaica rx pharmacy and Ponstel viagra offshore pharmacy
http://pharmaconnectusa.com/# giant eagle pharmacy simvastatin
PharmaJetzt: PharmaJetzt – Pharma Jetzt
luitpold-apotheke bad steben PharmaJetzt metaflow rabattcode
pharmacie de bonne: Pharma Confiance – Pharma Confiance
http://pharmaconnectusa.com/# Pharma Connect USA
Medicijn Punt: MedicijnPunt – medicijnen aanvragen
online medicijnen kopen netherlands pharmacy online or apotheek online
http://maps.google.mw/url?q=https://medicijnpunt.shop medicatie aanvragen
de online apotheek apotheken nederland and online apotheke wat is mijn apotheek
discount pharmacy tadalafil lorazepam online pharmacy percocet no prescription pharmacy
j ai pris 2 doliprane 1000 au lieu de 1 parapharmacie. or grossiste parapharmacie
https://www.systemtool.co.jp/_m/index.php?a=free_page/goto_mobile&referer=https://pharmaconfiance.com pharmacie commande
parapharmaci avene diagnostic peau and peut on avoir du monuril sans ordonnance pharmacie en ligne 24 en france
PharmaJetzt: Pharma Jetzt – PharmaJetzt
Pharma Confiance: newpharma paiement en plusieurs fois – metronidazole et grossesse
online pharmacy no prescription adipex legitimate online pharmacy or vipps certified pharmacy viagra
https://www.anybeats.jp/jump/?https://pharmaconnectusa.shop pharmacy global rx
purchase adipex from an online pharmacy reddit best online pharmacy and pharmacy drug store buy cialis bangkok pharmacy
https://medicijnpunt.shop/# Medicijn Punt
https://pharmajetzt.shop/# versandapotheke vergleich
ordonnance francaise en espagne: Pharma Confiance – Pharma Confiance
Pharma Confiance: Pharma Confiance – Pharma Confiance
Apcalis SX Pharma Connect USA Pharma Connect USA
https://medicijnpunt.com/# med apotheek
farmacia paris: Pharma Confiance – distribution de rhum express
TijuanaMeds: TijuanaMeds – TijuanaMeds
pharmacy in canada canadianpharmacymeds com canadian drug stores
http://canrxdirect.com/# canadian mail order pharmacy
https://indimedsdirect.com/# buy medicines online in india
buying from online mexican pharmacy: TijuanaMeds – mexico drug stores pharmacies
india pharmacy: IndiMeds Direct – indian pharmacy paypal
http://tijuanameds.com/# mexican drugstore online
mexican drugstore online: mexican drugstore online – mexican online pharmacies prescription drugs
http://indimedsdirect.com/# IndiMeds Direct
https://indimedsdirect.com/# IndiMeds Direct
online canadian pharmacy: CanRx Direct – canadian pharmacy 1 internet online drugstore
canadian world pharmacy CanRx Direct canadianpharmacyworld com
mexican border pharmacies shipping to usa: TijuanaMeds – purple pharmacy mexico price list
What i don’t realize is actually how you’re no longer really
much more smartly-appreciated than you might be right now.
You are so intelligent. You know therefore considerably in the case
of this subject, produced me for my part believe it from so many numerous
angles. Its like men and women are not fascinated except it is something to do with
Lady gaga! Your individual stuffs nice. Always care for it up!
https://tijuanameds.com/# TijuanaMeds
TijuanaMeds: TijuanaMeds – TijuanaMeds
pharmacies in mexico that ship to usa best online pharmacies in mexico or mexico drug stores pharmacies
http://cse.google.nu/url?q=http://tijuanameds.shop best online pharmacies in mexico
mexican border pharmacies shipping to usa mexico pharmacies prescription drugs and mexico drug stores pharmacies mexican online pharmacies prescription drugs
TijuanaMeds pharmacies in mexico that ship to usa mexican mail order pharmacies
best canadian online pharmacy canadian pharmacy 24 or canada pharmacy online
https://maps.google.co.nz/url?q=https://canrxdirect.com onlinecanadianpharmacy 24
canada pharmacy 24h reddit canadian pharmacy and canadian valley pharmacy onlinecanadianpharmacy
https://canrxdirect.com/# canadian neighbor pharmacy
canadian pharmacy victoza: canadian pharmacy price checker – my canadian pharmacy
canadapharmacyonline canadian pharmacy king reviews northwest pharmacy canada
https://indimedsdirect.com/# IndiMeds Direct
http://canrxdirect.com/# canadian pharmacy 24h com safe
https://o.fd8jl.com
Every weekend i used to visit this website, as i wish for enjoyment, as
this this site conations truly nice funny data too.
mexico drug stores pharmacies: TijuanaMeds – medicine in mexico pharmacies
online shopping pharmacy india indian pharmacies safe indianpharmacy com
mexican pharmaceuticals online п»їbest mexican online pharmacies or mexican drugstore online
https://www.google.li/url?q=https://tijuanameds.shop buying prescription drugs in mexico online
medicine in mexico pharmacies pharmacies in mexico that ship to usa and best online pharmacies in mexico buying from online mexican pharmacy
canadian pharmacies compare canada drugstore pharmacy rx or canadian pharmacies compare
https://cse.google.co.za/url?q=https://canrxdirect.com buy drugs from canada
canada pharmacy 24h best rated canadian pharmacy and maple leaf pharmacy in canada canadianpharmacyworld
http://canrxdirect.com/# buying from canadian pharmacies
reputable indian pharmacies indianpharmacy com or indian pharmacies safe
http://images.google.az/url?q=https://indimedsdirect.com п»їlegitimate online pharmacies india
best india pharmacy pharmacy website india and india online pharmacy Online medicine home delivery
https://www.aajogo-br.com/
cheapest online pharmacy india: best online pharmacy india – IndiMeds Direct
http://canrxdirect.com/# best canadian pharmacy
http://canrxdirect.com/# canadian pharmacy online
best india pharmacy: best india pharmacy – IndiMeds Direct
safe canadian pharmacy canada discount pharmacy canadian pharmacy india
IndiMeds Direct: IndiMeds Direct – IndiMeds Direct
https://tijuanameds.shop/# TijuanaMeds
https://wr8363.com/???%20??-2025-06-16/33f6899898/
I am extremely inspired along with your writing talents
and also with the format to your weblog. Is this a paid theme or did you customize
it your self? Either way stay up the excellent high quality writing,
it’s uncommon to see a great weblog like this one today..
https://lqq3865.com/l3b1dihr72a7m0zhoxvz/livel-list.html
I pay a quick visit day-to-day some web sites and information sites to read posts,
but this weblog offers feature based writing.
https://winzada777-br.com/
https://hk5272.com/2025-06-16/28d780492167/
Marvelous, what a website it is! This webpage provides useful
information to us, keep it up.
farmacia zaragoza online: farmacias abiertas hoy zaragoza – pranarom opiniones
https://ct4ot3lu.com/nao-tenho-essa-informacao/
Farmacia Asequible: Farmacia Asequible – efecto citrafleet
https://enclomiphenebestprice.com/# enclomiphene buy
http://enclomiphenebestprice.com/# enclomiphene
Farmacia Asequible farmacias vigo Farmacia Asequible
enclomiphene for men: enclomiphene online – enclomiphene best price
https://vpubize2.com/
https://enclomiphenebestprice.com/# enclomiphene online
farmacia mГЎs cerca: Farmacia Asequible – citrafleet estreГ±imiento
https://0duz0kzu.com/david-luiz-faz-video-de-despedida-no-fla-e-alfineta-diretoria/
Great beat ! I would like to apprentice while you amend your web site, how
could i subscribe for a blog site? The account aided me a acceptable deal.
I had been a little bit acquainted of this your broadcast provided bright clear idea
https://bowri857.com/onde-assistir-real-brasilia-x-corinthians/
I always used to study piece of writing in news papers
but now as I am a user of net thus from now I am using net
for content, thanks to web.
crema cbd opiniones farmacia abierta vigo Farmacia Asequible
farmacias abiertas en bilbao: comprar viagra online – ozempic farmacia online
enclomiphene best price: enclomiphene – enclomiphene
http://enclomiphenebestprice.com/# enclomiphene buy
https://enclomiphenebestprice.com/# enclomiphene best price
oferta trabajo farmaceutico: Farmacia Asequible – Farmacia Asequible
terbinafine online pharmacy RxFree Meds isotretinoin pharmacy
https://win2888-vn.com/
https://r8bi3qmx.com/onde-assistir-river-plate-x-atletico-mineiro/
Farmacia Asequible: Farmacia Asequible – ed farmacia espaГ±a opiniones
https://football-stadium-eg.com/d8a8d98ad8b3d98ad8b1d988-d985d8a7-d98ad8add8afd8ab-d985d8b9-d8a7d984d8b2d985d8a7d984d983-d984d98ad8b3-d8b9d8afd984d98bd8a7/
productos farmasi precios veterinario murcia barato Farmacia Asequible
enclomiphene buy: enclomiphene – enclomiphene testosterone
https://farmaciaasequible.com/# Farmacia Asequible
enclomiphene buy enclomiphene or enclomiphene
https://cse.google.by/url?q=https://enclomiphenebestprice.com enclomiphene testosterone
enclomiphene online enclomiphene testosterone and enclomiphene buy enclomiphene online
https://dobrowin-br.com/lucratividade-das-maquinas-caca-niqueis-dobrowin-2023/
https://t1djsh47.com/voce-quis-dizer-o-que-se-ve-no-raio-x-do-torax/
I am truly happy to glance at this weblog posts which includes lots
of useful information, thanks for providing these information.
enclomiphene for sale: enclomiphene buy – enclomiphene online
http://farmaciaasequible.com/# Farmacia Asequible
https://rxfreemeds.shop/# correct rx pharmacy
https://p5eje2xi.com/voce-ja-sabe-quando-sera-o-sorteio-das-oitavas-de-final-da-copa-do-brasil/
I enjoy, lead to I found just what I used to be looking for.
You’ve ended my four day lengthy hunt! God Bless you man. Have a nice day.
Bye
Farmacia Asequible farmacia portugal envГo espaГ±a Farmacia Asequible
enclomiphene price: enclomiphene best price – enclomiphene price
https://tjk80nw9.com/onde-assistir-al-ahly-x-al-ain/
Having read this I believed it was really informative. I appreciate
you spending some time and effort to put this informative article together.
I once again find myself personally spending a lot of time both reading
and leaving comments. But so what, it was still worth it!
https://uagbobz8.com/onde-assistir-vasco-da-gama-x-athletico-pr/
Hello, i believe that i noticed you visited my blog so i came to go back the desire?.I
am attempting to in finding things to enhance my site!I assume
its adequate to make use of a few of your ideas!!
online pharmacy sildenafil citrate adipex pharmacy card or viagra indian pharmacy
https://maps.google.gy/url?sa=t&url=https://rxfreemeds.com Super Kamagra
what pharmacy sells viagra mebendazole online pharmacy and viagra in london pharmacy inhouse pharmacy proscar
https://vck2ws73.com/onde-sera-chile-x-brasil/
This site was… how do you say it? Relevant!!
Finally I have found something that helped me. Appreciate it!
https://tqtvu7qx.com/qual-canal-vai-transmitir-o-jogo-entre-portuguesa-e-corinthians/
It’s a pity you don’t have a donate button! I’d definitely donate to this excellent blog!
I suppose for now i’ll settle for book-marking
and adding your RSS feed to my Google account. I look
forward to fresh updates and will share this blog with my Facebook group.
Talk soon!
https://wv3heffq.com/a-copa-do-brasil-e-um-torneio-anual-entao-a-proxima-edicao-sera-em-2025-se-voce-esta-se-referindo-a-uma-edicao-especifica-por-favor-especifique-o-ano-ou-a-edicao-desejada/
Does your website have a contact page? I’m having a tough time locating it but,
I’d like to shoot you an e-mail. I’ve got some ideas
for your blog you might be interested in hearing.
Either way, great website and I look forward to seeing it develop over time.
https://rxfreemeds.com/# leflunomide online pharmacy
farmacia ortopedia cerca de mi ubicaciГіn: mifepristona espaГ±a precio – Farmacia Asequible
tadalafilo 5 mg precio mГЎs barato efecto citrafleet tienda farmacia
Farmacia Asequible: recigarum precio amazon – Farmacia Asequible
enclomiphene enclomiphene online or enclomiphene best price
http://vab.ua/bitrix/rk.php?goto=http://enclomiphenebestprice.com enclomiphene best price
enclomiphene citrate enclomiphene and enclomiphene testosterone enclomiphene for men
https://rxfreemeds.com/# RxFree Meds
enclomiphene online: enclomiphene for men – enclomiphene
Take a peek here https://vp.ww6678.com
omeprazole uk pharmacy bradleys pharmacy artane RxFree Meds
https://enclomiphenebestprice.shop/# buy enclomiphene online
RxFree Meds: RxFree Meds – lexapro online pharmacy no prescription
https://rxfreemeds.shop/# target pharmacy lexapro price
Check out more content here https://slot-ram-acer-aspire-e14.xyz525.com
enclomiphene testosterone: enclomiphene – buy enclomiphene online
enclomiphene enclomiphene for sale enclomiphene buy
Farmacia Asequible: farmacia algeciras – farmacia barata tenerife
farmaceuticos pastillas vichy or durex efecto calor opiniones
http://www2.pure.cc/~mikimomo/zaccess/acc.cgi?redirect=http://farmaciaasequible.com iraltone champГє opiniones
crema emla comprar mounjaro opiniones and para que sirve la diprogenta pedir medicamentos online
enclomiphene for men enclomiphene online or enclomiphene price
http://qsinnovations.ashopcart.com/affiliate.php?id=12&redirect=http://enclomiphenebestprice.com/ enclomiphene buy
enclomiphene online enclomiphene online and enclomiphene citrate buy enclomiphene online
https://rxfreemeds.com/# RxFree Meds
Take a look at this page https://wz9225.com?slot=dnv
enclomiphene testosterone enclomiphene best price or enclomiphene
http://www.everettpost.com/Redirect.aspx?destination=http://enclomiphenebestprice.shop/ enclomiphene buy
enclomiphene buy enclomiphene buy and enclomiphene best price enclomiphene price
enclomiphene citrate: buy enclomiphene online – enclomiphene price
enclomiphene enclomiphene testosterone enclomiphene
https://rxfreemeds.com/# RxFree Meds
https://enclomiphenebestprice.shop/# enclomiphene best price
enclomiphene price: enclomiphene – enclomiphene price
brentan precio Farmacia Asequible Farmacia Asequible
Visit the site https://392714.zx2831.com
https://farmaciaasequible.com/# barata farmacia
cephalexin online pharmacy remote consultation online pharmacy or erectile dysfunction treatment
http://clients1.google.com.lb/url?q=https://rxfreemeds.com:: best online pharmacy klonopin
online pharmacy viagra generic cialis from india online pharmacy and online pharmacy diflucan generic wellbutrin pharmacy
compounding pharmacy: RxFree Meds – RxFree Meds
vibrador embarazo farmacia comprar online or total energy reseГ±as
http://www.guitar.import-sales.com/cgi/cala/indi.cgi?spot=7&agst=http://farmaciaasequible.com farmacia de guardia sevilla abierto ahora
farmacia murcia cerca de mi elocom precio sin receta and precio ozempic 0 50 farmacia badajoz 5
enclomiphene online enclomiphene buy or enclomiphene for men
http://publicaciones.adicae.net/turnjs4/slider.php?file=180&total_images=1&id=793&pdf=https://enclomiphenebestprice.com buy enclomiphene online
enclomiphene online enclomiphene online and enclomiphene for men enclomiphene buy
See what’s new https://zs8827.com/ja-jp/shop/deals
citrafleet precio con receta: Farmacia Asequible – Farmacia Asequible
enclomiphene buy buy enclomiphene online enclomiphene citrate
https://farmaciaasequible.shop/# Farmacia Asequible
buy enclomiphene online enclomiphene for sale or enclomiphene online
https://www.google.com.om/url?sa=t&url=https://enclomiphenebestprice.shop enclomiphene for men
enclomiphene buy enclomiphene for men and enclomiphene for sale enclomiphene for sale
kamagra pharmacy uk: RxFree Meds – lorazepam pharmacy
https://farmaciaasequible.com/# Farmacia Asequible
enclomiphene citrate: buy enclomiphene online – enclomiphene testosterone
enclomiphene: enclomiphene online – enclomiphene testosterone
enclomiphene online enclomiphene best price or enclomiphene testosterone
http://www.google.com.om/url?q=https://enclomiphenebestprice.com enclomiphene testosterone
enclomiphene best price buy enclomiphene online and enclomiphene price enclomiphene for men
https://farmaciaasequible.com/# Farmacia Asequible
celestone cronodose opiniones vimovo cuanto tarda en hacer efecto or producto farmacГ©utico
https://maps.google.com.ly/url?sa=t&url=http://farmaciaasequible.com tadalafilo 20 mg precio
fumar tramadol farmacia diaria and descuento farmacia barata farmacia online barata sin gastos de envГo
RxFree Meds: Apcalis SX – pharmacy online degrees
enclomiphene for men enclomiphene enclomiphene online
https://enclomiphenebestprice.com/# enclomiphene buy
enclomiphene best price enclomiphene online or enclomiphene testosterone
https://images.google.com.kh/url?q=https://enclomiphenebestprice.shop enclomiphene for men
enclomiphene buy enclomiphene for sale and enclomiphene enclomiphene buy
https://farmaciaasequible.shop/# farmacias perto de mim
Farmacia Asequible: Farmacia Asequible – Farmacia Asequible
qatar pharmacy cialis: mexican pharmacy rohypnol – RxFree Meds
enclomiphene online: enclomiphene for sale – enclomiphene buy
https://rxfreemeds.com/# RxFree Meds
enclomiphene for sale enclomiphene price buy enclomiphene online
enclomiphene online enclomiphene buy or enclomiphene online
http://313news.net/redirect.php?url=http://enclomiphenebestprice.com enclomiphene citrate
enclomiphene best price enclomiphene citrate and enclomiphene for sale enclomiphene buy
https://enclomiphenebestprice.com/# enclomiphene testosterone
enclomiphene buy: enclomiphene citrate – enclomiphene price
celebrex northwest pharmacy scripts rx pharmacy or accutane pharmacy prices
https://images.google.com.ng/url?sa=t&url=https://rxfreemeds.com Super ED Trial Pack
ativan no prescription online pharmacy veterinary online pharmacy and buy lortab online pharmacy united rx pharmacy
eucerin black friday: farmacia 23 – donde comprar todacitan
RxFree Meds mexican pharmacy azithromycin RxFree Meds
live pharmacy continuing education online: RxFree Meds – RxFree Meds
http://enclomiphenebestprice.com/# enclomiphene best price
enclomiphene for men enclomiphene for men or enclomiphene online
https://www.google.gm/url?q=https://enclomiphenebestprice.com enclomiphene for men
enclomiphene citrate enclomiphene and buy enclomiphene online enclomiphene citrate
https://enclomiphenebestprice.shop/# enclomiphene buy
farmacia online vigo productos de droguerГa or farmacias cerca de mi abiertas hoy
https://toolbarqueries.google.co.ve/url?sa=t&url=https://farmaciaasequible.com parafarmacia valladolid
diprogenta crema para que sirve parafarmcia and isla natura sevilla opiniones far.acia
enclomiphene price: enclomiphene online – enclomiphene for men
Farmacia Asequible Farmacia Asequible pure de platano para bebe
https://farmaciaasequible.shop/# Farmacia Asequible
enclomiphene testosterone enclomiphene or enclomiphene best price
http://www.traditionsalive.ca/Redirect.aspx?destination=http://enclomiphenebestprice.shop/ enclomiphene price
enclomiphene for men enclomiphene best price and enclomiphene citrate enclomiphene for sale
zyprexa pharmacy online: lexapro indian pharmacy – RxFree Meds
RxFree Meds pharmacy store RxFree Meds
https://farmaciaasequible.shop/# Farmacia Asequible
oral b io 7 duo: Farmacia Asequible – casenlax amazon
http://enclomiphenebestprice.com/# enclomiphene
enclomiphene testosterone: enclomiphene testosterone – enclomiphene
enclomiphene online enclomiphene for men or enclomiphene citrate
http://www.google.com.gi/url?q=https://enclomiphenebestprice.com enclomiphene
enclomiphene price enclomiphene price and buy enclomiphene online enclomiphene testosterone
tallas durex parafarmacia granada or farmacia venta online
https://toolbarqueries.google.com.vn/url?q=https://farmaciaasequible.com farmacias a la venta
soolantra crema opiniones farmacias online espaГ±a and farmacias cerca de aqui soolantra crema amazon
https://rxfreemeds.com/# pharmacies online
enclomiphene for men enclomiphene best price enclomiphene citrate
epiduo gel opiniones: Farmacia Asequible – Farmacia Asequible
rx choice pharmacy online pharmacy lamotrigine or online pharmacies in usa
http://radio-kanal.ru/index.php?name=plugins&p=out&url=rxfreemeds.com fluoxetine india pharmacy
optum rx pharmacy propecia uk pharmacy and navarro discount pharmacy store locator pharmacy shop online
RxFree Meds: vipps online pharmacy viagra – RxFree Meds
buy enclomiphene online enclomiphene online or buy enclomiphene online
http://eijudou.com/_m/index.php?a=free_page/goto_mobile&referer=https://enclomiphenebestprice.shop enclomiphene for men
enclomiphene buy buy enclomiphene online and enclomiphene buy enclomiphene best price
enclomiphene testosterone enclomiphene online enclomiphene best price
viagra phuket pharmacy: viagra registered pharmacy – RxFree Meds
http://rxfreemeds.com/# how much does viagra cost at the pharmacy
http://rxfreemeds.com/# RxFree Meds
buy enclomiphene online enclomiphene price or enclomiphene citrate
https://clipperfund.com/?URL=https://enclomiphenebestprice.com:: enclomiphene
=cialis]enclomiphene best price enclomiphene price and enclomiphene online enclomiphene price
enclomiphene buy: enclomiphene best price – enclomiphene
farmacia web: Farmacia Asequible – Farmacia Asequible
Farmacia Asequible farmacia a domicilio valencia farmacia ventas
enclomiphene best price: buy enclomiphene online – enclomiphene for men
tadalafilo 5 mg 28 comprimidos precio comprar una farmacia precio or direct seguros reseГ±as
https://www.google.com.vc/url?sa=t&url=https://farmaciaasequible.com crema elocom para que sirve
para que sirve el movicol sobres farmacia online espaГ±a envГo internacional and farmacia europa online elocom soluciГіn capilar
Farmacia Asequible Farmacia Asequible Farmacia Asequible
cuanto tarda en hacer efecto movicol sobres: dolmen comprimidos – compra venta de farmacias
https://farmaciaasequible.shop/# Farmacia Asequible
RxFree Meds: RxFree Meds – RxFree Meds
enclomiphene for sale enclomiphene best price or enclomiphene price
http://www.jachta.lt/mecstats/index.php?page=reffer_detail&dom=enclomiphenebestprice.shop buy enclomiphene online
enclomiphene online enclomiphene buy and enclomiphene testosterone enclomiphene for men
enclomiphene for men enclomiphene or enclomiphene best price
https://toolbarqueries.google.ki/url?sa=t&url=https://enclomiphenebestprice.com enclomiphene for sale
enclomiphene enclomiphene price and enclomiphene citrate enclomiphene testosterone
Farmacia Asequible vimovo in english Farmacia Asequible
new zealand online pharmacy motilium: RxFree Meds – Imdur
http://farmaciaasequible.com/# Farmacia Asequible
https://rxfreemeds.com/# RxFree Meds
enclomiphene citrate: enclomiphene for men – enclomiphene price
enclomiphene price: enclomiphene buy – enclomiphene testosterone
RxFree Meds RxFree Meds RxFree Meds
vimovo precio iraltone aga plus contraindicaciones or farmacia 24 cerca de mi
https://cse.google.hn/url?sa=i&url=https://farmaciaasequible.com antibiotic cream spain
todacitan comprar farmacia getafe 3 and tadalafil 5 mg precio mycostatin espaГ±a
https://rxfreemeds.shop/# RxFree Meds
enclomiphene citrate: enclomiphene online – enclomiphene price
Hey very nice blog!
enclomiphene enclomiphene citrate or buy enclomiphene online
https://cse.google.es/url?sa=i&url=http://enclomiphenebestprice.shop enclomiphene citrate
enclomiphene price enclomiphene for sale and enclomiphene testosterone enclomiphene testosterone
buy enclomiphene online: buy enclomiphene online – enclomiphene for men
https://farmaciaasequible.com/# Farmacia Asequible
lico forte Farmacia Asequible garmacia
enclomiphene citrate enclomiphene citrate or enclomiphene buy
http://air-hose-reel-fitting.com/info.php?a=cialis+online enclomiphene online
enclomiphene citrate enclomiphene for sale and buy enclomiphene online enclomiphene best price
naproxen pharmacy pharmacy store online or community rx pharmacy
https://maps.google.com.ar/url?sa=t&url=https://rxfreemeds.com apollo pharmacy store locator
target pharmacy clindamycin naproxen pharmacy and abc pharmacy online no rx pharmacy
farmacia y parafarmacia online: Farmacia Asequible – Farmacia Asequible
http://rxfreemeds.com/# purdue pharmacy store
RxFree Meds: RxFree Meds – RxFree Meds
https://rxfreemeds.shop/# RxFree Meds
Farmacia Asequible stromectol precio Farmacia Asequible
dodot baratos enfamil estreГ±imiento or dodot talla 3 plus
https://images.google.co.kr/url?q=https://farmaciaasequible.com productos parafarmacia
farma farmacias 24h barcelona and avatar 2 online castellano mejores farmacias online ocu
MexiMeds Express: medicine in mexico pharmacies – purple pharmacy mexico price list
enalapril online pharmacy: MediSmart Pharmacy – Aebgjoync
http://meximedsexpress.com/# mexican online pharmacies prescription drugs
world pharmacy viagra MediSmart Pharmacy proscar online pharmacy
https://medismartpharmacy.shop/# ketoconazole pharmacy
concerta online pharmacy: MediSmart Pharmacy – ranitidine online pharmacy
india online pharmacy: IndoMeds USA – IndoMeds USA
https://medismartpharmacy.shop/# pharmacy store viagra + cialis spam
hy-vee pharmacy MediSmart Pharmacy us viagra online pharmacy
Aristocort: worldwide pharmacy kamagra – rite aid 24 hour pharmacy store locator
https://indomedsusa.shop/# IndoMeds USA
indianpharmacy com: п»їlegitimate online pharmacies india – IndoMeds USA
http://medismartpharmacy.com/# heb pharmacy online
rx pharmacy glendale [url=https://medismartpharmacy.com/#]pharmacy o reilly artane[/url] target pharmacy fluoxetine
boots pharmacy viagra cost: sands rx pharmacy – cialis pharmacy australia
http://medismartpharmacy.com/# Aebgmearp
onlinecanadianpharmacy 24: MediSmart Pharmacy – canadian pharmacy 365
reputable indian online pharmacy mail order pharmacy india IndoMeds USA
best online pharmacy india: buy prescription drugs from india – indian pharmacy online
https://medismartpharmacy.com/# Levitra Professional
https://indomedsusa.com/# pharmacy website india
canadian pharmacies: tamsulosin pharmacy – canadian pharmacy no rx needed
MexiMeds Express MexiMeds Express buying prescription drugs in mexico online
MexiMeds Express: pharmacies in mexico that ship to usa – MexiMeds Express
indian pharmacy accutane late night pharmacy artane or gen rx pharmacy
https://toolbarqueries.google.com.ni/url?sa=i&url=http://medismartpharmacy.com reliable online pharmacy
wellbutrin people’s pharmacy generic viagra cialis online pharmacy and losartan pharmacy reputable online pharmacy cialis
http://medismartpharmacy.com/# people’s pharmacy prozac
pharmacies in mexico that ship to usa mexican online pharmacies prescription drugs or mexican drugstore online
https://www.thri.xxx/redirect?url=http://meximedsexpress.com/ best online pharmacies in mexico
mexico drug stores pharmacies buying from online mexican pharmacy and best online pharmacies in mexico medicine in mexico pharmacies
IndoMeds USA: mail order pharmacy india – IndoMeds USA
online pharmacy vardenafil best rogue online pharmacy tricare pharmacy crestor
online medicine shopping: MediSmart Pharmacy – clomid in pharmacy
https://meximedsexpress.shop/# medicine in mexico pharmacies
https://medismartpharmacy.shop/# online viagra us pharmacy
Hey there! Would you mind if I share your blog with my
twitter group? There’s a lot of people that I think would
really appreciate your content. Please let me know.
Thanks
indian pharmacy IndoMeds USA india pharmacy
https://medismartpharmacy.com/# Thorazine
top 10 pharmacies in india: MediSmart Pharmacy – percocet mexico pharmacy
mexican pharmaceuticals online medication from mexico pharmacy or п»їbest mexican online pharmacies
https://www.google.co.vi/url?q=https://meximedsexpress.com mexico pharmacies prescription drugs
mexican drugstore online mexico drug stores pharmacies and buying prescription drugs in mexico online mexico pharmacies prescription drugs
cheapest pharmacy viagra Retrovir or albendazole online pharmacy
https://www.google.tt/url?sa=t&url=https://medismartpharmacy.com mexico pharmacy adipex
zyrtec d behind pharmacy counter online cialis pharmacy and online pharmacy pain relief the pharmacy store
mexico drug stores pharmacies: medicine in mexico pharmacies – MexiMeds Express
https://meximedsexpress.com/# MexiMeds Express
online shopping pharmacy india IndoMeds USA IndoMeds USA
india online pharmacy: IndoMeds USA – IndoMeds USA
http://meximedsexpress.com/# MexiMeds Express
Persantine online pharmacy reviews viagra or prometrium online pharmacy
http://maps.google.com.py/url?q=https://medismartpharmacy.com:: cobix generic celebrex pharmacy
pharmacy online store publix pharmacy bactrim and fred’s dollar store pharmacy propranolol pharmacy
MexiMeds Express: mexican mail order pharmacies – MexiMeds Express
cheapest online pharmacy india mail order pharmacy india or online shopping pharmacy india
http://theamericanmuslim.org/tam.php?URL=indomedsusa.com reputable indian online pharmacy
top online pharmacy india india pharmacy and top 10 pharmacies in india top 10 pharmacies in india
https://meximedsexpress.shop/# buying prescription drugs in mexico online
pharmacy customer care viagra MediSmart Pharmacy viagra international pharmacy
online pharmacies that use paypal: MediSmart Pharmacy – cheap pharmacy no prescription
mexican drugstore online mexico drug stores pharmacies or п»їbest mexican online pharmacies
http://artistsbook.lt/wp-content/plugins/wp-js-external-link-info/redirect.php?url=http://meximedsexpress.com mexico pharmacies prescription drugs
pharmacies in mexico that ship to usa mexico pharmacies prescription drugs and best online pharmacies in mexico buying from online mexican pharmacy
https://medismartpharmacy.shop/# pharmacy continuing education online
buy accutane pharmacy flonase pharmacy or Allopurinol
http://bangkok-hotels.fr/redirecturl.php?url=https://medismartpharmacy.com online us pharmacy viagra
Levitra cialis online pharmacy uk and mexican pharmacy viagra reputable overseas online pharmacies
buying from online mexican pharmacy: MexiMeds Express – best online pharmacies in mexico
clozaril pharmacy registry: MediSmart Pharmacy – save on pharmacy
best online pharmacy india top online pharmacy india IndoMeds USA
https://medismartpharmacy.com/# how much is adipex at the pharmacy
https://meximedsexpress.com/# mexico pharmacies prescription drugs
top 10 online pharmacy in india п»їlegitimate online pharmacies india or indianpharmacy com
https://toolbarqueries.google.dk/url?q=https://indomedsusa.com best online pharmacy india
indianpharmacy com indian pharmacy and reputable indian online pharmacy reputable indian pharmacies
IndoMeds USA: reputable indian pharmacies – IndoMeds USA
propecia proscar men’s pharmacy silkroad online pharmacy best online pharmacy no prescription
http://medismartpharmacy.com/# hometown pharmacy
mexican border pharmacies shipping to usa mexican mail order pharmacies or buying from online mexican pharmacy
http://smtnn.ru/forum/away.php?s=http://meximedsexpress.com mexico drug stores pharmacies
buying from online mexican pharmacy mexican mail order pharmacies and buying from online mexican pharmacy mexican drugstore online
MexiMeds Express: best online pharmacies in mexico – mexico pharmacies prescription drugs
MexiMeds Express MexiMeds Express mexican online pharmacies prescription drugs
https://indomedsusa.com/# IndoMeds USA
https://indomedsusa.shop/# indianpharmacy com
IndoMeds USA: indianpharmacy com – indian pharmacy
indianpharmacy com world pharmacy india or buy prescription drugs from india
http://www.slotgemeinde.de/go.php?url=http://indomedsusa.com п»їlegitimate online pharmacies india
world pharmacy india online shopping pharmacy india and india pharmacy mail order best online pharmacy india
Levitra with Dapoxetine zyrtec d behind pharmacy counter wedgewood pharmacy tacrolimus
https://medismartpharmacy.shop/# pharmacy at home viagra
best online pharmacies in mexico pharmacies in mexico that ship to usa or mexican drugstore online
https://www.ehso.com/ehsord.php?URL=https://meximedsexpress.com best online pharmacies in mexico
mexican rx online п»їbest mexican online pharmacies and pharmacies in mexico that ship to usa purple pharmacy mexico price list
IndoMeds USA: indianpharmacy com – IndoMeds USA
nizoral online pharmacy MediSmart Pharmacy Viagra capsules
drug store near me viagra pharmacy checker or derm rx pharmacy
https://www.google.bj/url?sa=t&url=https://medismartpharmacy.com dostinex online pharmacy
rexall pharmacy store hours birth control online pharmacy and kamagra online pharmacy uk best pharmacy prices cialis
http://medismartpharmacy.com/# wg online pharmacy review
Nice blog here! Also your website loads up very fast!
What web host are you using? Can I get your affiliate link to
your host? I wish my site loaded up as fast as yours lol
good value pharmacy: omeprazole pharmacy only – strattera pharmacy coupon
MexiMeds Express mexican pharmaceuticals online MexiMeds Express
india pharmacy top 10 online pharmacy in india or best india pharmacy
http://clients1.google.mk/url?q=https://indomedsusa.com world pharmacy india
indian pharmacy online mail order pharmacy india and Online medicine home delivery reputable indian online pharmacy
http://meximedsexpress.com/# MexiMeds Express
http://meximedsexpress.com/# mexico drug stores pharmacies
IndoMeds USA: IndoMeds USA – IndoMeds USA
MexiMeds Express п»їbest mexican online pharmacies mexican online pharmacies prescription drugs
mГ©dicament anti stress sur ordonnance: tadalafil en ligne avec ordonnance – rhumatologue ordonnance
https://ordinasalute.shop/# ciproxin 500
prelectal 5 mg/1 25 mg prezzo OrdinaSalute nicetile fiale
As a Newbie, I am continuously exploring online for articles that can be of assistance to me. Thank you
tachipirina 1000 fiale prezzo: OrdinaSalute – lucen 40 prezzo
http://pharmadirecte.com/# monuril ordonnance ou pas
samyr 400 fiale intramuscolo: dicloreum compresse prezzo – toradol prezzo
https://clinicagaleno.shop/# puedo comprar metronidazol sin receta médica
valium gocce: brufen 600 granulato effervescente – impetex crema prezzo
https://ordinasalute.shop/# seroquel 50 mg prezzo
olio vea controindicazioni: OrdinaSalute – pappataci puntura
combantrin prezzo OrdinaSalute oki bustine 80 mg prezzo
https://clinicagaleno.com/# app de farmacia online
prorhinel dosette: commander tadalafil 20 mg – duphaston prix sans ordonnance
http://ordinasalute.com/# bivis 40/10
curso de farmacia veterinaria online lorazepam comprar sin receta farmacia online tarazona de la mancha
cialis avec ou sans ordonnance viagra prix france or scalpel pharmacie sans ordonnance
https://www.google.com.sl/url?q=https://pharmadirecte.com peut on avoir des medicaments sans ordonnance dans une pharmacie de garde
pharmacie canadienne sans ordonnance bГ©quille pharmacie sans ordonnance and peut on acheter la pilule en pharmacie sans ordonnance gel aderma
migliori siti farmacia online nerixia 25 mg prezzo or clasteon a cosa serve
http://vapingblips.com/proxy.php?link=https://ordinasalute.com muscoril fiale prezzo
farmacia san vito toujeo 300 and eumovate crema prezzo tachifene a cosa serve
se puede comprar anestesia sin receta se puede comprar permetrina sin receta or farmacia online .com.es
http://appyet.com/handler/disqus.ashx?id=45fee95b8971b2435e0570d007b5f281&locale=ar&shortname=aqoal&title=&type=1&url=http://clinicagaleno.com farmacia online mascarilla reutilizable
farmacia online | mi farmacia madrid fotos farmacia online shop and farmacia de guardia serie completa online venta online de productos de farmacia
https://ordinasalute.shop/# augmentin costo
farmacia online villanueva de la caГ±ada: Clinica Galeno – farmacia online mГЎs barata espaГ±a
minulet pillola prezzo OrdinaSalute didrogyl gocce
pentacol gel rettale telefil 20 mg prezzo or п»їfarmacia online
https://www.google.ml/url?q=https://ordinasalute.com farmacia online spedizione 24 ore
mercilon pillola prezzo oxycontin prezzo and viscaplus 120 compresse prezzo entumin gocce prezzo
http://pharmadirecte.com/# clomid pharmacie acheter sans ordonnance
mascarilla mГ©dica farmacia online: Clinica Galeno – curso gestion oficina de farmacia online
momendol mal di gola ursacol 50 mg gocce toradol
antibiotiques sans ordonnance pharmacie viagra en pharmacie sans ordonnance or <a href=" http://www.1491.com.tw/phpinfo.php?a= “>malarone generique
https://www.google.cat/url?sa=t&url=https://pharmadirecte.com solupred 20 mg sans ordonnance
cystite remede sans ordonnance pommade antibiotique sans ordonnance and percutafГ©ine gel pharmacie donne antibiotique sans ordonnance
https://ordinasalute.com/# colirei bustine
smecta enfant: PharmaDirecte – ordonnance pour radio
motilex a cosa serve brintellix prezzo mutuabile or argento proteinato neonati
https://images.google.com.fj/url?q=https://ordinasalute.com tareg 40
plaunac principio attivo lansoprazolo 30 mg and plavix 75 prezzo monuril costo
curso online auxiliar farmacia comprar farmacia online barcelona or mba online en farmacia con practicas
https://scanverify.com/siteverify.php?site=clinicagaleno.com puedo comprar acido folico en farmacia sin receta
se puede comprar robaxisal sin receta loreto gallo farmacia online and la viagra se puede comprar sin receta en espaГ±a saxenda se puede comprar sin receta mГ©dica
se puede comprar cetraxal otico sin receta Clinica Galeno se pueden comprar ovulos sin receta
http://clinicagaleno.com/# farmacia online n95
mascarilla online farmacia: Clinica Galeno – se puede comprar valaciclovir sin receta
https://pharmadirecte.com/# medicament pour mal de dent sans ordonnance
när ska man sluta sova på rygg gravid SnabbApoteket hund hemorrojder
apotheken in holland: MedicijnPunt – snel medicijnen bestellen
http://tryggmed.com/# benzoylperoksid apotek
bestellen apotheek Medicijn Punt apotheek bestellen
apotek hemoroider: Trygg Med – apotek resept nett
narkotika test apotek: Trygg Med – brokkbind apotek
https://snabbapoteket.com/# apotek tandkräm
online medicijnen bestellen zonder recept: Medicijn Punt – medicatie aanvragen
medicin hemleverans apotek i danmark apotek on line
pil online bestellen online apotheek – gratis verzending or online pharmacy
https://cse.google.com.ph/url?sa=t&url=https://zorgpakket.com dokter online medicijnen bestellen
mijn apotheek medicijnen medicijnen bestellen apotheek and farmacia online viata online apotheek
http://tryggmed.com/# fullmakt apotek digitalt
sГёndags ГҐpent apotek: Trygg Med – rosenrot apotek
https://tryggmed.com/# flex apotek
apotek sjukhuset Г¶ppettider: fГ¶rstoppning feber – apotek inloggning
http://snabbapoteket.com/# mitella apotek
apotheker medicatie: medicatie apotheker review – med apotheek
temperaturmГҐler apotek djevelklo apotek or apotek nett resept
https://buscador.recolecta.fecyt.es/dnet-web-generic/redirect.action?docId=d3241445-e9af-41f8-ba10-01dd6d74856c_UmVwb3NpdG9yeVNlcnZpY2VSZXNvdXJjZXMvUmVwb3NpdG9yeVNlcnZpY2VSZXNvdXJjZVR5cGU=::oai:www.ucm.es:20035&url=http://tryggmed.com selvbruning apotek
bandasje apotek nattlysolje apotek and billig frakt testosteron tilskudd reseptfritt apotek
kräm för blåmärken SnabbApoteket se recept apotek
apoteka: natriumbenzoat apotek – apotek priser
apotheek on line apotheek producten or apothekers
https://feedroll.com/rssviewer/feed2js.php?src=http://zorgpakket.com online recept
apotheek on line recept online and medicatie online de apotheek
https://zorgpakket.com/# mijn apotheek online
https://tryggmed.com/# sГёndagsГҐpne apotek
apotek spania: TryggMed – munnskold apotek
hiv test hemma apotek billigt solskydd mensvärk utan mens graviditet
http://zorgpakket.com/# medicijnen zonder recept
glykos apotek munskydd för barn apotek or apotek munskydd
http://64.psyfactoronline.com/new/forum/away.php?s=http://snabbapoteket.com collagen piller
nätapoteket apotek logga and apotek medlem apotek outlet
medicijnen aanvragen: apotheek inloggen – mijn apotheek medicijnen
https://medimexicorx.com/# mexico pharmacies prescription drugs
IndiaMedsHub: IndiaMedsHub – IndiaMedsHub
lansoprazole pharmacy ExpressCareRx online pharmacy generic valtrex
http://medimexicorx.com/# п»їbest mexican online pharmacies
MediMexicoRx: rybelsus from mexican pharmacy – order azithromycin mexico
http://medimexicorx.com/# reputable mexican pharmacies online
mexico pharmacy buy kamagra oral jelly mexico best mexican pharmacy online
viagra in hong kong pharmacy: ativan pharmacy – ExpressCareRx
http://indiamedshub.com/# top 10 online pharmacy in india
rx pharmacy cialis: reputable overseas online pharmacies – ExpressCareRx
MediMexicoRx: order kamagra from mexican pharmacy – cheap cialis mexico
https://medimexicorx.shop/# mexican drugstore online
buy medicines online in india cheapest online pharmacy india or world pharmacy india
https://cse.google.sm/url?q=https://indiamedshub.com online shopping pharmacy india
online pharmacy india india pharmacy mail order and indian pharmacy india pharmacy mail order
ExpressCareRx publix pharmacy store hours indian pharmacy
https://indiamedshub.shop/# indian pharmacies safe
Online medicine order: online pharmacy india – Online medicine order
ExpressCareRx: real online pharmacy – mypharmacy
https://expresscarerx.org/# shoprite pharmacy
indian pharmacy online top online pharmacy india mail order pharmacy india
https://indiamedshub.com/# IndiaMedsHub
world pharmacy india: indianpharmacy com – IndiaMedsHub
pharmacies in mexico that ship to usa mexican mail order pharmacies or mexican border pharmacies shipping to usa
https://www.google.mu/url?q=https://medimexicorx.com mexican border pharmacies shipping to usa
mexican mail order pharmacies buying prescription drugs in mexico online and mexico drug stores pharmacies medicine in mexico pharmacies
zithromax pharmacy price online pharmacy glucophage or uk pharmacy viagra
https://www.infodrogy.sk/poradna/sprava/538?returnURL=http://expresscarerx.org Retrovir
online pharmacy flovent xalatan pharmacy and best pharmacy price on viagra nps online pharmacy reviews
buy medicines online in india Online medicine order or india pharmacy mail order
https://www.google.com.jm/url?q=https://indiamedshub.com Online medicine order
indian pharmacy online india online pharmacy and Online medicine home delivery indian pharmacy paypal
buy viagra from mexican pharmacy buy viagra from mexican pharmacy or prescription drugs mexico pharmacy
https://www.google.com.mt/url?q=https://medimexicorx.shop cheap cialis mexico
cheap cialis mexico trusted mexican pharmacy and buy antibiotics over the counter in mexico order azithromycin mexico
MediMexicoRx accutane mexico buy online modafinil mexico online
http://expresscarerx.org/# xeloda specialty pharmacy
legit mexican pharmacy without prescription: prescription drugs mexico pharmacy – cheap cialis mexico
zithromax mexican pharmacy: buy cialis from mexico – mexican pharmacy for americans
https://77win-vi.com cung cấp dịch vụ chăm sóc khách
hàng chuyên nghiệp, hoạt động liên tục 24/7. Đội ngũ hỗ trợ giàu kinh nghiệm sẽ giải đáp mọi thắc mắc về tài khoản, nạp/rút tiền và khuyến mãi.
Kết nối với 77win ngay để
nhận sự hỗ trợ nhanh chóng, chính xác.
ExpressCareRx people’s pharmacy wellbutrin xl ExpressCareRx
http://expresscarerx.org/# ExpressCareRx
pharmacy global rx reviews: Macrobid – mexican pharmacy cipro
top 10 pharmacies in india: top 10 online pharmacy in india – IndiaMedsHub
http://expresscarerx.org/# ExpressCareRx
real mexican pharmacy USA shipping legit mexican pharmacy without prescription cheap cialis mexico
india pharmacy reputable indian online pharmacy or indian pharmacy paypal
https://csgotraders.net/linkfilter/?url=https://indiamedshub.com indian pharmacy paypal
best online pharmacy india best india pharmacy and online pharmacy india online shopping pharmacy india
semaglutide mexico price accutane mexico buy online or buy cialis from mexico
http://www.google.co.zm/url?q=https://medimexicorx.shop online mexico pharmacy USA
zithromax mexican pharmacy get viagra without prescription from mexico and finasteride mexico pharmacy п»їmexican pharmacy
buy meds from mexican pharmacy: MediMexicoRx – buy from mexico pharmacy
tesco pharmacy orlistat: gabapentin discount pharmacy – ExpressCareRx
https://expresscarerx.org/# revive rx pharmacy
https://medimexicorx.com/# MediMexicoRx
isotretinoin from mexico order kamagra from mexican pharmacy order kamagra from mexican pharmacy
Online medicine home delivery: IndiaMedsHub – reputable indian online pharmacy
http://expresscarerx.org/# vardenafil
medication costs online pharmacy delivery delhi or online pharmacy baclofen
http://www.healthcarebuyinggroup.com/membersearch.aspx?returnurl=http://expresscarerx.org/ buy online pharmacy uk
provigil india pharmacy costa rica pharmacy percocet and health express pharmacy+artane castle finasteride target pharmacy
Lexapro for depression online Lexapro for depression online Lexapro for depression online
Propecia for hair loss online: Finasteride From Canada – cost propecia without a prescription
https://zoloft.company/# buy Zoloft online
generic Finasteride without prescription cheap Propecia Canada Finasteride From Canada
buy lexapro brand name online: Lexapro for depression online – Lexapro for depression online
cheap Accutane: Accutane for sale – cheap Accutane
https://zoloft.company/# cheap Zoloft
https://isotretinoinfromcanada.com/# purchase generic Accutane online discreetly
buy Accutane online buy Accutane online purchase generic Accutane online discreetly
lexapro brand name in india: where can i buy generic lexapro – Lexapro for depression online
tadalafil online no rx: Tadalafil From India – cheap Cialis Canada
https://tadalafilfromindia.com/# buy Cialis online cheap
buy Accutane online cheap Accutane buy Accutane online
lexapro 10 mg price in india: buy generic lexapro online – Lexapro for depression online
cheap Zoloft: buy Zoloft online without prescription USA – generic sertraline
http://finasteridefromcanada.com/# Finasteride From Canada
generic isotretinoin buy Accutane online or purchase generic Accutane online discreetly
http://gallery.kroatien-ferien.com/gallery/main.php?g2_view=core.UserAdmin&g2_subView=core.UserLogin&g2_return=https://isotretinoinfromcanada.com cheap Accutane
isotretinoin online generic isotretinoin and order isotretinoin from Canada to US Accutane for sale
generic propecia no prescription propecia brand name or buying propecia without rx
http://maps.google.com.co/url?q=http://finasteridefromcanada.com buy generic propecia without prescription
cost cheap propecia without prescription get propecia tablets and cost of cheap propecia without dr prescription how cЙ‘n i get cheap propecia pills
https://lexapro.pro/# Lexapro for depression online
generic Finasteride without prescription generic Finasteride without prescription Propecia for hair loss online
cheap Cialis Canada: Cialis without prescription – Tadalafil From India
http://isotretinoinfromcanada.com/# order isotretinoin from Canada to US
tadalafil 20 mg best price tadalafil online 10mg or buy tadalafil online canada
http://0.7ba.info/out.php?url=http://tadalafilfromindia.com buy tadalafil europe
tadalafil price in india tadalafil tablets price in india and generic tadalafil no prescription canadian online pharmacy tadalafil
Zoloft for sale cheap Zoloft or generic sertraline
http://www.krovatka.ru/f/rr.cgi?http://zoloft.company/ Zoloft for sale
buy Zoloft online cheap Zoloft and Zoloft Company buy Zoloft online without prescription USA
Accutane for sale order isotretinoin from Canada to US buy Accutane online
Tadalafil From India: cheap Cialis Canada – Cialis without prescription
http://tadalafilfromindia.com/# cheap Cialis Canada
how do poker machines work in australia, united kingdom pub pokies and online casino united statesn dollars, or top online pokies
and casinos in united states 4k
Also visit my webpage – five dollar blackjack vegas
(Elton)
buy Zoloft online: generic sertraline – Zoloft for sale
cheap Accutane buy Accutane online or Isotretinoin From Canada
http://7ba.org/out.php?url=http://isotretinoinfromcanada.com USA-safe Accutane sourcing
USA-safe Accutane sourcing Isotretinoin From Canada and Accutane for sale cheap Accutane
https://lexapro.pro/# Lexapro for depression online
USA-safe Accutane sourcing: buy Accutane online – purchase generic Accutane online discreetly
cheap Propecia Canada generic Finasteride without prescription Finasteride From Canada
Cialis without prescription: Tadalafil From India – tadalafil 5mg cost
https://lexapro.pro/# Lexapro for depression online
lexapro cheapest price: buy lexapro no prescription – Lexapro for depression online
generic Finasteride without prescription Propecia for hair loss online generic Finasteride without prescription
https://zoloft.company/# generic sertraline
USA-safe Accutane sourcing Isotretinoin From Canada or cheap Accutane
https://maps.google.nu/url?q=https://isotretinoinfromcanada.com order isotretinoin from Canada to US
cheap Accutane Accutane for sale and order isotretinoin from Canada to US order isotretinoin from Canada to US
https://isotretinoinfromcanada.shop/# order isotretinoin from Canada to US
buy Zoloft online without prescription USA: Zoloft online pharmacy USA – Zoloft online pharmacy USA
Propecia for hair loss online rx propecia generic Finasteride without prescription
get propecia without a prescription cheap propecia without a prescription or get propecia online
http://j-a-net.jp/top/redirect?url=http://finasteridefromcanada.com cheap propecia prices
propecia rx cheap propecia prices and get generic propecia online buy generic propecia without a prescription
buy Cialis online cheap: generic Cialis from India – Tadalafil From India
generic sertraline: buy Zoloft online without prescription USA – buy Zoloft online
buy Zoloft online without prescription USA buy Zoloft online without prescription USA purchase generic Zoloft online discreetly
Lexapro for depression online: Lexapro for depression online – price for lexapro 10 mg
http://isotretinoinfromcanada.com/# Isotretinoin From Canada
https://lexapro.pro/# lexapro brand name in india
generic isotretinoin order isotretinoin from Canada to US or Isotretinoin From Canada
https://images.google.gl/url?sa=t&url=https://isotretinoinfromcanada.com USA-safe Accutane sourcing
order isotretinoin from Canada to US Accutane for sale and Accutane for sale purchase generic Accutane online discreetly
Zoloft Company: buy Zoloft online – sertraline online
Lucky Feet Shoes Palm Desert
72345 СA-111,
Palm Desert, СA 92260, United Stateѕ
+17606663939
orthopedic shoe store near me
Lexapro for depression online compare lexapro prices Lexapro for depression online
cheap Zoloft: sertraline online – generic sertraline
https://tadalafilfromindia.com/# cost of tadalafil in india
https://lexapro.pro/# Lexapro for depression online
tadalafil online cost buy tadalafil online canada or generic cialis tadalafil uk
https://toolbarqueries.google.co.ls/url?q=http://tadalafilfromindia.com tadalafil uk pharmacy
cheapest tadalafil us buy tadalafil online no prescription and canadian pharmacy generic tadalafil tadalafil canada
https://lexapro.pro/# Lexapro for depression online
USA-safe Accutane sourcing Accutane for sale or isotretinoin online
http://maps.google.com.eg/url?q=https://isotretinoinfromcanada.com isotretinoin online
cheap Accutane Isotretinoin From Canada and generic isotretinoin cheap Accutane
lexapro online no prescription: Lexapro for depression online – generic lexapro 20 mg cost
propecia without insurance buy propecia price Propecia for hair loss online
lexapro 20 mg discount: where to buy generic lexapro – Lexapro for depression online
cheap Zoloft: generic sertraline – cheap Zoloft
sertraline online buy Zoloft online without prescription USA or generic sertraline
https://www.google.com.au/url?q=https://zoloft.company generic sertraline
buy Zoloft online cheap Zoloft and sertraline online generic sertraline
buy Zoloft online without prescription USA Zoloft for sale Zoloft online pharmacy USA
tadalafil online no rx: canadian pharmacy tadalafil – buy Cialis online cheap
lexapro brand name discount: Lexapro for depression online – Lexapro for depression online
https://lexapro.pro/# buy lexapro from canada
brand name lexapro from canada Lexapro for depression online buy generic lexapro online
tadalafil 10mg coupon: medicine tadalafil tablets – Tadalafil From India
buy Zoloft online buy Zoloft online without prescription USA or purchase generic Zoloft online discreetly
http://newagestyle.net/forum/away.php?s=https://zoloft.company Zoloft Company
buy Zoloft online purchase generic Zoloft online discreetly and buy Zoloft online without prescription USA Zoloft for sale
buy Cialis online cheap generic Cialis from India tadalafil online no rx
Propecia for hair loss online: Finasteride From Canada – cheap Propecia Canada
tadalafil online prescription tadalafil 20 mg mexico or buy tadalafil 10mg india
https://www.google.li/url?sa=t&url=https://tadalafilfromindia.com cheap 10 mg tadalafil
tadalafil 10mg coupon buy cheap tadalafil online and tadalafil tablets price in india generic tadalafil without prescription
https://lexapro.pro/# where can i get lexapro brand medication
cheap Propecia Canada: generic Finasteride without prescription – Finasteride From Canada
cheap Accutane: order isotretinoin from Canada to US – cheap Accutane
tadalafil 5 mg tablet coupon tadalafil 5mg tablets price or tadalafil 20 mg over the counter
http://xiuang.tw/debug/frm-s/tadalafilfromindia.com generic cialis tadalafil uk
cost of tadalafil generic tadalafil tablets price in india and canadian pharmacy tadalafil 20mg tadalafil 20mg online canada
cheap Propecia Canada: Propecia for hair loss online – Propecia for hair loss online
http://finasteridefromcanada.com/# Finasteride From Canada
order Provigil without prescription: prescription-free Modafinil alternatives – nootropic Modafinil shipped to USA
prednisolone prednisone: buy prednisone online uk – ReliefMeds USA
order amoxicillin without prescription: low-cost antibiotics delivered in USA – Clear Meds Direct
https://neuroreliefrx.com/# gabapentin life saver
Clomid Hub where to buy cheap clomid prices where to buy generic clomid without insurance
WakeMedsRX: safe Provigil online delivery service – safe Provigil online delivery service
low-cost antibiotics delivered in USA: over the counter amoxicillin – amoxicillin tablets in india
can you take nexium with gabapentin get high gabapentin NeuroRelief Rx
https://wakemedsrx.shop/# Modafinil for focus and productivity
Clomid Hub: Clomid Hub – where buy clomid prices
what is shelf life of gabapentin gabapentin and the contraceptive pill NeuroRelief Rx
gabapentin 300 mg cvs gabapentin cpt code or neurontin vs generic gabapentin
https://illuster.nl/variete?ref=https://neuroreliefrx.com gabapentin headache prophylaxis
gabapentin tramadol dosage gabapentin online and can you take gabapentin and acetaminophen pill gabapentin 800
NeuroRelief Rx: NeuroRelief Rx – NeuroRelief Rx
can i order cheap clomid pill can i buy generic clomid no prescription or how to buy generic clomid no prescription
http://images.google.co.bw/url?q=https://clomidhubpharmacy.com where can i buy clomid prices
where can i get cheap clomid pills can i order clomid and can you get generic clomid tablets generic clomid no prescription
can you buy clomid without insurance: Clomid Hub – can i get clomid price
ReliefMeds USA: Relief Meds USA – buy prednisone without a prescription best price
Clear Meds Direct low-cost antibiotics delivered in USA ClearMeds Direct
prednisone canada prices: anti-inflammatory steroids online – Relief Meds USA
https://clearmedsdirect.com/# antibiotic treatment online no Rx
ReliefMeds USA: purchase prednisone no prescription – ReliefMeds USA
amoxicillin capsules 250mg buy amoxicillin 500mg uk or amoxicillin tablets in india
http://www.burstek.com/RedirectPage.php?reason=4&value=Anonymizers&proctoblocktimeout=1&ip=89.78.118.181&url=http://clearmedsdirect.com/ can i purchase amoxicillin online
amoxicillin 500mg for sale uk amoxicillin without a doctors prescription and amoxicillin pharmacy price amoxicillin 50 mg tablets
amoxicillin 500 mg purchase without prescription generic amoxicillin over the counter order amoxicillin without prescription
can you purchase amoxicillin online: order amoxicillin without prescription – order amoxicillin without prescription
buy prednisone 10mg: ReliefMeds USA – order corticosteroids without prescription
clomid prices cost cheap clomid price or buy clomid without rx
https://www.google.bt/url?sa=t&url=https://clomidhubpharmacy.com how to buy cheap clomid without prescription
can you get cheap clomid without insurance can i get cheap clomid tablets and where to buy clomid without dr prescription where buy clomid without a prescription
ReliefMeds USA prednisone 20 mg order corticosteroids without prescription
NeuroRelief Rx: NeuroRelief Rx – gabapentin ipotensione
where to buy prednisone 20mg can you buy prednisone over the counter uk or buy prednisone canada
http://cse.google.ad/url?sa=t&url=http://reliefmedsusa.com buy prednisone 20mg
order prednisone prednisone 30 mg coupon and prednisone 20mg buy online prednisone 50mg cost
ReliefMeds USA: canine prednisone 5mg no prescription – Relief Meds USA
affordable Modafinil for cognitive enhancement: Modafinil for ADHD and narcolepsy – WakeMedsRX
https://clomidhubpharmacy.shop/# can i get cheap clomid online
amoxicillin online no prescription cost of amoxicillin 875 mg or amoxicillin from canada
https://images.google.ci/url?q=https://clearmedsdirect.com purchase amoxicillin 500 mg
buy amoxicillin 500mg usa buy amoxicillin 500mg online and generic amoxicillin online amoxicillin 500mg capsules
WakeMedsRX [url=http://wakemedsrx.com/#]Wake Meds RX[/url] Modafinil for ADHD and narcolepsy
seizure medications gabapentin side effects: NeuroRelief Rx – NeuroRelief Rx
Relief Meds USA: anti-inflammatory steroids online – Relief Meds USA
20 mg of prednisone: ReliefMeds USA – ReliefMeds USA
can you get clomid online buying clomid tablets or where to buy generic clomid now
https://cse.google.com.fj/url?q=https://clomidhubpharmacy.com order generic clomid no prescription
cost of clomid online can i get generic clomid pill and where to get cheap clomid prices get generic clomid
order Provigil without prescription affordable Modafinil for cognitive enhancement nootropic Modafinil shipped to USA
NeuroRelief Rx: NeuroRelief Rx – NeuroRelief Rx
ReliefMeds USA: anti-inflammatory steroids online – prednisone daily use
gabapentin complaints forum fibromyalgia gabapentin or where can i get gabapentin
https://www.google.fi/url?q=https://neuroreliefrx.com gabapentin and elevated blood sugar
gabapentin for radicular pain does cymbalta interact with gabapentin and gabapentin and elevated blood sugar fluoxetine generics
Relief Meds USA: buy prednisone tablets uk – ReliefMeds USA
where to get prednisone can i buy prednisone from canada without a script or prednisone 40 mg
https://www.goodbusinesscomm.com/siteverify.php?ref=stp&site=reliefmedsusa.com/collections/somnuz-mattress::: prednisone cream rx
prednisone drug costs prednisone brand name and prednisone 2 mg daily prednisone 60 mg
generic amoxicillin online cost of amoxicillin prescription or amoxicillin 500 mg brand name
https://forum.unity.com/proxy.php?link=https://clearmedsdirect.com amoxicillin without a doctors prescription
amoxicillin 500 mg where to buy amoxicillin 500mg without prescription and buy amoxicillin online mexico amoxicillin pharmacy price
order corticosteroids without prescription prednisone 15 mg tablet order corticosteroids without prescription
http://wakemedsrx.com/# affordable Modafinil for cognitive enhancement
antibiotic treatment online no Rx: antibiotic treatment online no Rx – low-cost antibiotics delivered in USA
Clomid Hub: Clomid Hub Pharmacy – can i buy cheap clomid no prescription
buying prednisone on line: order corticosteroids without prescription – cheap generic prednisone
anti-inflammatory steroids online anti-inflammatory steroids online prednisone 60 mg price
ReliefMeds USA: order corticosteroids without prescription – buy 40 mg prednisone
NeuroRelief Rx: NeuroRelief Rx – gabapentin dosing in renal disease
NeuroRelief Rx can i take gabapentin and klonopin together what is gabapentin 100mg
prednisone 2 mg daily buy prednisone without a prescription or prednisone 50 mg price
https://maps.google.gg/url?q=https://reliefmedsusa.com prednisone 50 mg tablet cost
prednisone canada prices buy prednisone online from canada and by prednisone w not prescription prednisone 1 mg for sale
Relief Meds USA: ReliefMeds USA – buy generic prednisone online
https://clomidhubpharmacy.shop/# Clomid Hub Pharmacy
Clomid Hub: Clomid Hub – can you get clomid tablets
smart drugs online US pharmacy smart drugs online US pharmacy Modafinil for ADHD and narcolepsy
can i order cheap clomid tablets can you buy cheap clomid prices or where can i get clomid now
http://maps.google.mg/url?q=https://clomidhubpharmacy.com cheap clomid now
how can i get clomid where can i buy generic clomid without prescription and how to get generic clomid pill buy clomid
Clear Meds Direct: buy amoxicillin 500mg usa – ClearMeds Direct
CanadRx Nexus: CanadRx Nexus – CanadRx Nexus
cheap mexican pharmacy: finasteride mexico pharmacy – buy antibiotics from mexico
best canadian pharmacy online CanadRx Nexus CanadRx Nexus
is canadian pharmacy legit: reputable canadian online pharmacies – global pharmacy canada
http://canadrxnexus.com/# CanadRx Nexus
IndiGenix Pharmacy: IndiGenix Pharmacy – IndiGenix Pharmacy
MexiCare Rx Hub isotretinoin from mexico MexiCare Rx Hub
п»їlegitimate online pharmacies india: IndiGenix Pharmacy – buy medicines online in india
IndiGenix Pharmacy: п»їlegitimate online pharmacies india – IndiGenix Pharmacy
http://mexicarerxhub.com/# buying prescription drugs in mexico
IndiGenix Pharmacy: indian pharmacy – top 10 pharmacies in india
CanadRx Nexus: CanadRx Nexus – canadian pharmacy tampa
top online pharmacy india: online pharmacy india – IndiGenix Pharmacy
MexiCare Rx Hub low cost mexico pharmacy online MexiCare Rx Hub
trustworthy canadian pharmacy: canadian pharmacy price checker – canadian pharmacy uk delivery
mexico drug stores pharmacies: mexican border pharmacies shipping to usa – MexiCare Rx Hub
pharmacies in canada that ship to the us CanadRx Nexus CanadRx Nexus
reputable indian pharmacies: IndiGenix Pharmacy – IndiGenix Pharmacy
canadian online pharmacy: CanadRx Nexus – canadian pharmacy online store
buying prescription drugs in mexico: MexiCare Rx Hub – MexiCare Rx Hub
buy antibiotics over the counter in mexico viagra pills from mexico or zithromax mexican pharmacy
https://cse.google.co.bw/url?q=http://mexicarerxhub.shop buy antibiotics over the counter in mexico
buy neurontin in mexico trusted mexico pharmacy with US shipping and п»їmexican pharmacy sildenafil mexico online
mexican mail order pharmacies mexican pharmaceuticals online or mexican border pharmacies shipping to usa
https://membership.gwsgiants.com.au/analytics/outbound?url=http://mexicarerxhub.com medication from mexico pharmacy
buying from online mexican pharmacy medication from mexico pharmacy and mexico pharmacies prescription drugs п»їbest mexican online pharmacies
CanadRx Nexus pharmacy in canada canada rx pharmacy world
MexiCare Rx Hub: MexiCare Rx Hub – MexiCare Rx Hub
CanadRx Nexus: canadianpharmacymeds com – CanadRx Nexus
online pharmacy india top 10 pharmacies in india or indian pharmacies safe
https://forum.phun.org/proxy.php?link=https://indigenixpharm.com top 10 pharmacies in india
best online pharmacy india Online medicine home delivery and reputable indian online pharmacy online pharmacy india
legitimate canadian online pharmacies canada drugs reviews or pharmacy wholesalers canada
https://wiki.ood.ch/api.php?action=https://canadrxnexus.com rate canadian pharmacies
canadianpharmacy com reliable canadian pharmacy reviews and certified canadian international pharmacy canadian pharmacy mall
buying prescription drugs in mexico online: buying prescription drugs in mexico – mexican online pharmacies prescription drugs
CanadRx Nexus CanadRx Nexus canadian pharmacy meds
Online medicine order: IndiGenix Pharmacy – IndiGenix Pharmacy
reputable indian online pharmacy: online shopping pharmacy india – best india pharmacy
https://indigenixpharm.com/# IndiGenix Pharmacy
buying from online mexican pharmacy: mexican pharmaceuticals online – mexican mail order pharmacies
top 10 pharmacies in india IndiGenix Pharmacy Online medicine home delivery
buying prescription drugs in mexico online medication from mexico pharmacy or buying prescription drugs in mexico online
https://maps.google.com.do/url?sa=t&url=https://mexicarerxhub.com п»їbest mexican online pharmacies
reputable mexican pharmacies online mexican online pharmacies prescription drugs and best online pharmacies in mexico buying from online mexican pharmacy
buy drugs from canada: CanadRx Nexus – CanadRx Nexus
buy antibiotics from mexico buy kamagra oral jelly mexico or trusted mexican pharmacy
http://www.georgewbushlibrary.smu.edu/exit.aspx?url=http://mexicarerxhub.shop isotretinoin from mexico
buy kamagra oral jelly mexico safe place to buy semaglutide online mexico and best prices on finasteride in mexico cheap cialis mexico
Online medicine order: indian pharmacy – top 10 pharmacies in india
legitimate canadian online pharmacies canadian family pharmacy or canadian pharmacy scam
https://clients1.google.gr/url?sa=t&url=https://canadrxnexus.com certified canadian pharmacy
canada rx pharmacy best mail order pharmacy canada and canadian compounding pharmacy onlinecanadianpharmacy
IndiGenix Pharmacy: IndiGenix Pharmacy – india pharmacy
indian pharmacy paypal top 10 online pharmacy in india world pharmacy india
order kamagra from mexican pharmacy: trusted mexican pharmacy – п»їmexican pharmacy
CanadRx Nexus: onlinecanadianpharmacy – legal to buy prescription drugs from canada
IndiGenix Pharmacy: IndiGenix Pharmacy – india pharmacy mail order
CanadRx Nexus CanadRx Nexus CanadRx Nexus
https://canadrxnexus.shop/# canadian pharmacy service
northern pharmacy canada: CanadRx Nexus – reputable canadian pharmacy
indianpharmacy com: IndiGenix Pharmacy – reputable indian online pharmacy
cheap mexican pharmacy isotretinoin from mexico or cheap mexican pharmacy
https://hr.bjx.com.cn/go.aspx?u=http://mexicarerxhub.shop order from mexican pharmacy online
mexican pharmacy for americans low cost mexico pharmacy online and legit mexican pharmacy without prescription buy antibiotics over the counter in mexico
online canadian pharmacy review best canadian online pharmacy or canadapharmacyonline com
http://brentwoodadvisors.com/redirect.php?link=canadrxnexus.com canadian drugs pharmacy
canada drugs online canada drugs reviews and canadian drugs online canadian pharmacy 24 com
IndiGenix Pharmacy: indian pharmacy – cheapest online pharmacy india
CanadRx Nexus CanadRx Nexus canadian pharmacy checker
CanadRx Nexus: reliable canadian online pharmacy – legit canadian pharmacy online
best online canadian pharmacy: CanadRx Nexus – best canadian pharmacy
MexiCare Rx Hub: purple pharmacy mexico price list – buying prescription drugs in mexico online
best canadian pharmacy online CanadRx Nexus CanadRx Nexus
pharmacy website india online pharmacy india or top 10 online pharmacy in india
https://wiki.ood.ch/api.php?action=https://indigenixpharm.com india pharmacy mail order
indian pharmacy online mail order pharmacy india and india pharmacy mail order pharmacy india
http://canadrxnexus.com/# CanadRx Nexus
real mexican pharmacy USA shipping: MexiCare Rx Hub – tadalafil mexico pharmacy
MexiCare Rx Hub: buy cialis from mexico – MexiCare Rx Hub
Hello there! This is my 1st comment here so I just wanted to give a quick shout out and tell you I really
enjoy reading through your articles. Can you suggest
any other blogs/websites/forums that deal with the same topics?
Appreciate it!
п»їbest mexican online pharmacies buying prescription drugs in mexico online or buying prescription drugs in mexico
https://cse.google.co.za/url?q=https://mexicarerxhub.com п»їbest mexican online pharmacies
mexican pharmaceuticals online mexico pharmacies prescription drugs and mexican rx online buying prescription drugs in mexico
zithromax mexican pharmacy tadalafil mexico pharmacy or best prices on finasteride in mexico
https://images.google.com.bz/url?q=http://mexicarerxhub.shop safe place to buy semaglutide online mexico
mexico pharmacy buy cheap meds from a mexican pharmacy and gabapentin mexican pharmacy buy cheap meds from a mexican pharmacy
my canadian pharmacy: CanadRx Nexus – canadian pharmacy king
AsthmaFree Pharmacy AsthmaFree Pharmacy AsthmaFree Pharmacy
lasix pills: generic lasix – furosemida 40 mg
AsthmaFree Pharmacy: AsthmaFree Pharmacy – ventolin usa
Tizanidine tablets shipped to USA prescription-free muscle relaxants order Tizanidine without prescription
https://relaxmedsusa.com/# relief from muscle spasms online
FluidCare Pharmacy: FluidCare Pharmacy – lasix tablet
AsthmaFree Pharmacy: AsthmaFree Pharmacy – semaglutide calculator
AsthmaFree Pharmacy pastillas rybelsus para que sirve AsthmaFree Pharmacy
semaglutide eye side effects: AsthmaFree Pharmacy – AsthmaFree Pharmacy
ventolin free shipping purchase ventolin online ventolin tablets
trusted pharmacy Zanaflex USA: trusted pharmacy Zanaflex USA – Tizanidine tablets shipped to USA
muscle relaxants online no Rx: buy Zanaflex online USA – Tizanidine 2mg 4mg tablets for sale
IverCare Pharmacy: ivermectin 3mg dose – liquid ivermectin for humans
https://asthmafreepharmacy.com/# albuterol ventolin
safe online source for Tizanidine cheap muscle relaxer online USA Tizanidine tablets shipped to USA
can i buy ventolin over the counter australia: AsthmaFree Pharmacy – ventolin inhaler no prescription
lasix furosemide 40 mg lasix generic name or furosemida 40 mg
https://masteram.us/away?url=http://fluidcarepharmacy.com/ lasix 100 mg tablet
buy lasix online furosemide 100 mg and lasix 100 mg tablet lasix furosemide 40 mg
AsthmaFree Pharmacy AsthmaFree Pharmacy generic ventolin medication
ivermectin for ringworm in cattle: stromectol dosage chart in pounds – IverCare Pharmacy
FluidCare Pharmacy: lasix furosemide 40 mg – lasix furosemide
ivermectin injectable for horses ivermectin dosage for cats or ivermectin australian shepherd
https://www.techjobscafe.com/goto.php?s=Top&goto=https://ivercarepharmacy.com ivermectin dosage for humans lice
ivermectin wormers for horses ivermectin 0.08 oral solution and ivermectin safety ivermectin paste dosage for dogs
https://relaxmedsusa.shop/# prescription-free muscle relaxants
order Tizanidine without prescription Zanaflex medication fast delivery Tizanidine 2mg 4mg tablets for sale
what to eat on semaglutide: rybelsus doses for weight loss – AsthmaFree Pharmacy
lasix generic lasix 100 mg or lasix pills
https://cse.google.tm/url?q=https://fluidcarepharmacy.com furosemida 40 mg
lasix 100 mg lasix pills and lasix furosemide furosemida
ivermectin paste for cattle dosage of ivermectin for dogs ivermectin cream for dogs
AsthmaFree Pharmacy: ventolin generic – AsthmaFree Pharmacy
does rybelsus work for weight loss oral rybelsus or rybelsus 3 mg precio farmacia guadalajara
https://maps.google.bs/url?q=http://glucosmartrx.com rybelsus fda approval for weight loss
semaglutide for pcos rybelsus singapore and empower pharmacy lawsuit semaglutide is rybelsus a semaglutide
https://glucosmartrx.com/# doses of rybelsus
how does ivermectin work: IverCare Pharmacy – ivermectin 50ml
relief from muscle spasms online RelaxMeds USA buy Zanaflex online USA
FluidCare Pharmacy: lasix side effects – FluidCare Pharmacy
lasix 100 mg tablet lasix uses or furosemide 100 mg
http://pogrzeby-bielsko.firmeo.biz/redir.php?target=fluidcarepharmacy.com lasix side effects
furosemide 100 mg lasix 20 mg and lasix medication furosemida
mectizan stromectol: IverCare Pharmacy – IverCare Pharmacy
IverCare Pharmacy ivermectin paste for scabies stromectol dosage for scabies
AsthmaFree Pharmacy: rybelsus 14 mg precio walmart – can you take rybelsus every other day
FluidCare Pharmacy FluidCare Pharmacy generic lasix
https://relaxmedsusa.shop/# prescription-free muscle relaxants
relief from muscle spasms online affordable Zanaflex online pharmacy or relief from muscle spasms online
https://www.google.nr/url?rct=j&url=https://relaxmedsusa.com prescription-free muscle relaxants
RelaxMedsUSA safe online source for Tizanidine and trusted pharmacy Zanaflex USA trusted pharmacy Zanaflex USA
ivermectin dosage for covid durvet ivermectin sheep drench or ivermectin for head lice
https://www.boemighausen.de/redirect.php?ad=83&to=http://ivercarepharmacy.com goat wormer ivermectin
ivermectin demodex tractor supply ivermectin for dogs and ivermectin 9 mg ivermectin overdose
AsthmaFree Pharmacy: rybelsus 14 mg uses – AsthmaFree Pharmacy
how to take rybelsus 3mg for weight loss what are the most common side effects of rybelsus oral semaglutide for weight loss in non diabetics
furosemida lasix furosemide 40 mg or furosemida 40 mg
https://images.google.com.fj/url?sa=t&url=https://fluidcarepharmacy.com generic lasix
lasix furosemide furosemide 40mg and lasix 100mg lasix for sale
I really appreciate this post. I have been looking everywhere for this! Thank goodness I found it on Bing. You’ve made my day! Thank you again
FluidCare Pharmacy: furosemide 100 mg – FluidCare Pharmacy
FluidCare Pharmacy: furosemida 40 mg – FluidCare Pharmacy
IverCare Pharmacy ivermectin for bed bugs stromectol 3mg tablets
AsthmaFree Pharmacy: ventolin buy – AsthmaFree Pharmacy
https://relaxmedsusa.com/# Tizanidine tablets shipped to USA
ventolin 4mg tablet: cheap ventolin inhalers – AsthmaFree Pharmacy
ventolin proventil: cheapest ventolin online uk – how much is ventolin
buy furosemide online lasix uses furosemida
rybelsus treats what semaglutide vs liraglutide or does rybelsus cause nausea
http://forum.growkind.com/proxy.php?link=https://glucosmartrx.com how often do you take rybelsus
pill form of semaglutide can semaglutide cause diabetes and rybelsus tablet rybelsus formulation
lasix pills lasix uses or buy lasix online
https://www.google.ms/url?sa=t&url=https://fluidcarepharmacy.com lasix dosage
lasix generic lasix 100mg and furosemida lasix dosage
ventolin: can you buy ventolin over the counter nz – ventolin online uk
ventolin cost uk: buy ventolin pharmacy – AsthmaFree Pharmacy
IverCare Pharmacy ivermectin ebay ivermectin dose for human lice
IverCare Pharmacy: IverCare Pharmacy – IverCare Pharmacy
FluidCare Pharmacy: generic lasix – lasix 20 mg
AsthmaFree Pharmacy no prescription ventolin AsthmaFree Pharmacy
http://ivercarepharmacy.com/# IverCare Pharmacy
semaglutide no insurance how to inject semaglutide or semaglutide with b12 for weight loss reviews
http://www.wzdh123.com/go.php?url=https://glucosmartrx.com semaglutide prescription online
alcohol and semaglutide switching from rybelsus to wegovy and semaglutide new jersey rybelsus anxiety
lasix side effects lasix 20 mg or buy lasix online
https://www.dawgshed.com/proxy.php?link=https://fluidcarepharmacy.com:: lasix generic name
furosemide 100mg lasix for sale and lasix pills generic lasix
ventolin prescription online: ventolin from mexico to usa – AsthmaFree Pharmacy
FluidCare Pharmacy: FluidCare Pharmacy – FluidCare Pharmacy
ventolin cost australia ventolin canadian pharmacy AsthmaFree Pharmacy
Bonus new member 100% Mandiribet: Link alternatif Mandiribet – Bonus new member 100% Mandiribet
Yuks?k RTP slotlar: Pinco il? real pul qazan – Qeydiyyat bonusu Pinco casino
Slot gacor hari ini: Slot gacor hari ini – Situs judi resmi berlisensi
Nha cai uy tin Vi?t Nam: Ca cu?c tr?c tuy?n GK88 – Slot game d?i thu?ng
Slot oyunlar? Pinco-da: Pinco kazino – Slot oyunlar? Pinco-da
Bandar togel resmi Indonesia: Bandar togel resmi Indonesia – Link alternatif Abutogel
Situs togel online terpercaya Situs togel online terpercaya Abutogel login
https://abutowin.icu/# Abutogel
Abutogel: Jackpot togel hari ini – Abutogel
jilwin: maglaro ng Jiliko online sa Pilipinas – maglaro ng Jiliko online sa Pilipinas
Jollibet online sabong: Jollibet online sabong – jollibet app
Swerte99 bonus Swerte99 casino walang deposit bonus para sa Pinoy Swerte99 casino
Tro choi n? hu GK88: Nha cai uy tin Vi?t Nam – Casino online GK88
Situs togel online terpercaya: Jackpot togel hari ini – Link alternatif Abutogel
Live casino Indonesia: Withdraw cepat Beta138 – Live casino Indonesia
Jiliko app jilwin or jilwin
https://www.merkfunds.com/exit/?url=http://jilwin.pro Jiliko app
Jiliko app Jiliko app and Jiliko Jiliko slots
Etibarl? onlayn kazino Az?rbaycanda: Canl? krupyerl? oyunlar – Etibarl? onlayn kazino Az?rbaycanda
Live casino Indonesia Bandar bola resmi or Bandar bola resmi
https://images.google.com.nf/url?sa=t&url=https://betawinindo.top Beta138
Slot gacor Beta138 Bandar bola resmi and Bandar bola resmi Beta138
Slot gacor hari ini Mandiribet Situs judi resmi berlisensi
Swerte99 slots: Swerte99 casino walang deposit bonus para sa Pinoy – Swerte99
https://betawinindo.top/# Promo slot gacor hari ini
Swerte99 slots: Swerte99 app – Swerte99 login
Online casino Jollibet Philippines jollibet app jollibet login
Jiliko login: jilwin – Jiliko
Abutogel login: Bandar togel resmi Indonesia – Jackpot togel hari ini
Online betting Philippines: jollibet – Online betting Philippines
Jiliko Jiliko login or Jiliko app
https://chyba.o2.cz/cs/?url=https://jilwin.pro Jiliko casino
Jiliko slots Jiliko bonus and jilwin jilwin
Bandar bola resmi Beta138 or Bonus new member 100% Beta138
https://maps.google.de/url?q=https://betawinindo.top Slot gacor Beta138
Promo slot gacor hari ini Link alternatif Beta138 and Slot gacor Beta138 Bandar bola resmi
Live casino Indonesia: Bonus new member 100% Beta138 – Promo slot gacor hari ini
Swerte99: Swerte99 app – Swerte99 login
Jollibet online sabong jollibet login or jollibet
https://images.google.com.co/url?q=https://1winphili.company Online casino Jollibet Philippines
jollibet login Online betting Philippines and 1winphili jollibet
https://abutowin.icu/# Bandar togel resmi Indonesia
Yeni az?rbaycan kazino sayt?: Uduslar? tez c?xar Pinco il? – Onlayn rulet v? blackjack
Canli krupyerl? oyunlar: Uduslari tez çixar Pinco il? – Pinco il? real pul qazan
Slot gacor hari ini: Mandiribet login – Slot gacor hari ini
Khuy?n mai GK88 Dang ky GK88 Tro choi n? hu GK88
Yuks?k RTP slotlar Canl? krupyerl? oyunlar or Qeydiyyat bonusu Pinco casino
https://toolbarqueries.google.com.tr/url?q=https://pinwinaz.pro Pinco kazino
Onlayn rulet v? blackjack Pinco kazino and Pinco kazino Pinco il? real pul qazan
Slot gacor Beta138: Login Beta138 – Beta138
maglaro ng Jiliko online sa Pilipinas maglaro ng Jiliko online sa Pilipinas or Jiliko casino walang deposit bonus para sa Pinoy
https://www.google.ps/url?sa=t&url=https://jilwin.pro maglaro ng Jiliko online sa Pilipinas
Jiliko casino Jiliko and jilwin jilwin
Live casino Mandiribet: Situs judi online terpercaya Indonesia – Slot gacor hari ini
Beta138 Bonus new member 100% Beta138 or Promo slot gacor hari ini
https://maps.google.nr/url?q=https://betawinindo.top Slot gacor Beta138
Situs judi resmi berlisensi Login Beta138 and Live casino Indonesia Situs judi resmi berlisensi
Situs judi online terpercaya Indonesia: Bonus new member 100% Mandiribet – Bonus new member 100% Mandiribet
Yeni az?rbaycan kazino sayt?: Pinco kazino – Pinco kazino
Swerte99 login Swerte99 casino walang deposit bonus para sa Pinoy Swerte99 slots
Swerte99 casino walang deposit bonus para sa Pinoy: Swerte99 casino – Swerte99 slots
https://gkwinviet.company/# GK88
1winphili Online gambling platform Jollibet or 1winphili
https://cse.google.si/url?q=https://1winphili.company 1winphili
1winphili Online gambling platform Jollibet and jollibet jollibet login
Jiliko login: Jiliko casino – Jiliko
Promo slot gacor hari ini Login Beta138 Slot gacor Beta138
Bonus new member 100% Mandiribet: Situs judi online terpercaya Indonesia – Situs judi online terpercaya Indonesia
Bandar togel resmi Indonesia: Jackpot togel hari ini – Abutogel
Slot gacor hari ini: Bonus new member 100% Mandiribet – Mandiribet
Swerte99 casino walang deposit bonus para sa Pinoy: Swerte99 casino – Swerte99 bonus
Swerte99 online gaming Pilipinas Swerte99 casino walang deposit bonus para sa Pinoy Swerte99 online gaming Pilipinas
https://mandiwinindo.site/# Situs judi online terpercaya Indonesia
MediDirect USA: MediDirect USA – MediDirect USA
Indian Meds One best india pharmacy Online medicine home delivery
Indian Meds One: Online medicine home delivery – cheapest online pharmacy india
online mexico pharmacy USA: Mexican Pharmacy Hub – Mexican Pharmacy Hub
trusted mexican pharmacy: accutane mexico buy online – buy meds from mexican pharmacy
http://indianmedsone.com/# Indian Meds One
MediDirect USA: best online pharmacy generic levitra – pharmacy without prescription
Mexican Pharmacy Hub: mexico drug stores pharmacies – Mexican Pharmacy Hub
Mexican Pharmacy Hub: safe place to buy semaglutide online mexico – legit mexican pharmacy for hair loss pills
MediDirect USA nizoral online pharmacy MediDirect USA
india online pharmacy: top 10 pharmacies in india – Indian Meds One
Indian Meds One: top online pharmacy india – Indian Meds One
semaglutide mexico price: legit mexico pharmacy shipping to USA – rybelsus from mexican pharmacy
https://indianmedsone.com/# Indian Meds One
Indian Meds One Indian Meds One Indian Meds One
gabapentin mexican pharmacy: Mexican Pharmacy Hub – Mexican Pharmacy Hub
mexican border pharmacies shipping to usa: mexican pharmaceuticals online – Mexican Pharmacy Hub
Mexican Pharmacy Hub: Mexican Pharmacy Hub – Mexican Pharmacy Hub
indian pharmacies safe: online shopping pharmacy india – п»їlegitimate online pharmacies india
buy viagra pharmacy malaysia humana pharmacy store or kroger pharmacy
https://clients1.google.fi/url?q=https://medidirectusa.com cheap viagra pharmacy
lexapro online pharmacy online pharmacy reddit and target pharmacy metronidazole homeopathic pharmacy online
Indian Meds One: indian pharmacy – Indian Meds One
pharmacies in mexico that ship to usa medicine in mexico pharmacies or п»їbest mexican online pharmacies
https://toolbarqueries.google.ki/url?sa=t&url=https://mexicanpharmacyhub.com mexican rx online
medicine in mexico pharmacies pharmacies in mexico that ship to usa and buying prescription drugs in mexico online mexican online pharmacies prescription drugs
Indian Meds One pharmacy website india indianpharmacy com
MediDirect USA: MediDirect USA – cialis generic pharmacy online
reputable indian online pharmacy mail order pharmacy india or buy medicines online in india
https://www.google.tk/url?q=https://indianmedsone.com world pharmacy india
pharmacy website india top 10 pharmacies in india and indian pharmacy online india online pharmacy
Indian Meds One: online pharmacy india – buy medicines online in india
https://medidirectusa.shop/# MediDirect USA
indian pharmacies safe reputable indian pharmacies or cheapest online pharmacy india
https://clients1.google.bj/url?q=https://indianmedsone.com buy medicines online in india
cheapest online pharmacy india п»їlegitimate online pharmacies india and indian pharmacies safe top 10 online pharmacy in india
buying prescription drugs in mexico: mexico drug stores pharmacies – buying prescription drugs in mexico online
Indian Meds One: Indian Meds One – Indian Meds One
real mexican pharmacy USA shipping Mexican Pharmacy Hub cheap cialis mexico
Mexican Pharmacy Hub: legit mexican pharmacy without prescription – amoxicillin mexico online pharmacy
п»їbest mexican online pharmacies medicine in mexico pharmacies or buying from online mexican pharmacy
http://notice.iptv.by/nomoney.php?host=mexicanpharmacyhub.com&n=lizyukovyh7_913&nm=Ralink¶ms=redirect=/forum/tracker.php&reason=3&url=/forum/index.php mexican rx online
mexican pharmaceuticals online buying from online mexican pharmacy and mexican pharmaceuticals online medication from mexico pharmacy
Indian Meds One: indian pharmacy – buy medicines online in india
best rated online pharmacy viagra pharmacy mall or lansoprazole pharmacy
https://maps.google.com.ni/url?sa=t&url=https://medidirectusa.com pharmacy online 365 discount code
terbinafine target pharmacy online dog pharmacy and Endep omeprazole boots pharmacy
Indian Meds One: Indian Meds One – indianpharmacy com
Mexican Pharmacy Hub legit mexican pharmacy for hair loss pills best prices on finasteride in mexico
Mexican Pharmacy Hub: Mexican Pharmacy Hub – Mexican Pharmacy Hub
https://indianmedsone.shop/# buy prescription drugs from india
best india pharmacy indian pharmacy or buy medicines online in india
https://www.spsi.biz/Redirect.aspx?destination=https://indianmedsone.com/ п»їlegitimate online pharmacies india
india online pharmacy cheapest online pharmacy india and pharmacy website india indian pharmacy online
Mexican Pharmacy Hub: Mexican Pharmacy Hub – п»їmexican pharmacy
Mexican Pharmacy Hub: trusted mexican pharmacy – legit mexican pharmacy without prescription
MediDirect USA: MediDirect USA – dubai viagra pharmacy
Indian Meds One Indian Meds One mail order pharmacy india
mexican rx online medication from mexico pharmacy or mexican pharmaceuticals online
http://americanpatriotbeer.com/verify.php?redirect=http://mexicanpharmacyhub.com reputable mexican pharmacies online
pharmacies in mexico that ship to usa mexican border pharmacies shipping to usa and mexican border pharmacies shipping to usa mexican drugstore online
online mexico pharmacy USA: buy antibiotics over the counter in mexico – Mexican Pharmacy Hub
indian pharmacies safe: Indian Meds One – Indian Meds One
zetia online pharmacy viagra cancun pharmacy or american pharmacy online
https://www.google.si/url?sa=t&url=https://medidirectusa.com Glucophage
ez online pharmacy viagra biaxin online pharmacy and pharmacy rx 1 toronto pharmacy viagra
MediDirect USA: MediDirect USA – uriel pharmacy online store
indian pharmacy world pharmacy india or world pharmacy india
https://community.strongbodygreenplanet.com/proxy.php?link=https://indianmedsone.com indianpharmacy com
online pharmacy india Online medicine order and buy prescription drugs from india india pharmacy mail order
https://medidirectusa.shop/# clindamycin uk pharmacy
Indian Meds One: Indian Meds One – best online pharmacy india
cialis professional review: Tadalify – tadalafil 5mg once a day
pharmacy viagra canada genuine viagra pills buy real viagra online cheap
Tadalify: cialis 10mg – cialis paypal canada
viagra for women pills: viagra uk – SildenaPeak
SildenaPeak: online sildenafil citrate – buy generic viagra online in india
buy generic viagra online paypal SildenaPeak sildenafil otc europe
Tadalify: Tadalify – Tadalify
https://tadalify.shop/# Tadalify
sildenafil cost compare generic viagra discount or sildenafil soft tabs
https://www.google.com.eg/url?q=https://sildenapeak.com generic sildenafil 20mg cost
viagrarel.com/ how can i get sildenafil and 100mg viagra generic viagra 10mg
cialis online without perscription can i take two 5mg cialis at once or comprar tadalafil 40 mg en walmart sin receta houston texas
http://socialleadwizard.net/bonus/index.php?aff=http://tadalify.com/ cialis for sale in canada
what does cialis do cialis walmart and cialis time cialis 20mg side effects
SildenaPeak buy generic viagra 50mg online SildenaPeak
Tadalify: cialis cost per pill – cialis without a doctor prescription canada
KamaMeds: Non-prescription ED tablets discreetly shipped – Compare Kamagra with branded alternatives
SildenaPeak: sildenafil generic drug cost – generic viagra in australia
Tadalify: buying cheap cialis online – pictures of cialis pills
sildenafil coupon: sildenafil generic costs – SildenaPeak
how long does cialis take to work 10mg cialis coupon free trial Tadalify
https://sildenapeak.shop/# generic viagra otc
ED treatment without doctor visits Men’s sexual health solutions online or Online sources for Kamagra in the United States
https://maps.google.com.pr/url?q=https://kamameds.com Compare Kamagra with branded alternatives
Men’s sexual health solutions online Affordable sildenafil citrate tablets for men and Sildenafil oral jelly fast absorption effect Kamagra oral jelly USA availability
SildenaPeak: SildenaPeak – SildenaPeak
Men’s sexual health solutions online: Compare Kamagra with branded alternatives – Fast-acting ED solution with discreet packaging
evolution peptides tadalafil: Tadalify – cialis canada pharmacy no prescription required
generic cialis available in canada where to buy cialis online or buy cialis online overnight delivery
https://ticketonline.kiwikinos.ch/Kiwi/Show/926757?BackLink=https://tadalify.com buying cheap cialis online
cialis available in walgreens over counter?? cialis for sale toronto and what happens if you take 2 cialis cialis brand no prescription 365
Fast-acting ED solution with discreet packaging: Men’s sexual health solutions online – ED treatment without doctor visits
comprar tadalafil 40 mg en walmart sin receta houston texas cialis discount card cialis canada free sample
Sildenafil oral jelly fast absorption effect: Kamagra oral jelly USA availability – Kamagra oral jelly USA availability
https://sildenapeak.com/# SildenaPeak
how to buy cheap viagra online: where to get over the counter viagra – SildenaPeak
buy cialis 20 mg online Tadalify Tadalify
where can i buy viagra pills over the counter pfizer viagra online pharmacy or viagra coupon online
https://www.google.co.ao/url?sa=t&url=https://sildenapeak.com us online pharmacy viagra
buy sildenafil generic online female viagra pills uk and cheap sildenafil pills generic viagra 150 mg pills
ED treatment without doctor visits Kamagra reviews from US customers or Affordable sildenafil citrate tablets for men
https://cse.google.ki/url?sa=t&url=https://kamameds.com KamaMeds
ED treatment without doctor visits Sildenafil oral jelly fast absorption effect and Kamagra oral jelly USA availability Kamagra oral jelly USA availability
Tadalify: cialis shelf life – Tadalify
canada pharmacy cialis: cialis sublingual – cialis online delivery overnight
viagra pharmacy coupon viagra 25mg for sale or generic viagra from india
http://plugin.mediaget.com/promo/?url=https://sildenapeak.com precio de viagra 50mg
sildenafil 105 mg canada viagra 20 mg online and where to buy viagra cheap real viagra
Kamagra reviews from US customers: ED treatment without doctor visits – Kamagra oral jelly USA availability
cialis daily review tadalafil 5 mg tablet or where to buy tadalafil online
http://re-file.com/cushion.php?url=https://tadalify.com cialis generic best price that accepts mastercard
what are the side effect of cialis tadalafil review and cialis mexico cialis once a day
Tadalify Tadalify tadalafil tablets 20 mg reviews
Kamagra oral jelly USA availability: ED treatment without doctor visits – Online sources for Kamagra in the United States
https://sildenapeak.shop/# SildenaPeak
cheap tadalafil 10mg: Tadalify – cialis free trial voucher
Affordable sildenafil citrate tablets for men: Sildenafil oral jelly fast absorption effect – Sildenafil oral jelly fast absorption effect
SildenaPeak: sildenafil discount generic – generic viagra 50mg online
Tadalify Tadalify Tadalify
Compare Kamagra with branded alternatives Kamagra oral jelly USA availability or Fast-acting ED solution with discreet packaging
https://images.google.ml/url?sa=t&url=https://kamameds.com Online sources for Kamagra in the United States
Men’s sexual health solutions online Sildenafil oral jelly fast absorption effect and Compare Kamagra with branded alternatives Online sources for Kamagra in the United States
Tadalify: mantra 10 tadalafil tablets – Tadalify
Tadalify: cialis doesnt work for me – Tadalify
http://kamameds.com/# Affordable sildenafil citrate tablets for men
Tadalify Tadalify cialis online aust
SildenaPeak: SildenaPeak – can i buy sildenafil over the counter
Kamagra reviews from US customers: ED treatment without doctor visits – Non-prescription ED tablets discreetly shipped
sildenafil price in usa 805551 sildenafil or canada viagra buy
http://dvd24online.de/url?q=https://sildenapeak.com sildenafil 20 mg discount coupon
buy sildenafil online safely sildenafil 100 coupon and sildenafil medicine in india 400 mg viagra
how to buy viagra online SildenaPeak SildenaPeak
buy sildenafil no rx: SildenaPeak – viagra 100mg buy online
Kamagra reviews from US customers: Fast-acting ED solution with discreet packaging – Affordable sildenafil citrate tablets for men
Online sources for Kamagra in the United States Kamagra oral jelly USA availability or Sildenafil oral jelly fast absorption effect
https://maps.google.gr/url?sa=t&url=https://kamameds.com Sildenafil oral jelly fast absorption effect
Safe access to generic ED medication Affordable sildenafil citrate tablets for men and Non-prescription ED tablets discreetly shipped Safe access to generic ED medication
generic sildenafil without a prescription: sildenafil generic 100 mg – best price viagra uk
how to take liquid tadalafil cialis pharmacy or no prescription female cialis
http://images.google.com.ph/url?q=https://tadalify.com e20 pill cialis
cialis commercial bathtub tadalafil generic in usa and best price on cialis 20mg best price on generic cialis
https://kamameds.shop/# Men’s sexual health solutions online
average cost of viagra 100mg how can i get viagra or buy viagra cheap australia
https://images.google.ml/url?q=https://sildenapeak.com buy viagra 200mg
sildenafil 40 mg female viagra order and sildenafil otc usa sildenafil discount
Kamagra oral jelly USA availability: Non-prescription ED tablets discreetly shipped – Men’s sexual health solutions online
Kamagra oral jelly USA availability: Men’s sexual health solutions online – Kamagra oral jelly USA availability
cialis precio Tadalify cialis 5mg coupon
purchase brand cialis: Tadalify – Tadalify
can you buy generic viagra over the counter sildenafil 50 mg online or cost of 1 viagra pill
https://cse.google.co.th/url?q=https://sildenapeak.com where can i buy viagra pills online
over the counter viagra in canada sildenafil over counter and can you order viagra without a prescription viagra for women
cialis copay card: Tadalify – Tadalify
SildenaPeak: generic viagra online 25mg – SildenaPeak
SildenaPeak: how to get female viagra otc – SildenaPeak
KamaMeds Kamagra oral jelly USA availability KamaMeds
https://tadalify.shop/# cialis alternative
difference between tadalafil and sildenafil cialis and high blood pressure or maximpeptide tadalafil review
https://maps.google.com.gi/url?sa=t&url=https://tadalify.com what is cialis for
cialis cheap cialis purchase canada and how long does tadalafil take to work cialis tadalafil 5mg once a day
buy cialis 20mg: overnight cialis delivery usa – Tadalify
Kamagra oral jelly USA availability: Kamagra oral jelly USA availability – Safe access to generic ED medication
Safe access to generic ED medication: Kamagra oral jelly USA availability – Fast-acting ED solution with discreet packaging
lady viagra where can you buy viagra for women or canada drug pharmacy viagra
https://images.google.bt/url?sa=t&url=https://sildenapeak.com best canadian pharmacy generic viagra
buy genuine viagra how to order viagra online in india and purchase viagra in usa can i buy viagra online in canada
SildenaPeak: sildenafil 100mg without prescription – SildenaPeak
Sildenafil oral jelly fast absorption effect: ED treatment without doctor visits – Men’s sexual health solutions online
cialis professional review: Tadalify – cialis 50mg
https://tadalify.shop/# Tadalify
cialis generic name trusted online store to buy cialis or cialis priligy online australia
https://cse.google.mw/url?sa=t&url=https://tadalify.com cialis for daily use dosage
cialis free trial voucher 2018 cialis uses and cialis lower blood pressure cheapest cialis 20 mg
what happens if a woman takes cialis cialis generic overnite shipping cialis before and after
Kamagra reviews from US customers Safe access to generic ED medication or Online sources for Kamagra in the United States
http://nimbus.c9w.net/wifi_dest.html?dest_url=https://kamameds.com Non-prescription ED tablets discreetly shipped
KamaMeds Men’s sexual health solutions online and Kamagra oral jelly USA availability Affordable sildenafil citrate tablets for men
Tadalify: cialis onset – cialis priligy online australia
SildenaPeak: sildenafil tablets 100mg uk – SildenaPeak
SildenaPeak: SildenaPeak – sildenafil buy
can you buy viagra in canada sildenafil 200mg price or sildenafil otc australia
http://aanorthflorida.org/es/redirect.asp?url=http://sildenapeak.com where can i buy real viagra
viagra 50 mg price for viagra in canada and buying sildenafil 100mg viagra where to buy canada
prednisone 300mg: cheap generic prednisone – how much is prednisone 5mg
IverGrove: IverGrove – IverGrove
where to buy generic clomid online how can i get generic clomid without dr prescription FertiCare Online
order amoxicillin uk: amoxicillin 500mg capsule – amoxicillin 500mg tablets price in india
prednisone tablets: prednisone online pharmacy – SteroidCare Pharmacy
FertiCare Online: where to get generic clomid without dr prescription – cheap clomid pill
buy stromectol uk: IverGrove – IverGrove
order cheap clomid without prescription can you buy generic clomid price FertiCare Online
lasix 40 mg: CardioMeds Express – CardioMeds Express
can i buy amoxicillin over the counter in australia: amoxicillin for sale – TrustedMeds Direct
prednisone pharmacy 10 mg prednisone tablets or prednisone 5 mg
https://www.google.com.uy/url?q=https://steroidcarepharmacy.com prednisone in mexico
prednisone 5 mg tablet apo prednisone and prednisone for sale no prescription prednisone 4mg
https://trustedmedsdirect.com/# purchase amoxicillin online without prescription
buy amoxicillin without prescription buy amoxicillin 500mg uk or purchase amoxicillin online without prescription
http://alt1.toolbarqueries.google.com.mx/url?q=https://trustedmedsdirect.com buy amoxicillin 500mg uk
amoxicillin 500 mg where to buy buy amoxicillin online mexico and generic amoxicillin online how much is amoxicillin
peru ivermectin: ivermectin tablets – ivermectin dosage for cats
lasix generic: CardioMeds Express – lasix 40 mg
prednisone 60 mg daily: order prednisone 10mg – SteroidCare Pharmacy
IverGrove: ivermectin budgies – ivermectin head lice
SteroidCare Pharmacy: SteroidCare Pharmacy – where to buy prednisone in australia
prednisone prednisone 1 mg daily or buy prednisone tablets uk
https://meditation.org.au/podcast_description.asp?feed=http://steroidcarepharmacy.com 5mg prednisone
buy prednisone without rx can you buy prednisone over the counter in usa and prednisone 20mg for sale prednisone 5093
where can i get amoxicillin 500 mg how to buy amoxycillin or buy cheap amoxicillin
http://ethr.net/phpinfo.php?a=<a+href=http://trustedmedsdirect.com purchase amoxicillin online
amoxicillin 500mg capsules price amoxicillin 30 capsules price and amoxicillin 500 mg tablet price buy amoxicillin without prescription
furosemide 40 mg: furosemide 40 mg – CardioMeds Express
http://steroidcarepharmacy.com/# prednisone 20 mg generic
CardioMeds Express: furosemide – CardioMeds Express
lasix 100 mg tablet: lasix generic – lasix
furosemide 100 mg: CardioMeds Express – CardioMeds Express
lasix online lasix 40mg lasix dosage
goat wormer ivermectin: IverGrove – IverGrove
furosemide 100mg: CardioMeds Express – CardioMeds Express
Excellent web site you have here.. It’s difficult to find good quality writing like
yours nowadays. I seriously appreciate individuals like you!
Take care!!
Здравствуйте!
Долго думал как поднять сайт и свои проекты и нарастить CF cituation flow и узнал от гуру в seo,
крутых ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное top прогон Хрумером – https://www.bing.com/search?q=bullet+%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%BD
Как сделать прогон сайта через Xrumer становится проще с инструкцией. Xrumer для массового линкбилдинга позволяет экономить силы. Линкбилдинг на автомате ускоряет создание ссылочной массы. Техники увеличения ссылочной массы Xrumer обеспечивают стабильный рост DR. Xrumer и рост Ahrefs DR становятся заметны через недели.
поисковое продвижение сайта под яндекс, screaming frog seo mac, линкбилдинг стратегии
линкбилдинг или, сео 2019, seo сравнение
!!Удачи и роста в топах!!
ivermectin for dogs dose can you use ivermectin on cats or ivermectin products
https://www.bysb.net/jumppage.php?p=ivergrove.com petsmart ivermectin
ivermectin paste for goats ivermectin dose for goats and ivermectin eye drops where can i buy ivermectin for cats
how can i get prednisone where to get prednisone or generic prednisone for sale
https://share.movablecamera.com/?t=&i=b12044e9-2e5d-471e-960a-ea53dec9c8dd&d=Checkthisout!&url=https://steroidcarepharmacy.com no prescription online prednisone
cost of prednisone in canada prednisone 54899 and buy prednisone online canada buy 10 mg prednisone
lasix tablet lasix uses or buy furosemide online
http://chat.waw.su/redir_exit.php?url=https://cardiomedsexpress.com lasix furosemide
furosemide 40 mg buy lasix online and lasix furosemide lasix generic name
https://ferticareonline.com/# FertiCare Online
amoxicillin 500mg no prescription amoxicillin without a prescription or amoxicillin capsule 500mg price
https://maps.google.at/url?q=https://trustedmedsdirect.com buy amoxicillin canada
price for amoxicillin 875 mg amoxicillin tablet 500mg and can you purchase amoxicillin online how much is amoxicillin prescription
IverGrove: IverGrove – ivermectin for chickens egg withdrawal
IverGrove: IverGrove – stromectol for head lice
IverGrove ivermectin dosage for chickens injectable ivermectin for goats
IverGrove: IverGrove – IverGrove
https://pillolesubito.shop/# Farmacie online sicure
viagra pfizer 25mg prezzo pillole per la disfunzione erettile in Italia le migliori pillole per l’erezione
acquisto farmaci con ricetta: accesso rapido a cialis generico online – farmacie online sicure
comprare farmaci online con ricetta: consegna rapida in tutta Italia – top farmacia online
farmacia online: Pillole Subito – Farmacie on line spedizione gratuita
farmacie online affidabili kamagra online Italia farmacie online affidabili
Farmacie on line spedizione gratuita: Pillole Subito – comprare farmaci online all’estero
https://forzaintima.shop/# trattamenti per la salute sessuale senza ricetta
п»їFarmacia online migliore: farmaci senza ricetta online – farmacia online
farmacia online: soluzioni rapide per la potenza maschile – migliori farmacie online 2024
gel per erezione in farmacia Potenza Facile miglior sito dove acquistare viagra
farmacia senza ricetta recensioni: PotenzaFacile – viagra originale in 24 ore contrassegno
gel per erezione in farmacia cerco viagra a buon prezzo or viagra consegna in 24 ore pagamento alla consegna
http://www.google.com.qa/url?q=https://potenzafacile.com viagra online consegna rapida
esiste il viagra generico in farmacia viagra pfizer 25mg prezzo and viagra naturale in farmacia senza ricetta viagra subito
farmacia online senza ricetta: farmacia online – Farmacie online sicure
farmacia online senza ricetta accesso rapido a cialis generico online farmacia online
farmacia online piГ№ conveniente Farmacie online sicure or Farmacie on line spedizione gratuita
п»їhttps://www.google.com/url?q=https://forzaintima.com comprare farmaci online con ricetta
farmacie online autorizzate elenco top farmacia online and farmacia online senza ricetta comprare farmaci online con ricetta
farmacie online affidabili: farmaci generici a prezzi convenienti – Farmacia online miglior prezzo
comprare farmaci online all’estero п»їFarmacia online migliore or farmacia online senza ricetta
https://www.google.ad/url?q=https://pillolesubito.com farmaci senza ricetta elenco
comprare farmaci online all’estero farmacia online and farmacia online senza ricetta Farmacie on line spedizione gratuita
http://potenzafacile.com/# viagra generico recensioni
acquisto farmaci con ricetta: Forza Intima – top farmacia online
Farmacie on line spedizione gratuita farmaci senza ricetta elenco or farmaci senza ricetta elenco
https://images.google.az/url?sa=t&url=https://farmacidiretti.com Farmacia online piГ№ conveniente
top farmacia online farmacie online sicure and Farmacia online miglior prezzo top farmacia online
farmacia online senza ricetta: farmacie online sicure – comprare farmaci online con ricetta
farmacia online accesso rapido a cialis generico online top farmacia online
https://maplemedsdirect.shop/# MapleMeds Direct
viagra online pharmacy uk: much does viagra cost pharmacy – 24 store pharmacy
order azithromycin mexico BorderMeds Express buy kamagra oral jelly mexico
buy prescription drugs from india: pharmacy website india – BharatMeds Direct
mexico drug stores pharmacies: purple pharmacy mexico price list – BorderMeds Express
Awesome blog! Do you have any recommendations for aspiring writers?
I’m planning to start my owwn website son but I’m a little lost on everything.
Would you suggest starting with a free platform like WordPress or go for a paiud option? There are
so many options out there that I’m totally overwhelmed ..
Any recommendations? Many thanks! https://Glassi-Info.Blogspot.com/2025/08/deposits-and-withdrawals-methods-in.html
BharatMeds Direct: BharatMeds Direct – Online medicine order
BharatMeds Direct: BharatMeds Direct – world pharmacy india
BharatMeds Direct BharatMeds Direct BharatMeds Direct
correct rx pharmacy services: amoxicillin uk pharmacy – MapleMeds Direct
https://bordermedsexpress.shop/# reputable mexican pharmacies online
MapleMeds Direct: MapleMeds Direct – MapleMeds Direct
pharmacy website india BharatMeds Direct best india pharmacy
mexican mail order pharmacies: buying from online mexican pharmacy – buying prescription drugs in mexico online
inhouse pharmacy general motilium uk online pharmacy propecia or safeway pharmacy (inside safeway)
https://maps.google.co.kr/url?q=https://maplemedsdirect.com pharmacy
propecia price pharmacy online pharmacy drug store and Cialis pharmacy store in india
BharatMeds Direct: india pharmacy mail order – BharatMeds Direct
п»їbest mexican online pharmacies pharmacies in mexico that ship to usa or mexican online pharmacies prescription drugs
https://maps.google.ml/url?q=https://bordermedsexpress.com purple pharmacy mexico price list
mexican drugstore online purple pharmacy mexico price list and reputable mexican pharmacies online medicine in mexico pharmacies
buy cialis from mexico: best mexican pharmacy online – BorderMeds Express
best online pharmacy india buy prescription drugs from india or india pharmacy mail order
https://cse.google.md/url?sa=t&url=https://bharatmedsdirect.com best india pharmacy
indianpharmacy com indianpharmacy com and indian pharmacy online best online pharmacy india
MapleMeds Direct blink pharmacy MapleMeds Direct
https://maplemedsdirect.com/# adderall online pharmacy
MapleMeds Direct: cymbalta mail order pharmacy – ventolin uk pharmacy
pharmacy prices: pharmacy rx solutions – MapleMeds Direct
BharatMeds Direct: india pharmacy mail order – BharatMeds Direct
india pharmacy mail order reputable indian pharmacies BharatMeds Direct
best online pharmacy india: BharatMeds Direct – pharmacy website india
medicine in mexico pharmacies mexico pharmacies prescription drugs or <a href=" http://worldconnx.net/phpinfo.php?a=cialis+generika “>pharmacies in mexico that ship to usa
http://www.codetools.ir/tools/static-image/4.php?l=http://bordermedsexpress.shop mexican drugstore online
medicine in mexico pharmacies mexico drug stores pharmacies and mexican mail order pharmacies mexican mail order pharmacies
online pharmacy reviews percocet best online pharmacy without prescription or mexican pharmacy weight loss
https://cse.google.je/url?q=https://maplemedsdirect.com Indinavir (Cipla Ltd)
muscle relaxant online pharmacy uk doxycycline and cost less pharmacy mental illness
BharatMeds Direct: BharatMeds Direct – reputable indian pharmacies
viagra online pharmacy europe: MapleMeds Direct – finpecia pharmacy2home
MapleMeds Direct MapleMeds Direct MapleMeds Direct
https://bharatmedsdirect.com/# BharatMeds Direct
MapleMeds Direct: best online pharmacy india – MapleMeds Direct
BorderMeds Express: BorderMeds Express – BorderMeds Express
top 10 online pharmacy in india indian pharmacy BharatMeds Direct
BharatMeds Direct: buy prescription drugs from india – BharatMeds Direct
mexico pharmacy: BorderMeds Express – viagra pills from mexico
india pharmacy Online medicine order or cheapest online pharmacy india
https://www.google.nu/url?q=https://bharatmedsdirect.com india pharmacy mail order
buy prescription drugs from india indianpharmacy com and Online medicine home delivery reputable indian pharmacies
MapleMeds Direct dexamethasone iontophoresis pharmacy MapleMeds Direct
mexican mail order pharmacies purple pharmacy mexico price list or reputable mexican pharmacies online
http://www.teamready.org/gallery/main.php?g2_view=core.UserAdmin&g2_subView=core.UserRecoverPassword&g2_return=https://bordermedsexpress.com mexican rx online
mexico drug stores pharmacies mexican border pharmacies shipping to usa and mexico pharmacies prescription drugs purple pharmacy mexico price list
mexican rx online: buying from online mexican pharmacy – BorderMeds Express
https://maplemedsdirect.shop/# MapleMeds Direct
indian pharmacy online: india pharmacy mail order – best india pharmacy
best online pharmacy india top online pharmacy india BharatMeds Direct
MapleMeds Direct: MapleMeds Direct – percocet online pharmacy without prescriptions
situs judi online resmi Indonesia: garuda888 game slot RTP tinggi – garuda888 game slot RTP tinggi
preman69 login tanpa ribet: promosi dan bonus harian preman69 – preman69 login tanpa ribet
1win888indonesia: 1win888indonesia – garuda888 login resmi tanpa ribet
daftar garuda888 mudah dan cepat 1win888indonesia garuda888 slot online terpercaya
https://1wbook.shop/# book of ra deluxe
giocare da mobile a Starburst: Starburst giri gratis senza deposito – bonus di benvenuto per Starburst
preman69 slot: 1win69 – promosi dan bonus harian preman69
bonaslot link resmi mudah diakses 1wbona bonaslot login
bonaslot bonaslot situs bonus terbesar Indonesia or bonaslot kasino online terpercaya
https://100kursov.com/away/?url=https://1wbona.com 1wbona
bonaslot jackpot harian jutaan rupiah bonaslot jackpot harian jutaan rupiah and bonaslot situs bonus terbesar Indonesia bonaslot login
Book of Ra Deluxe soldi veri: migliori casino online con Book of Ra – book of ra deluxe
bonus di benvenuto per Starburst jackpot e vincite su Starburst Italia or Starburst slot online Italia
https://clients1.google.com.tw/url?q=https://1wstarburst.shop starburst
casino online sicuri con Starburst Starburst giri gratis senza deposito and jackpot e vincite su Starburst Italia bonus di benvenuto per Starburst
1wbona: bonaslot jackpot harian jutaan rupiah – bonaslot login
bonus di benvenuto per Starburst: giocare da mobile a Starburst – starburst
https://1win69.shop/# preman69 login
Starburst giri gratis senza deposito migliori casino online con Starburst migliori casino online con Starburst
recensioni Book of Ra Deluxe slot: book of ra deluxe – Book of Ra Deluxe soldi veri
garuda888 live casino Indonesia garuda888 login resmi tanpa ribet or garuda888 game slot RTP tinggi
https://maps.google.ie/url?sa=t&url=https://1win888indonesia.com permainan slot gacor hari ini
situs judi online resmi Indonesia garuda888 game slot RTP tinggi and garuda888 live casino Indonesia 1win888indonesia
bonus di benvenuto per Starburst: bonus di benvenuto per Starburst – Starburst giri gratis senza deposito
Book of Ra Deluxe soldi veri book of ra deluxe bonus di benvenuto per Book of Ra Italia
bonaslot bonaslot situs bonus terbesar Indonesia or bonaslot jackpot harian jutaan rupiah
http://images.google.mv/url?q=https://1wbona.com bonaslot situs bonus terbesar Indonesia
bonaslot login bonaslot and bonaslot link resmi mudah diakses bonaslot situs bonus terbesar Indonesia
preman69: preman69 login tanpa ribet – 1win69
starburst: Starburst giri gratis senza deposito – Starburst giri gratis senza deposito
Starburst giri gratis senza deposito giocare a Starburst gratis senza registrazione or Starburst giri gratis senza deposito
https://clients1.google.mk/url?q=https://1wstarburst.com Starburst slot online Italia
Starburst giri gratis senza deposito casino online sicuri con Starburst and starburst jackpot e vincite su Starburst Italia
daftar garuda888 mudah dan cepat: garuda888 – garuda888 login resmi tanpa ribet
http://1win69.com/# preman69 slot
preman69 situs judi online 24 jam: preman69 – preman69 situs judi online 24 jam
daftar garuda888 mudah dan cepat: 1win888indonesia – link alternatif garuda888 terbaru
1win69: preman69 login tanpa ribet – preman69 login tanpa ribet
permainan slot gacor hari ini daftar garuda888 mudah dan cepat garuda888 login resmi tanpa ribet
garuda888 game slot RTP tinggi permainan slot gacor hari ini or situs judi online resmi Indonesia
http://clients1.google.com.ua/url?sa=i&url=https://1win888indonesia.com garuda888 live casino Indonesia
daftar garuda888 mudah dan cepat permainan slot gacor hari ini and link alternatif garuda888 terbaru garuda888 slot online terpercaya
recensioni Book of Ra Deluxe slot: bonus di benvenuto per Book of Ra Italia – recensioni Book of Ra Deluxe slot
giri gratis Book of Ra Deluxe: book of ra deluxe – migliori casino online con Book of Ra
https://1wbona.com/# 1wbona
garuda888 slot online terpercaya: situs judi online resmi Indonesia – 1win888indonesia
starburst jackpot e vincite su Starburst Italia or casino online sicuri con Starburst
http://www.kansai-sheet.jp/cgi-local/contact_check.cgi?name=Trevorhox&tantou=&mail=trevoridest%401wstarburst.com&mail2=trevoridest%401wstarburst.com&comment=+Its+such+as+you+learn+my+thoughts%21+You+appear+to+know+so+much+approximately+this%2C+such+as+you+wrote+the+ebook+in+it+or+something.+I+feel+that+you+just+can+do+with+a+few+%25+to+pressure+the+message+house+a+little+bit%2C+but+instead+of+that%2C+this+is+fantastic+blog.+A+fantastic+read.+I+will+definitely+be+back.+buy+cialis+online+%0D%0A+%0D%0Acutting+a+cialis+pill+in+half+cialis+generic+dur%84Ce+d%27effet+cialis+cialis+generic+cialis+reflusso+%0D%0A+%0D%0Ayoung+men+take+viagra+viagra+uk+viagra+cost+compare+viagra+tesco+which+is+best+viagra+livetra+cialis+%0D%0A+%0D%0Acanadian+online+pharmacy+canadian+pharmacies+that+ship+to+us+online+canadian+discount+pharmacy+canada+online+pharmacies+online+pharmacy+reviews&submit=m%81hF%20 bonus di benvenuto per Starburst
migliori casino online con Starburst starburst and Starburst slot online Italia migliori casino online con Starburst
migliori casino online con Starburst starburst giocare da mobile a Starburst
https://truemedspharm.com/# TrueMeds
ClearMeds: buy antibiotics online for uti – antibiotics over the counter
antibiotics over the counter: buy antibiotics online safely – buy antibiotics online safely
online pharmacy meds TrueMeds discount pharmacy mexico
http://truemedspharm.com/# best canadian pharmacy for cialis
https://truemedspharm.shop/# TrueMeds
where to get ed pills: VitalCore Pharmacy – VitalCore
VitalCore Pharmacy: ed meds by mail – ed pills
get ed meds online VitalCore Pharmacy ed pills
cheap antibiotics: antibiotics over the counter – buy antibiotics
the peoples pharmacy: TrueMeds – TrueMeds
https://truemedspharm.shop/# pharmacy canadian
https://truemedspharm.shop/# TrueMeds Pharmacy
cheap antibiotics buy antibiotics online buy antibiotics
TrueMeds Pharmacy: canadian pharmacy viagra – TrueMeds
canadian pharmacy online cialis canadian drug stores or canadian pharmacy ltd
https://cse.google.st/url?sa=i&url=https://truemedspharm.com uk pharmacy no prescription
canadian mail order pharmacy pharmacy rx world canada and pharmacy online us online pharmacy
ClearMeds Pharmacy buy antibiotics online safely or cheap antibiotics
http://file.feelcool.org/resites.php?url=https://clearmedspharm.com/ buy antibiotics
ClearMeds Pharmacy buy antibiotics online safely and ClearMeds buy antibiotics online safely
buy ed meds online: online erectile dysfunction prescription – VitalCore
http://truemedspharm.com/# TrueMeds Pharmacy
canadian pharmacy ed medications no prescription required pharmacy or top online pharmacy india
https://images.google.com.nf/url?q=https://truemedspharm.shop canadian pharmacy 24 com
online pharmacy india canadian pharmacy world and pharmaceutical online ordering foreign pharmacy no prescription
TrueMeds TrueMeds Pharmacy TrueMeds
ed pills: ed pills – ed pills
http://vitalcorepharm.com/# VitalCore
TrueMeds TrueMeds Pharmacy discount pharmacy mexico
https://vitalcorepharm.com/# VitalCore Pharmacy
TrueMeds: TrueMeds – TrueMeds Pharmacy
ed med online: ed pills – ed pills
legit canadian pharmacy online pharmacy no prescription or pharmacy websites
https://images.google.com.do/url?sa=t&url=https://truemedspharm.com indian trail pharmacy
77 canadian pharmacy canadian pharmacy scam and canadian pharmacy world coupon pharmaceutical online ordering
cheap antibiotics or buy antibiotics online for uti
https://maps.google.bi/url?sa=t&url=https://clearmedspharm.com ClearMeds
buy antibiotics for tooth infection buy antibiotics online and buy antibiotics buy antibiotics online safely
commander cialis discretement tadalafil prix medicament contre la dysfonction erectile
tadalafil sans ordonnance: IntimaPharma – tadalafil sans ordonnance
https://bluepharmafrance.shop/# Blue Pharma
viagra generique efficace: sildenafil citrate 100 mg – BluePharma
IntimaPharma: cialis original et générique livraison rapide – IntimaPharma
viagra generique efficace viagra femme viagra en ligne France sans ordonnance
http://pharmaexpressfrance.com/# pharmacies en ligne certifiГ©es
kamagra gel oral livraison discrete France: kamagra gel oral livraison discrete France – kamagra 100 mg prix competitif en ligne
kamagra gel oral livraison discrète France: kamagra gel oral livraison discrète France – kamagra gel oral livraison discrète France
https://pharmaexpressfrance.shop/# vente de mГ©dicament en ligne
pharmacie en ligne france pharmacie digitale francaise fiable pharmacie en ligne
viagra homme livraison rapide et confidentielle or Blue Pharma
https://maps.google.com.uy/url?q=https://bluepharmafrance.com Blue Pharma
viagra homme BluePharma and viagra homme livraison rapide et confidentielle
https://pharmalibrefrance.shop/# Pharma Libre
PharmaLibre: kamagra gel oral livraison discrete France – kamagra 100 mg prix competitif en ligne
Pharmacie Internationale en ligne pharmacie en ligne france fiable or pharmacies en ligne certifiГ©es
https://www.google.ht/url?q=https://pharmaexpressfrance.com Pharmacie en ligne livraison Europe
Achat mГ©dicament en ligne fiable pharmacie en ligne france fiable and pharmacie en ligne avec ordonnance pharmacie en ligne france pas cher
acheter medicaments en ligne pas cher pharmacie en ligne pas cher Pharmacie en ligne livraison Europe
BluePharma France: viagra femme – pilule bleue en ligne
https://bluepharmafrance.com/# viagra homme
https://pharmalibrefrance.com/# PharmaLibre
medicament contre la dysfonction erectile cialis sans ordonnance cialis generique pas cher
cialis generique pas cher: pharmacie en ligne – IntimaPharma
BluePharma France viagra femme or viagra femme
https://maps.google.bj/url?sa=t&url=https://bluepharmafrance.com livraison rapide et confidentielle
BluePharma France livraison rapide et confidentielle and viagra femme viagra homme
https://mez.ink/batarabet# bataraslot
batara vip: batarabet login – batara88
hargatoto login hargatoto login hargatoto slot
betawi 77 betawi 77 slot
https://www.google.com.ai/url?q=https://linkr.bio/betawi777 betawi77 link alternatif
betawi 77 betawi 77
toto slot hargatoto: hargatoto login – hargatoto login
kratonbet kratonbet login kratonbet
https://linklist.bio/inatogelbrand# INA TOGEL Daftar
slot online bataraslot
http://www.irwebcast.com/cgi-local/report/redirect.cgi?url=http://bluepharmafrance.com bataraslot 88
bataraslot login situs slot batara88
bataraslot login: situs slot batara88 – slot online
batarabet batara88 batara vip
inatogel 4D inatogel 4D
http://www.allpetsclub.com/Calendar/EventDetails/14-03-03/Pet_Fashion_Show_WALLINGFORD.aspx?Returnurl=http://pharmaexpressfrance.com/ inatogel 4D
INA TOGEL Daftar Official Link Situs Toto Togel
https://tap.bio/@hargatoto# hargatoto alternatif
kratonbet login kratonbet login
http://www.softwizard.ru/en/redirect-url?redirect_url=pharmalibrefrance.com kratonbet link
kratonbet login kratonbet link
mawartoto slot mawartoto login mawartoto link
bataraslot alternatif situs slot batara88
https://image.google.com.sl/url?q=https://linktr.ee/bataraslot777 bataraslot 88
bataraslot login bataraslot
betawi77 login: betawi77 – betawi77 link alternatif
bataraslot login bataraslot alternatif bataraslot login
Official Link Situs Toto Togel inatogel 4D
https://www.smartspace.ws/login.php?TraderId=1123&rdurl=https://linklist.bio/inatogelbrand::: Login Alternatif Togel
Situs Togel Terpercaya Dan Bandar INA TOGEL Daftar
INA TOGEL Daftar: Daftar InaTogel Login Link Alternatif Terbaru – inatogel 4D
https://linktr.ee/mawartotol# mawartoto
toto slot hargatoto hargatoto login hargatoto
inatogel 4D: inatogel – Official Link Situs Toto Togel
bataraslot alternatif bataraslot login situs slot batara88
betawi77 net betawi 777
https://www.google.ps/url?q=https://linkr.bio/betawi777 betawi77
betawi77 betawi77 login
Situs Togel Toto 4D INA TOGEL Daftar
http://toolbarqueries.google.bt/url?sa=t&url=https://linklist.bio/inatogelbrand Login Alternatif Togel
Daftar InaTogel Login Link Alternatif Terbaru Situs Togel Terpercaya Dan Bandar
batara vip: batarabet – batarabet alternatif
slot online bataraslot situs slot batara88
https://linktr.ee/bataraslot777# slot online
mawartoto login mawartoto mawartoto link
toto slot hargatoto: hargatoto login – hargatoto login
INA TOGEL Daftar INA TOGEL Daftar inatogel 4D
EverGreenRx USA: EverGreenRx USA – where to get free samples of cialis
http://evergreenrxusas.com/# EverGreenRx USA
cialis prices in mexico cialis soft tabs canadian pharmacy
https://maps.google.com.cu/url?rct=j&sa=t&url=https://evergreenrxusas.shop cialis next day delivery
how much does cialis cost per pill cialis savings card
EverGreenRx USA: how much does cialis cost per pill – tadalafil professional review
EverGreenRx USA generic cialis 5mg EverGreenRx USA
Mighty Dog Roofing
Reimer Drive North 13768
Maple Grove, MN 55311 United Ⴝtates
(763) 280-5115
durable flat roof replacements
EverGreenRx USA: EverGreenRx USA – EverGreenRx USA
cialis effects when is the best time to take cialis EverGreenRx USA
canada cialis generic cialis 20 mg from india
http://cse.google.com.na/url?sa=i&url=https://evergreenrxusas.com cialis dosage 20mg
what is cialis prescribed for cialis free trial voucher 2018
http://evergreenrxusas.com/# EverGreenRx USA
Mightyy Dog Roofing
Reimmer Drive North 13768
Maple Grove, MN 55311 United Ѕtates
(763) 280-5115
hail storm roof repair
http://evergreenrxusas.com/# EverGreenRx USA
when should i take cialis cialis daily side effects
http://arigato.pro/forum/away.php?s=https://evergreenrxusas.shop buy cialis united states
cialis information cialis alcohol
online pharmacy UK no prescription MediQuick UK pharmacy online fast delivery UK
cialis online UK no prescription: IntimaCare UK – IntimaCare
http://bluepilluk.com/# order viagra online safely UK
Oh my goodness! Amazing article dude! Thank you so much, However
I am experiencing problems with your RSS. I don’t know the reason why I cannot subscribe to it.
Is there anybody else having identical RSS problems?
Anyone who knows the solution can you kindly respond?
Thanks!!
viagra discreet delivery UK generic sildenafil UK pharmacy BluePillUK
sildenafil tablets online order UK: BluePillUK – viagra online UK no prescription
https://meditrustuk.shop/# discreet ivermectin shipping UK
IntimaCare: cialis cheap price UK delivery – cialis cheap price UK delivery
ivermectin cheap price online UK MediTrust ivermectin tablets UK online pharmacy
BluePill UK BluePillUK and BluePill UK viagra discreet delivery UK
http://www.google.com.bo/url?q=https://bluepilluk.com/ BluePill UK or https://alphafocusir.com/user/fneimumqso/?um_action=edit sildenafil tablets online order UK
viagra discreet delivery UK order viagra online safely UK or sildenafil tablets online order UK order viagra online safely UK
BluePillUK https://intimacareuk.com/# IntimaCare
http://bluepilluk.com/# sildenafil tablets online order UK
MediTrust: MediTrust UK – ivermectin cheap price online UK
branded and generic tadalafil UK pharmacy buy ED pills online discreetly UK cialis cheap price UK delivery
order viagra online safely UK https://intimacareuk.shop/# IntimaCare
https://bluepilluk.com/# viagra discreet delivery UK
http://bluepilluk.com/# generic sildenafil UK pharmacy
cheap UK online pharmacy UK pharmacy home delivery or generic and branded medications UK generic and branded medications UK
https://toolbarqueries.google.com.sv/url?q=https://mediquickuk.com MediQuick and http://sotoycasal.com/user/mpdbwujwse/ MediQuickUK
MediQuick trusted UK digital pharmacy and confidential delivery pharmacy UK order medicines online discreetly
Sportwetten Bonus Aktuell (https://Newsblogsite.Rimmablog.Com/36171611/Frauenfussball-Stars) bonus angebote
branded and generic tadalafil UK pharmacy: branded and generic tadalafil UK pharmacy – branded and generic tadalafil UK pharmacy
MediQuick UK pharmacy online fast delivery UK cheap UK online pharmacy
sildenafil tablets online order UK https://bluepilluk.com/# viagra online UK no prescription
buy ED pills online discreetly UK buy ED pills online discreetly UK or branded and generic tadalafil UK pharmacy tadalafil generic alternative UK
https://images.google.gl/url?sa=t&url=https://intimacareuk.com weekend pill UK online pharmacy and http://clubdetenisalbatera.es/user/ontikznsig/ buy ED pills online discreetly UK
<a href=http://www.hk-pub.com/forum/dedo_siteindex.php?q=buy ED pills online discreetly UK cialis cheap price UK delivery and confidential delivery cialis UK weekend pill UK online pharmacy
ivermectin without prescription UK: ivermectin cheap price online UK – MediTrust
MediTrust ivermectin cheap price online UK MediTrust UK
generic sildenafil UK pharmacy https://intimacareuk.com/# cialis cheap price UK delivery
https://bluepilluk.com/# fast delivery viagra UK online
order medicines online discreetly online pharmacy UK no prescription or cheap UK online pharmacy UK pharmacy home delivery
https://www.systemtool.co.jp/_m/index.php?a=free_page/goto_mobile&referer=https://mediquickuk.com MediQuick UK and https://gicleeads.com/user/ndwuueohpa/?um_action=edit MediQuickUK
confidential delivery pharmacy UK MediQuickUK or MediQuickUK trusted UK digital pharmacy
IntimaCare UK buy ED pills online discreetly UK cialis online UK no prescription
IntimaCareUK: buy ED pills online discreetly UK – IntimaCare
ivermectin without prescription UK MediTrust UK MediTrust UK
cheap UK online pharmacy MediQuick UK or UK pharmacy home delivery MediQuick UK
http://www.bssystems.org/url?q=https://mediquickuk.com trusted UK digital pharmacy or https://sierraseo.com/user/gopgpsmujd/?um_action=edit trusted UK digital pharmacy
generic and branded medications UK MediQuick or generic and branded medications UK cheap UK online pharmacy
generic and branded medications UK online pharmacy UK no prescription pharmacy online fast delivery UK
http://mediquickuk.com/# UK pharmacy home delivery
sildenafil tablets online order UK: fast delivery viagra UK online – viagra online UK no prescription
buy ED pills online discreetly UK confidential delivery cialis UK IntimaCare
generic sildenafil UK pharmacy: BluePill UK – order viagra online safely UK
http://truenorthpharm.com/# canadianpharmacymeds com
https://curabharatusa.com/# CuraBharat USA
SaludFrontera: SaludFrontera – mexican pharmacy online
TrueNorth Pharm buying drugs from canada TrueNorth Pharm
SaludFrontera: mexican online pharmacy – SaludFrontera
https://saludfrontera.shop/# SaludFrontera
pharma mexicana: medication in mexico – order meds from mexico
https://saludfrontera.shop/# mexico pharmacy
CuraBharat USA buy oxycontin CuraBharat USA
TrueNorth Pharm: TrueNorth Pharm – TrueNorth Pharm
CuraBharat USA: pharmacy india – CuraBharat USA
SaludFrontera: mexican pharmacies – pharmacia mexico
http://curabharatusa.com/# CuraBharat USA
trustworthy canadian pharmacy onlinecanadianpharmacy 24 or reputable canadian online pharmacy canadianpharmacy com
http://www.rheinische-gleisbautechnik.de/url?q=https://truenorthpharm.com canada drugs reviews and https://www.trendyxxx.com/user/vehzpgbolg/videos safe canadian pharmacy
canadian pharmacy price checker best canadian online pharmacy and northwest canadian pharmacy canadian pharmacy reviews
online pharmacy in mexico SaludFrontera SaludFrontera
TrueNorth Pharm: TrueNorth Pharm – certified canadian international pharmacy
medicine from mexico mexican drugstore and mexico drug store mexican pharmacy online
http://www.taskmanagementsoft.com/bitrix/redirect.php?event1=tm_sol&event2=task-tour-flash&goto=https://saludfrontera.com mexican medicine or https://brueckrachdorf.de/user/pnayqfazzn/ purple pharmacy
purple pharmacy online order meds from mexico or farmacias mexicanas online pharmacy mexico
http://curabharatusa.com/# online meds
mexico prescription online: SaludFrontera – SaludFrontera
https://curabharatusa.com/# ordering medicines online
order medication from mexico pharmacy in mexico mexico pharmacy
canadian pharmacy online reviews reliable canadian online pharmacy and canada ed drugs best canadian online pharmacy
https://www.google.com.mt/url?q=https://truenorthpharm.com my canadian pharmacy review or https://www.snusport.com/user/pmhbzvcadv/?um_action=edit real canadian pharmacy
canada drug pharmacy cross border pharmacy canada and legal canadian pharmacy online canada drugs
online medicine delivery in india: online medicine india – CuraBharat USA
wett tipps erfahrungen
Also visit my web-site … beste sportwetten app österreich –
vspmscop.edu.in
–
http://saludfrontera.com/# SaludFrontera
SaludFrontera mexico pharmacy SaludFrontera
safe reliable canadian pharmacy canadian world pharmacy and my canadian pharmacy canadian pharmacy 24h com
http://x89mn.peps.jp/jump.php?url=http://pharmaexpressfrance.com onlinecanadianpharmacy and https://dongzong.my/forum/home.php?mod=space&uid=40720 canadian pharmacy prices
canadapharmacyonline legit trustworthy canadian pharmacy and canadian pharmacy king reviews escrow pharmacy canada
pharmacy mexico online mexico online farmacia and mexico pet pharmacy mexico online pharmacy
http://www.mitte-recht.de/url?q=https://saludfrontera.com mexican medicine store or https://act2day.eu/profile/aocwngosic/ farmacia mexicana en chicago
farmacia mexicana en chicago purple pharmacy online or mexico pharmacy list mexican mail order pharmacy
https://truenorthpharm.com/# TrueNorth Pharm
TrueNorth Pharm: TrueNorth Pharm – adderall canadian pharmacy
https://saludfrontera.com/# best pharmacy in mexico
buy medication from india buy medicines online or online pharmacy sites order medicine online india
http://www.city-escort.net/url/?url=http://intimapharmafrance.com indian medicine in usa or https://istinastroitelstva.xyz/user/vbzdbzjkjl/ medicine from india
medicine online shopping online medicine order and indian pharma network vicodin in india
farmacia mexicana online mexico medication phentermine in mexico pharmacy
canadian 24 hour pharmacy trustworthy canadian pharmacy and canadian pharmacy ltd canadian neighbor pharmacy
http://www.masekaihatsu.com/feed2js/feed2js.php?src=https://truenorthpharm.com canada pharmacy and http://www.blackinseattle.com/profile/wwkzfdioxo/ pharmacy canadian superstore
canada rx pharmacy legitimate canadian mail order pharmacy and my canadian pharmacy review canadian pharmacy near me
CuraBharat USA: medicines online india – how to get indian medicine in usa
http://gesunddirekt24.com/# online apotheke deutschland
online apotheke versandkostenfrei: Manner Kraft – europa apotheke
Viagra kaufen gГјnstig Deutschland kamagra erfahrungen deutschland generisches sildenafil alternative
online apotheke versandkostenfrei: viagra ohne rezept deutschland – online apotheke preisvergleich
https://blaukraftde.com/# medikamente rezeptfrei
europa apotheke: Gesund Direkt 24 – beste online-apotheke ohne rezept
http://mannerkraft.com/# online apotheke versandkostenfrei
cialis generika ohne rezept: rezeptfreie medikamente für erektionsstörungen – günstige online apotheke
online apotheke preisvergleich: sildenafil tabletten online bestellen – online apotheke rezept
medikamente rezeptfrei п»їshop apotheke gutschein or medikamente rezeptfrei online apotheke rezept
https://cse.google.co.bw/url?sa=t&url=https://blaukraftde.com medikament ohne rezept notfall or https://www.yourporntube.com/user/ahpuginrdl/videos online apotheke versandkostenfrei
europa apotheke apotheke online and europa apotheke europa apotheke
https://intimgesund.com/# kamagra erfahrungen deutschland
Intim Gesund: potenzmittel diskret bestellen – Viagra rezeptfreie bestellen
online apotheke beste online-apotheke ohne rezept and eu apotheke ohne rezept medikament ohne rezept notfall
http://mrg-sbyt.ru/bitrix/rk.php?goto=https://mannerkraft.shop:: eu apotheke ohne rezept and http://iapple.minfish.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=5631437 online apotheke rezept
online apotheke preisvergleich gГјnstigste online apotheke or eu apotheke ohne rezept europa apotheke
wettstrategie gerade ungerade
Have a look at my web blog – wettprognose – Corey,
kamagra erfahrungen deutschland: kamagra erfahrungen deutschland – Viagra online kaufen legal
Viagra rezeptfreie bestellen Viagra Generika kaufen Schweiz or Viagra kaufen gГјnstig Deutschland Sildenafil kaufen online
https://images.google.com.vn/url?sa=t&url=https://intimgesund.com Viagra online bestellen Schweiz Erfahrungen or https://4k-porn-video.com/user/eqezokixzb/ Viagra kaufen gГјnstig Deutschland
Viagra 100 mg ohne Rezept Viagra diskret bestellen or Viagra kaufen ohne Rezept Schweiz Sildenafil 100mg online bestellen
eu apotheke ohne rezept diskrete lieferung von potenzmitteln medikament ohne rezept notfall
gГјnstige online apotheke п»їshop apotheke gutschein or apotheke online apotheke online
https://cse.google.co.th/url?q=https://blaukraftde.com online apotheke deutschland or https://kamayegaindia.com/user/hfnntljuxy/?um_action=edit europa apotheke
online apotheke online apotheke preisvergleich and online apotheke versandkostenfrei apotheke online
п»їshop apotheke gutschein eu apotheke ohne rezept and internet apotheke online apotheke deutschland
http://maps.google.com.ua/url?q=https://mannerkraft.shop internet apotheke and https://armandohart.com/user/cikuscfzab/?um_action=edit beste online-apotheke ohne rezept
internet apotheke beste online-apotheke ohne rezept or medikament ohne rezept notfall medikamente rezeptfrei
https://blaukraftde.shop/# eu apotheke ohne rezept
http://intimgesund.com/# kamagra kaufen ohne rezept online
Эта информационная статья охватывает широкий спектр актуальных тем и вопросов. Мы стремимся осветить ключевые факты и события с ясностью и простотой, чтобы каждый читатель мог извлечь из нее полезные знания и полезные инсайты.
Разобраться лучше – https://quick-vyvod-iz-zapoya-1.ru/
kamagra kaufen ohne rezept online: kamagra kaufen ohne rezept online – Viagra Generika online kaufen ohne Rezept
online apotheke deutschland online apotheke deutschland and online apotheke preisvergleich online apotheke preisvergleich
http://maps.google.vu/url?q=https://potenzapothekede.shop online apotheke versandkostenfrei or https://www.snusport.com/user/stcurnyulc/?um_action=edit online apotheke versandkostenfrei
online apotheke preisvergleich п»їshop apotheke gutschein or internet apotheke gГјnstige online apotheke
https://intimgesund.shop/# kamagra kaufen ohne rezept online
ohne rezept apotheke online apotheke rezept and beste online-apotheke ohne rezept internet apotheke
https://images.google.st/url?sa=t&url=https://blaukraftde.com п»їshop apotheke gutschein and https://www.packadvisory.com/user/ngxxhdqkiw/ internet apotheke
eu apotheke ohne rezept medikamente rezeptfrei and apotheke online online apotheke preisvergleich
eu apotheke ohne rezept: viagra ohne rezept deutschland – internet apotheke
https://gesunddirekt24.com/# apotheke online
medikament ohne rezept notfall cialis generika ohne rezept tadalafil 20mg preisvergleich
Viagra kaufen ohne Rezept legal Viagra rezeptfreie Länder or Viagra kaufen ohne Rezept Schweiz Viagra Preis Schwarzmarkt
http://www.diversitybusiness.com/specialfunctions/newsitereferences.asp?nwsiteurl=https://intimgesund.com/ Viagra Tabletten and https://cv.devat.net/user/kklstvbghp/?um_action=edit Viagra kaufen gГјnstig Deutschland
Viagra Generika kaufen Deutschland Generika Potenzmittel rezeptfrei online kaufen and Viagra rezeptfreie Länder Viagra diskret bestellen
kamagra erfahrungen deutschland: kamagra kaufen ohne rezept online – Sildenafil Generika 100mg
http://gesunddirekt24.com/# ohne rezept apotheke
http://vitaledgepharma.com/# VitalEdge Pharma
Clear Meds Hub Clear Meds Hub Clear Meds Hub
: ClearMedsHub – Clear Meds Hub
https://vitaledgepharma.com/# ed medication online
http://evertrustmeds.com/# Ever Trust Meds
ClearMedsHub Clear Meds Hub
EverTrustMeds: Ever Trust Meds – EverTrustMeds
ClearMedsHub: ClearMedsHub – ClearMedsHub
online ed prescription erectile dysfunction medicine online or online ed medicine online ed medications
http://sanopedia.es/api.php?action=https://vitaledgepharma.shop buy ed medication online and https://bbs.hy2001.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=574130 online ed prescription
where can i buy erectile dysfunction pills buy ed pills online or online erectile dysfunction pills edmeds
or
https://www.google.by/url?q=https://clearmedshub.shop and https://www.liveviolet.net/user/vcmvhxvfge/videos
and
http://evertrustmeds.com/# Generic Cialis without a doctor prescription
https://clearmedshub.com/#
VitalEdgePharma VitalEdge Pharma erectile dysfunction medications online
VitalEdge Pharma: VitalEdge Pharma – VitalEdge Pharma
https://evertrustmeds.shop/# EverTrustMeds
Buy Cialis online Tadalafil price and Buy Cialis online Cialis over the counter
https://www.asm.com/Pages/Press-releases/ASMI-ANNOUNCES-AVAILABILITY-AND-TIMING-OF-THE-FIRST-QUARTER-2018-CONFERENCE-CALL-AND-WEBCAST.aspx?overview=http://pharmaexpressfrance.com/ Cialis 20mg price in USA or https://cv.devat.net/user/dbbaomaoga/?um_action=edit Buy Cialis online
cialis for sale Tadalafil Tablet or Buy Tadalafil 20mg Generic Cialis without a doctor prescription
erectile dysfunction pills online ed treatments online or ed medications cost best online ed medication
http://dsl.sk/article_forum.php?action=reply&forum=255549&entry_id=147673&url=http://bluepharmafrance.com ed online pharmacy or https://mantiseye.com/community/eutjcypbvz online ed prescription
get ed meds today ed pills or cheapest erectile dysfunction pills ed meds online
http://vitaledgepharma.com/# VitalEdgePharma
VitalEdge Pharma: erectile dysfunction drugs online – VitalEdge Pharma
https://vitaledgepharma.shop/# best ed pills online
Cialis over the counter buy cialis pill and buy cialis pill Generic Tadalafil 20mg price
https://www.google.bj/url?sa=t&url=https://evertrustmeds.shop Generic Tadalafil 20mg price or https://www.news-adhoc.com/author/ufaremlghi/ Tadalafil Tablet
Generic Cialis without a doctor prescription Buy Tadalafil 10mg and Cheap Cialis Generic Tadalafil 20mg price
VitalEdgePharma VitalEdgePharma cheapest erectile dysfunction pills
Ever Trust Meds: Generic Cialis price – Generic Cialis without a doctor prescription
http://clearmedshub.com/#
and
http://www.google.fm/url?q=https://clearmedshub.shop and http://georgiantheatre.ge/user/qlmwisxcop/
and
VitalEdge Pharma [url=http://vitaledgepharma.com/#]VitalEdge Pharma[/url] VitalEdge Pharma
https://clearmedshub.shop/# Clear Meds Hub
Clear Meds Hub: ClearMedsHub –
https://clearmedshub.shop/# ClearMedsHub
online ed treatments ed drugs online or erection pills online ed med online
https://images.google.cf/url?q=https://vitaledgepharma.shop buy ed medication online or http://iapple.minfish.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=5642550 ed online prescription
ed pills cheap affordable ed medication or ed online pharmacy ed online treatment
Ever Trust Meds: Buy Tadalafil 5mg – EverTrustMeds
EverTrustMeds [url=https://evertrustmeds.com/#]EverTrustMeds[/url] Tadalafil Tablet
best ed pills online buying erectile dysfunction pills online and online erectile dysfunction medication buy ed pills
https://www.google.cm/url?q=https://vitaledgepharma.com п»їed pills online or http://lostfilmhd.com/user/gjuginypeg/ cheapest ed treatment
erectile dysfunction medication online erectile dysfunction medication online or erectile dysfunction pills for sale best online ed medication
https://evertrustmeds.shop/# Ever Trust Meds
india pharmacy: buy online medicine – Indian pharmacy ship to USA
reliable canadian pharmacy Canadian pharmacy online canadian pharmacy antibiotics
http://curamedsindia.com/# CuraMedsIndia
Mexican pharmacy price list: Mexican pharmacy price list – mexico pharmacy
indian pharmacy: Best online Indian pharmacy – indian pharmacy
Indian pharmacy international shipping Indian pharmacy international shipping Indian pharmacy online
https://maplecarerx.shop/# Canadian pharmacy online
Mexican pharmacy ship to USA: Best Mexican pharmacy online – Mexican pharmacy price list
Indian pharmacy international shipping: Indian pharmacy to USA – india pharmacy
ed drugs online from canada canadian pharmacy price checker and canadianpharmacymeds canadian mail order pharmacy
http://mail.51uc.com/cgi-bin/safe.php?s=21&t=https://maplecarerx.com canadapharmacyonline com and http://www.blackinseattle.com/profile/cyeccybdmo/ trustworthy canadian pharmacy
canadian pharmacy online ship to usa canada pharmacy reviews or canadian drugs ed meds online canada
Indian pharmacy to USA: Best Indian pharmacy – CuraMedsIndia
Indian pharmacy online: india pharmacy – CuraMedsIndia
Pharmacies in Canada that ship to the US Pharmacies in Canada that ship to the US Pharmacies in Canada that ship to the US
mexican pharmacy: Online Mexican pharmacy – mexican pharmacy
online pharmacy india online medicine order or online medicine buy norco online
https://clients1.google.com.nf/url?q=https://curamedsindia.com online india pharmacy or http://www.psicologiasaludable.es/user/bpyceacfxe/ shop medicine online
how to get indian medicine in usa india pharmacy online and medicine online delivery now buy medicine online india
mexican meds mexican pharmacy las vegas or mexican pharmacies that ship to the united states purple pharmacy online ordering
https://www.the-mainboard.com/proxy.php?link=https://bajamedsdirect.com:: mexicanrxpharm or http://njmoli.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=2448 los algodones pharmacy online
online pharmacy in mexico buying prescriptions in mexico and buying prescription drugs in mexico mexico pharmacy online
Best online Indian pharmacy Indian pharmacy international shipping Best online Indian pharmacy
Canadian pharmacy prices: the canadian drugstore – Canadian pharmacy prices
https://curamedsindia.com/# Indian pharmacy online
online apotheke rezept NordicApotek apotek utan receptkrav
PharmaRapide: pharmacie en ligne France fiable – pharmacie en ligne avec ordonnance
beste online-apotheke ohne rezept: Kamagra online bestellen – apotheke online
online apotheke gГјnstig: Kamagra kaufen ohne Rezept – online apotheke gГјnstig
online apotheke preisvergleich Medikamente ohne Rezept bestellen apotheke online
online apotheke: Kamagra online bestellen – online apotheke versandkostenfrei
Pharmacie en ligne livraison Europe: acheter medicaments en ligne pas cher – pharmacie en ligne france pas cher
online apotheke versandkostenfrei: Kamagra online bestellen – online apotheke versandkostenfrei
bestalla medicin utan recept Nordic Apotek and halsolosningar online Sverige diskret leverans av mediciner
https://clients1.google.com.bd/url?q=https://nordicapotek.shop generiska lakemedel online and https://hiresine.com/user/lccoopiraz/?um_action=edit billiga lakemedel pa natet
halsolosningar online Sverige Nordic Apotek and diskret leverans av mediciner tryggt svenskt apotek pa natet
onlineapotek Sverige: generiska lakemedel online – online apotheke versandkostenfrei
online apotheke deutschland onlineapotek Sverige generiska lakemedel online
shop apotheke gutschein: Medikamente ohne Rezept bestellen – online apotheke rezept
https://farmaciafacileit.shop/# farmacia online Italia affidabile
online apotheek nederland: discrete levering van medicijnen – online apotheek
kundevurderinger av nettapotek: apotek pa nett billigst – nettapotek Norge trygt og palitelig
farmacia espanola en linea economica farmacias online seguras pedir farmacos por Internet
farmacia española en línea económica: farmacia española en línea económica – medicamentos sin receta a domicilio
top farmacia online top farmacia online or farmaci senza ricetta elenco Farmacie online sicure
http://www.google.mg/url?q=http://pharmaexpressfrance.com comprare farmaci online all’estero and https://www.news-adhoc.com/author/havwfmmkwp/ farmacia online
farmacie online autorizzate elenco comprare farmaci online con ricetta or migliori farmacie online 2024 migliori farmacie online 2024
farmacias online seguras pedir farmacos por Internet farmacia espanola en linea economica
farmacia barata farmacias online seguras en espaГ±a or farmacia online barata y fiable farmacias online baratas
https://images.google.gl/url?sa=t&url=https://saludexpresses.shop farmacias direct or https://brueckrachdorf.de/user/ftrgbipsjj/ farmacia online barcelona
farmacia barata farmacia online barcelona or farmacia online barcelona farmacia online madrid
ordinare farmaci senza ricetta: medicinali generici a basso costo – farmacia online Italia affidabile
apotek pa nett billigst reseptfrie medisiner pa nett nettapotek Norge trygt og palitelig
goedkope medicijnen online HollandApotheek or veilig online apotheek NL discrete levering van medicijnen
https://maps.google.com.pr/url?q=https://hollandapotheeknl.com veilig online apotheek NL and https://www.bsnconnect.co.uk/profile/xhwwyvgiuw/ goedkope medicijnen online
geneesmiddelen zonder recept bestellen online apotheek nederland and Holland Apotheek geneesmiddelen zonder recept bestellen
opinioni su farmacia online italiana: spedizione rapida farmaci Italia – spedizione rapida farmaci Italia
HollandApotheek online apotheek Nederland betrouwbaar apotheek zonder receptplicht
farmacie online autorizzate elenco farmacia online senza ricetta and п»їFarmacia online migliore comprare farmaci online con ricetta
https://toolbarqueries.google.co.nz/url?q=http://pharmaexpressfrance.com acquisto farmaci con ricetta or http://jonnywalker.net/user/nunwtwcbke/ Farmacie online sicure
Farmacie on line spedizione gratuita comprare farmaci online all’estero or comprare farmaci online all’estero farmacie online autorizzate elenco
farmacia en casa online descuento farmacia online barata or farmacias online seguras en espaГ±a farmacia online envГo gratis
https://maps.google.jo/url?q=https://saludexpresses.shop farmacia online barata and https://vintage-car.eu/user/pxozfjktfk/ farmacias online seguras en espaГ±a
farmacias online seguras farmacia barata and farmacia en casa online descuento farmacia en casa online descuento
apotheek zonder receptplicht: generieke geneesmiddelen Nederland – generieke geneesmiddelen Nederland
FarmaciaFacile: ordinare farmaci senza ricetta – ordinare farmaci senza ricetta
bestille medisiner online diskret kundevurderinger av nettapotek apotek uten resept med levering hjem
FarmaciaFacile: medicinali generici a basso costo – farmacie online affidabili
comprare farmaci online all’estero comprare farmaci online con ricetta and Farmacia online piГ№ conveniente comprare farmaci online all’estero
https://www.diabetesforo.com/home/leaving?target=https://farmaciafacileit.com farmacie online affidabili and https://www.stqld.com.au/user/noiyfvinxz/ farmacia online
farmacia online farmacia online or top farmacia online comprare farmaci online all’estero
apotek på nett billigst billige generiske legemidler Norge or billige generiske legemidler Norge apotek på nett billigst
http://andreasgraef.de/url?q=https://nordapotekno.shop:: apotek på nett med gode priser or http://www.9kuan9.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=4043020 reseptfrie medisiner på nett
billige generiske legemidler Norge nettapotek Norge trygt og pålitelig and kundevurderinger av nettapotek bestille medisiner online diskret
bonus Plinko slot Italia: gioco Plinko mobile Italia – giocare Plinko con soldi veri
how to win Chicken Road slot game: how to win Chicken Road slot game – how to win Chicken Road slot game
https://plinkoslotitalia.shop/# gioco Plinko mobile Italia
slot a tema fattoria Italia casino online italiani con Chicken Road casino online italiani con Chicken Road
bonus Plinko slot Italia Plinko RTP e strategie or bonus Plinko slot Italia Plinko casino online Italia
https://www.chuchle.cz/?p=sendPageLink&value=https://hollandapotheeknl.com:: Plinko demo gratis or https://501tracking.com/user/trbhmeqrmv/?um_action=edit Plinko casino online Italia
migliori casino italiani con Plinko Plinko casino online Italia and migliori casino italiani con Plinko bonus Plinko slot Italia
Chicken Road slot game India bonus spins Chicken Road casino India and play Chicken Road casino online Chicken Road slot game India
https://telemail.jp/_pcsite/?des=015660&gsn=0156603&url=pharmaexpressfrance.com mobile Chicken Road slot app and https://gikar.it/user/coiacxicar/ free demo Chicken Road game
real money Chicken Road slots play Chicken Road casino online and how to win Chicken Road slot game Chicken Road slot game India
migliori casinò italiani con Plinko: Plinko RTP e strategie – scommesse Plinko online
giocare Plinko con soldi veri bonus Plinko slot Italia gioco Plinko mobile Italia
gioco Plinko mobile Italia: Plinko RTP e strategie – scommesse Plinko online
real money slot Chicken Road UK play Chicken Road casino online UK casino promotions Chicken Road game
Chicken Road slot UK licensed UK casino sites Chicken Road or real money slot Chicken Road UK British online casinos with Chicken Road
http://www.c9wiki.com/link.php?url=http://bluepharmafrance.com/ British online casinos with Chicken Road and http://clubdetenisalbatera.es/user/mjjhimagim/ real money slot Chicken Road UK
Chicken Road slot UK licensed UK casino sites Chicken Road and real money slot Chicken Road UK real money slot Chicken Road UK
Plinko gioco Plinko mobile Italia gioco Plinko mobile Italia
Chicken Road slot game India mobile Chicken Road slot app and secure online gambling India mobile Chicken Road slot app
http://www.boosterblog.net/vote-146-144.html?adresse=pharmaexpressfrance.com&popup=1 real money Chicken Road slots and http://georgiantheatre.ge/user/xwwxjupuht/ secure online gambling India
real money Chicken Road slots free demo Chicken Road game or real money Chicken Road slots secure online gambling India
slot a tema fattoria Italia: casino online italiani con Chicken Road – giocare Chicken Road gratis o con soldi veri
https://tadalmedspharmacy.com/# Generic tadalafil 20mg price
uptown pokies australia review, real online money casino redeem codes;
Mari, canada and fastest paying online casino usa, or tips for pokies australia
Online Mexican pharmacy: Mexican pharmacy price list – mexican border pharmacies shipping to usa
gabapentin mexican pharmacy Legit online Mexican pharmacy Legit online Mexican pharmacy
Legit online Mexican pharmacy: Best online Mexican pharmacy – Mexican pharmacy price list
http://medicexpressmx.com/# Legit online Mexican pharmacy
sildenafil: Sildenafil 100mg – Buy sildenafil online usa
https://medicexpressmx.shop/# Online Mexican pharmacy
Buy Tadalafil online Buy Tadalafil online Generic Cialis without a doctor prescription
Buy Tadalafil online: Buy Tadalafil online – Buy Tadalafil online
https://medicexpressmx.com/# Online Mexican pharmacy
Generic tadalafil 20mg price Buy Tadalafil 20mg Generic tadalafil 20mg price
mexican pharmacy: mexican pharmacy – mexican pharmacy
https://truevitalmeds.com/# Sildenafil 100mg
best sildenafil pills sildenafil citrate online pharmacy and sildenafil generic 20mg chewable sildenafil
https://images.google.sk/url?q=http://pharmaexpressfrance.com sildenafil soft tabs or https://www.freshdew.tv/user/vmpmshasqe/?um_action=edit canada rx sildenafil
generic sildenafil 100mg price sildenafil 96743 and sildenafil nz price best sildenafil in india
https://truevitalmeds.com/# Sildenafil 100mg
https://truevitalmeds.com/# Sildenafil 100mg
tadalafil – generic tadalafil tablets in india tadalafil
buy tadalafil 20mg uk: tadalafil – generic – tadalafil cost india
mexican pharmaceuticals online pharmacies in mexico that ship to usa and mexican online pharmacies prescription drugs medicine in mexico pharmacies
http://www.gaxclan.de/url?q=https://medicexpressmx.shop best online pharmacies in mexico or https://alphafocusir.com/user/lgzcfnhsca/?um_action=edit best online pharmacies in mexico
mexico pharmacies prescription drugs medication from mexico pharmacy and buying prescription drugs in mexico online pharmacies in mexico that ship to usa
http://truevitalmeds.com/# Buy sildenafil
Buy Tadalafil 20mg: tadalafil tablet buy online – best tadalafil tablets in india
cheap sildenafil citrate uk sildenafil gel uk or sildenafil 150 mg online buy online sildenafil
https://www.google.lu/url?sa=t&url=https://truevitalmeds.shop generic sildenafil 20 mg tablet or http://asresin.cn/home.php?mod=space&uid=111635 sildenafil 75 mg
sildenafil canada price sildenafil citrate buy and sildenafil generic canada sildenafil order
https://medicexpressmx.com/# Mexican pharmacy price list
https://tadalmedspharmacy.com/# Generic tadalafil 20mg price
cheap sildenafil citrate tablets sildenafil best price or sildenafil for sale online sildenafil online
https://cse.google.com.sv/url?sa=t&url=https://truevitalmeds.shop buy sildenafil with paypal or http://www.88moli.top/home.php?mod=space&uid=22655 best price for generic sildenafil
sildenafil uk paypal sildenafil 50 mg tablet buy online and buy sildenafil online nz cheap sildenafil
where to buy tadalafil 20mg tadalafil compare prices or tadalafil 20mg pills 20 mg tadalafil cost
http://images.google.hr/url?q=http://bluepharmafrance.com canada tadalafil generic and https://act2day.eu/profile/blmivdqtzz/ online pharmacy tadalafil 20mg
tadalafil 20mg online canada buy tadalafil online paypal and tadalafil 5mg uk buy generic tadalafil 20mg
https://truevitalmeds.shop/# Sildenafil 100mg price
http://truevitalmeds.com/# sildenafil
buy zithromax online: buy zithromax – cheap zithromax
Amoxicillin 500mg buy online AmoxDirect USA Buy Amoxicillin for tooth infection
ZithroMeds Online: buy zithromax – zithromax antibiotic without prescription
zithromax online usa no prescription: zithromax z- pak buy online – generic zithromax
https://zithromedsonline.com/# zithromax z- pak buy online
http://amoxdirectusa.com/# buy amoxicillin
Purchase amoxicillin online: Buy Amoxicillin for tooth infection – buy amoxil
can you get cheap clomid can i purchase generic clomid tablets or get cheap clomid without a prescription cheap clomid now
http://fotos24.org/url?q=https://clomicareusa.com generic clomid without insurance or http://bbs.dubu.cn/home.php?mod=space&uid=424693 can i get generic clomid price
buy clomid no prescription get clomid without rx or where can i buy generic clomid now how can i get generic clomid without dr prescription
http://amoxdirectusa.com/# Amoxicillin 500mg buy online
ClomiCare USA: buy clomid – Buy Clomid online
Buy Clomid online buy clomid Generic Clomid
http://clomicareusa.com/# Buy Clomid online
amoxicillin 875 mg tablet amoxicillin without prescription and buying amoxicillin online amoxicillin 500 tablet
http://toolbarqueries.google.cz/url?q=https://amoxdirectusa.com over the counter amoxicillin or https://www.packadvisory.com/user/xgfxxlkqtg/ amoxicillin 500 mg without prescription
where can i buy amoxicillin without prec buying amoxicillin online or buy amoxicillin over the counter uk amoxicillin 500 mg online
https://zithromedsonline.shop/# zithromax online usa
buy clomid: Clomid for sale – Clomid price
https://zithromedsonline.shop/# zithromax pill
deposit 10 30 free spins (Tanesha) slots united
states, bet365 free casino usa and online gambling poker australia, or best casino
sign up offers uk
zithromax without prescription buy azithromycin zithromax and generic zithromax 500mg india how to get zithromax online
https://sambastore.com/en/mandeparaumamigo.php?url=http://bluepharmafrance.com buy zithromax or http://www.88moli.top/home.php?mod=space&uid=444 cheap zithromax pills
zithromax 1000 mg online zithromax z-pak price without insurance and zithromax capsules cost of generic zithromax
buy amoxil: AmoxDirect USA – Purchase amoxicillin online
Buy Amoxicillin for tooth infection AmoxDirect USA Purchase amoxicillin online
Amoxicillin 500mg buy online: generic amoxicillin cost – buy amoxicillin
Propecia prescription: Best place to buy propecia – RegrowRx Online
low-cost ivermectin for Americans: low-cost ivermectin for Americans – ivermectin 0.5
tadalafil united states: EverLastRx – EverLastRx
https://predniwellonline.shop/# online pharmacy Prednisone fast delivery
gabapentin capsules for nerve pain neuropathic pain relief treatment online NeuroCare Direct
Stromectol ivermectin tablets for humans USA ivermectin and coronavirus generic ivermectin online pharmacy
Neurontin online without prescription USA affordable Neurontin medication USA affordable Neurontin medication USA
order Stromectol discreet shipping USA ivermectin for snake mites low-cost ivermectin for Americans
ivermectin 80 mg: generic ivermectin online pharmacy – trusted Stromectol source online
tadalafil pills for sale tadalafil pills for sale or tadalafil 40 mg online india buy generic tadalafil 20mg
https://images.google.com.mx/url?sa=t&url=https://everlastrx.com tadalafil capsules 21 mg and https://raygunmvp.com/user/wfahjjkjay-wfahjjkjay/?um_action=edit where to buy tadalafil 20mg
cheap tadalafil 5mg best online tadalafil or tadalafil over the counter uk tadalafil tablets 20 mg online
https://medivermonline.com/# order Stromectol discreet shipping USA
buy tadalafil cialis: tadalafil tablets 10 mg online – discreet delivery for ED medication
online order prednisone buy prednisone online fast shipping and prednisone cost canada prednisone for sale without a prescription
http://www.google.com.nf/url?q=https://predniwellonline.com prednisone capsules and https://cv.devat.net/user/zcabyinlne/?um_action=edit prednisone 5 50mg tablet price
prednisone brand name in usa how to purchase prednisone online and 50 mg prednisone from canada order prednisone on line
can gabapentin cause anger can you get high on gabapentin 600 mg or gabapentin for tooth extraction pain gabapentin class of drugs
https://maps.google.com.pg/url?sa=t&url=https://neurocaredirect.com side effects of gabapentin medication or https://gikar.it/user/blvkvdmeky/ gabapentin und fibromyalgie
gabapentin 300 mg capsule side effects what class is gabapentin in or gabapentin 100mg high gabapentin capsules 300 mg
prednisone without prescription medication 6 prednisone and prednisone canada prescription prednisone uk price
https://www.google.pn/url?q=https://predniwellonline.com prednisone 20 mg prices and http://lostfilmhd.com/user/orqsbldtec/ cheap generic prednisone
prednisone generic cost prednisone 250 mg or prednisone uk prednisone buy cheap
Prednisone tablets online USA: Prednisone without prescription USA – cost of prednisone tablets
Prednisone without prescription USA Prednisone without prescription USA how to get Prednisone legally online
wie funktioniert kombiwette
Here is my website :: wettbüro ingolstadt [Ricky]
online pharmacy Prednisone fast delivery PredniWell Online prednisone generic brand name
http://britpharmonline.com/# viagra
buy prednisolone best UK online chemist for Prednisolone best UK online chemist for Prednisolone
private online pharmacy UK: order medication online legally in the UK – UK online pharmacy without prescription
UK online pharmacy without prescription private online pharmacy UK order medication online legally in the UK
buy sildenafil tablets UK BritPharm Online or Viagra online UK viagra uk
http://www.kukuts.info/engine/redirect.php?url=http://pharmaexpressfrance.com order ED pills online UK or https://www.sanmateocountyguide.com/profile/ngromhzdyq/ Viagra online UK
British online pharmacy Viagra buy viagra online and buy sildenafil tablets UK Viagra online UK
https://amoxicareonline.com/# Amoxicillin online UK
Prednisolone tablets UK online: order steroid medication safely online – UK chemist Prednisolone delivery
buy prednisolone buy prednisolone UK chemist Prednisolone delivery
https://medreliefuk.com/# UK chemist Prednisolone delivery
buy penicillin alternative online: cheap amoxicillin – generic Amoxicillin pharmacy UK
https://amoxicareonline.shop/# Amoxicillin online UK
buy sildenafil tablets UK: viagra uk – viagra uk
UK chemist Prednisolone delivery Prednisolone tablets UK online or buy prednisolone buy corticosteroids without prescription UK
http://sotofone.ru/bitrix/rk.php?goto=http://pharmalibrefrance.com/ Prednisolone tablets UK online or https://memekrapet.com/user/hxhgitowtk/videos buy corticosteroids without prescription UK
MedRelief UK best UK online chemist for Prednisolone and best UK online chemist for Prednisolone buy corticosteroids without prescription UK
https://britpharmonline.shop/# buy viagra online
buy penicillin alternative online: UK online antibiotic service – UK online antibiotic service
cheap amoxicillin: amoxicillin uk – UK online antibiotic service
bestes sportwetten portal
Here is my homepage … wettanbieter bester bonus; Bohemianglass.de,
http://medreliefuk.com/# UK chemist Prednisolone delivery
Viagra online UK: buy viagra – viagra uk
amoxicillin uk UK online antibiotic service or buy penicillin alternative online amoxicillin uk
https://images.google.si/url?q=https://amoxicareonline.com Amoxicillin online UK or https://forum.expert-watch.com/index.php?action=profile;u=489056 generic amoxicillin
buy penicillin alternative online amoxicillin uk or Amoxicillin online UK generic Amoxicillin pharmacy UK
British online pharmacy Viagra: order ED pills online UK – buy viagra
generic amoxicillin: UK online antibiotic service – buy amoxicillin
pharmacy online UK: order medication online legally in the UK – pharmacy online UK
https://britpharmonline.com/# buy viagra
https://amoxicareonline.com/# buy penicillin alternative online
order ED pills online UK buy viagra Viagra online UK
https://medicosur.com/# farmacia pharmacy mexico
tadalafil tablets without prescription discreet ED pills delivery in the US cialis
affordable online pharmacy for Americans: legal online pharmacies in the us – safe online medication store
http://medicosur.com/# mexico pharmacy
cialis: tadalafil tablets without prescription – buy cialis online
https://medicosur.shop/# MedicoSur
sportwetten kombi tipps tipps von profis
pferderennen wetten tipps
Also visit my webpage – wettseiten Ohne oasis (scholarlyediting.co.in)
online pharmacy: buy amoxil – buy clomid
ZenCareMeds: online pharmacy – ZenCare Meds
https://tadalifepharmacy.com/# trusted online pharmacy for ED meds
world pharmacy india pharmaceutical online and best canadian pharmacy to order from canada pharmacy coupon
https://maps.google.com.sg/url?sa=t&url=https://zencaremeds.shop generic pharmacy online and http://www.orangepi.org/orangepibbsen/home.php?mod=space&uid=6004653 pharmacy express
maple leaf pharmacy in canada best rogue online pharmacy and express scripts pharmacy reputable overseas online pharmacies
https://medicosur.shop/# mexican pharmacy
safe online medication store ZenCare Meds safe online medication store
https://medicosur.shop/# MedicoSur
MedicoSur mexico pharmacy mexican pharmacy
best mexican pharmacy online order medicine from mexico and pharmacy in mexico online order meds from mexico
http://alkrsan.net/forum/go.php?url=//bluepharmafrance.com purple pharmacy online or https://alphafocusir.com/user/aynwcmpqws/?um_action=edit farmacia mexicana online
mexico pharmacy price list medication from mexico and worldwide pharmacy mexico farmacia
https://medicosur.shop/# medication from mexico
express scripts com pharmacies medical pharmacy west or canadian pharmacy viagra 100mg no rx needed pharmacy
http://clients1.google.com.au/url?q=https://zencaremeds.com safe online pharmacy or https://www.liveviolet.net/user/qqqmpktftm/videos international pharmacy no prescription
pharmacy prices specialty pharmacy and canadian pharmacy without prescription canadadrugpharmacy com
Cialis online USA buy cialis online discreet ED pills delivery in the US
https://zencaremeds.shop/# buy propecia
canada drug pharmacy trustworthy canadian pharmacy or canadian pharmacies comparison southern pharmacy
https://maps.google.nl/url?sa=t&url=https://zencaremeds.shop canadadrugpharmacy com or https://vedicnutraceuticals-uk.com/user/rmtnpwqizh/?um_action=edit canadian online pharmacy reviews
best rated canadian pharmacy legitimate online pharmacy or cheapest pharmacy for prescription drugs reliable rx pharmacy
PilloleVerdi: acquistare Cialis online Italia – cialis generico
IntimiSanté: cialis sans ordonnance – pharmacie qui vend du cialis sans ordonnance
http://tadalafiloexpress.com/# tadalafilo
tadalafilo 5 mg precio: cialis precio – cialis generico
https://tadalafiloexpress.com/# farmacia online fiable en Espana
tadalafil 20 mg preis cialis kaufen ohne rezept cialis generika
tadalafil italiano approvato AIFA: farmacia online italiana Cialis – compresse per disfunzione erettile
cialis kaufen ohne rezept: PotenzVital – cialis kaufen
http://potenzvital.com/# Tadalafil 20mg Bestellung online
Cialis générique pas cher pharmacie qui vend du cialis sans ordonnance cialis prix
https://potenzvital.com/# Cialis Preisvergleich Deutschland
cialis precio farmacia online fiable en España cialis generico
acquistare Cialis online Italia: tadalafil senza ricetta – tadalafil italiano approvato AIFA
pharmacie en ligne sans ordonnance Pharmacie Internationale en ligne and Pharmacie sans ordonnance pharmacie en ligne france livraison belgique
http://images.google.bt/url?q=https://intimisante.com pharmacie en ligne france livraison internationale and http://lostfilmhd.com/user/enditldugm/ п»їpharmacie en ligne france
acheter mГ©dicament en ligne sans ordonnance pharmacie en ligne france pas cher or Achat mГ©dicament en ligne fiable pharmacie en ligne france livraison belgique
gГјnstigste online apotheke apotheke online or online apotheke rezept europa apotheke
https://clients1.google.com.sl/url?q=https://potenzvital.shop п»їshop apotheke gutschein or https://armandohart.com/user/rpgvzqiezk/?um_action=edit europa apotheke
online apotheke eu apotheke ohne rezept and online apotheke rezept europa apotheke
farmacia barata farmacia online barcelona and farmacias online seguras en espaГ±a farmacias online seguras
http://www.enquetes.com.br/popenquete.asp?id=73145&origem=https://tadalafiloexpress.com farmacia en casa online descuento or http://www.xgmoli.com/bbs/home.php?mod=space&uid=16857 farmacia online madrid
farmacias online seguras farmacia online envГo gratis and п»їfarmacia online espaГ±a farmacia online barata y fiable
dove comprare Cialis in Italia: cialis prezzo – pillole verdi
https://pilloleverdi.com/# cialis generico
http://potenzvital.com/# Cialis generika gunstig kaufen
Cialis generika günstig kaufen cialis generika potenzmittel cialis
pharmacie en ligne pas cher pharmacie en ligne france fiable and Achat mГ©dicament en ligne fiable pharmacie en ligne sans ordonnance
https://greencircle.vmturbo.com/external-link.jspa?url=http://pharmaexpressfrance.com pharmacie en ligne france livraison belgique or https://radiationsafe.co.za/user/cymlgwzagg/?um_action=edit acheter mГ©dicament en ligne sans ordonnance
pharmacie en ligne sans ordonnance pharmacie en ligne france pas cher or Pharmacie sans ordonnance pharmacie en ligne avec ordonnance
tadalafil sans ordonnance: pharmacie qui vend du cialis sans ordonnance – IntimiSanté
Cialis générique pas cher Intimi Santé tadalafil sans ordonnance
Viagra sans ordonnance avis: prix du Viagra générique en France – prix du Viagra générique en France
http://bluepeakmeds.com/# Sildenafil side effects and safe dosage
https://santehommefrance.com/# prix du Viagra generique en France
https://medivertraut.com/# Sildenafil ohne Rezept
https://santehommefrance.com/# sildenafil 50 mg ou 100 mg posologie
best price for viagra 100mg best price for viagra 100mg or Sildenafil 100mg price buy viagra here
http:”//www.is.kyusan-u.ac.jp/htmllint/htmllint.cgi?ViewSource=on;URL=https://bluepeakmeds.shop” sildenafil 50 mg price and https://www.liveviolet.net/user/fvyigtonoa/videos Order Viagra 50 mg online
buy viagra here Cheap Viagra 100mg or viagra canada viagra without prescription
BritMedsUk trusted British pharmacy Viagra online UK
BluePeakMeds: Viagra generic price comparison – BluePeakMeds
sichere Online-Apotheke Deutschland Sildenafil ohne Rezept Sildenafil 100 mg bestellen
Medi Uomo: Viagra generico con pagamento sicuro – Medi Uomo
https://mediuomo.com/# ordinare Viagra generico in modo sicuro
Viagra sin prescripción médica: farmacia online para hombres – pastillas de potencia masculinas
https://herengezondheid.com/# officiele Sildenafil webshop
MediUomo Viagra generico con pagamento sicuro pillole per disfunzione erettile
MannensApotek: köpa Viagra online Sverige – köpa Viagra online Sverige
https://mediuomo.com/# Viagra generico con pagamento sicuro
https://mediuomo.com/# MediUomo
Viagra generico online Italia: pillole per disfunzione erettile – comprare Sildenafil senza ricetta
http://mannensapotek.com/# mannens apotek
Viagra sin prescripción médica Viagra sin prescripción médica or Viagra sin prescripción médica farmacia online para hombres
https://www.google.com.np/url?q=https://confiafarmacia.com Viagra sin prescripción médica or http://forum.drustvogil-galad.si/index.php?action=profile;u=318974 Viagra sin prescripción médica
ConfiaFarmacia ConfiaFarmacia and Viagra sin prescripción médica farmacia con entrega rápida
farmacia confiable en España pastillas de potencia masculinas farmacia online para hombres
schweiz wettanbieter
Check out my website Sport Wett
http://confiafarmacia.com/# Confia Farmacia
Confia Farmacia: ConfiaFarmacia – pastillas de potencia masculinas
miglior sito per acquistare Sildenafil online: MediUomo – Viagra generico online Italia
Viagra generico online Italia trattamento ED online Italia and miglior sito per acquistare Sildenafil online Medi Uomo
http://home4dsi.com/chat/redirect.php?url=http://pharmalibrefrance.com/ Medi Uomo or http://bbs.51pinzhi.cn/home.php?mod=space&uid=7302702 ordinare Viagra generico in modo sicuro
miglior sito per acquistare Sildenafil online ordinare Viagra generico in modo sicuro and ordinare Viagra generico in modo sicuro trattamento ED online Italia
Viagra online kopen Nederland Viagra online kopen Nederland erectiepillen discreet bestellen
https://mediuomo.com/# farmaci per potenza maschile
apotek online utan recept: köp receptfria potensmedel online – köpa Viagra online Sverige
onlineapotek för män diskret leverans i Sverige and köp receptfria potensmedel online mannens apotek
https://www.google.fm/url?q=https://mannensapotek.com köp receptfria potensmedel online and https://virtualchemicalsales.ca/user/xvdciaebls/?um_action=edit Sildenafil-tabletter pris
Viagra utan läkarbesök köp receptfria potensmedel online and Sildenafil-tabletter pris billig Viagra Sverige
http://mannensapotek.com/# erektionspiller pa natet
online apotheek zonder recept: HerenGezondheid – online apotheek zonder recept
HerenGezondheid veilige online medicijnen Nederland ED-medicatie zonder voorschrift
Viagra sin prescripción médica: Confia Farmacia – Confia Farmacia
Viagra online kopen Nederland Sildenafil zonder recept bestellen HerenGezondheid
Viagra online kopen Nederland: betrouwbare online apotheek – ED-medicatie zonder voorschrift
erektionspiller på nätet: diskret leverans i Sverige – köp receptfria potensmedel online
https://confiafarmacia.com/# ConfiaFarmacia
Viagra genérico online España Confia Farmacia and Confia Farmacia comprar Sildenafilo sin receta
https://www.google.gp/url?sa=t&url=https://confiafarmacia.com pastillas de potencia masculinas or https://pramias.com/profile/sktuidvimi/ Confia Farmacia
pastillas de potencia masculinas Viagra sin prescripción médica or farmacia confiable en España Viagra sin prescripción médica
online apotheek zonder recept betrouwbare online apotheek or goedkope Viagra tabletten online HerenGezondheid
https://images.google.com.br/url?sa=t&url=http://intimapharmafrance.com erectiepillen discreet bestellen or http://www.garmoniya.uglich.ru/user/yyvnsyxwvb/ Sildenafil zonder recept bestellen
goedkope Viagra tabletten online ED-medicatie zonder voorschrift or Viagra online kopen Nederland Viagra online kopen Nederland
Kamagra sans ordonnance Vita Homme kamagra
http://farmaciavivait.com/# acquistare Spedra online
vitalpharma24: Potenzmittel ohne ärztliches Rezept – Potenzmittel ohne ärztliches Rezept
sportwetten bonus übersicht
Look into my blog post :: ecopayz buchmacher (Smartcodes.fr)
https://farmaciavivait.com/# FarmaciaViva
Potenzmittel ohne ärztliches Rezept: Kamagra 100mg bestellen – Erfahrungen mit Kamagra 100mg
differenza tra Spedra e Viagra: differenza tra Spedra e Viagra – Spedra
Viagra reseptfritt Norge: MannVital – Sildenafil tabletter pris
Kamagra 100mg bestellen: Erfahrungen mit Kamagra 100mg – Kamagra 100mg bestellen
Sugar Rush Fever door RubyPlay The product is meant for grown-ups and children from the age of 12 years. Lezers die meer van mijn besprekingen lezen weten dat ik een fan ben van clusterspellen. Maar dat betekent ook dat ik ze met argusogen aan een onderzoek onderwerp. Sugar Rush is wat mij betreft in zijn opzet geslaagd. Het spel biedt wel geen spectaculaire vernieuwingen, de fans van cluster fruitspellen krijgen wat ze verwachten. Een mooi 7×7 rooster met leuk ontworpen snoepjes. ©Cavex Holland BV Dit nieuwe spel met een klassiek thema beschikt over vijf rollen, je vaardigheden te verbeteren en te zien of het geluk aan jouw kant staat. En er zijn extra zwembad belastingen en paard inzetkosten voor spelers die kunnen eten in de winst, waardoor het meer sociale. FREE SPINS Echter, sugar Rush High volatility slot with tumbling reels en hij geeft alle nieuwe spelers een royale welkomstbonus om ze te beginnen.
https://bilightsolutions.com/sugar-rush-1000-review-een-zoete-kans-voor-nederlandse-spelers/
Hoewel vrijwel alle gokkasten tegenwoordig beter uitbetalen dan vroeger, zijn er altijd game providers die het uitbetalingspercentage nét wat meer opschroeven. Baas boven baas, zeg maar. Ontdek alle andere live games of bezoek onze live casino lobby’s voor het complete overzicht. Along with this, “Buzz Lightyear’s Astro Blaster” will be closed in October 2024. Sugar Rush 1000 is het nieuwste “supercharged” vervolg in de Pragmatic Play-portfolio, na Gates of Olympus 1000 en Starlight Princess 1000. Online casino slots komen in allerlei varianten, met verschillende thema’s en genres om uit te kiezen. Een opvallende trend van de afgelopen tijd zijn slots met snoep als thema. Dit heeft geresulteerd in talloze titels ontwikkeld door toonaangevende aanbieders in de branche. Denk aan populaire spellen zoals Sugar Rush en Sweet Bonanza , maar er valt nog veel meer te ontdekken. We hebben al deze snoep-geïnspireerde slots verzameld op een speciale pagina, zodat je er meer over kunt lezen en ze gratis kunt uitproberen!
Hey there! I just wanted to ask if you ever have any issues with hackers?
My last blog (wordpress) was hacked and I ended up losing many months of hard work due to no
back up. Do you have any solutions to stop hackers?
Howdy! This post couldn’t be written any better!
Reading through this post reminds me of my old room mate!
He always kept chatting about this. I will forward this
page to him. Fairly certain he will have a good read.
Many thanks for sharing!
Today, I went to the beachfront with my kids.
I found a sea shell and gave it to my 4 year old daughter and said “You can hear the ocean if you put this to your ear.” She placed the shell to her ear and screamed.
There was a hermit crab inside and it pinched her ear.
She never wants to go back! LoL I know this is totally off topic but I had to tell someone!
Great web site you have here.. It’s hard to find good quality writing like yours these days.
I honestly appreciate individuals like you! Take care!!
Hey there! I know this is kind of off topic but I was wondering if
you knew where I could find a captcha plugin for my comment form?
I’m using the same blog platform as yours and I’m having trouble finding one?
Thanks a lot!
Hi, i read your blog occasionally and i own a similar one and i was just wondering if you get
a lot of spam feedback? If so how do you protect against it,
any plugin or anything you can recommend? I get so much lately it’s driving me insane so any help is very much appreciated.
Greate post. Keep posting such kind of info on your site.
Im really impressed by it.
Hey there, You’ve performed an excellent job. I will definitely digg it and in my view recommend
to my friends. I’m confident they’ll be benefited from
this web site.
Your way of describing all in this post is actually nice, every
one be capable of effortlessly understand it, Thanks a lot.
Every weekend i used to visit this site, as i wish for enjoyment, since this this web page conations genuinely nice funny
material too.
I constantly spent my half an hour to read this web site’s articles all the time
along with a cup of coffee.
I’m really impressed with your writing skills as well as with the layout on your
blog. Is this a paid theme or did you modify it yourself?
Anyway keep up the nice quality writing, it is
rare to see a great blog like this one today.
Thanks for finally talking about > Immersive Learning at the School Level:
Transforming Education for the 21st Century – Teacher'
s Guide < Liked it!
wettbüro essen
My web-site wettanbieter ohne steuer (Willie)
Hey there! Quick question that’s totally off topic.
Do you know how to make your site mobile friendly? My website looks
weird when browsing from my iphone4. I’m trying to find a template or plugin that might be able to correct this problem.
If you have any recommendations, please share. Many
thanks!
Hey, I think your website might be having browser compatibility issues.
When I look at your blog site in Opera, it looks fine but when opening in Internet Explorer, it has some
overlapping. I just wanted to give you a quick heads up!
Other then that, amazing blog!
I was recommended this web site by means of
my cousin. I am not positive whether this publish is written through him as nobody else recognize such designated approximately my trouble.
You are incredible! Thank you!
Appreciation to my father who shared with me about this web
site, this web site is truly amazing.
Slotnya cocok buat support.
You actually make it seem so easy with your presentation but I find this topic
to be really something that I think I would never understand.
It seems too complex and extremely broad for me.
I am looking forward for your next post, I will try to get the hang of it!
https://spelmani.com/ggbet/
Hello colleagues, how is the whole thing, and what you desire to say about this article, in my view its actually remarkable in favor of me.
https://spelmani.com/ggbet/
gute wett app
Look at my webpage – tipster sportwetten (Ada)
Aphrodisias Roman ruins Travelshopbooking delivered a very organized and enjoyable tour. The guide was knowledgeable and helpful, and the itinerary was well paced. Hotels and transportation were comfortable. Overall, it was a smooth and satisfying travel experience. https://t.co/dx48wczcZj
tur kategorileri bazıları I’ve never felt so taken care of on a vacation before. The organization was flawless. https://linke.to/travelshopbooking-is
**balmorex**
balmorex is an exceptional solution for individuals who suffer from chronic joint pain and muscle aches.
Hello, I wish for to subscribe for this blog to obtain newest updates, so where can i do it please assist.
When I initially commented I clicked the “Notify me when new comments are added” checkbox and now each time a comment is added I get four emails with the same comment. Is there any way you can remove me from that service? Appreciate it!
Real Money Wins Pokies Australia The Feeling Is Indescribable
Hello just wanted to give you a brief heads up and let you know a few of the pictures aren’t loading properly. I’m not sure why but I think its a linking issue. I’ve tried it in two different internet browsers and both show the same results.
Someone essentially help to make seriously posts I would state. This is the first time I frequented your web page and thus far? I surprised with the research you made to create this particular publish amazing. Wonderful job!
Interesting blog! Is your theme custom made or did you download it from somewhere? A design like yours with a few simple adjustements would really make my blog stand out. Please let me know where you got your theme. With thanks
I am genuinely pleased to glance at this webpage posts which includes lots of helpful
data, thanks for providing such statistics.
Very shortly this web site will be famous amid all blogging and
site-building visitors, due to it’s pleasant articles
Greetings! This is my first visit to your blog! We are a group of
volunteers and starting a new initiative in a
community in the same niche. Your blog provided us useful information to work on. You have done a wonderful job!
Prіmе Secured
3603 N 222nd St, Suite 102,
Elkhorn, ΝE 68022, United Տtates
402-289-4126
Tһorough Cyber Evaluation (Go.Bubbl.Us)
Wow that was odd. I just wrote an really long comment but after I clicked submit my comment didn’t appear.
Grrrr… well I’m not writing all that over again. Anyways, just wanted to say wonderful blog!
It’s in fact very complex in this full of activity life to listen news on TV, thus I simply use the web for that purpose, and obtain the latest news.
Hi there friends, pleasant paragraph and fastidious arguments commented
at this place, I am truly enjoying by these.
Pretty! This was an extremely wonderful article. Thank you for supplying this information.
Excellent site you have got here.. It’s hard to find good quality writing like yours nowadays.
I honestly appreciate individuals like you! Take care!!
Hey very nice web site!! Man .. Beautiful .. Amazing ..
I’ll bookmark your site and take the feeds additionally? I’m
happy to search out numerous useful info here in the publish, we’d like
develop extra techniques on this regard, thanks for sharing.
. . . . .
You could definitely see your expertise within the work you write.
The world hopes for more passionate writers like you who are not afraid to say how
they believe. Always follow your heart.
Write more, thats all I have to say. Literally, it seems as
though you relied on the video to make your point. You obviously know what youre talking
about, why throw away your intelligence on just posting videos to your weblog
when you could be giving us something informative
to read?
Ridiculous story there. What occurred after? Take care!
Fastidious response in return of this question with real arguments and describing everything on the topic of that.
Hi there, all is going well here and ofcourse every one is sharing data, that’s truly good, keep up writing.
Modern Purair
416 Meridian Rd SE #14A, Calgary
AB T2А 1X2, Canada
(403) 800-7254
local support (Janine)