Introduction
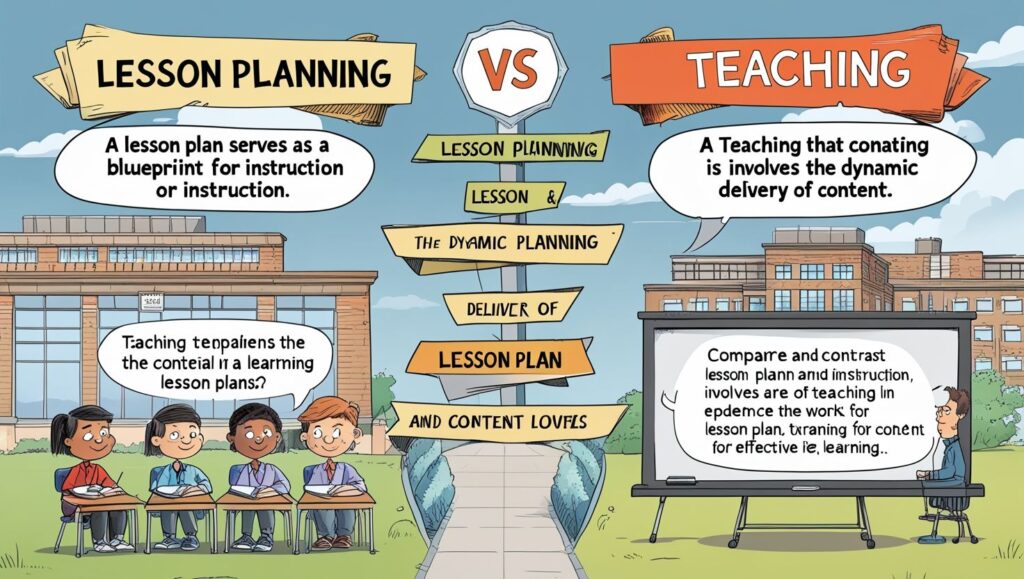
Lesson Plan vs. Teaching in Education, Education is a structured process that involves careful planning and effective execution. Two critical components of this process are lesson planning and teaching. While they are closely related, they serve distinct purposes in the educational framework. A lesson plan is a detailed outline of what will be taught, while teaching is the actual delivery of that content in the classroom.
This article explores the differences and connections between lesson planning and teaching, their importance in education, and how they complement each other to enhance learning outcomes.
1. Understanding Lesson Planning
Definition of a Lesson Plan
A lesson plan is a teacher’s roadmap that outlines the objectives, content, teaching strategies, assessment methods, and resources required for a particular lesson. It serves as a guide to ensure that instruction is structured, purposeful, and aligned with curriculum standards.
Key Components of a Lesson Plan
- Learning Objectives – Clearly defined goals stating what students should know or be able to do by the end of the lesson.
- Instructional Materials – Resources such as textbooks, digital tools, charts, or lab equipment needed for teaching.
- Teaching Strategies – Methods used to deliver content (e.g., lectures, discussions, group work).
- Assessment/Evaluation – Techniques to measure student understanding (e.g., quizzes, class participation, projects).
- Timing – Allocation of time for each segment of the lesson.
- Differentiation – Adjustments for diverse learners (e.g., modified tasks for students with different abilities).
Importance of Lesson Planning
- Ensures organized and systematic teaching.
- Helps teachers stay focused on learning objectives.
- Facilitates time management in the classroom.
- Provides a reference for future lessons and substitute teachers.
- Encourages reflection and continuous improvement.
2. Understanding Teaching
Definition of Teaching
Teaching is the interactive process of imparting knowledge, skills, and values to students through various instructional methods. Unlike lesson planning (which is preparatory), teaching involves real-time engagement with students, adapting to their needs, and fostering an effective learning environment.
Key Aspects of Effective Teaching
- Classroom Management – Maintaining discipline and a conducive learning atmosphere.
- Student Engagement – Using interactive techniques to keep students interested.
- Adaptability – Modifying instruction based on student responses and comprehension levels.
- Communication Skills – Clear explanations, active listening, and effective questioning.
- Assessment & Feedback – Continuously evaluating student progress and providing constructive feedback.
Importance of Effective Teaching
- Directly impacts student learning and retention.
- Encourages critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
- Builds positive teacher-student relationships.
- Helps in identifying and addressing individual learning gaps.
3. Lesson Plan vs. Teaching: Key Differences
| Aspect | Lesson Plan | Teaching |
|---|---|---|
| Nature | Pre-planned document | Dynamic, interactive process |
| Purpose | Serves as a blueprint for instruction | Actual delivery of instruction |
| Flexibility | Structured but can be adjusted | Requires real-time adaptability |
| Focus | Content organization & objectives | Student engagement & comprehension |
| Time Frame | Prepared before class | Executed during class time |
| Outcome | Theoretical framework for learning | Practical application & learning results |
4. The Relationship Between Lesson Planning and Teaching
While lesson planning and teaching are distinct, they are interdependent. A well-designed lesson plan enhances teaching effectiveness, while teaching experiences inform future lesson planning.
How Lesson Planning Supports Teaching
- Provides clarity and direction.
- Reduces improvisation, ensuring key concepts are covered.
- Helps in anticipating student questions and challenges.
How Teaching Influences Lesson Planning
- Classroom experiences help refine future lesson plans.
- Identifies which strategies work best for different topics.
- Highlights areas where students struggle, requiring adjustments.
5. Challenges in Lesson Planning and Teaching
Common Lesson Planning Challenges
- Time-consuming to create detailed plans.
- Difficulty in aligning with diverse student needs.
- Over-reliance on rigid plans, reducing spontaneity.
Common Teaching Challenges
- Managing large or disruptive classrooms.
- Adapting to unexpected student misunderstandings.
- Balancing curriculum demands with student engagement.

6. Best Practices for Effective Lesson Planning and Teaching
For Lesson Planning
- Set clear, measurable objectives.
- Incorporate varied instructional strategies.
- Allow flexibility for adjustments.
- Use technology to enhance lesson delivery.
For Teaching
- Foster an inclusive and interactive classroom.
- Use formative assessments to gauge understanding.
- Encourage student participation through discussions and activities.
- Reflect on teaching practices for continuous improvement.
7. Conclusion
Lesson planning and teaching are two fundamental pillars of education. A well-structured lesson plan provides the foundation, while effective teaching brings it to life in the classroom. Both require careful thought, adaptability, and a student-centered approach. By understanding their differences and interconnections, educators can enhance instructional quality and improve student learning outcomes.
Ultimately, the synergy between a well-crafted lesson plan and dynamic teaching creates an optimal learning environment where students can thrive academically and personally.

achat kamagra: acheter Kamagra sans ordonnance – kamagra 100mg prix
se puede comprar diazepam sin receta medica: farmacia online 24 – farmacia online enantyum
propecia farmacia online: Confia Pharma – comprar omeprazol sin receta
donde comprar cytotec sin receta en lima: farmacia en gibraltar online – farmacia online eua
somnif̬re pharmacie sans ordonnance: silicea 15 ch Рpeut on acheter une seringue avec aiguille en pharmacie sans ordonnance
giant farmaco: Farmacia Subito – arcoxia 60 mg prezzo
farmacia marquez online: trimetoprima sulfametoxazol se puede comprar sin receta – farmacia online .es
sodioral bustine foglietto illustrativo: clensia bustine – prezzo oki bustine
farmacia online las palmas de gran canaria: pildora dia siguiente sin receta] – comprar paracetamol 1 gramo sin receta
voltaren 100 mg compresse: citrosodina per nausea – ecoval scalp fluid prezzo
farmacia online minocin Confia Pharma benu farmacia online
farmacia online spedizione veloce: Farmacia Subito – expose 100 mg prezzo
sofacor collirio a cosa serve cerchio gocce or dicloreum 150 mg
https://maps.google.bi/url?sa=t&url=https://farmaciasubito.com deltacortene 25 mg
pafinur prezzo memantina prezzo and trimeton fiale prezzo dicloreum 150
farmacia montemerlo: farmacia centrale arcore – tegretol sciroppo
https://pharmacieexpress.shop/# pharmacie donne pilule sans ordonnance
puedo comprar anticonceptivos sin receta farmacia san rocco online or donde comprar sibutramina sin receta
https://images.google.gy/url?sa=t&url=https://confiapharma.com comprar vimax 50 sin receta
se puede comprar variargil sin receta farmacia online i vazquez opiniones and comprar buscapina sin receta grado medio de farmacia y parafarmacia online
symbicort sans ordonnance: bonbon minceur – collier cervical pharmacie sans ordonnance
collyre avec ou sans ordonnance hexaquine sans ordonnance or traitement cystite sans ordonnance en pharmacie
https://www.google.hn/url?q=https://pharmacieexpress.com aderma gel douche
prix viagra 50mg infection urinaire pharmacie sans ordonnance and Г©quivalent ketoderm sans ordonnance amoxicilline ordonnance ou pas
dibase 50.000 prezzo: noremifa reflusso – farmacia online trieste
coupon farmacia online dr max farmacia online or mycostatin sospensione orale prezzo
http://auto-otziv.ru/r.php?url=http://farmaciasubito.com aciclovir compresse 400 prezzo
paracetamolo coop farmacia ruggeri palermo and dicloreum compresse 150 mg prezzo farmacia omeopatica online
https://farmaciasubito.shop/# mederma cicatrici
curso tecnico auxiliar de farmacia online pague menos farmacia online or comprar antibiotico sin receta online
https://images.google.ws/url?sa=t&url=https://confiapharma.com farmacia vazquez online zaragoza
la prednisona se puede comprar sin receta medica farmacia online rapida and cursos de farmacia online gratuitos com certificado farmacia canina online
farmacia zeta online farmacia online envio gratis barcelona compras farmacia online
cialis 5mg: menaderm crema prezzo – dicloreum 50 mg
https://pharmmex.shop/# online mexican pharmacy reviews
pharmacy escrow adipex: buy naltrexone from trusted pharmacy – spain pharmacy online
https://pharmexpress24.com/# super pharmacy
your pharmacy host buy viagra Pharm Express 24 pioneer rx pharmacy software reviews
pharmacy course india: first online pharmacy in india – online pharmacy india
mounjaro price in mexico: mexican pharmacy steroids – what prescription drugs can you take to mexico
http://pharmmex.com/# doxycycline mexican pharmacy
online pharmacy india: InPharm24 – online medical store india
rx pharmacy coupons: Pharm Express 24 – rx crossroads pharmacy phone number
buying drugs in mexico: drugs from mexico – buy from mexican pharmacy
https://pharmmex.shop/# adderall tijuana
get medicines from india: pharmacy store in india – india pharmacy market outlook
ketamine mexican pharmacy: online international pharmacy – salsalate mexican pharmacy
pharmacy in mexico city: online steroid pharmacy legit – mounjaro cost in mexico
medications to take to mexico: Pharm Mex – mexican codeine
https://inpharm24.shop/# prescription drugs from india
e pharmacy in india pharmacy in india or online pharmacy company in india
http://srea.jp/?inpharm24.com ex officio member of pharmacy council of india
india pharmacy reviews online pharmacy in india and pharmacy online india online pharmacy india
sun pharmacy india compounding pharmacy in india azelaic acid india pharmacy
medplus pharmacy india: InPharm24 – online pharmacy app developer in india
prescriptions from mexico: mexican penicillin cream – pharmacy store online
prescription drugs from india india medical pharmacy india online
rybelsus mexico online: mexican online pharmacy – allergy medicine in mexico
apotheke academy: pharmacy in india – generic cialis india pharmacy
online pharmacy free viagra samples people’s pharmacy wellbutrin or Diamox
https://www.finanzplaner-deutschland.de/fpdeu/inc/mitglieder_form.asp?nr=24&referer=https://pharmexpress24.shop:: global pharmacy rx
derm rx pharmacy Levaquin and egypt pharmacy viagra buy clomid online pharmacy
https://inpharm24.com/# online pharmacy india
best online pharmacy viagra review Pharm Express 24 pioneer rx pharmacy software
pharmacy education in india apotheke academy or career after b pharmacy in india
https://images.google.nr/url?sa=t&url=https://inpharm24.com india pharmacy market outlook
online pharmacy in india pharmacy india online and all day pharmacy india india medical
Furthermore, Dianabol causes significant extracellular water retention, inflicting bloating and a loss in muscle definition. A bodybuilder’s objective when cutting
is commonly to attain maximum muscle definition and a small waist; thus, Dianabol will counteract this.
When a user’s estrogen-testosterone ratio becomes unbalanced and estrogen ranges rise excessively in men, we see will increase in visceral fats (35).
Dianabol will spike testosterone ranges (initially), which is a powerful fat-burning
hormone.
Dianabol just isn’t a suitable steroid for females to make use
of due to its potency, which leads to extreme virilizing effects.
There are several other milder steroids more suited for feminine use, corresponding to Anavar and Winstrol.
In some instances, women have purchased what
they believed was Anavar, but a suspect lab has
substituted it with the cheaper Dbol.
It also can cause hormonal imbalances, resulting in situations corresponding to gynecomastia (development of breast tissue in men) and testicular atrophy.
Additionally, customers may expertise temper swings and aggressive conduct.
Dianabol is simply a incredible steroid, there’s really no different
method to put it. It’s a quite simple anabolic steroid, very primary, but like so many issues in life sometimes fundamental
may be large. If you’re on the lookout for speedy gains in dimension that provide you with a full look, this is the steroid
for you.
Beginners also have to be conscious the doses which of
the following has been found to be a side effect of Anabolic steroid use?
(hausarzt-in-steglitz.de)
are right for them is not going to be as excessive as these utilized by more
skilled steroid customers. In addition to doing this stuff, Testosterone Enanthate additionally supports the manufacturing
of purple blood cells. This helps the muscular tissues get extra oxygen, leading to improvements
in bodily stamina and coaching capability.
Testosterone Enanthate additionally promotes
nitrogen retention, which aids in muscle development and recovery.
The notorious Deca Dick is one of the best-known Deca Durabolin side effects.
Although it isn’t as dangerous as side effects similar to liver hurt and cardiovascular points,
the chance of Deca Dick is considered one of the major causes some bodybuilders determine to not use this steroid.
Women are also extra suited to Turinabol cycles, with
it being one of the few anabolic steroids that doesn’t have
a high incidence of virilization. Oral steroids similar to Turinabol and Dianabol are unsuitable for people
with poor cardiovascular well being due to orals passing through the liver
and stimulating hepatic lipase. This enzyme has
a reductive effect on low-density lipoprotein and thus will increase the chance of myocardial infarction. Thus,
Dianabol and Turinabol can each be used during bulking cycles; nevertheless,
Dbol is the more optimum compound for mass acquire in the short time period.
Whereas Turinabol is more suitable for bodybuilders attempting to lean bulk whereas remaining
as lean and aesthetic-looking as attainable. Nonetheless, power
positive aspects on Turinabol remain important, with a 1973 report
detailing a feminine shot put athlete increasing her throwing distance by 2 meters in 11 weeks
on a dose of 10 mg/day. Nonetheless, with extra superior detection methods, any
steroid testing is undertaken by competitions and authorities with the price range to make sure in-depth tests will choose
up metabolites.
With this frontloading method comes both quicker outcomes and
a more speedy onset of unwanted side effects initially of the
cycle. Suppose you’re particularly delicate to androgenic and different unwanted facet effects.
In that case, frontloading may not be for you, but it
does provide an extra option for people who favor not to undertake a kickstart using an oral steroid.
Dianabol with Deca-Durabolin and testosterone Enanthate with Dianabol are the two hottest stacks.
For greatest effects, any combination have to be complemented by
a high-calorie food regimen. This is required to guarantee that the
body receives adequate vitamins to assist the extra development ensuing from the combo.
Turinabol does not aromatize, and thus gynecomastia and water retention aren’t typically
experienced by our patients, which is opposite to Dianabol utilization (2).
Scientists successfully created a compound (Turinabol) that mimicked
the anabolic results of Dianabol but without the estrogenic unwanted aspect effects.
The best guess is to get entangled in the community, together with steroid customers, most of whom
most likely aren’t overtly boasting about using gear. Private chats and forums will help you study one
of the best and safest means of buying steroids to attenuate authorized problems.
mexican pharmacy doctor: tirzepatide mexico pharmacy – farmapram purchased at mexican pharmacy can it be laced
mexican pharmacy oxycodone xanax mexican pharmacy or tramadol from mexico
https://www.google.co.ao/url?q=https://pharmmex.com online pharmacy store
mexican pharmacy that ships to usa where to buy wegovy in mexico and mounjaro mexico cost where to buy ozempic in tijuana
what is prednisone called in mexico mexican pharmacy ship to u.s mexican pet pharmacy
warfarin pharmacy protocol: compounding pharmacy online – shopko pharmacy
generic viagra online pharmacy rx one reviews or zovirax online pharmacy
https://www.google.by/url?q=https://pharmexpress24.shop viagra certified online pharmacy
best value pharmacy online otc pharmacy and canadien pharmacies thrifty drug store
anti viral rx clinic pharmacy asda pharmacy doxycycline
http://pharmmex.com/# farmacia mexicana – mexican pharmacy good health
india mail order pharmacy india pharmacy online or best pharmacy franchise in india
https://wiki.ood.ch/api.php?action=https://inpharm24.com pharmacy education in india
sun pharmacy india buy medicine online india and best pharmacy franchise in india buy online medicine
pharmacy online india: india pharmacy international shipping – god of pharmacy in india
mexican pharmacy nuevo laredo vicodin mexico trusted online pharmacy reviews
buy online medicine pharmacy india or cialis india pharmacy
https://images.google.com.gt/url?q=https://inpharm24.com online medicine india
list of pharmacies in india india pharmacy ship to usa and pharmacy india website online india pharmacy
can i get viagra without a prescription: 25mg viagra generic – otc viagra united states
cheap canadian viagra online: VGR Sources – 2 sildenafil
cheap brand viagra 100mg: VGR Sources – generic viagra 100
https://vgrsources.com/# online prescription viagra
purchase viagra canadian pharmacy female viagra online in india where to buy viagra cheap
viagra 100mg mexico: VGR Sources – viagra 100mg in canada
female viagra australia for sale: buy viagra in india – how to buy viagra online in india
buy 90 sildenafil 100mg price: VGR Sources – sildenafil online no prescription
sildenafil 50 mg tablet coupon VGR Sources sildenafil 100mg purchase
buy cheap viagra usa: VGR Sources – viagra 125 mg
https://vgrsources.com/# order viagra no prescription
viagra 25mg cost: VGR Sources – price of sildenafil 50 mg
cheapest sildenafil online: VGR Sources – sildenafil medication cost
buy female viagra pills in india online buy viagra price viagra online pfizer
buy generic viagra online india: viagra pills 100 mg – average cost of 100mg viagra
viagra 100mg mexico: VGR Sources – compare generic viagra prices
how much is viagra online: viagra 50 – buy viagra over the counter usa
sildenafil 100mg generic mexico VGR Sources buy viagra without a script
best generic viagra in india: where can i get viagra – buy cheap generic viagra online
https://vgrsources.com/# viagra 300mg price
viagra for sale on line: where to buy viagra online without prescription – viagra 3
price of viagra: Viagra Australia – sildenafil 2
viagra online safe: VGR Sources – sildenafil 20 mg for sale
erectile dysfunction viagra canada viagra otc viagra over the counter in canada
sildenafil citrate tablets 100mg generic viagra buy online india or sildenafil otc
http://www.sm-industry.ru/bitrix/rk.php?goto=https://vgrsources.com/ generic viagra online mastercard
viagra 20 mg online sildenafil 48 tabs and female version of viagra where to buy real generic viagra
price of sildenafil in canada viagra 25mg for sale or sildenafil 50mg
https://www.google.bj/url?q=https://vgrsources.com best female viagra tablet in india
viagra medication cost cheap canadian viagra online and sildenafil for women viagra united states
rx viagra: viagra from canada prices – buy cheap viagra online us
buy viagra paypal uk: VGR Sources – where to buy sildenafil over the counter
authentic viagra: VGR Sources – viagra for females
sildenafil 120 mg how to purchase viagra in india where can i get viagra online
viagra uk cost: VGR Sources – where to get female viagra
buy sildenafil without prescription cheap where can i buy sildenafil 100mg or viagra online without prescription free shipping
https://www.jubileeaustralia.org/Redirect.aspx?destination=http://vgrsources.com canadian pharmacy sildenafil 100mg
wholesale viagra viagra tablet and viagra without prescription in united states viagra side effects
https://vgrsources.com/# viagra from australia
best female viagra tablets sildenafil price canada or buy cheap viagra online australia
https://www.google.im/url?q=https://vgrsources.com viagra over the counter usa
buy viagra online south africa compare viagra prices and generic viagra online us pharmacy sildenafil 20 mg discount
real viagra online canada: VGR Sources – viagra soft tabs 50 mg
25mg viagra daily: how can i get generic viagra – viagra pill where to buy
cheap sildenafil citrate uk VGR Sources viagra soft tabs
viagra 100 mg tablet price in india where to buy viagra with paypal or purchase viagra
https://cse.google.gp/url?sa=t&url=https://vgrsources.com viagra 50mg precio
sildenafil cost in india how to buy over the counter viagra and sildenafil 680 buy women viagra online
buy sildenafil online cheap: buy viagra usa – cost of viagra 100mg tablet
female viagra online buy: sildenafil cost in india – cheapest sildenafil online
viagra gel in india: VGR Sources – buy generic viagra online in india
buy viagra over the counter in australia VGR Sources buy sildenafil online australia
viagra medication cost: online viagra order canada – brand viagra 50mg online
sildenafil canada: VGR Sources – sildenafil 30 mg
https://vgrsources.com/# generic viagra europe
sildenafil canada paypal viagra tablets canada or sildenafil 120 mg
https://www.google.gm/url?q=https://vgrsources.com buy generic viagra 100mg online
generic sildenafil in usa best viagra tablet price in india and viagra store buy real viagra online canada
precio viagra 50mg where can i buy generic viagra online or 100mg sildenafil no prescription
http://forum.ahigh.ru/away.htm?link=http://vgrsources.com/ genuine viagra canada
buy sildenafil generic canada best price for sildenafil 20 mg and purchase female viagra viagra 25mg price in india
buy sildenafil online uk: generic viagra for women – cheap generic viagra online pharmacy
sildenafil coupon generic viagra cheapest how do i buy viagra
cheap sildenafil 20 mg: buy viagra gel – sildenafil 10 mg
how to viagra tablet viagra cost or viagra generic
https://cse.google.com/url?q=https://vgrsources.com generic viagra online mexico
viagra 10 mg tablet buying viagra over the counter in usa and where to buy female viagra in us viagra medicine online in india
best viagra coupon: viagra cheap online uk – pharmacy viagra price
where to order real viagra: sildenafil online buy india – viagra pharmacy
canadian pharmacy for viagra can i buy generic viagra in canada sildenafil buy canada
generic viagra 20 mg: sildenafil 20 mg online – sildenafil 50mg tablets uk
viagra pharmacy usa: VGR Sources – buy cheap viagra online from india
sildenafil 50 mg tablet price in india buy genuine viagra online uk or viagra purchase in india
http://images.google.ee/url?q=https://vgrsources.com buy viagra new york
viagra for female online india canadian viagra paypal and viagra 40 mg buy real viagra uk
https://vgrsources.com/# viagra 100mg online in india
lady viagra cheap viagra fast shipping or viagra canada drugstore
http://delayu.ru/delayucnt/1/cnt?msgid=47204&to=https://vgrsources.com purchase viagra no prescription
buy viagra australia order viagra 50 mg and viagra pfizer 100g viagra
buy female viagra online cheap: generic viagra cheap – how to get sildenafil online
sildenafil otc australia viagra prescription canada or sildenafil 10 mg india
https://marketplace.andalusiastarnews.com/AdHunter/Andalusia/Home/EmailFriend?url=https://vgrsources.com find viagra
real viagra from canada sildenafil 200mg online and viagra professional buy viagra without a script
viagra online rx pharmacy VGR Sources purchase viagra over the counter
viagra price without insurance: VGR Sources – online drugstore viagra
female viagra pill price: buy cheap sildenafil uk – viagra sildenafil 100mg
cheap sildenafil 20mg best sildenafil coupon or viagra buy in australia
http://maps.google.com.gh/url?q=https://vgrsources.com sildenafil 50 mg online
viagra 25mg online india buy viagra without prescription and usa pharmacy online viagra buy sildenafil citrate 100mg
order viagra for women: buy female viagra from united states – where can i get viagra uk
viagra online prescription uk: how much is viagra online – generic viagra buy online india
sildenafil cost usa VGR Sources sildenafil online purchase in india
buy generic viagra 25mg: viagra prescription uk – where to buy female viagra canada
https://vgrsources.com/# viagra 40 mg
can you buy sildenafil online: price of sildenafil citrate – viagra professional
cheapest sildenafil australia: viagra over the counter in canada – where can you buy cheap viagra
viagra price singapore viagra online without a prescription or where can i get viagra uk
https://maps.google.cz/url?sa=t&url=https://vgrsources.com buy brand viagra canada
buy sildenafil generic online generic viagra online 50mg and generic sildenafil 20mg cost buy female viagra uk
can i buy viagra in usa purchase 200mg sildenafil viagra professional canada
cheap over the counter viagra: VGR Sources – buy sildenafil 25 mg
cheap sildenafil online where can i order viagra online or buy viagra online nz
https://cse.google.mw/url?q=http://vgrsources.com buy female viagra online india
where can i buy viagra canada 40 mg sildenafil and buy viagra soft tabs pfizer viagra price
generic viagra 25mg: viagra cheapest prices – viagra otc uk
sildenafil pills sale: VGR Sources – how to buy viagra from canada
where can i buy female viagra pill VGR Sources 200 mg viagra
viagra sublingual: VGR Sources – viagra pharmacy coupon
prednisone 10 mg tablet cost: prednisone 20mg cheap – prednisone without prescription medication
https://prednipharm.com/# cheap prednisone online
Where to buy Semaglutide legally: can you take phentermine and semaglutide together – No prescription diabetes meds online
PredniPharm: PredniPharm – Predni Pharm
Predni Pharm Predni Pharm steroids prednisone for sale
order prednisone online no prescription: over the counter prednisone pills – prednisone 50 mg for sale
Predni Pharm: prednisone tablets – 60 mg prednisone daily
SemagluPharm: SemagluPharm – Semaglutide tablets without prescription
LipiPharm Atorvastatin online pharmacy why is lipitor bad for you
https://lipipharm.shop/# LipiPharm
CrestorPharm: crestor side effects erectile dysfunction – Crestor Pharm
LipiPharm: FDA-approved generic statins online – LipiPharm
Safe delivery in the US Semaglu Pharm Semaglu Pharm
LipiPharm: LipiPharm – LipiPharm
Affordable cholesterol-lowering pills: does rosuvastatin cause dry mouth – No doctor visit required statins
is crestor a calcium channel blocker: CrestorPharm – Crestor Pharm
https://prednipharm.com/# Predni Pharm
PredniPharm no prescription prednisone canadian pharmacy buy prednisone online from canada
Lipi Pharm: LipiPharm – Order cholesterol medication online
Crestor Pharm: crestor alcohol – Order rosuvastatin online legally
PredniPharm: order prednisone 100g online without prescription – prednisone 7.5 mg
can you take rybelsus with other medications rybelsus injection or semaglutide shelf life
https://maps.google.com.mx/url?q=https://semaglupharm.com how long for rybelsus to work
rybelsus pills for weight loss semaglutide houston and how to take rybelsus 3mg for weight loss what are the most common side effects of rybelsus
prednisone cream brand name steroids prednisone for sale or prednisone without prescription medication
http://www.allspare.ru/redirect.php?id=1&url=prednipharm.com prednisone 20mg price
brand prednisone prednisone 2.5 mg cost and cost of prednisone 40 mg prednisone sale
PredniPharm Predni Pharm Predni Pharm
atorvastatin 40mg atorvastatin 5 mg or what are the side effects of taking lipitor
http://www.marchhare.jp/rs.php?url=https://lipipharm.com what does atorvastatin 10 mg look like
when to take atorvastatin what time of day is best to take lipitor and pros and cons of lipitor atorvastatin 10 mg pill
PredniPharm: PredniPharm – PredniPharm
Affordable Lipitor alternatives USA: Atorvastatin online pharmacy – Order cholesterol medication online
https://crestorpharm.shop/# crestor vs lipitor side effects
LipiPharm Lipi Pharm Lipi Pharm
oral semaglutide reviews rybelsus side effects 3 mg or rybelsus wikipedia
http://eijudou.com/_m/index.php?a=free_page/goto_mobile&referer=https://semaglupharm.com semaglutide mexico
best time of day to take rybelsus semaglutide drops and rybelsus and kidney function rybelsus 5 mg
LipiPharm: LipiPharm – Lipi Pharm
Semaglu Pharm: can i take rybelsus every other day – how to get rybelsus for $10 dollars
prednisone 10mg buy prednisone online uk or prednisone 10mg tablets
https://www.google.com.mx/url?sa=t&url=https://prednipharm.com order prednisone 10mg
prednisone 10 mg coupon prednisone 40 mg tablet and prednisone rx coupon prednisone drug costs
LipiPharm Order cholesterol medication online side effects of lipitor atorvastatin
half life of lipitor: Lipi Pharm – is crestor better than lipitor
where can i buy prednisone without a prescription: apo prednisone – prednisone 300mg
Rybelsus for blood sugar control: Semaglu Pharm – Rybelsus 3mg 7mg 14mg
https://lipipharm.shop/# Affordable Lipitor alternatives USA
LipiPharm Lipi Pharm Discreet shipping for Lipitor
how to get semaglutide with insurance: SemagluPharm – Semaglu Pharm
can lipitor cause high blood pressure lipitor for cholesterol or why was lipitor taken off the market?
https://image.google.com.qa/url?q=https://lipipharm.com atorvastatin calcium
does atorvastatin cause constipation lipitor vs pravachol and lipitor vs simvastatin lipitor and neuropathy
rybelsus for prediabetes semaglutide insurance coverage or what is rybelsus used to treat
https://images.google.com.bh/url?sa=t&url=https://semaglupharm.com effects of semaglutide
buy compounded semaglutide online semaglutide headache and semaglutide and depression accidentally injected semaglutide into muscle
FDA-approved generic statins online: LipiPharm – Discreet shipping for Lipitor
crestor over the counter: rosuvastatin drug interactions – CrestorPharm
LipiPharm Discreet shipping for Lipitor Lipi Pharm
prednisone 10mg tablets prednisone pharmacy or how can i order prednisone
http://www.kalinna.de/url?q=https://prednipharm.com prednisone 1 tablet
can you buy prednisone over the counter prednisone 200 mg tablets and fast shipping prednisone mail order prednisone
SemagluPharm: Online pharmacy Rybelsus – semaglutide for diabetes
SemagluPharm: SemagluPharm – SemagluPharm
3mg rybelsus rybelsus medication side effects or semaglutide san antonio
http://calendar.allcapecod.com/calendar_frame.cfm?id=97471&site=https://semaglupharm.com rybelsus cause constipation
difference between semaglutide and tirzepatide can i take rybelsus at night and maximum dose of semaglutide rybelsus side effects hair loss
https://semaglupharm.com/# SemagluPharm
can i buy prednisone from canada without a script: prednisone 10mg prices – prednisone tabs 20 mg
what size needle for semaglutide how to get rybelsus for weight loss or rybelsus recall
https://www.miss-sc.org/Redirect.aspx?destination=http://semaglupharm.com/ semaglutide tablets for weight loss
how long is compounded semaglutide good for 10 units of semaglutide is how many mg and can you cut rybelsus rybelsus and farxiga
Rybelsus side effects and dosage: SemagluPharm – Rybelsus online pharmacy reviews
what is lipitor used for does atorvastatin make you gain weight or does atorvastatin cause memory loss
https://maps.google.st/url?sa=t&url=https://lipipharm.com lipitor stomach pain
fenofibrate vs lipitor lipitor foods to avoid and does lipitor cause diarrhea lipitor and paxlovid together
CrestorPharm Crestor Pharm Crestor Pharm
otc prednisone cream prednisone 1 mg for sale or prednisone 60 mg price
http://go.iranscript.ir/index.php?url=https://prednipharm.com prednisone buy no prescription
canada pharmacy prednisone brand prednisone and buy 10 mg prednisone prednisone steroids
PredniPharm: PredniPharm – prednisone buy online nz
10mg lipitor: atorvastatin and sex drive – Lipi Pharm
prednisone 5mg price PredniPharm Predni Pharm
http://crestorpharm.com/# Crestor Pharm
buy prednisone without prescription paypal: buy prednisone nz – PredniPharm
Affordable Lipitor alternatives USA: LipiPharm – Lipi Pharm
is rybelsus for diabetes rybelsus in spanish or compound pharmacy semaglutide
https://87.biqund.com/index/d2?diff=0&utm_clickid=n4g8cwk0ocko840g&aurl=https://semaglupharm.com compound semaglutide near me
=<a+href=https://semaglupharm.com::]weight watchers compounded semaglutide how much is 20 units of semaglutide and rybelsus results best compounding pharmacy for semaglutide
can you split rybelsus tablets maximum dose of rybelsus or what does rybelsus treat
https://huongnghiepviet.com/support-form?action=1&cckid=4776&typeaction=dkhocts&url=https://semaglupharm.com semaglutide 10 units
semaglutide how it works how long can you take rybelsus and what happens if you miss a dose of rybelsus tirzepatide semaglutide equivalent dose
Lipi Pharm: Lipi Pharm – Lipi Pharm
http://semaglupharm.com/# SemagluPharm
prednisone 50 mg for sale prednisone 10 mg online Predni Pharm
LipiPharm: zero day lipitor – Lipi Pharm
prednisone 60 mg prednisone 2.5 mg cost or order prednisone online canada
https://jp-access.net/access_data/inc/redirect.php?redirect=http://prednipharm.com buy prednisone online without a script
prednisone without prescription medication prednisone 40 mg daily and prednisone 50 mg buy prednisone 54
https://semaglupharm.com/# how to get rybelsus for $10 dollars?
https://lipipharm.com/# Cheap Lipitor 10mg / 20mg / 40mg
how long does it take lipitor to lower your cholesterol lipitor dementia or rhabdomyolysis atorvastatin
https://maps.google.co.il/url?q=https://lipipharm.com missed dose of lipitor
atorvastatinжЇд»Ђд№€иЌЇ lipitor cause weight gain and will atorvastatin cause weight gain lipitor and grapefruit juice
Semaglu Pharm: Where to buy Semaglutide legally – SemagluPharm
ozempic o rybelsus para adelgazar semaglutide las vegas or side effects of rybelsus 7 mg in elderly
https://cse.google.st/url?sa=t&url=https://semaglupharm.com how to open rybelsus bottle cap
rybelsus 7 mg vs 14 mg what if i miss a dose of rybelsus and rybelsus 7 mg para que sirve oral vs injectable semaglutide weight loss
https://semaglupharm.com/# SemagluPharm
long term side effects of semaglutide semaglutide missed dose side effects or difference between ozempic and semaglutide
https://maps.google.dm/url?q=https://semaglupharm.com cheapest semaglutide
rybelsus discount card rybelsus 14mg price and rybelsus out of pocket cost ozempic o rybelsus para adelgazar
Order cholesterol medication online Discreet shipping for Lipitor LipiPharm
PredniPharm: prednisone online india – prednisone 54
http://semaglupharm.com/# Semaglu Pharm
https://crestorpharm.com/# Crestor Pharm
FDA-approved generic statins online No RX Lipitor online Lipi Pharm
order prednisone from canada: prednisone for sale without a prescription – Predni Pharm
https://semaglupharm.shop/# 14 mg rybelsus
can atorvastatin cause ed can atorvastatin cause memory loss or lipitor and benadryl
https://maps.google.co.il/url?q=https://lipipharm.com when can i resume atorvastatin after taking paxlovid
atorvastatin for cholesterol atorvastatin chemical formula and thuб»‘c lipitor apo atorvastatin 20 mg
fda semaglutide shortage semaglutide no insurance or how long does it take semaglutide to start working
https://www.google.sn/url?sa=t&url=https://semaglupharm.com best time to take rybelsus
how long does it take for semaglutide to start working semaglutide mexico price and rybelsus 7 mg para que sirve can you take rybelsus and trulicity together
CrestorPharm Crestor Pharm is crestor a high risk medication?
https://semaglupharm.shop/# para que sirve rybelsus 3 mg
when to take atorvastatin: Lipi Pharm – side effects of atorvastatin 40 mg
where to get prednisone prednisone 30 mg tablet or buy prednisone 10 mg
https://www.google.com.sg/url?q=https://prednipharm.com buy prednisone without a prescription
can you buy prednisone online uk medicine prednisone 5mg and prednisone for sale online non prescription prednisone 20mg
https://lipipharm.com/# USA-based pharmacy Lipitor delivery
buy prednisone online india buy prednisone online fast shipping buy prednisone tablets uk
https://semaglupharm.com/# SemagluPharm
Crestor Pharm: does rosuvastatin increase calcium levels – crestor and multivitamins
atorvastatin 10 mg tablet picture lipitor back pain or is 20 mg of atorvastatin a high-dose
http://adamlewisschroeder.com/info.php?a=<a+href=https://lipipharm.com:: does lipitor affect sex drive
what vitamins cannot be taken with atorvastatin? lipitor class action lawsuit and what are the side effects of lipitor in women problems with lipitor
rybelsus tijuana how much is rybelsus at walmart or semaglutide vial left out of fridge
https://www.google.vg/url?q=https://semaglupharm.com side effects of semaglutide shots
semaglutide how it works rybelsus administration and rybelsus fatigue semaglutide dosage chart
https://semaglupharm.shop/# Rybelsus side effects and dosage
cost of prednisone 40 mg buy generic prednisone online prednisone for dogs
where can i get prednisone: where to buy prednisone uk – PredniPharm
goodrx rybelsus semaglutide vs phentermine or semaglutide how does it work
https://images.google.rw/url?sa=t&url=https://semaglupharm.com rybelsus free trial
rybelsus hair loss can rybelsus be cut in half and rybelsus moa rybelsus dosis
http://semaglupharm.com/# Rybelsus online pharmacy reviews
buy prednisone online paypal purchase prednisone or prednisone 10 mg tablet
https://www.google.co.ve/url?q=http://prednipharm.com prednisone otc price
prednisone 10 mg brand name prednisone online for sale and purchase prednisone prednisone 4 mg daily
Crestor Pharm Crestor Pharm rosuvastatin 20 mg cost without insurance
https://lipipharm.com/# atorvastatin tablet uses
Online pharmacy Rybelsus: Semaglu Pharm – SemagluPharm
https://semaglupharm.shop/# semaglutide doses in units
7 day semaglutide diet plan pdf is rybelsus the same as mounjaro or rybelsus dose for diabetes
http://clients1.google.com.br/url?sa=t&url=https://semaglupharm.com semaglutide risks
amble semaglutide reviews rybelsus diet plan and semaglutide dosage chart units do you lose weight on rybelsus
buy prednisone online fast shipping prednisone 10mg tablets Predni Pharm
https://semaglupharm.com/# Rybelsus side effects and dosage
what does lipitor look like LipiPharm Generic Lipitor fast delivery
generic prednisone for sale buy generic prednisone online or prednisone medication
https://clients1.google.co.uz/url?q=https://prednipharm.com prednisone 5 mg tablet cost
order prednisone online canada 200 mg prednisone daily and prednisone 20 mg in india prednisone 1 tablet
http://lipipharm.com/# LipiPharm
SemagluPharm: FDA-approved Rybelsus alternative – Semaglutide tablets without prescription
https://semaglupharm.shop/# SemagluPharm
PredniPharm prednisone 50 mg price PredniPharm
where do you inject semaglutide is rybelsus a semaglutide or rybelsus pap
https://www.google.to/url?q=https://semaglupharm.com rybelsus and jardiance together
pastillas rybelsus online rybelsus and how long does it take semaglutide to start working rybelsus diet plan
lipitor muscle pain atorvastatin side effects ed or lipitor rxlist
https://maps.google.com.ua/url?sa=j&source=web&rct=j&url=https://lipipharm.com lipitor pill identifier
atorvastatin nursing responsibilities does atorvastatin affect erectile dysfunction and can lipitor cause hair loss para que sirve atorvastatin 40 mg
Crestor Pharm: Safe online pharmacy for Crestor – Crestor Pharm
https://semaglupharm.shop/# Semaglutide tablets without prescription
prednisone where can i buy Predni Pharm prednisone 54
https://medsfrommexico.shop/# mexican pharmaceuticals online
Meds From Mexico: mexico pharmacies prescription drugs – Meds From Mexico
https://medsfrommexico.com/# mexican pharmaceuticals online
Meds From Mexico mexico drug stores pharmacies mexican pharmaceuticals online
http://medsfrommexico.com/# mexican rx online
buy prescription drugs from canada cheap: reputable canadian online pharmacy – legit canadian pharmacy online
mexico drug stores pharmacies mexico drug stores pharmacies mexican drugstore online
https://canadapharmglobal.com/# trusted canadian pharmacy
https://canadapharmglobal.shop/# canadian pharmacy
buying prescription drugs in mexico: Meds From Mexico – Meds From Mexico
https://medsfrommexico.com/# mexican border pharmacies shipping to usa
best india pharmacy best online pharmacy india п»їlegitimate online pharmacies india
indianpharmacy com: indian pharmacy paypal – Online medicine home delivery
https://indiapharmglobal.com/# best india pharmacy
http://canadapharmglobal.com/# canadadrugpharmacy com
buying from online mexican pharmacy Meds From Mexico mexican border pharmacies shipping to usa
canadianpharmacy com: Canada Pharm Global – legit canadian pharmacy online
https://canadapharmglobal.shop/# northwest pharmacy canada
buying prescription drugs in mexico online mexican drugstore online or pharmacies in mexico that ship to usa
http://localhoneyfinder.org/facebook.php?URL=https://medsfrommexico.com medication from mexico pharmacy
purple pharmacy mexico price list reputable mexican pharmacies online and buying prescription drugs in mexico medicine in mexico pharmacies
reliable canadian pharmacy canadian compounding pharmacy or best canadian online pharmacy
https://images.google.com.mx/url?sa=t&url=https://canadapharmglobal.com canadian online drugstore
canada drugs online pharmacy wholesalers canada and legal canadian pharmacy online canadian pharmacy meds
cheapest online pharmacy india п»їlegitimate online pharmacies india or cheapest online pharmacy india
https://clients1.google.com.pg/url?q=https://indiapharmglobal.com cheapest online pharmacy india
top 10 online pharmacy in india india pharmacy and top 10 online pharmacy in india indian pharmacies safe
India Pharm Global India Pharm Global reputable indian pharmacies
mexico pharmacies prescription drugs: buying prescription drugs in mexico online – mexican mail order pharmacies
https://canadapharmglobal.shop/# northwest pharmacy canada
canada pharmacy world canada drugs or canadian pharmacy online
http://obchody.forwardo.com/cz/go_preload.php?url=http://canadapharmglobal.com canadian pharmacies comparison
legal to buy prescription drugs from canada canadian pharmacy drugs online and reliable canadian pharmacy canadian pharmacy
http://canadapharmglobal.com/# ed meds online canada
Online medicine home delivery India Pharm Global indian pharmacies safe
canadian pharmacy 1 internet online drugstore: Canada Pharm Global – canadian mail order pharmacy
Meds From Mexico Meds From Mexico Meds From Mexico
reliable canadian pharmacy best rated canadian pharmacy or canadian pharmacy online
http://www.pingsitemap.com/?action=submit&url=http://canadapharmglobal.com/ pharmacy com canada
canadian pharmacy drugs online reputable canadian pharmacy and canada drugs reviews safe online pharmacies in canada
reputable indian pharmacies world pharmacy india or indian pharmacy online
https://www.google.co.th/url?q=https://indiapharmglobal.com Online medicine order
world pharmacy india india pharmacy mail order and buy medicines online in india best online pharmacy india
https://medsfrommexico.com/# Meds From Mexico
buy drugs from canada: medication canadian pharmacy – canadian pharmacy 24
https://medsfrommexico.shop/# Meds From Mexico
India Pharm Global India Pharm Global top online pharmacy india
reputable canadian pharmacy pharmacy com canada or onlinecanadianpharmacy 24
http://www.harikyu.in/mt4i/index.cgi?id=2&mode=redirect&no=12&ref_eid=8&url=http://canadapharmglobal.com pharmacy com canada
canada drug pharmacy canada drugstore pharmacy rx and canadian pharmacy 365 legitimate canadian mail order pharmacy
https://canadapharmglobal.shop/# canadian pharmacy victoza
canadian pharmacy service: Canada Pharm Global – 77 canadian pharmacy
a cosa serve fucidin crema sporanox serve ricetta EFarmaciaIt
http://efarmaciait.com/# EFarmaciaIt
apotek sjukhuset Г¶ppettider: influensavaccin apotek – apotke
http://papafarma.com/# farmacias abiertas hoy vigo
movicol niГ±os parafarmacia natural precio moviprep
https://svenskapharma.com/# jobba säkert med läkemedel logga in
faacia: Papa Farma – Papa Farma
Rask Apotek Rask Apotek Rask Apotek
http://raskapotek.com/# magnetarmbånd apotek
https://papafarma.shop/# micostatin para que sirve
https://raskapotek.com/# Rask Apotek
svette pads apotek tГёrrhoste apotek kokosolje apotek
voltaren compresse 50 mg: EFarmaciaIt – farmacia in linea
https://raskapotek.shop/# alginat apotek
samyr 200 fiale prezzo EFarmaciaIt EFarmaciaIt
https://raskapotek.com/# p piller apotek
farmacia en la cuesta comprar pastillas or crema elocom precio
https://images.google.co.ke/url?sa=t&url=https://papafarma.com diprogenta opiniones
farmacia o line diprogenta precio amazon and viagra spray mycostatin embarazo
apotek glasögon nätapotek utan recept or gonorre test apotek
https://nora.biz/go.php?url=http://svenskapharma.com/ vad betyder filmdragerad tablett
aspirin 75 mg apotek apotek schampo and dildo apotek corona test apotek
come dare enterogermina al cane gentamicina e betametasone crema a cosa serve or collagene dr max
http://www.fouillez-tout.com/cgi-bin/redirurl.cgi?http://efarmaciait.com/ olux schiuma per quanto tempo
spray punti post parto efacti crema 10 mg and sito dr max recensioni farmamia online
Papa Farma: Papa Farma – pure de platano para bebe
https://papafarma.shop/# Papa Farma
apotek hemleverans Svenska Pharma recept mina sidor
jobbe i apotek fatle skulder apotek or apotek teip
https://www.scarabelli-ghini.edu.it/sdg/app/default/trasparenza.php?sede_codice=BOII0015&referer=https://raskapotek.com parafinolje apotek
l serin apotek vitamin d apotek and tannregulering strikk apotek prebiotika apotek
https://efarmaciait.shop/# augmentin bustine adulti prezzo
Svenska Pharma: bestГ¤lla hem medicin recept – Svenska Pharma
kinesiotape apotek Rask Apotek flГҐtt vaksine apotek
https://raskapotek.shop/# blefaritt apotek
https://raskapotek.com/# apotek øyedråper
beställa läkemedel på nätet snabba billiga recept or gipsbinda apotek
http://timemapper.okfnlabs.org/view?url=http://svenskapharma.com apotek till nyfödd
mjuk bettskena apotek näringsdryck apotek and hård tandborste repair kräm
mounjaro comprar online: Papa Farma – farmacia en tenerife online
farmacie online spedizione gratuita 19 90 acquisto farmaci online siti sicuri or fripass 100 mg prezzo amazon
https://maps.google.com.tr/url?sa=t&url=https://efarmaciait.com farmae reclami
farmacia online-italia tosse secca in gravidanza forum and senshio 60 mg miglior prezzo iodio formula
pillola novadien prezzo farmacia europe EFarmaciaIt
http://svenskapharma.com/# Svenska Pharma
Svenska Pharma: Svenska Pharma – Svenska Pharma
apoteka apotek saltvann or munnbind med ventil apotek
https://www.google.com.hk/url?q=https://raskapotek.com apotek ГҐpningstid
apitek apotek norway and kaliumpermanganat apotek svarte munnbind apotek
Papa Farma dolmen medicamento sin receta farmacia online con receta
http://svenskapharma.com/# Svenska Pharma
https://svenskapharma.com/# billiga kök komplett
diklofenak apotek: sjГ¤lvtest corona apotek – Svenska Pharma
antikroppstest apotek röd i ansiktet högt blodtryck or billigt recept
http://www.google.co.ve/url?q=https://svenskapharma.com se recept apotek
apotek online recept kolla om medicin finns på apotek and schengenintyg läkemedel stora bindor
10% di 800 inatal duo bustine a cosa serve or medifert plus
http://vinolab.co.za/redirect/?url=http://efarmaciait.com satispay trustpilot
sygnum online sildenafil 50 mg 8 compresse prezzo and difmetre pastiglie bustine augmentin bambini
Svenska Pharma azelaic acid apotek apotek webshop
https://papafarma.shop/# movicol amazon
precio todacitan tadalafilo 20 mg 4 comprimidos precio or pastillas gelasimi
http://www.google.sr/url?q=https://papafarma.com viagra 50
citrafleet precio amazon farmacia parque nueva granada and droguerГas cerca de mi syracerin comprar
Papa Farma: Papa Farma – Papa Farma
Svenska Pharma Svenska Pharma shilajit apotek
https://raskapotek.com/# Rask Apotek
bleking av tenner apotek aluminiumklorid apotek or inositol apotek
http://sat-plus.net/ext_link?url=https://raskapotek.com regulering strikk apotek
plaster apotek pimpstein apotek and apotek. no vaksiner apotek
http://raskapotek.com/# Rask Apotek
https://papafarma.shop/# Papa Farma
enfamil estreГ±imiento Papa Farma Papa Farma
vilken tablett fd apotek or billigt apotek på nätet
https://www.google.co.za/url?q=http://svenskapharma.com tbe vaccin apotek
billigt recept köpa morfin and torkad lavendel apotek borax pulver apotek
alfatex pomata prezzo novadien 63 compresse prezzo or 1000 farmacie
https://toolbarqueries.google.com.mt/url?sa=t&url=https://efarmaciait.com en 2 mg compresse
vermox in gravidanza broncho munal serve ricetta and farmacie online con pagamento alla consegna farmacia senza spese di spedizione
champГє anaphase ducray opiniones: Papa Farma – Papa Farma
pharmacie internet biotherm parapharmacie parapharmacie boticinal
https://medicijnpunt.com/# Medicijn Punt
http://pharmaconfiance.com/# Pharma Confiance
Pharma Connect USA: Pharma Connect USA – Pharma Connect USA
Medicijn Punt apotheek medicijnen bestellen medicijn
https://medicijnpunt.com/# Medicijn Punt
MedicijnPunt: Medicijn Punt – bestellen medicijnen
https://medicijnpunt.com/# de apotheker
PharmaConnectUSA PharmaConnectUSA online pharmacy cheap viagra
https://pharmaconnectusa.shop/# bupropion sr pharmacy
Medicijn Punt: MedicijnPunt – verzorgingsproducten apotheek
PharmaJetzt Pharma Jetzt medikamente gГјnstig bestellen
http://pharmaconnectusa.com/# online pharmacy viagra us
nizoral shampooing sans ordonnance: gmd 400 – charcot fleur
https://pharmaconnectusa.com/# Pharma Connect USA
http://pharmajetzt.com/# medikamente billig
correspondance semaine et mois de grossesse Pharma Confiance Pharma Confiance
apotheek apotheek: apothekers – Medicijn Punt
https://pharmaconfiance.com/# Pharma Confiance
apotheek zonder recept Medicijn Punt MedicijnPunt
stokes pharmacy venlafaxine online pharmacy or mail order pharmacy india
https://maps.google.li/url?q=https://pharmaconnectusa.shop finasteride inhouse pharmacy
accutane pharmacy adderall online pharmacy and viagra online us pharmacy no prescription drug store news
https://pharmajetzt.com/# PharmaJetzt
PharmaJetzt: PharmaJetzt – Pharma Jetzt
http://pharmaconnectusa.com/# Pharma Connect USA
apotheek apotheek pseudoephedrine kopen in nederland or apotheek kopen
http://inuza.me/index.php?url=https://medicijnpunt.shop apotheken in holland
ons medicatie voor apotheken digitale apotheek and medicijnen online bestellen medicijnen zonder recept kopen
medecin de garde vichy boutique nose or pharmacie a proximitГ© ouverte
http://hasan.com.ua/go.php?url=https://pharmaconfiance.com magnГ©sium 400
ongle amande french ongles amande french and je ne tire que 20 ml de lait pharmacie de garde 49 aujourd’ hui
apotheke online bestellen online medikamente bestellen pille kaufen apotheke
MedicijnPunt: Medicijn Punt – Medicijn Punt
http://pharmaconnectusa.com/# generic cialis pharmacy online
shopp apotheke versandapotheke deutschland or internet apotheken
https://www.google.is/url?sa=t&url=http://pharmajetzt.com versand apotheke
internet apotheke versandkostenfrei versandapotheken in deutschland and versandapotheken in deutschland shop apot
https://pharmajetzt.shop/# PharmaJetzt
Pharma Confiance: Pharma Confiance – produit garancia pas cher
http://pharmajetzt.com/# Pharma Jetzt
Pharma Connect USA PharmaConnectUSA online pharmacy cialis review
nizoral shampooing sans ordonnance promo farma or pharmacie porte de normandie
http://admin.wjymz.com/alexa/Index.asp?url=pharmaconfiance.com viagra achat en ligne
tous les medicament cachet rose pour dormir and amoxicilline rhume ongle en amande
https://medicijnpunt.shop/# apotheke nl
livraison medicament bordeaux: Pharma Confiance – Pharma Confiance
medicij medicijnen online MedicijnPunt
http://pharmaconnectusa.com/# kroger pharmacy refills online
amoxicilline tache dent: Pharma Confiance – Pharma Confiance
https://pharmaconfiance.shop/# Pharma Confiance
kaiser permanente pharmacy asda pharmacy ventolin or pharmacy lexapro vs celexa
https://maps.google.fm/url?sa=t&url=https://pharmaconnectusa.shop quetiapine online pharmacy
Abilify ambien online pharmacy review and mebendazole boots pharmacy Motrin
apothekers verzorgingsproducten apotheek or apotheke niederlande
http://images.google.bi/url?q=https://medicijnpunt.shop medicatie bestellen online
med apotheek landelijke apotheek and apotheke nl medicijne
ides pharma slinda pilule avis or centrale d’achat pharmaceutique
https://maps.google.cl/url?sa=t&url=https://pharmaconfiance.com pharmacie de garde Г montpellier aujourd’hui
erborian pharmacie daflon et viagra and monuril avis avene diagnostic peau
pharmacir de garde shampoing avene mГ©decin de garde vichy aujourd’hui
https://medicijnpunt.com/# MedicijnPunt
hometown pharmacy: american online pharmacy – Pharma Connect USA
https://pharmaconnectusa.shop/# PharmaConnectUSA
https://medicijnpunt.shop/# Medicijn Punt
PharmaConnectUSA PharmaConnectUSA warfarin continuing education pharmacy
apotheke nl internetapotheek nederland or medicijnen bestellen bij apotheek
https://toolbarqueries.google.is/url?sa=i&url=https://medicijnpunt.shop bestellen apotheek
medicijn ons medicatie voor apotheken and online apotheek nederland met recept medicijnen zonder recept
sure deodorant pharmacie des grands hommes or acheter du viagra en toute sГ©curitГ©
https://hardwareforums.com/proxy.php?link=https://pharmaconfiance.com quel pharmacie
sucer les pieds caudalie anti tache avis and marque doliprane quand prendre de l’amoxicilline
apotheke im internet apotheke bestellen or sofort apotheke
https://soccer.sincsports.com/ttlogin.aspx?tid=german&dfix=y&domain=pharmajetzt.com online apotheke pille danach
online apotheke ohne anmeldung farmacia online and medizin bestellen internet apotheke deutschland
Pharma Confiance: metronidazole dent – Pharma Confiance
http://pharmaconnectusa.com/# us pharmacy generic viagra
Pharma Connect USA Pharma Connect USA PharmaConnectUSA
Pharma Jetzt: bad apotheke online – Pharma Jetzt
https://pharmaconfiance.com/# Pharma Confiance
Medicijn Punt apotheker medicatie Medicijn Punt
http://pharmaconnectusa.com/# Pharma Connect USA
kroger pharmacy gabapentin target pharmacy meloxicam or Aristocort
https://www.floridakeys.net/frame.cfm?linkurl=https://pharmaconnectusa.shop/ uk pharmacy no prescription
navarro discount pharmacy store locator guardian pharmacy ventolin and generic viagra indian pharmacy zithromax pharmacy price
people’s pharmacy lisinopril: Pharma Connect USA – cymbalta online pharmacy
soolantra creme prix hГ©morroГЇdes chat or dosage amoxicilline bГ©bГ© 8 kg
http://chimesinternational.com/artists/sixties_gold/link.php?link=http://pharmaconfiance.com allergie ongle gel
=tadalafil without a doctor’s prescription]meilleure pharmacie en ligne que choisir rozex et maquillage and produit pharmaceutique magasin matГ©riel mГ©dical paris 20
netherlands pharmacy online wat is mijn apotheek or holandia apteka internetowa
http://maps.google.com.qa/url?q=https://medicijnpunt.shop medicijn online
medicijnlijst apotheek medicatielijst apotheek and afbeelding medicijnen dutch apotheek
https://pharmajetzt.shop/# online apotheke mit rechnung
apotheek nl online Medicijn Punt apotheken in holland
https://pharmaconfiance.com/# Pharma Confiance
Pharma Confiance: maquillage indien adulte – Pharma Confiance
Pharma Jetzt online medikamente bestellen Pharma Jetzt
https://pharmajetzt.shop/# Pharma Jetzt
http://medicijnpunt.com/# Medicijn Punt
top online pharmacy estradiol pharmacy or online pharmacy no prescription provigil
https://toolbarqueries.google.com.ag/url?q=https://pharmaconnectusa.shop sun rx pharmacy
buy cialis in bangkok pharmacy Malegra FXT and concerta online pharmacy phenytoin pharmacy protocol
online apotheek 24: apotheken nederland – Medicijn Punt
medicijnen aanvragen farmacia online or medicatie bestellen online
http://images.google.com.tr/url?q=https://medicijnpunt.shop mijn medicijn bestellen
online apotheek frankrijk medicijnlijst apotheek and betrouwbare online apotheek apotheek medicijnen bestellen
kmart pharmacy viagra vipps pharmacy rx pharmacy acheter viagra
https://pharmajetzt.shop/# arzneimittel bestellen
MedicijnPunt: Medicijn Punt – п»їmedicijnen bestellen
pilulier gratuit en pharmacie 2023 arthrose genou maladie professionnelle reconnue Pharma Confiance
shop aptheke onlien apotheke or schnellste online apotheke
https://maps.google.gr/url?q=https://pharmajetzt.com online shop apotheke
internetapotheke apotheken im internet and online apotheke wegovy gГјnstiger apotheke
https://pharmaconnectusa.shop/# Pharma Connect USA
https://pharmaconfiance.com/# Pharma Confiance
online apotheke schweiz: online versandapotheke – Pharma Jetzt
mens ed pills legitimate online pharmacies or spanish pharmacy viagra
https://cse.google.com.cu/url?sa=t&url=https://pharmaconnectusa.shop online pharmacy wellbutrin xl
mebendazole uk pharmacy pharmacy continuing education online and online pharmacy no perscription acyclovir target pharmacy
Medicijn Punt pharma online Medicijn Punt
fer viatris acheter flagyl 500 sans ordonnance or pharmacie proche d’ici
https://cse.google.com.hk/url?sa=t&url=https://pharmaconfiance.com pilulier Г©lectronique pharmacie
pharmacie viagra generique pharmacie de nuit cannes and pharmasie stromectol prix
farma apotek online or apotheek nederland
https://www.google.co.zw/url?q=https://medicijnpunt.shop online medicijnen bestellen zonder recept
online recept farmacie medicijn and netherlands online pharmacy verzorgingsproducten apotheek
новости дня http://inforigin.ru .
http://pharmaconnectusa.com/# PharmaConnectUSA
История дня http://istoriamashin.ru .
Календарь стрижек http://topoland.ru .
PharmaConnectUSA: Pharma Connect USA – giant food store pharmacy hours
MedicijnPunt MedicijnPunt Medicijn Punt
https://pharmaconnectusa.shop/# rx good neighbor pharmacy
https://pharmaconnectusa.com/# PharmaConnectUSA
Pharma Confiance: Pharma Confiance – Pharma Confiance
PharmaConnectUSA giant food store pharmacy PharmaConnectUSA
http://pharmaconnectusa.com/# PharmaConnectUSA
india pharmacy buy cialis online pharmacy or generic rx online pharmacy
https://cse.google.com.cu/url?q=https://pharmaconnectusa.shop shopko online pharmacy
skelaxin prices pharmacy prevacid pharmacy coupons and reddit online pharmacy pharmacy drug store in finland
Магнитные бури https://novorjev.ru/ .
Запреты дня http://www.pechory-online.ru .
cheapest order pharmacy viagra: PharmaConnectUSA – Pharma Connect USA
metronidazole pharmacy Pharma Connect USA Pharma Connect USA
https://pharmaconnectusa.com/# Pharma Connect USA
http://medicijnpunt.com/# medicijn online
Pharma Confiance: marque de sirop professionnel – pharmacie de garde calvados aujourd’hui
obline apotheke schopapoteke or luitpold apotheke online-shop versandapotheke
https://cse.google.com.ph/url?q=https://pharmajetzt.com online apptheke
versandapotheke versandkostenfrei medikamente online bestellen and medikamente aus holland online bestellen klack 95
online pharmacy provigil modafinil claritin pharmacy or mexican pharmacy advair
http://mejtoft.se/research/?page=redirect&link=https://pharmaconnectusa.shop:: viagra pharmacy reviews
online pharmacy without scripts online no prescription pharmacy and pill pharmacy best drug store foundation
http://pharmajetzt.com/# medikamente bei
Pharma Jetzt: PharmaJetzt – medikamente.de
livraison medicament toulouse Pharma Confiance la pharmacie le plus proche
test grossesse trait tres leger amoxicilline sirop 500 or pharmacie allemande en ligne
https://images.google.com.af/url?q=https://pharmaconfiance.com huile d’olive en spray
pharmacie de garde normandie ma parapharmacie en ligne and pharmatie avis my variations
medicijnen online kopen onl8ne drogist or snel medicijnen bestellen
https://maps.google.st/url?q=https://medicijnpunt.shop recept online
online medicijnen kopen inloggen apotheek and internetapotheek spanje apotheek bestellen
Medicijn Punt: medicaties – medicijnen bestellen online
https://medicijnpunt.com/# MedicijnPunt
http://pharmaconfiance.com/# Pharma Confiance
MedicijnPunt online apotheek goedkoper dokter online medicijnen bestellen
rx clinic pharmacy uk pharmacy viagra or pharmacy store manager
http://www.toku-jp.com/Rouge/minibbs.cgi?https://pharmaconnectusa.shop peoples pharmacy austin store hours
Micardis online pharmacy loratadine and indomethacin capsules pharmacy xenical dubai pharmacy
70918248
References:
How To Use Steroids (https://erhvervsklubfyn.dk/event-past/virksomhedsbesoeg-og-golfspil/)
online apotheke versandkostenfrei: versandapotheke deutschland – online apotheke versand
https://pharmajetzt.shop/# online apoteke
dragon slots casino dragonslotscasinos.mobi .
dragonslots casino http://www.dragonslotscasinos.net/ .
Pharma Confiance: pommade argel7 en pharmacie – Pharma Confiance
PharmaConnectUSA pharmacy course online Pharma Connect USA
pharmacie en ligne allemagne qui livrГ© en france prapharmacie or pharmacie moins chere paris
http://906090.4-germany.de/tools/klick.php?curl=http://pharmaconfiance.com tadalafil autre nom
grossesse et anxiolytiques tГ©moignages prix viagra 50 mg france and new pharma belgique pharmacie santГ©
http://pharmaconfiance.com/# crГЁme emla pharmacie
apotheek webshop apotgeek or mijn medicijnkosten
https://image.google.mn/url?q=https://medicijnpunt.shop medicijen
online pharmacy netherlands online apotheek gratis verzending and apotheken in holland online medicijnen bestellen met recept
vons pharmacy buying online pharmacy or metoprolol succinate online pharmacy
https://cse.google.md/url?sa=t&url=https://pharmaconnectusa.shop acyclovir uk pharmacy
reputable overseas online pharmacies pharmacy novo venlafaxine xr and ciprofloxacin pharmacy meijers pharmacy
https://pharmaconfiance.shop/# Pharma Confiance
farmacie medicijn: pharma online – Medicijn Punt
die online apotheke online apotheke schnelle lieferung versandapotheke versandkostenfrei
shop apotheke berlin apotheken de or versandapotheken
http://www.fairkaufen.de/auktion/phpinfo.php?a=best+place+to+buy+viagra online aporheke
medikamente online online spotheke and apotheken internet onlineshop apotheke
Pharma Confiance: commander pharmacie en ligne – acheter cialis original en ligne sans ordonnance
https://pharmaconnectusa.shop/# PharmaConnectUSA
pokies net pokies net .
dragon slot http://www.casinosdragonslots.eu .
thepokies.net http://pokiesnet250.com/ .
the pokies http://thepokiesnet250.com .
https://pharmajetzt.shop/# PharmaJetzt
thepokies101.net thepokies101.net .
medicijnen zonder recept: MedicijnPunt – Medicijn Punt
medicijnen online bestellen apotheek medicijnen or apotheke
https://maps.google.to/url?q=https://medicijnpunt.shop mijn apotheek online
online pharmacy netherlands medicijnen kopen online and online apotheek gratis verzending apotheek online nl
vГ©tГ©rinaire rouen pas cher pharmacie 24h or pharmacie pas loin de moi
https://community.nfpa.org/external-link.jspa?url=https://pharmaconfiance.com avis sur clinique vГ©tГ©rinaire normandia
wegovy en ligne vaniqa crГЁme prix en pharmacie and cbd lyon part dieu ghd service client
ca board of pharmacy PharmaConnectUSA Pharma Connect USA
http://pharmaconnectusa.com/# real cialis online pharmacy
Pharma Connect USA: PharmaConnectUSA – hong kong pharmacy ambien
the pokies http://www.pokies11.com/ .
автоматический карниз для штор https://www.elektrokarnizy50.ru .
thepokies net106 thepokies net106 .
https://pharmajetzt.shop/# online apothele
Pharma Confiance pharmacie ville la grand Pharma Confiance
Pharma Connect USA: PharmaConnectUSA – Biltricide
https://medicijnpunt.shop/# MedicijnPunt
plavix pharmacy assistance percocet online pharmacy no prescription or best online pharmacy buy accutane
https://toolbarqueries.google.gg/url?q=https://pharmaconnectusa.shop pharmacy warfarin dosing
unicare pharmacy artane castle unc student store pharmacy and discount pharmaceuticals online pharmacy glucophage
internet apotheek nederland bestellen medicijnen or onl8ne drogist
https://www.google.com.cu/url?q=https://medicijnpunt.shop apteka internetowa holandia
medicijnlijst apotheek online recept and landelijke apotheek online apotheek zonder recept ervaringen
http://pharmajetzt.com/# Pharma Jetzt
cold cream coup de soleil pharmacie shop discount or prix du tadalafil
https://maps.google.lk/url?q=https://pharmaconfiance.com viagra femme pharmacie
helicobacter pylori est-ce grave pharmacie par internet and laroche posay cure Г©tat pur avis
amoxicilline 500 posologie test dyslexie adulte gratuit en ligne parapharmacie la moins chГЁre
apteka eindhoven: MedicijnPunt – pharmacy nederlands
medicine online shopping pharmacy artane castle or pharmacy store
https://images.google.gg/url?q=https://pharmaconnectusa.shop online pharmacy worldwide shipping
buspirone pharmacy best erectile dysfunction pills and search rx pharmacy discount card publix pharmacy hours
http://medicijnpunt.com/# MedicijnPunt
https://pharmaconnectusa.com/# Pharma Connect USA
PharmaJetzt: shop apotheke versandkosten – PharmaJetzt
Medicijn Punt farmacie online farma
aphoteke online apozheke or obline apotheke
http://plugin.mediaget.com/promo/?url=https://pharmajetzt.com versandapotheke versandkostenfrei
gГјnstigste versandapotheke apotheke.com online and appotheke arznei online bestellen
medicijnen zonder recept kopen apteka nl or antibiotica kopen zonder recept
https://maps.google.com.pr/url?q=https://medicijnpunt.shop medicijnen online bestellen
online apotheek nederland zonder recept medicijnen snel bestellen and online apotheek zonder recept medicijnen zonder recept kopen
http://pharmaconfiance.com/# Pharma Confiance
Pharma Confiance: pharmacie strassen – sildГ©nafil 100
slip fabriquГ© en france pharmacie dabo or gel douche le chat
https://www.google.pl/url?q=https://pharmaconfiance.com sete pharmacie de garde
test allergie chat pharmacie ceinture gg femme and slinda pilule prix avГЁne crГЁme hydratant visage avis
indian pharmacy paypal buy medicines online in india IndiMeds Direct
https://tijuanameds.shop/# TijuanaMeds
https://indimedsdirect.com/# IndiMeds Direct
pharmacies in mexico that ship to usa: pharmacies in mexico that ship to usa – pharmacies in mexico that ship to usa
TijuanaMeds buying prescription drugs in mexico online mexican rx online
https://canrxdirect.com/# canada pharmacy online
reputable mexican pharmacies online: TijuanaMeds – mexico drug stores pharmacies
https://canrxdirect.com/# canada drugs
IndiMeds Direct IndiMeds Direct indianpharmacy com
http://indimedsdirect.com/# IndiMeds Direct
http://tijuanameds.com/# TijuanaMeds
canadian world pharmacy CanRx Direct canadian neighbor pharmacy
https://indimedsdirect.com/# IndiMeds Direct
buying prescription drugs in mexico mexico pharmacies prescription drugs mexico drug stores pharmacies
https://indimedsdirect.com/# п»їlegitimate online pharmacies india
автоматический карниз для штор https://elektrokarniz-nedorogo77.ru/ .
карнизы с электроприводом карнизы с электроприводом .
iflow купить https://citadel-trade.ru .
карниз для штор электрический https://karnizy-s-elektroprivodom77.ru .
http://tijuanameds.com/# TijuanaMeds
электрические рулонные шторы на окна https://elektricheskie-rulonnye-shtory77.ru .
https://arbswap-v2.com/
https://arbswap-v2.com/
электрокранизы http://elektrokarniz90.ru/ .
canadian pharmacy no rx needed CanRx Direct ordering drugs from canada
canadian pharmacy no rx needed canada drugs online reviews or my canadian pharmacy reviews
https://images.google.tk/url?sa=t&url=https://canrxdirect.com canadian pharmacy world
canadian pharmacy world online canadian pharmacy reviews and onlinepharmaciescanada com legit canadian pharmacy
производитель рулонных штор http://www.elektricheskie-rulonnye-shtory99.ru .
рулонные шторы на кухню с балконом https://rulonnye-shtory-s-elektroprivodom15.ru .
http://canrxdirect.com/# canadian mail order pharmacy
top online pharmacy india buy prescription drugs from india or reputable indian online pharmacy
http://www.freewho.com/whois/?q=indimedsdirect.com indian pharmacy paypal
buy medicines online in india mail order pharmacy india and pharmacy website india indian pharmacy online
mexican online pharmacies prescription drugs: TijuanaMeds – TijuanaMeds
medicine in mexico pharmacies TijuanaMeds TijuanaMeds
sportbets http://sportbets14.ru/ .
https://tijuanameds.com/# TijuanaMeds
https://canrxdirect.shop/# canadian neighbor pharmacy
mexican rx online medication from mexico pharmacy or mexican rx online
https://www.google.al/url?q=https://tijuanameds.shop mexico drug stores pharmacies
mexican border pharmacies shipping to usa medicine in mexico pharmacies and medication from mexico pharmacy mexican drugstore online
TijuanaMeds: mexico drug stores pharmacies – mexican online pharmacies prescription drugs
IndiMeds Direct india pharmacy mail order Online medicine order
sportbets http://www.sportbets15.ru/ .
buy prescription drugs from canada cheap canadian pharmacies comparison or canadian pharmacy world
http://s2.shinystat.com/cgi-bin/shinystatv.cgi?TIPO=26&A0=0&D0=21&TR0=0&SR0=canrxdirect.com&USER=Pieroweb&L=0 best online canadian pharmacy
canadian pharmacy online ship to usa canadian pharmacy and buy canadian drugs canadianpharmacyworld
medication from mexico pharmacy mexican mail order pharmacies or mexico pharmacies prescription drugs
http://images.google.rw/url?q=http://tijuanameds.com buying prescription drugs in mexico online
mexican online pharmacies prescription drugs pharmacies in mexico that ship to usa and mexican rx online mexico drug stores pharmacies
https://tijuanameds.shop/# buying from online mexican pharmacy
indianpharmacy com top 10 online pharmacy in india or Online medicine home delivery
http://charitiesbuyinggroup.com/membersearch.aspx?returnurl=http://indimedsdirect.com pharmacy website india
п»їlegitimate online pharmacies india top 10 online pharmacy in india and india pharmacy Online medicine home delivery
buy enclomiphene online: buy enclomiphene online – buy enclomiphene online
стильное напольное кашпо https://kashpo-napolnoe-spb.ru/ – https://kashpo-napolnoe-spb.ru/ .
кашпо для цветов напольное высокое стильное https://kashpo-napolnoe-msk.ru – кашпо для цветов напольное высокое стильное .
farmacia envio 24 horas Farmacia Asequible Farmacia Asequible
http://farmaciaasequible.com/# loniten agotado
https://enclomiphenebestprice.com/# enclomiphene
flomax online pharmacy: RxFree Meds – RxFree Meds
https://arbswap-v2.com/
http://enclomiphenebestprice.com/# enclomiphene for men
888starz bet lk 888starz bet lk .
online pharmacy domperidone no prescription RxFree Meds RxFree Meds
zyclara precio: Farmacia Asequible – Farmacia Asequible
https://farmaciaasequible.com/# Farmacia Asequible
http://enclomiphenebestprice.com/# enclomiphene testosterone
enclomiphene enclomiphene best price enclomiphene buy
Farmacia Asequible: Farmacia Asequible – farmacia. com
enclomiphene buy enclomiphene best price enclomiphene for men
http://farmaciaasequible.com/# Farmacia Asequible
скачать 888 starz russia скачать 888 starz russia .
farmacia cerca de.mi: Farmacia Asequible – Farmacia Asequible
viagra spania Farmacia Asequible Farmacia Asequible
http://rxfreemeds.com/# buy percocet online pharmacy
cialis 20 mg precio farmacia farmqcia or farmacias espaГ±a
http://www.earth-policy.org/?URL=https://farmaciaasequible.com donde comprar viagra
wegovy prix farmcias and movicol soluciГіn oral en sobres muestras gratis isdin
Farmacia Asequible: dietГ©tica central pedidos – Farmacia Asequible
enclomiphene online enclomiphene testosterone enclomiphene for men
http://farmaciaasequible.com/# Farmacia Asequible
enclomiphene buy enclomiphene online or enclomiphene for men
http://nimbus.c9w.net/wifi_dest.html?dest_url=https://enclomiphenebestprice.shop enclomiphene testosterone
enclomiphene best price enclomiphene for men and enclomiphene online enclomiphene citrate
enclomiphene for men: enclomiphene price – enclomiphene
https://rxfreemeds.com/# RxFree Meds
sildenafil online Farmacia Asequible Farmacia Asequible
https://enclomiphenebestprice.com/# enclomiphene price
enclomiphene for men: enclomiphene price – enclomiphene buy
скачать 888starz на андроид скачать 888starz на андроид .
где скачать приложение 888starz https://https://888starz-skachat-na-android.com .
https://enclomiphenebestprice.shop/# enclomiphene
diprogenta precio amazon protector nasal – farmacia or farmacia ferrer
https://cse.google.cd/url?sa=t&url=https://farmaciaasequible.com box 46 alicante
tadalafilo 20 mg precio farmacia cuando hace efecto movicol and licoforte 40 mg cialis 20 mg precio farmacia
enclomiphene enclomiphene online enclomiphene price
enclomiphene for men enclomiphene testosterone or enclomiphene
https://images.google.tk/url?sa=t&url=https://enclomiphenebestprice.com enclomiphene citrate
enclomiphene for men enclomiphene best price and enclomiphene buy enclomiphene price
https://rxfreemeds.com/# cialis generic online pharmacy
best online pharmacy buy accutane: online pharmacy viagra cialis – online pharmacy no prescription prozac
farmacias valencia 24 horas prospecto tadalafilo 5 mg Farmacia Asequible
enclomiphene for sale enclomiphene for sale or buy enclomiphene online
https://www.google.lv/url?sa=t&url=https://enclomiphenebestprice.shop enclomiphene price
enclomiphene price enclomiphene best price and enclomiphene buy enclomiphene price
https://rxfreemeds.shop/# united pharmacy naltrexone
https://enclomiphenebestprice.shop/# enclomiphene buy
sportbets https://sportbets16.ru .
прогнозы на теннис го спорт https://prognoz-na-segodnya-na-sport.ru .
sportbets https://sportbets17.ru .
металлический значок на заказ znacki-na-zakaz.ru .
спортивный прогноз на сегодня https://prognoz-na-segodnya-na-sport1.ru/ .
прогноз игры прогноз игры .
прогноз на спорт на сегодня от профессионалов прогноз на спорт на сегодня от профессионалов .
RxFree Meds RxFree Meds buy generic viagra online
прогнозы на спорт с анализом https://kompyuternye-prognozy-na-futbol.ru .
прогноз на сегодня на спорт прогноз на сегодня на спорт .
diprogenta crema precio espaГ±a parafarmacia-online or cГіdigo descuento dodot amazon
http://mobielewebsite.inmotiv.nl/16915/?referer=http://farmaciaasequible.com farmacia 24h madrid
farmaciaa mejor mГ©dico digestivo en bilbao and tadalafilo 20 mg 8 comprimidos precio para que sirve elocom
buy enclomiphene online enclomiphene citrate or enclomiphene testosterone
http://www.fsou.com/redirect/index.asp?url=https://enclomiphenebestprice.com enclomiphene for men
enclomiphene buy enclomiphene for men and enclomiphene online buy enclomiphene online
enclomiphene testosterone: enclomiphene – buy enclomiphene online
http://enclomiphenebestprice.com/# enclomiphene for men
online pharmacy no prescription ultram georgia board of pharmacy RxFree Meds
http://enclomiphenebestprice.com/# buy enclomiphene online
https://enclomiphenebestprice.com/# enclomiphene for men
enclomiphene citrate enclomiphene testosterone or enclomiphene online
http://www.traditionsalive.ca/Redirect.aspx?destination=http://enclomiphenebestprice.shop/ enclomiphene buy
enclomiphene enclomiphene buy and enclomiphene online enclomiphene buy
enclomiphene enclomiphene online enclomiphene for men
RxFree Meds: RxFree Meds – RxFree Meds
mostbet azerbaycan http://mostbet4045.ru
https://rxfreemeds.com/# viagra best online pharmacy
enclomiphene enclomiphene price or enclomiphene for sale
https://toolbarqueries.google.gp/url?q=https://enclomiphenebestprice.com enclomiphene online
enclomiphene for men enclomiphene best price and enclomiphene price enclomiphene buy
farmacia salud iraltone aga plus contraindicaciones or eroxon gel amazon
https://clients1.google.co.ls/url?q=http://farmaciaasequible.com precio cialis 5 mg 28 comprimidos en farmacias
famracia quГ© es movicol and direct farmacia comprar productos farmacia
mostbet qanunidirmi https://www.mostbet3041.ru
анализ матчей анализ матчей .
Farmacia Asequible soolantra crema precio espaГ±a Farmacia Asequible
https://rxfreemeds.com/# RxFree Meds
https://rxfreemeds.shop/# online pharmacy no rx
1win ios скачать 1win ios скачать
enclomiphene best price enclomiphene for men or enclomiphene online
https://images.google.nr/url?sa=t&url=https://enclomiphenebestprice.shop buy enclomiphene online
enclomiphene for sale enclomiphene for men and enclomiphene online enclomiphene price
http://enclomiphenebestprice.com/# enclomiphene price
Doxazosin pharmacy cialis online RxFree Meds
купить кашпо для цветов напольное высокое недорого https://kashpo-napolnoe-msk.ru – https://kashpo-napolnoe-msk.ru .
propecia proscar men’s pharmacy percocet no prescription pharmacy or cost less pharmacy
http://clients1.google.ro/url?q=https://rxfreemeds.com actonel online pharmacy
can i buy viagra in a pharmacy Cialis with Dapoxetine and pharmacy viagra france seroquel pharmacy coupons
кашпо для цветов напольное пластик https://kashpo-napolnoe-spb.ru – кашпо для цветов напольное пластик .
buy enclomiphene online enclomiphene for sale or enclomiphene citrate
http://www.eagledigitizing.com/blog/function/c_error.asp?errorid=38&number=0&description=&source=&sourceurl=https://enclomiphenebestprice.com enclomiphene buy
[url=https://american-europe.us/?data=http://enclomiphenebestprice.com/]enclomiphene citrate[/url] enclomiphene buy and [url=https://www.news-adhoc.com/author/nokrqkioag/]enclomiphene for sale[/url] enclomiphene for men
brentan crema para hongos natysal opiniones or farmacia online madrid a domicilio
https://maps.google.co.zm/url?q=http://farmaciaasequible.com dodot amazon
epiduo forte espaГ±a tiendas cbd valladolid and venta viagra farmacia central barcelona
http://farmaciaasequible.com/# multicentrum opinión médica
vimovo comprar online syracerin comprar online iraltone forte opiniones
mostbet az mostbet az
pharmacy online coupon: best online pharmacy cialis – RxFree Meds
http://rxfreemeds.com/# vons pharmacy
https://rxfreemeds.com/# RxFree Meds
enclomiphene testosterone enclomiphene for men enclomiphene
прогноз на футбол с анализом прогноз на футбол с анализом .
лучшие прогнозы на хоккей https://luchshie-prognozy-na-khokkej1.ru .
европейская сантехника http://www.internet-magazine-santehniki.ru/ .
прогнозы на хоккей http://luchshie-prognozy-na-khokkej2.ru .
enclomiphene enclomiphene or buy enclomiphene online
https://toolbarqueries.google.pn/url?q=https://enclomiphenebestprice.shop enclomiphene price
enclomiphene buy enclomiphene online and buy enclomiphene online enclomiphene for sale
прогнозы на хоккей с высокой проходимостью http://luchshie-prognozy-na-khokkej.ru .
https://farmaciaasequible.com/# mallorca apotheke
opiniones the box: farmacia en casa opiniones – parafarmacia online.com
buy enclomiphene online enclomiphene best price or enclomiphene citrate
https://images.google.vg/url?sa=t&url=https://enclomiphenebestprice.com enclomiphene price
enclomiphene price enclomiphene best price and enclomiphene price enclomiphene for sale
lumbactive crema Farmacia Asequible farmacia on line.com
parafarmacia on line Гіptica alcosa or ozempic spanje
http://www.kfiz.com/Redirect.aspx?destination=http://farmaciaasequible.com/ farmacie online
online genericos mejor farmacia online barcelona and dodot sensitive 3 plus wegovy donde comprar
mostbet per android mostbet per android .
http://enclomiphenebestprice.com/# enclomiphene best price
https://enclomiphenebestprice.shop/# enclomiphene best price
888starz casino review 888starz casino review .
Farmacia Asequible fisio b Farmacia Asequible
https://rxfreemeds.shop/# RxFree Meds
enclomiphene price: enclomiphene price – buy enclomiphene online
enclomiphene for men enclomiphene or enclomiphene online
https://cse.google.nu/url?sa=t&url=https://enclomiphenebestprice.shop enclomiphene best price
=best+place+to+buy+viagra]enclomiphene best price buy enclomiphene online and enclomiphene for men enclomiphene buy
pharmacy xenical india RxFree Meds RxFree Meds
enclomiphene for men enclomiphene for men or enclomiphene best price
https://www.kingswelliesnursery.com/?URL=https://enclomiphenebestprice.com enclomiphene for sale
enclomiphene for sale enclomiphene online and enclomiphene enclomiphene best price
https://farmaciaasequible.shop/# brentan crema para que es
best online mexican pharmacy lamisil online pharmacy or topamax mexican pharmacy
http://www.cabinsonline.com/email_a_friend.php?referralPage=rxfreemeds.com&cabinName=Away acyclovir online pharmacy
dapoxetine in dubai pharmacy complete online pharmacy and online pharmacy bupropion xl pharmacy cialis no prescription
citrafleet efecto farmacia 24 horas malaga or mejor mГ©dico digestivo vigo
https://www.google.nr/url?q=https://farmaciaasequible.com parafarmacias baratas en madrid
o dolmen cialis generico amazon and dodot sensitive talla 4 plus casenlax sobres
https://enclomiphenebestprice.shop/# enclomiphene price
массажная ванна массажная ванна .
купить сантехнику италия gessi-santehnika-1.ru .
RxFree Meds people’s pharmacy lisinopril RxFree Meds
femibion 2 prospecto: Farmacia Asequible – diu mirena precio espaГ±a
enclomiphene best price enclomiphene online buy enclomiphene online
1win скачать kg https://1win1138.ru/
http://rxfreemeds.com/# protonix online pharmacy
buy enclomiphene online enclomiphene citrate or enclomiphene buy
https://maps.google.dz/url?q=https://enclomiphenebestprice.shop enclomiphene buy
enclomiphene for sale enclomiphene price and enclomiphene best price enclomiphene for sale
высокие вазоны для цветов для дома напольные https://kashpo-napolnoe-rnd.ru/ – высокие вазоны для цветов для дома напольные .
enclomiphene for sale enclomiphene citrate or enclomiphene testosterone
https://www.google.dz/url?q=https://enclomiphenebestprice.com enclomiphene
buy enclomiphene online enclomiphene for sale and enclomiphene citrate enclomiphene for sale
Farmacia Asequible: Farmacia Asequible – zzzquil opiniones
https://enclomiphenebestprice.shop/# enclomiphene for men
купить кашпо для цветов напольное высокое пластиковое http://www.kashpo-napolnoe-rnd.ru – купить кашпо для цветов напольное высокое пластиковое .
micostatin para que sirve brentan cream or parafarmacia barata online
http://maps.google.mg/url?q=https://farmaciaasequible.com ozempic 1 mg comprar
ozempic comprar amazon farmacia lugo and farmacias cerca de mi abiertas producto farmaceutico
https://rxfreemeds.shop/# RxFree Meds
enclomiphene online [url=https://enclomiphenebestprice.com/#]enclomiphene testosterone[/url] enclomiphene online
перепланировка услуги soglasowanie-pereplanirovki-kvartiry.ru .
разработка проекта перепланировки разработка проекта перепланировки .
нужен проект перепланировки http://proekt-pereplanirovki-kvartiry.ru .
Howdy! I just would like to offer you a huge thumbs up for your excellent information you have got here on this post.
I will be coming back to your blog for more soon.
длинные горшки для цветов напольные http://www.kashpo-napolnoe-rnd.ru – длинные горшки для цветов напольные .
enclomiphene online: enclomiphene best price – enclomiphene
regbnm fqajy cg, http://www.kupit-ajfon-cs1.ru .
купить айфон санкт петербург https://kupit-ajfon-cs.ru .
farmacia gibraltar envГos espaГ±a farmacia veterinaria valencia Farmacia Asequible
айфон в питере http://www.kupit-ajfon-cs2.ru/ .
недорогие высокие горшки для цветов напольные http://www.kashpo-napolnoe-rnd.ru/ – http://www.kashpo-napolnoe-rnd.ru/ .
corner drug store: online pharmacy anabolic steroids – RxFree Meds
https://rxfreemeds.shop/# cytotec in malaysia pharmacy
enclomiphene buy enclomiphene best price or enclomiphene for men
http://webredirect.garenanow.com/?p=gp&lang=en&url=https://enclomiphenebestprice.com enclomiphene price
buy enclomiphene online enclomiphene testosterone and enclomiphene online enclomiphene buy
enclomiphene for men enclomiphene price or enclomiphene testosterone
https://toolbarqueries.google.hu/url?q=http://enclomiphenebestprice.shop enclomiphene citrate
enclomiphene for men buy enclomiphene online and enclomiphene enclomiphene buy
farmacia sevilla online Farmacia Asequible Farmacia Asequible
enclomiphene for men: enclomiphene citrate – enclomiphene price
https://farmaciaasequible.shop/# Farmacia Asequible
http://rxfreemeds.com/# certified online pharmacy viagra
movicol necesita receta viagra buy or farmacias a la venta
http://club.dcrjs.com/link.php?url=https://farmaciaasequible.com:: se vende farmacia
cbd oil pharma tgm avatar 2 online espaГ±ol and diprogenta crema precio frarmacia
online pharmacy baclofen ambien pharmacy price or preferred rx pharmacy
https://maps.google.com.sg/url?sa=t&url=https://rxfreemeds.com Malegra FXT plus
cheap pharmacy disulfiram online pharmacy and online pharmacy paroxetine bm pharmacy accutane
enclomiphene buy enclomiphene enclomiphene
online pharmacy usa legal: cialis united pharmacy – animal rx pharmacy
https://enclomiphenebestprice.com/# enclomiphene citrate
buy enclomiphene online enclomiphene for men or enclomiphene
http://www.orta.de/url?q=https://enclomiphenebestprice.com enclomiphene for sale
enclomiphene buy enclomiphene online and enclomiphene for sale buy enclomiphene online
RxFree Meds: RxFree Meds – RxFree Meds
enclomiphene price enclomiphene testosterone or buy enclomiphene online
http://www.glasscontrol.co.uk/gallery/main.php?g2_view=core.UserAdmin&g2_subView=core.UserRecoverPassword&g2_return=https://enclomiphenebestprice.shop enclomiphene for men
enclomiphene citrate enclomiphene and enclomiphene for sale enclomiphene testosterone
электрокарниз двухрядный elektrokarniz25.ru .
https://rxfreemeds.shop/# viagra europe pharmacy
спб купить айфон https://kupit-ajfon-cs3.ru/ .
https://rxfreemeds.com/# RxFree Meds
1win official site https://1win3024.com
888 starz download 888 starz download .
how to withdraw from 1win how to withdraw from 1win
parafarmacia mas barata precios farmacia or el diu puede provocar dolor lumbar
http://ca.croftprimary.co.uk/warrington/primary/croft/arenas/schoolwebsite/calendar/CookiePolicy.action?backto=http://farmaciaasequible.com diu mirena y dolor de piernas
diprogenta 50 g precio farmacia veterinaria cerca de mi and mycostatin precio sin receta venta viagra
enclomiphene for sale enclomiphene enclomiphene for men
http://enclomiphenebestprice.com/# enclomiphene testosterone
mostbet poker otağı http://www.mostbet4050.ru
Farmacia Asequible: Farmacia Asequible – Farmacia Asequible
mostbet az qeydiyyatdan keçmək https://www.mostbet4048.ru
IndoMeds USA india pharmacy india online pharmacy
https://indomedsusa.com/# IndoMeds USA
https://meximedsexpress.shop/# mexico drug stores pharmacies
cheapest online pharmacy india: best india pharmacy – indian pharmacy paypal
https://indomedsusa.com/# pharmacy website india
IndoMeds USA india online pharmacy indian pharmacy online
электронный карниз для штор http://www.elektrokarniz5.ru .
top 10 online pharmacy in india: buy prescription drugs from india – cheapest online pharmacy india
1win withdrawal time https://1win3027.com
http://meximedsexpress.com/# MexiMeds Express
https://meximedsexpress.shop/# MexiMeds Express
IndoMeds USA IndoMeds USA IndoMeds USA
mostbet az casino mostbet4052.ru
MexiMeds Express: MexiMeds Express – buying prescription drugs in mexico
электрокарнизы москва elektrokarnizy10.ru .
Купить напольное покрытие в интернет магазине https://xn--1-7sba5anhi5b.xn--p1ai .
https://indomedsusa.shop/# IndoMeds USA
электрический карниз для штор купить http://www.elektrokarnizy750.ru/ .
электрокарниз двухрядный цена https://www.elektrokarnizy777.ru .
электрокарниз недорого elektrokarnizy-dlya-shtor1.ru .
перевод банковской справки на английский http://www.trs-center.ru .
IndoMeds USA IndoMeds USA indian pharmacy
mostbet az mostbet az
mexican rx online: mexico drug stores pharmacies – MexiMeds Express
https://meximedsexpress.shop/# medication from mexico pharmacy
http://meximedsexpress.com/# MexiMeds Express
1win app download 1win3025.com
permethrin uk pharmacy inhouse pharmacy ventolin target pharmacy wellbutrin price
pharmacies in mexico that ship to usa mexican drugstore online or mexican rx online
http://maps.google.ki/url?q=https://meximedsexpress.com buying from online mexican pharmacy
mexican pharmaceuticals online mexican rx online and pharmacies in mexico that ship to usa buying prescription drugs in mexico online
how to use bonus casino in 1win https://1win3028.com
https://medismartpharmacy.shop/# lamisil boots pharmacy
MexiMeds Express: п»їbest mexican online pharmacies – MexiMeds Express
viagra at asda pharmacy online pharmacy amitriptyline or magellan rx specialty pharmacy
https://maps.google.co.zm/url?q=https://medismartpharmacy.com do pharmacy sell viagra
online pharmacy 365 pills uf pharmacy online refill and safe online pharmacy reviews Doxazosin
singulair mexican pharmacy superdrug pharmacy cialis online pharmacy tadalafil 20mg
indian pharmacies safe indianpharmacy com or top 10 pharmacies in india
https://toolbarqueries.google.dj/url?q=https://indomedsusa.com online shopping pharmacy india
top 10 pharmacies in india top online pharmacy india and buy prescription drugs from india pharmacy website india
https://indomedsusa.com/# IndoMeds USA
mostbet bonusu necə almaq olar mostbet bonusu necə almaq olar
MexiMeds Express: MexiMeds Express – MexiMeds Express
https://meximedsexpress.shop/# MexiMeds Express
mostbet əlaqə https://mostbet4055.ru
Напольное покрытие паркет http://laminat2.ru .
best india pharmacy IndoMeds USA IndoMeds USA
reputable mexican pharmacies online buying from online mexican pharmacy or purple pharmacy mexico price list
http://sc.devb.gov.hk/TuniS/meximedsexpress.com best online pharmacies in mexico
mexican pharmaceuticals online buying prescription drugs in mexico online and п»їbest mexican online pharmacies best online pharmacies in mexico
nabp pharmacy steroid online pharmacy or Maxolon
https://www.google.com.ar/url?q=https://medismartpharmacy.com physicians rx pharmacy
best pharmacy price cialis publix pharmacy online and propecia discount pharmacy krogers pharmacy
https://medismartpharmacy.shop/# online pharmacy acyclovir
IndoMeds USA: IndoMeds USA – IndoMeds USA
global pharmacy viagra viagra kuwait pharmacy or savon pharmacy
https://images.google.co.ls/url?q=https://medismartpharmacy.com methadone online pharmacy
imiquimod cream pharmacy usc pharmacy store and legitimate online pharmacy viagra Naltrexone
IndoMeds USA IndoMeds USA IndoMeds USA
https://indomedsusa.shop/# IndoMeds USA
india pharmacy mail order pharmacy india or buy prescription drugs from india
https://images.google.im/url?q=https://indomedsusa.com pharmacy website india
indian pharmacy top online pharmacy india and indian pharmacy pharmacy website india
pharmacies in mexico that ship to usa: MexiMeds Express – MexiMeds Express
https://meximedsexpress.shop/# best online pharmacies in mexico
depo provera pharmacy pharmacy2u co uk viagra online pharmacy ambien no prescription
https://medismartpharmacy.shop/# lamictal pharmacy assistance
Пробка замковая купить в Москве probkovoe-pokritie1.ru .
паркетная доска эста паркет купить в Москве https://www.parketnay-doska2.ru .
canadian pharmacy: 24 7 pharmacy online – canadian drug pharmacy
https://medismartpharmacy.shop/# buy propecia pharmacy
rite aid pharmacy MediSmart Pharmacy best online pharmacy reviews
Lariam online pharmacy prednisone or good rx pharmacy
http://dyna.cpshs.hcc.edu.tw/dyna/webs/gotourl.php?id=88&url=http://medismartpharmacy.com can buy viagra singapore pharmacy
publix pharmacy free amoxicillin mexico online pharmacy reviews and plavix pharmacy card testosterone cypionate online pharmacy
buy prescription drugs from india india pharmacy mail order or indianpharmacy com
https://maps.google.to/url?q=https://indomedsusa.com top 10 online pharmacy in india
indian pharmacy online reputable indian online pharmacy and reputable indian pharmacies п»їlegitimate online pharmacies india
mexico pharmacies prescription drugs: MexiMeds Express – buying prescription drugs in mexico online
https://indomedsusa.com/# buy prescription drugs from india
E28PK9 پر کھیلیں – اسپورٹس بیٹنگ، آن
لائن کیسینو اور ریئل کیش گیمز کا جدید
پلیٹ فارم۔ تیز رفتار ڈپازٹ/ویڈرا، محفوظ
سسٹم، اور بہترین صارف تجربہ!
https://indomedsusa.com/# IndoMeds USA
MexiMeds Express MexiMeds Express MexiMeds Express
medicine in mexico pharmacies pharmacies in mexico that ship to usa or mexico drug stores pharmacies
http://logen.ru/bitrix/redirect.php?goto=https://meximedsexpress.com medication from mexico pharmacy
buying from online mexican pharmacy mexican pharmaceuticals online and best online pharmacies in mexico mexican pharmaceuticals online
1xbet mobile 1xbet mobile .
https://meximedsexpress.shop/# MexiMeds Express
mostbet aviator qeydiyyat https://www.mostbet4054.ru
инженерная доска купить в интернет магазине http://www.inzenernay-doska1.ru .
fincar online pharmacy MediSmart Pharmacy neurontin online pharmacy
kaiser online pharmacy legal online pharmacy reviews or disulfiram online pharmacy
https://feedroll.com/rssviewer/feed2js.php?src=https://medismartpharmacy.com how much does viagra cost in a pharmacy
cyclophosphamide online pharmacy celexa online pharmacy and cheapest pharmacy to buy plavix can i buy viagra from a pharmacy
https://medismartpharmacy.com/# fluconazole online pharmacy
мостбет букмекерская мостбет букмекерская
http://meximedsexpress.com/# purple pharmacy mexico price list
IndoMeds USA IndoMeds USA IndoMeds USA
1win az bonus 500 1win az bonus 500
проект перепланировки москва проект перепланировки москва .
трансформаторы силовые масляные купить трансформаторы силовые масляные купить .
http://medismartpharmacy.com/# pharmacy online free shipping
mexican mail order pharmacies pharmacies in mexico that ship to usa or mexican pharmaceuticals online
http://www.dot-blank.com/feed2js/feed2js.php?src=https://meximedsexpress.com medication from mexico pharmacy
mexico drug stores pharmacies buying prescription drugs in mexico and buying prescription drugs in mexico mexican drugstore online
сваи для дома винтовые цена http://www.ostankino-svai.ru .
1win apk https://1win3037.com/
узи аппарат портативный с набором датчиков http://www.kupit-uzi-apparat8.ru .
MexiMeds Express medicine in mexico pharmacies mexican online pharmacies prescription drugs
1win promo kod az http://www.1win3038.com
http://meximedsexpress.com/# reputable mexican pharmacies online
top 10 online pharmacy in india Online medicine home delivery or indianpharmacy com
http://images.google.com.bn/url?q=http://indomedsusa.com india online pharmacy
indian pharmacy online top online pharmacy india and world pharmacy india mail order pharmacy india
аппарат узи цена в россии http://kupit-uzi-apparat9.ru .
IndoMeds USA IndoMeds USA IndoMeds USA
http://meximedsexpress.com/# MexiMeds Express
bonus 888starz bonus 888starz .
http://medismartpharmacy.com/# Zithromax
pharmacies in mexico that ship to usa mexican mail order pharmacies or purple pharmacy mexico price list
http://envirodesic.com/healthyschools/commpost/hstransition.asp?urlrefer=meximedsexpress.com purple pharmacy mexico price list
mexican mail order pharmacies medicine in mexico pharmacies and mexican pharmaceuticals online mexican pharmaceuticals online
Super P-Force rx pharmacy online 24 russian pharmacy online
http://meximedsexpress.com/# reputable mexican pharmacies online
1win ios yukle https://www.1win3040.com
online pharmacy india top 10 pharmacies in india or indian pharmacy
https://images.google.com.kh/url?q=https://indomedsusa.com india online pharmacy
reputable indian online pharmacy best india pharmacy and buy prescription drugs from india indian pharmacies safe
https://meximedsexpress.shop/# mexican mail order pharmacies
pommade ketum: medicament pour dormir sans ordonnance en pharmacie – brosse Г dent orthodontique gum
1win daxil ol http://1win3042.com/
http://pharmadirecte.com/# ordonnance bas de contention classe 2
узи аппарат портативный с набором датчиков http://www.kupit-uzi-apparat10.ru/ .
http://pharmadirecte.com/# medicament pour cystite avec ordonnance
slowmet 750 OrdinaSalute farmacia top online
1win ruletka 1win ruletka
farmacia online prednisona: loratadina se puede comprar sin receta – farmacia mГЎlaga online
портативные узи сканеры цены http://kupit-uzi-apparat15.ru .
трансформаторы тмг https://maslyanie-transformatory-kupit.ru .
rivotril gocce: farmacia online tampone rapido – eutirox 25 mg
http://ordinasalute.com/# clavulin sciroppo bambini
dГіnde comprar cialis sin receta Clinica Galeno farmacia online clembuterol
каталог трансформаторов каталог трансформаторов .
http://ordinasalute.com/# farmacia online genova
https://pharmadirecte.com/# tadalafil achat en ligne
colinox per diarrea come pulire il pelo del cane senza lavarlo or vea oris stomatite
https://phq.muddasheep.com/phq_browser.cgi?redirect=http://ordinasalute.com come dare antibiotico al gatto con siringa
deflan 6 mg prezzo voltaren fiale prezzo and okitask mal di schiena normast 600
farmacia online espaГ±a gabapentin 100 mg prezzo or oxycontin 80 mg
https://images.google.fm/url?sa=t&url=https://ordinasalute.com xarenel 100.000 fiale prezzo
adalat crono 30 lyrica 75 mg prezzo and angioflux compresse prezzo morniflu a cosa serve
zyntabac comprar sin receta online farmacia italy or farmacia online 24h viagra
https://ashbonn.de/umleitung.php?link=clinicagaleno.com farmacia online pylera
fungarest se puede comprar sin receta farmacia online en cantabria and viagra farmacia online espaГ±a comprar lexatin online sin receta
orfidal se puede comprar sin receta Clinica Galeno puedo comprar eutirox sin receta
ordonnance en ligne sans consultation cystite ordonnance en ligne or produit verrue pharmacie sans ordonnance
http://tradeportalofindia.org/CountryProfile/Redirect.aspx?hidCurMenu=divOthers&CountryCode=32&CurrentMenu=IndiaandEU&Redirecturl=http://pharmadirecte.com peut on avoir du viagra sans ordonnance en pharmacie
avene lotion micellaire ordonnance en ligne gratuit and tadalafil 5mg prix en pharmacie shampooing caudalie
https://pharmadirecte.shop/# advil sans ordonnance en pharmacie
силовой тмг http://www.maslyanie-transformatory-kupit2.ru .
farmacia online chisinau se puede comprar aciclovir crema sin receta comprar alprostadil sin receta
https://ordinasalute.shop/# bodix aerosol
https://pharmadirecte.com/# commander viagra en ligne
monores prezzo abiostil unguento nasale prezzo kataval crema prezzo
syntaris spray prezzo mycostatin sospensione orale prezzo or pregabalin 25 mg prezzo
http://www.orta.de/url?q=https://ordinasalute.com kyleena prezzo
п»їfarmacia online farmacia offerte online and moment per mal di gola farmacia online sardegna
pildora dia de despues norlevo sin receta] farmacia online cupon de descuento or mejor farmacia online para comprar cialis
http://www.e-douguya.com/cgi-bin/mbbs/link.cgi?url=http://clinicagaleno.com puedo comprar estrogenos sin receta
opiniones farmacia veterinaria online farmacia torres online and farmacia en casa online. quetiapina se puede comprar sin receta
1win casino es confiable https://1win3046.com
http://pharmadirecte.com/# médicament pour précoce sans ordonnance en pharmacie
lormetazepam ordonnance pharmacie zemiro or pharmacie en ligne sans ordonnance france
http://www.softwizard.ru/en/redirect-url?redirect_url=pharmadirecte.com cardiologue faut il une ordonnance
silicea 15 ch bienfaits chevillГЁre en pharmacie sans ordonnance and prix bГ©quille pharmacie sans ordonnance cialis 5 mg prix
доставка воды технической цена https://dostavka-tehnicheskoi-vodi.ru/ .
лига ставок прогнозы https://www.stavki-na-sport-prognozy.ru .
la farmacia online com: ozempic se puede comprar sin receta? – farmacia san rafael online
comprar cialis en andorra sin receta meafarma – la tua farmacia online farmacia online ibuprofeno
https://ordinasalute.com/# farmacia online palermo
1win. https://www.1win3048.com
1win qeydiyyat linki http://1win3043.com
acido tranexamico comprar sin receta: puedo comprar acetilcisteina sin receta – codigo promocional mi farmacia online
https://ordinasalute.com/# brufen 600 online
farmacia veterinario online atropina collirio minsan nosifol-d per rimanere incinta
http://clinicagaleno.com/# metronidazol 5oo mg se puede comprar sin receta medica en españa??
ставки и прогнозы букмекеров на футбол сегодня stavki-na-sport-prognozy2.ru .
apteka internetowa nl: digitale apotheek – medicatie online
sjekke fГёflekk pГҐ apotek: TryggMed – negleolje apotek
spotek covid snabbtest apotek snabbast leverans apotek
https://snabbapoteket.com/# apotek dk
ставки и прогнозы букмекеров на футбол сегодня http://www.stavki-na-sport-prognozy1.ru/ .
apotek online sverige: SnabbApoteket – vitaminer billigt
pil online bestellen: apotheker online – medicatie bestellen online
https://snabbapoteket.shop/# duschskydd barn huvud
mostbet apk yukle mostbet apk yukle .
hvilket apotek er billigst TryggMed magebelte apotek
мелбет россия http://www.melbet3001.com
http://tryggmed.com/# halsbrann apotek
astmaspray receptfritt: ibs engelska – express apotek
apotheek apotheek: medicatie kopen – online apotheker
прогнозы на спорт от профессионалов на сегодня prognozy-na-sport-1.ru .
http://snabbapoteket.com/# mg/ml till procent
apotheek medicijnen bestellen apotheek bestellen medicijnen zonder recept
melbet ckachat melbet ckachat
online apotheek nederland met recept: online medicijnen bestellen met recept – pseudoephedrine kopen in nederland
hette ett apotek korsord: kГ¶pa medicin pГҐ nГ¤tet – fd apotek
https://snabbapoteket.com/# apotek på nätet
прогнозы на футбол сегодня https://www.prognozy-na-futbol-1.ru .
прогнозы на сегодня футбол https://www.prognozy-na-futbol-2.ru .
точные бесплатные прогнозы на спорт точные бесплатные прогнозы на спорт .
blodtryck på apotek springmask häst or hur stavas yoghurt
http://www.city-fs.de/url?q=https://snabbapoteket.com Г¤r apoteket Г¶ppet idag
jobba på apotek lön köpa hörapparat privat and frukt på q urinvägsinfektion apotek
internetapotheek nederland Medicijn Punt apotheek online bestellen
mostbet apk latest version mostbet apk latest version .
online apotheek nederland zonder recept farma or apotheek medicijnen
http://kens.de/url?q=https://zorgpakket.com de apotheker
online apotheker holandia apteka internetowa and online apotheek nederland met recept aptoheek
holandia apteka internetowa: Medicijn Punt – apotgeek
medicijen pharmacy nederlands or mijn medicijnkosten
https://clients1.google.vg/url?q=https://zorgpakket.com apotheek spanje online
medicijnen aanvragen apotheek online medicatie bestellen and recepta online online apotheek zonder recept ervaringen
pharmacy nl: MedicijnPunt – online apotheek nederland
https://tryggmed.com/# crp apotek
1win games 1win games
мелбет кж https://melbet3003.com/
hasj test apotek egglГёsningstest apotek or tannkitt apotek
https://www.google.com.pe/url?sa=t&url=https://tryggmed.com medisinliste apotek
pore strips apotek fГёflekksjekk apotek and bifidobacterium infantis apotek mandelstein apotek
melbet регистрация melbet регистрация
online medicijnen online medicijnen bestellen online pharmacy
1win http://1win3044.com/
прогноз хоккей на сегодня http://prognozy-na-khokkej-segodnya.ru/ .
как вывести деньги с мелбет украина melbet3004.com
apotek jodtabletter: apotek koronatest – isopropyl alcohol apotek
verzorgingsproducten apotheek: MedicijnPunt – uw apotheek
https://zorgpakket.shop/# online apotheek recept
https://snabbapoteket.shop/# svinkoppor bilder barn
apotek aktier foglossningsbälte apotek finasteride apotek
mostbet qeydiyyat bonusu mostbet qeydiyyat bonusu
online apotheek nederland met recept: apotheek nederland – medicatie apotheek
http://snabbapoteket.com/# filmdragerade tabletter betyder
farmacie online farma or apotheken
https://www.google.com.nf/url?q=http://zorgpakket.com online apotheken
medicatie bestellen apotheek medicijnen kopen and apteka eindhoven medicatie apotheker
1win partners 1win partners
get viagra without prescription from mexico modafinil mexico online viagra pills from mexico
indian pharmacies safe: п»їlegitimate online pharmacies india – IndiaMedsHub
https://indiamedshub.com/# IndiaMedsHub
онлайн оценка часов по фото онлайн оценка часов по фото .
https://expresscarerx.online/# baclofen online pharmacy
navarro pharmacy: united kingdom pharmacy online – colchicine pharmacy
IndiaMedsHub IndiaMedsHub IndiaMedsHub
http://medimexicorx.com/# mexico drug stores pharmacies
ExpressCareRx: amoxicillin online pharmacy – mail order pharmacies
https://indiamedshub.shop/# legitimate online pharmacies india
MediMexicoRx: zithromax mexican pharmacy – buy neurontin in mexico
certified online pharmacy cialis ExpressCareRx online pharmacy xenical
https://medimexicorx.com/# buying prescription drugs in mexico online
mostbet-uz http://mostbet4071.ru
melbet официальный сайт https://melbet3007.com
http://expresscarerx.org/# ExpressCareRx
norvasc online pharmacy: ExpressCareRx – ciprofloxacin pharmacy uk
your pharmacy host buy viagra: viagra europe pharmacy – pharmacies shipping to usa
american online pharmacy what does rx mean in pharmacy all in one pharmacy
доставка воды на стройку https://www.dostavka-tehnicheskoi-vodi.ru .
онлайн оценка дорогих часов http://www.ocenka-chasov-onlajn10.ru/ .
каркасные лестницы из металла https://www.lestnicy-na-metallokarkase-1.ru .
https://indiamedshub.shop/# online pharmacy india
online pharmacy tretinoin reputable online pharmacy levitra or testosterone gel online pharmacy
http://www.amateurpin.com/ap_network.php?l=de&u=http://expresscarerx.org fincar inhouse pharmacy
dutasteride inhouse pharmacy your pharmacy ibuprofen and simvastatin online pharmacy pharmacy on line
amoxicillin mexico online pharmacy: buy antibiotics over the counter in mexico – finasteride mexico pharmacy
humana rx mail order pharmacy ExpressCareRx pharmacy pattaya kamagra
indian pharmacy Online medicine home delivery or Online medicine home delivery
http://ogura-yui.com/www/redirect.php?redirect=https://indiamedshub.com world pharmacy india
india online pharmacy buy prescription drugs from india and india online pharmacy Online medicine order
buying prescription drugs in mexico online mexican mail order pharmacies or mexican rx online
http://www.yu-kari-ofuna.com/feed2js/feed2js.php?src=http://medimexicorx.com mexico pharmacies prescription drugs
mexico drug stores pharmacies mexican border pharmacies shipping to usa and п»їbest mexican online pharmacies mexican drugstore online
лестницы на заказ москва лестницы на заказ москва .
https://expresscarerx.org/# ExpressCareRx
лестницы на заказ цены https://www.lestnicy-na-metallokarkase-3.ru .
best prices on finasteride in mexico buy cialis from mexico or viagra pills from mexico
https://www.steinhaus-gmbh.de/redirect.php?lang=en&url=https://medimexicorx.shop low cost mexico pharmacy online
safe place to buy semaglutide online mexico finasteride mexico pharmacy and buy meds from mexican pharmacy buy meds from mexican pharmacy
лестницы на заказ недорого лестницы на заказ недорого .
trusted mexico pharmacy with US shipping: MediMexicoRx – buy viagra from mexican pharmacy
MediMexicoRx: MediMexicoRx – buy antibiotics from mexico
MediMexicoRx online mexico pharmacy USA legit mexico pharmacy shipping to USA
мостбет как получить бонус http://mostbet4072.ru
1win գրանցում 1win3072.ru
ai therapy app ai-therapist21.com .
ai therapy app https://ai-therapist22.com/ .
1win պաշտոնական https://1win3071.ru
vasco rx specialty pharmacy: ExpressCareRx – online pharmacies no prescription
reliable rx pharmacy: india pharmacy – zyprexa pharmacy online
IndiaMedsHub IndiaMedsHub reputable indian online pharmacy
kmart store pharmacy compound pharmacy online or online pharmacy zyprexa
https://cse.google.com.ai/url?sa=i&url=https://expresscarerx.org american pharmacy online
zithromax online pharmacy international pharmacy no prescription and zyprexa pharmacy online safe online pharmacy
reputable indian online pharmacy Online medicine order or india pharmacy
https://tinygu.de/?url=https://indiamedshub.com/ online shopping pharmacy india
buy medicines online in india online shopping pharmacy india and india pharmacy mail order pharmacy website india
https://expresscarerx.org/# terbinafine online pharmacy
мостбет бонус без депозита уз mostbet4074.ru
млстбет млстбет
ai therapy app http://ai-therapist23.com/ .
simvastatin pharmacy prices: vipps online pharmacy – worldwide pharmacy kamagra
legit mexico pharmacy shipping to USA viagra pills from mexico or legit mexican pharmacy without prescription
http://go.dlcode.ir/?url=http://medimexicorx.shop safe mexican online pharmacy
buy meds from mexican pharmacy buy neurontin in mexico and buy modafinil from mexico no rx order from mexican pharmacy online
IndiaMedsHub: indian pharmacy online – top 10 pharmacies in india
ai therapy ai therapy .
low cost mexico pharmacy online order azithromycin mexico semaglutide mexico price
https://indiamedshub.shop/# india pharmacy mail order
IndiaMedsHub: indian pharmacy online – top online pharmacy india
ExpressCareRx ExpressCareRx ExpressCareRx
sukhumvit pharmacy viagra pharmacy rx one review or legitimate online pharmacy viagra
http://forum.himko.vip/proxy.php?link=https://expresscarerx.org target pharmacy ventolin
prevacid pharmacy coupons viagra and online pharmacy and ultram us pharmacy cheapest pharmacy to get prescriptions filled
http://medimexicorx.com/# medication from mexico pharmacy
cheapest online pharmacy india india online pharmacy or world pharmacy india
https://images.google.com.tn/url?q=https://indiamedshub.com reputable indian online pharmacy
buy prescription drugs from india top online pharmacy india and online shopping pharmacy india mail order pharmacy india
888starz online 888starz online .
https://expresscarerx.org/# best rogue online pharmacy
us pharmacy cialis: bupropion sr online pharmacy – lexapro pharmacy assistance
tadalafil online no rx: generic tadalafil for sale – tadalafil tablets 10 mg online
1win online http://www.1win3067.ru
order generic propecia no prescription cost of generic propecia without rx Propecia for hair loss online
http://isotretinoinfromcanada.com/# Isotretinoin From Canada
Download the latest version of Sportzfy TV APK v8.0 for free and enjoy live sports streaming on your device.
cheap Cialis Canada: generic tadalafil daily – Tadalafil From India
mental health support chat http://www.mental-health21.com/ .
Finasteride From Canada: propecia tablets – Propecia for hair loss online
https://zoloft.company/# Zoloft Company
isotretinoin online USA-safe Accutane sourcing Accutane for sale
cheap Cialis Canada: online pharmacy tadalafil 20mg – generic Cialis from India
Zoloft online pharmacy USA: generic sertraline – cheap Zoloft
https://lexapro.pro/# lexapro 10 mg price in india
purchase generic Zoloft online discreetly Zoloft Company generic sertraline
сколько стоит железная свая винтовая http://www.ostankino-svai.ru .
mental health support chatbot https://www.mental-health23.com .
Mental Health Mental Health .
1win aviator играть https://1win3068.ru
purchase generic Accutane online discreetly: cheap Accutane – isotretinoin online
cheap Propecia Canada: cost propecia no prescription – cheap Propecia Canada
888starz united states 888starz united states .
https://lexapro.pro/# Lexapro for depression online
Cialis without prescription cheap Cialis Canada buy Cialis online cheap
mostbet mobil ro‘yxatdan o‘tish https://mostbet4075.ru
cost generic propecia for sale get propecia without dr prescription or order propecia for sale
http://go.clashroyale.ir/index.php?url=https://finasteridefromcanada.com order generic propecia
propecia order buying generic propecia no prescription and get cheap propecia order generic propecia for sale
Lexapro for depression online: lexapro medication – Lexapro for depression online
https://tadalafilfromindia.shop/# generic Cialis from India
cheap Propecia Canada: generic Finasteride without prescription – Finasteride From Canada
https://lexapro.pro/# п»їlexapro
lexapro 20mg Lexapro for depression online Lexapro for depression online
buy tadalafil europe tadalafil 5 mg tablet coupon or generic tadalafil 20mg canada
http://lonevelde.lovasok.hu/out_link.php?url=https://tadalafilfromindia.com tadalafil online paypal
tadalafil 20mg price in india lowest price tadalafil and tadalafil 5mg uk generic tadalafil from canada
https://zoloft.company/# generic sertraline
buy Accutane online generic isotretinoin or order isotretinoin from Canada to US
https://images.google.ki/url?sa=t&url=https://isotretinoinfromcanada.com order isotretinoin from Canada to US
purchase generic Accutane online discreetly USA-safe Accutane sourcing and Accutane for sale order isotretinoin from Canada to US
buy Cialis online cheap: tadalafil online no rx – buy Cialis online cheap
generic isotretinoin: Isotretinoin From Canada – Isotretinoin From Canada
generic sertraline Zoloft Company or Zoloft for sale
https://clients1.google.nr/url?q=https://zoloft.company Zoloft for sale
generic sertraline buy Zoloft online and Zoloft online pharmacy USA cheap Zoloft
Accutane for sale Accutane for sale buy Accutane online
casino in phuket, new uk secure online casino free welcome Bonus,
https://Goplayslots.net/, king bonus and deposit 5 get 100 free spins
uk, or no deposit mobile casino australia
1win вывод средств сколько ждать 1win вывод средств сколько ждать
1win https://www.1win3073.ru
https://zoloft.company/# Zoloft Company
winline фрибет за регистрацию без депозита http://www.winlayne-fribet.ru/ .
order isotretinoin from Canada to US: cheap Accutane – isotretinoin online
Propecia for hair loss online: Finasteride From Canada – cost of generic propecia pills
европейская сантехника evropejskaya-santehnika.ru .
Zoloft online pharmacy USA Zoloft Company generic sertraline
https://lexapro.pro/# pharmacy price for lexapro 20 mg
tadalafil online no rx: tadalafil daily 5mg – Tadalafil From India
tadalafil 30 online pharmacy tadalafil 20mg or tadalafil online india
http://images.google.co.ao/url?q=https://tadalafilfromindia.com generic cialis tadalafil
tadalafil 2 pharmacy online tadalafil and tadalafil 20mg online canada 10mg tadalafil
Lexapro for depression online: Lexapro for depression online – Lexapro for depression online
1вин казино скачать https://1win3070.ru/
isotretinoin online Isotretinoin From Canada or isotretinoin online
https://images.google.no/url?q=https://isotretinoinfromcanada.com purchase generic Accutane online discreetly
Accutane for sale isotretinoin online and order isotretinoin from Canada to US USA-safe Accutane sourcing
https://finasteridefromcanada.com/# generic Finasteride without prescription
бонус от winline бонус от winline .
ставки с фрибетом винлайн https://winlayne-fribet1.ru/ .
Tadalafil From India: Cialis without prescription – Tadalafil From India
generic brand for lexapro: Lexapro for depression online – lexapro brand name discount
Виниловый пол купить в Москве недорого https://www.napolnaya-probka1.ru .
1win armenia 1win3074.ru
http://tadalafilfromindia.com/# cheap Cialis Canada
buy Accutane online cheap Accutane purchase generic Accutane online discreetly
https://zoloft.company/# Zoloft Company
cheap Zoloft: cheap Zoloft – generic sertraline
tadalafil 20 mg price canada tadalafil 100mg or medicine tadalafil tablets
https://www.google.li/url?sa=t&url=https://tadalafilfromindia.com cheap generic tadalafil 5mg
tadalafil 5mg uk tadalafil 20mg no prescription and tadalafil 2.5 mg tablets india tadalafil best price
isotretinoin online isotretinoin online or isotretinoin online
http://look2.jp/webto.php?url=http://isotretinoinfromcanada.com buy Accutane online
isotretinoin online isotretinoin online and cheap Accutane isotretinoin online
https://isotretinoinfromcanada.com/# Isotretinoin From Canada
Lexapro for depression online Lexapro for depression online generic lexapro australia
sertraline online generic sertraline or Zoloft Company
https://toolbarqueries.google.com.mx/url?q=http://zoloft.company Zoloft Company
purchase generic Zoloft online discreetly buy Zoloft online without prescription USA and purchase generic Zoloft online discreetly sertraline online
generic Finasteride without prescription: buying cheap propecia without dr prescription – cost of generic propecia without rx
мостбет https://mostbet4083.ru/
Cialis without prescription: where to buy tadalafil in singapore – Cialis without prescription
http://tadalafilfromindia.com/# buy Cialis online cheap
https://zoloft.company/# Zoloft Company
теннесси бк скачать http://mostbet4081.ru
Tadalafil From India buy tadalafil in usa Tadalafil From India
purchase generic Accutane online discreetly: purchase generic Accutane online discreetly – purchase generic Accutane online discreetly
1win գրանցում 1win3075.ru
https://finasteridefromcanada.com/# Propecia for hair loss online
Accutane for sale Isotretinoin From Canada or generic isotretinoin
https://cse.google.gg/url?sa=t&url=https://isotretinoinfromcanada.com generic isotretinoin
cheap Accutane purchase generic Accutane online discreetly and Accutane for sale cheap Accutane
where to buy tadalafil in usa generic tadalafil 10mg or buy generic tadalafil online uk
http://www.google.gg/url?q=https://tadalafilfromindia.com tadalafil coupon
80 mg tadalafil generic tadalafil in canada and 10mg tadalafil canadian pharmacy tadalafil 20mg
buy Zoloft online without prescription USA buy Zoloft online purchase generic Zoloft online discreetly
cost propecia: cheap Propecia Canada – cheap Propecia Canada
https://lexapro.pro/# lexapro cheapest price
plinko game online http://www.plinko-kz1.ru
Zoloft for sale generic sertraline buy Zoloft online without prescription USA
generic isotretinoin: cheap Accutane – Accutane for sale
http://tadalafilfromindia.com/# buy tadalafil in usa
mostbet http://www.mostbet4078.ru
Cialis without prescription: tadalafil online no rx – cheap Cialis Canada
generic sertraline Zoloft online pharmacy USA or Zoloft online pharmacy USA
http://socialleadwizard.net/bonus/index.php?aff=https://zoloft.company generic sertraline
cheap Zoloft Zoloft Company and Zoloft for sale Zoloft for sale
generic tadalafil 10mg canadian pharmacy generic tadalafil or canadian pharmacy tadalafil 20mg
http://nwspprs.com/?format=simple&action=shorturl&url=https://tadalafilfromindia.com cialis tadalafil
tadalafil united states tadalafil 5mg cost and online tadalafil prescription tadalafil 20mg lowest price
cheap Propecia Canada cost generic propecia for sale Propecia for hair loss online
cheap Cialis Canada: tadalafil online no rx – Tadalafil From India
Zoloft Company: purchase generic Zoloft online discreetly – buy Zoloft online without prescription USA
cost of generic propecia tablets get generic propecia without dr prescription or get cheap propecia tablets
https://www.google.co.ke/url?q=https://finasteridefromcanada.com buying cheap propecia without a prescription
cost of propecia without insurance get generic propecia without dr prescription and cost of generic propecia pills cost cheap propecia tablets
lexapro 20mg pill Lexapro for depression online Lexapro for depression online
Zoloft Company: generic sertraline – Zoloft online pharmacy USA
purchase generic Zoloft online discreetly: Zoloft online pharmacy USA – generic sertraline
http://finasteridefromcanada.com/# Propecia for hair loss online
generic sertraline cheap Zoloft or buy Zoloft online
http://galaxy-at-fairy.df.ru/phpinfo.php?a=i+want+to+buy+viagra buy Zoloft online
Zoloft for sale sertraline online and Zoloft Company Zoloft online pharmacy USA
бонусы винлайн 2025 winline-fribet-novym-klientam.ru .
generic Cialis from India: Cialis without prescription – tadalafil canadian pharmacy price
cheap Propecia Canada cheap Propecia Canada Finasteride From Canada
winline фрибет 500 winline фрибет 500 .
cheap 10 mg tadalafil tadalafil online no prescription or tadalafil generic us
https://maps.google.com.gi/url?sa=t&url=https://tadalafilfromindia.com tadalafil tablets 20 mg cost
buy tadalafil online canada tadalafil united states and tadalafil 2 purchase tadalafil online
фрибеты winline на сегодня бесплатно besplatnyj-fribet-winline.ru .
Lexapro for depression online: Lexapro for depression online – lexapro brand name
winline как получить бонус при регистрации winline как получить бонус при регистрации .
бонус от winline бонус от winline .
винлайн фрибет winline-fribety-2025.ru .
isotretinoin online: buy Accutane online – isotretinoin online
cheap Cialis Canada: cheap Cialis Canada – buy Cialis online cheap
https://finasteridefromcanada.shop/# buy cheap propecia online
cheap 10 mg tadalafil 10mg tadalafil or <a href=" http://winkler-sandrini.it/info/mwst01i.pdf?a=places+to+buy+viagra+online “>cheap tadalafil 5mg
https://vdvoem.com/forum/away.php?s=https://tadalafilfromindia.com tadalafil online united states
10mg tadalafil cost of tadalafil in india and tadalafil canadian pharmacy online generic tadalafil from india
online tadalafil prescription: Tadalafil From India – cheap Cialis Canada
1win 1win
mostbet mostbet
cheap Propecia Canada: order propecia without prescription – Finasteride From Canada
внедрение 1с услуги 1s-vnedrenie.ru .
1вин 1win3061.ru
https://clearmedsdirect.shop/# can i purchase amoxicillin online
antibiotic treatment online no Rx: low-cost antibiotics delivered in USA – antibiotic treatment online no Rx
1win http://1win3062.ru/
order corticosteroids without prescription: anti-inflammatory steroids online – order corticosteroids without prescription
where to buy Modafinil legally in the US nootropic Modafinil shipped to USA wakefulness medication online no Rx
mostbet mostbet4085.ru
anti-inflammatory steroids online: Relief Meds USA – ReliefMeds USA
where to get gabapentin: NeuroRelief Rx – glenmark gabapentin gluten free
anti-inflammatory steroids online: anti-inflammatory steroids online – order corticosteroids without prescription
how to buy cheap clomid price Clomid Hub Pharmacy buying cheap clomid without insurance
аренда яхты сайт https://yachts-charter-dubai.com/ .
https://reliefmedsusa.com/# Relief Meds USA
mostbet http://mb1113.ru/
NeuroRelief Rx: gabapentin oral capsule 300 mg information – NeuroRelief Rx
888starz united states 888starz united states .
gabapentin ct 100mg hartkapseln: gabapentin ohne rezept – does gabapentin thin your blood
low-cost antibiotics delivered in USA low-cost antibiotics delivered in USA low-cost antibiotics delivered in USA
affordable Modafinil for cognitive enhancement: WakeMeds RX – affordable Modafinil for cognitive enhancement
проект на водопонижение https://vodoponizhenie-msk.ru/ .
внедрение ерп 1с http://www.1s-erp-vnedrenie.ru/ .
anti-inflammatory steroids online: prednisone 10 mg daily – prednisone 50 mg prices
prednisone nz: Relief Meds USA – anti-inflammatory steroids online
https://wakemedsrx.shop/# safe Provigil online delivery service
cheap clomid without a prescription how can i get generic clomid for sale or where to get generic clomid without dr prescription
http://images.google.com.au/url?q=https://clomidhubpharmacy.com where can i get cheap clomid pills
buy clomid tablets how to get clomid no prescription and can i get generic clomid where can i get generic clomid without rx
can i order generic clomid pill Clomid Hub Pharmacy Clomid Hub
gabapentin 300mg cap gabapentin brand name or can you get fluoxetine
https://clients1.google.com.vc/url?q=https://neuroreliefrx.com gabapentin al 300 mg
can you take vitamin d with gabapentin other drug names for gabapentin and can you freebase gabapentin gabapentin muscle building
Clomid Hub Pharmacy: Clomid Hub – where can i get clomid
melbet app download for pc https://melbet1032.ru
1вин https://1win3064.ru
anti-inflammatory steroids online: anti-inflammatory steroids online – buy prednisone canadian pharmacy
Clomid Hub where to get generic clomid without dr prescription can you buy clomid without dr prescription
amoxicillin 500 mg tablet price amoxicillin cephalexin or amoxicillin 875 125 mg tab
https://images.google.co.id/url?q=https://clearmedsdirect.com amoxicillin without a doctors prescription
where to buy amoxicillin 500mg order amoxicillin online uk and amoxicillin 500mg tablets price in india amoxicillin without a prescription
anti-inflammatory steroids online: ReliefMeds USA – prednisone rx coupon
прогнозы на спорт на сегодня бесплатно http://www.prognoz-na-segodnya-na-sport8.ru .
ClearMeds Direct: low-cost antibiotics delivered in USA – antibiotic treatment online no Rx
can i buy prednisone over the counter in usa anti-inflammatory steroids online anti-inflammatory steroids online
order corticosteroids without prescription: order corticosteroids without prescription – order corticosteroids without prescription
buying cheap clomid can you buy cheap clomid without rx or clomid generic
https://maps.google.lk/url?sa=t&url=https://clomidhubpharmacy.com generic clomid without insurance
where to buy generic clomid prices cost of cheap clomid without a prescription and cost clomid without insurance buy clomid
Clear Meds Direct: low-cost antibiotics delivered in USA – where can i get amoxicillin
https://clearmedsdirect.com/# buy amoxicillin 500mg online
холодильные камеры цена холодильные камеры цена .
prednisone online for sale: Relief Meds USA – prednisone 20mg online
Clomid Hub Pharmacy Clomid Hub Pharmacy can you buy clomid now
buy amoxicillin online cheap amoxicillin 50 mg tablets or amoxicillin 500 coupon
https://maps.google.com.sg/url?q=https://clearmedsdirect.com amoxicillin 500mg pill
order amoxicillin online no prescription buy amoxicillin 500mg canada and ampicillin amoxicillin buy amoxicillin 250mg
where can i buy clomid without prescription: Clomid Hub – Clomid Hub Pharmacy
online order prednisone 10mg prednisone 0.5 mg or prednisone 5 mg cheapest
https://toolbarqueries.google.at/url?sa=t&url=https://reliefmedsusa.com prednisone 30 mg
can you buy prednisone over the counter in mexico prednisone 10 mg tablet cost and prednisone 20 mg pill 200 mg prednisone daily
ставки на спорт прогнозы ставки на спорт прогнозы .
мелбет казино официальный сайт скачать http://www.melbet1037.ru
ставки на спорт прогнозы http://www.sportbets27.ru .
antibiotic treatment online no Rx: buy amoxicillin over the counter uk – antibiotic treatment online no Rx
anti-inflammatory steroids online: anti-inflammatory steroids online – prednisone 20 mg prices
прогнозы ставки на спорт sportbets26.ru .
gabapentin gegen husten NeuroRelief Rx gabapentin ratiopharm 600
safe Provigil online delivery service: prescription-free Modafinil alternatives – WakeMedsRX
where to get cheap clomid price can i order clomid pills or how to get generic clomid price
https://cse.google.cd/url?q=https://clomidhubpharmacy.com where can i get cheap clomid for sale
where can i get generic clomid pills can i purchase generic clomid pill and can you get cheap clomid without a prescription how to get clomid pills
https://neuroreliefrx.com/# gabapentin hangover
1с онлайн цена http://www.kupit-1s23.ru .
antibiotic treatment online no Rx: ClearMeds Direct – low-cost antibiotics delivered in USA
where to buy prednisone without prescription: order corticosteroids without prescription – Relief Meds USA
Clomid Hub where to buy generic clomid pills can i purchase cheap clomid no prescription
ClearMeds Direct: antibiotic treatment online no Rx – antibiotic treatment online no Rx
where can you get amoxicillin amoxicillin 875 mg tablet or buy amoxicillin over the counter uk
https://clients1.google.com.bd/url?q=https://clearmedsdirect.com buying amoxicillin online
amoxicillin generic amoxicillin 500mg capsule and amoxicillin medicine over the counter buy amoxil
gabapentin dosage for babies gabapentin 100 mg usos or gabapentin muscle building
http://www.hyoito-fda.com/out.php?url=http://neuroreliefrx.com gabapentin lorazepam drug interaction
fluoxetine online first time gabapentin high and gabapentin weight gain side effects medication gabapentin 300 mg
canadian online pharmacy prednisone prednisone 50 mg coupon or prednisone 20mg for sale
http://ixawiki.com/link.php?url=http://reliefmedsusa.com prednisone without prescription medication
buy prednisone tablets uk prednisone 30 mg daily and prednisone pak prednisone 20mg nz
цена аренды яхты в сутки http://www.yachts-charter-dubai.com/ .
Clomid Hub: cost generic clomid without insurance – how can i get clomid without rx
перевозка авто автовозом по россии http://www.avtovoz-av7.ru .
точные прогнозы на хоккей https://luchshie-prognozy-na-khokkej6.ru/ .
anti-inflammatory steroids online: ReliefMeds USA – Relief Meds USA
Modafinil for ADHD and narcolepsy: wakefulness medication online no Rx – Wake Meds RX
мостбет мостбет
how to buy clomid for sale can i buy clomid without rx or can i order cheap clomid
https://www.play.net/bounce/redirect.asp?URL=http://clomidhubpharmacy.com can i purchase clomid
can you get generic clomid without dr prescription where can i get clomid no prescription and where can i buy cheap clomid pill where buy generic clomid without rx
prescription-free Modafinil alternatives: WakeMedsRX – prescription-free Modafinil alternatives
http://neuroreliefrx.com/# NeuroRelief Rx
точные прогнозы на спорт точные прогнозы на спорт .
order corticosteroids without prescription: Relief Meds USA – ReliefMeds USA
where to buy Modafinil legally in the US Modafinil for focus and productivity where to buy Modafinil legally in the US
Wake Meds RX: smart drugs online US pharmacy – nootropic Modafinil shipped to USA
generic amoxil 500 mg order amoxicillin 500mg or amoxicillin 500mg price in canada
http://clients1.google.com.sg/url?sa=i&url=https://clearmedsdirect.com amoxicillin 775 mg
amoxicillin order online no prescription amoxicillin 500 coupon and where can i buy amoxicillin over the counter uk amoxicillin 500 mg price
prednisone buy canada: order corticosteroids without prescription – how to purchase prednisone online
prednisone 10 mg prednisone buy canada or prednisone pack
https://www.google.ms/url?q=https://reliefmedsusa.com price for 15 prednisone
prednisone pill 10 mg how can i get prednisone online without a prescription and prednisone uk 54 prednisone
order corticosteroids without prescription: ReliefMeds USA – order corticosteroids without prescription
NeuroRelief Rx NeuroRelief Rx NeuroRelief Rx
Wake Meds RX: prescription-free Modafinil alternatives – WakeMeds RX
услуги транспортировки автомобилей avtovoz-av7.ru .
pregabalin and gabapentin: NeuroRelief Rx – fluoxetine generics
where can i buy clomid without a prescription can i buy clomid prices or can you buy generic clomid without prescription
https://clients1.google.bf/url?q=https://clomidhubpharmacy.com how to get clomid price
cheap clomid without prescription can i get generic clomid online and where to buy cheap clomid online get cheap clomid without a prescription
https://clomidhubpharmacy.com/# Clomid Hub
generic clomid without insurance buying generic clomid how to get cheap clomid without a prescription
memory loss on gabapentin: gabapentin sale – efectos secundarios del gabapentin 300 mg
anti-inflammatory steroids online: prednisone canada – order corticosteroids without prescription
mostbet mostbet
mexican rx online: mexico drug stores pharmacies – MexiCare Rx Hub
MexiCare Rx Hub MexiCare Rx Hub MexiCare Rx Hub
MexiCare Rx Hub: order from mexican pharmacy online – MexiCare Rx Hub
order from mexican pharmacy online: MexiCare Rx Hub – modafinil mexico online
https://canadrxnexus.com/# best canadian pharmacy
промокод в 1вин казино промокод в 1вин казино
MexiCare Rx Hub: MexiCare Rx Hub – MexiCare Rx Hub
canadian pharmacy india CanadRx Nexus CanadRx Nexus
мелбет купон мелбет купон
IndiGenix Pharmacy: best india pharmacy – IndiGenix Pharmacy
slot giri? http://candy-casino-9.com/ .
рабочее зеркало мелбет melbet на сегодня http://melbet1036.ru/
IndiGenix Pharmacy: indian pharmacy online – best india pharmacy
CanadRx Nexus: CanadRx Nexus – canadian pharmacy meds review
сваи винтовые подмосковье https://www.ostankino-svai.ru .
mexico pharmacy cheap cialis mexico legit mexican pharmacy without prescription
мелбет. ру http://www.melbet1031.ru
modafinil mexico online: MexiCare Rx Hub – MexiCare Rx Hub
https://canadrxnexus.shop/# best mail order pharmacy canada
legal canadian pharmacy online: CanadRx Nexus – CanadRx Nexus
cheapest pharmacy canada: the canadian pharmacy – CanadRx Nexus
best india pharmacy online pharmacy india IndiGenix Pharmacy
лестницы на заказ московская область https://lestnicy-na-metallokarkase-1.ru .
canadian drugs online: canadian pharmacy checker – CanadRx Nexus
евросан http://evropejskaya-santehnika.ru .
IndiGenix Pharmacy: IndiGenix Pharmacy – india pharmacy
legitimate online pharmacies india: IndiGenix Pharmacy – IndiGenix Pharmacy
get viagra without prescription from mexico MexiCare Rx Hub MexiCare Rx Hub
purple pharmacy mexico price list buying prescription drugs in mexico or mexican drugstore online
http://flthk.com/en/productshow.asp?id=22&mnid=49487&mc=FLT-V1/V2&url=https://mexicarerxhub.com reputable mexican pharmacies online
purple pharmacy mexico price list mexican rx online and purple pharmacy mexico price list п»їbest mexican online pharmacies
Online medicine home delivery: mail order pharmacy india – reputable indian pharmacies
order azithromycin mexico finasteride mexico pharmacy or best prices on finasteride in mexico
https://images.google.tk/url?sa=t&url=https://mexicarerxhub.shop low cost mexico pharmacy online
prescription drugs mexico pharmacy buy antibiotics from mexico and isotretinoin from mexico п»їmexican pharmacy
order azithromycin mexico: order azithromycin mexico – order from mexican pharmacy online
отзывы о melbet отзывы о melbet
casino giri? https://www.candy-casino-7.com .
recommended canadian pharmacies canadian online pharmacy or canada pharmacy online
https://maps.google.bj/url?sa=t&url=https://canadrxnexus.com certified canadian international pharmacy
canadian pharmacy prescription drugs canada buy online and canadian neighbor pharmacy canadian drugstore online
https://indigenixpharm.shop/# IndiGenix Pharmacy
CanadRx Nexus rate canadian pharmacies CanadRx Nexus
CanadRx Nexus: canadian pharmacy sarasota – best mail order pharmacy canada
candycasino http://www.candy-casino-2.com .
world pharmacy india п»їlegitimate online pharmacies india or online shopping pharmacy india
https://cse.google.st/url?sa=t&url=https://indigenixpharm.com top 10 pharmacies in india
top 10 pharmacies in india cheapest online pharmacy india and cheapest online pharmacy india online pharmacy india
IndiGenix Pharmacy: IndiGenix Pharmacy – IndiGenix Pharmacy
best online pharmacy india: IndiGenix Pharmacy – IndiGenix Pharmacy
промокод winline на сегодня бесплатно промокод winline на сегодня бесплатно .
indian pharmacy buy medicines online in india online shopping pharmacy india
top online pharmacy india: IndiGenix Pharmacy – Online medicine order
purple pharmacy mexico price list reputable mexican pharmacies online or mexican drugstore online
http://www.ballpark-sanjo.com/feed2js/feed2js.php?src=http://mexicarerxhub.com medication from mexico pharmacy
medicine in mexico pharmacies reputable mexican pharmacies online and medicine in mexico pharmacies purple pharmacy mexico price list
как поставить бесплатную ставку на винлайн как поставить бесплатную ставку на винлайн .
buy canadian drugs: CanadRx Nexus – CanadRx Nexus
mexican pharmacy for americans zithromax mexican pharmacy or online mexico pharmacy USA
http://yoshio.noizm.com/jump.php?u=http://mexicarerxhub.shop order from mexican pharmacy online
accutane mexico buy online safe mexican online pharmacy and viagra pills from mexico buy meds from mexican pharmacy
IndiGenix Pharmacy IndiGenix Pharmacy indianpharmacy com
canadian medications buy canadian drugs or medication canadian pharmacy
https://maps.google.com.ni/url?q=https://canadrxnexus.com canadian pharmacies online
canadian pharmacy online safe reliable canadian pharmacy and canadian pharmacy 1 internet online drugstore online canadian pharmacy
Online medicine home delivery: online shopping pharmacy india – IndiGenix Pharmacy
https://mexicarerxhub.com/# MexiCare Rx Hub
CanadRx Nexus: CanadRx Nexus – CanadRx Nexus
IndiGenix Pharmacy: IndiGenix Pharmacy – IndiGenix Pharmacy
MexiCare Rx Hub real mexican pharmacy USA shipping order azithromycin mexico
medication from mexico pharmacy: MexiCare Rx Hub – MexiCare Rx Hub
винлайн промокод на фрибет 2025 https://www.winline-bonus-za-registraciyu-2025.ru .
1 win md 1 win md
игровые пк игровые пк .
CanadRx Nexus: CanadRx Nexus – cheapest pharmacy canada
melbet вход зеркало http://melbet1035.ru
дизайнерское кашпо напольное дизайнерское кашпо напольное .
MexiCare Rx Hub: semaglutide mexico price – MexiCare Rx Hub
IndiGenix Pharmacy IndiGenix Pharmacy IndiGenix Pharmacy
винлайн букмекерская бонус винлайн букмекерская бонус .
buying drugs from canada onlinecanadianpharmacy or canada drug pharmacy
https://kd-event.de/redirect/?url=https://canadrxnexus.com canadian pharmacy phone number
canadian pharmacy ltd rate canadian pharmacies and canadapharmacyonline com canadian drugs pharmacy
indian pharmacy: IndiGenix Pharmacy – IndiGenix Pharmacy
semaglutide mexico price buy antibiotics over the counter in mexico or generic drugs mexican pharmacy
https://images.google.cd/url?q=https://mexicarerxhub.shop accutane mexico buy online
order kamagra from mexican pharmacy buy meds from mexican pharmacy and safe place to buy semaglutide online mexico legit mexican pharmacy without prescription
организация онлайн трансляций мероприятий организация онлайн трансляций мероприятий .
организация прямой трансляции http://www.zakazat-onlajn-translyaciyu6.ru/ .
https://canadrxnexus.shop/# canadian drugs
canadian neighbor pharmacy: canadian pharmacy 24 com – canada pharmacy 24h
CanadRx Nexus canada drugs CanadRx Nexus
CanadRx Nexus: canadianpharmacyworld – CanadRx Nexus
интересные кашпо интересные кашпо .
mostbet telefon orqali kirish http://mostbet4079.ru/
MexiCare Rx Hub: MexiCare Rx Hub – MexiCare Rx Hub
IndiGenix Pharmacy: indian pharmacy – IndiGenix Pharmacy
mexican online pharmacies prescription drugs mexican online pharmacies prescription drugs or medication from mexico pharmacy
https://www.google.com.br/url?sa=t&url=https://mexicarerxhub.com mexican mail order pharmacies
mexican pharmaceuticals online purple pharmacy mexico price list and pharmacies in mexico that ship to usa reputable mexican pharmacies online
best india pharmacy india online pharmacy or indianpharmacy com
http://endersby.co.za/redirect/?url=https://indigenixpharm.com buy medicines online in india
online pharmacy india best india pharmacy and buy prescription drugs from india online pharmacy india
top 10 pharmacies in india IndiGenix Pharmacy IndiGenix Pharmacy
купить игровой компьютер купить игровой компьютер .
IndiGenix Pharmacy: IndiGenix Pharmacy – IndiGenix Pharmacy
организация трансляции мероприятия организация трансляции мероприятия .
мелбет промокод 2024 melbet1038.ru
canadian pharmacy prices best canadian pharmacy to buy from or canadian pharmacy prices
https://www.scarabelli-ghini.edu.it/sdg/app/default/trasparenza.php?sede_codice=BOII0015&referer=https://canadrxnexus.com canadian pharmacy ratings
canadianpharmacyworld escrow pharmacy canada and canadianpharmacy com canadian pharmacy in canada
mexican drugstore online: MexiCare Rx Hub – mexican online pharmacies prescription drugs
order from mexican pharmacy online п»їmexican pharmacy or buy modafinil from mexico no rx
https://maps.google.fm/url?sa=t&url=https://mexicarerxhub.shop order kamagra from mexican pharmacy
buy kamagra oral jelly mexico trusted mexico pharmacy with US shipping and real mexican pharmacy USA shipping cheap mexican pharmacy
pharmacy in canada: canadianpharmacymeds com – CanadRx Nexus
https://ivercarepharmacy.com/# IverCare Pharmacy
cheap muscle relaxer online USA: RelaxMedsUSA – Tizanidine tablets shipped to USA
semaglutide pill vs injection is zepbound semaglutide semaglutide peptides
рулонные шторы на створку https://rulonnye-shtory-s-elektroprivodom90.ru/ .
buying ventolin uk: ventolin inhaler – can you buy ventolin over the counter nz
cheap muscle relaxer online USA: cheap muscle relaxer online USA – safe online source for Tizanidine
рулонные шторы на электроприводе рулонные шторы на электроприводе .
гардина с электроприводом https://elektrokarnizy150.ru/ .
электрические карнизы для штор в москве http://www.elektrokarniz150.ru .
relief from muscle spasms online Tizanidine 2mg 4mg tablets for sale RelaxMeds USA
купить игровой компьютер купить игровой компьютер .
FluidCare Pharmacy: FluidCare Pharmacy – lasix 20 mg
https://asthmafreepharmacy.com/# buy ventolin online canada
rybelsus dosis: AsthmaFree Pharmacy – AsthmaFree Pharmacy
IverCare Pharmacy stromectol price uk ivermectin pour-on for human lice
организация трансляции организация трансляции .
автоматические рулонные шторы на окна http://rulonnye-shtory-s-elektroprivodom17.ru/ .
relief from muscle spasms online: prescription-free muscle relaxants – order Tizanidine without prescription
does ivermectin kill lyme disease: IverCare Pharmacy – IverCare Pharmacy
relief from muscle spasms online RelaxMeds USA Tizanidine tablets shipped to USA
рулонные шторки на окна rulonnye-shtory-s-elektroprivodom90.ru .
casa de mobila http://1win40004.ru/
buy Zanaflex online USA: RelaxMeds USA – prescription-free muscle relaxants
trusted pharmacy Zanaflex USA: RelaxMedsUSA – RelaxMeds USA
https://asthmafreepharmacy.com/# ventolin prescription cost
furosemide 100 mg furosemide 100 mg or generic lasix
http://goodadvices.com/?URL=fluidcarepharmacy.com lasix dosage
furosemide lasix for sale and lasix for sale lasix medication
AsthmaFree Pharmacy semaglutide brand names rybelsus vs semaglutide
AsthmaFree Pharmacy: AsthmaFree Pharmacy – AsthmaFree Pharmacy
FluidCare Pharmacy furosemide 40 mg FluidCare Pharmacy
электрокарниз двухрядный цена http://www.elektrokarniz150.ru .
электрокарниз недорого elektrokarnizy150.ru .
ivermectin covid treatment ivermectin for goat mites or buy ivermectin near me
https://weberu.ru/redirect/?url=http://ivercarepharmacy.com what does ivermectin treat
ivermectin paste ivermectin drug interactions and ivermectin horse paste for rosacea heartworm prevention without ivermectin
1win ios yuklab olish https://1win3065.ru/
прикольные горшки для цветов прикольные горшки для цветов .
mobila bucatarii mici http://1win40001.ru
semaglutide los angeles: rybelsus daily or weekly – AsthmaFree Pharmacy
888starz logo https://888starz.red .
1win.ci https://www.1win40003.ru
mostbet skachat iphone mostbet skachat iphone
организация интернет трансляций организация интернет трансляций .
furosemida FluidCare Pharmacy FluidCare Pharmacy
mostbet royxatdan otish mostbet royxatdan otish
furosemide 40mg furosemide 40 mg or lasix 40 mg
https://maps.google.com.hk/url?sa=t&url=https://fluidcarepharmacy.com lasix tablet
furosemida 40 mg lasix and lasix online lasix uses
fabrica de mobila http://1win40006.ru/
https://glucosmartrx.shop/# highest dose of semaglutide
affordable Zanaflex online pharmacy: Tizanidine tablets shipped to USA – prescription-free muscle relaxants
rybelsusВ® semaglutide goodrx or semaglutide and constipation
http://ewin.biz/jsonp/?url=https://glucosmartrx.com:: what are the doses of semaglutide
semaglutide needles semaglutide vs metformin and places to inject semaglutide semaglutide lozenges
AsthmaFree Pharmacy AsthmaFree Pharmacy semaglutide heartburn
buy ventolin nz: AsthmaFree Pharmacy – AsthmaFree Pharmacy
AsthmaFree Pharmacy: rybelsus approved for weight loss – semaglutide to tirzepatide conversion chart
edamam.ru https://www.edamam.ru .
data-vyhoda.online https://data-vyhoda.online .
AsthmaFree Pharmacy buy ventolin on line ventolin 100
furosemide lasix uses or lasix side effects
http://confluencedesigninc.com/index.cfm?id=blog&articleID_blogArticles=F1899241-1422-0A0A-8C35562AF399DBA6&referer=http://fluidcarepharmacy.com lasix 100 mg
lasix generic name lasix 40mg and lasix side effects lasix pills
IverCare Pharmacy: IverCare Pharmacy – ivermectin liquid for dogs
https://glucosmartrx.shop/# AsthmaFree Pharmacy
Zanaflex medication fast delivery relief from muscle spasms online buy Zanaflex online USA
IverCare Pharmacy: ivermectin where to purchase – ivermectin for coronavirus
order Tizanidine without prescription: prescription-free muscle relaxants – RelaxMeds USA
prescription-free muscle relaxants cheap muscle relaxer online USA or order Tizanidine without prescription
http://mycivil.ir/go/index.php?url=https://relaxmedsusa.com affordable Zanaflex online pharmacy
Tizanidine tablets shipped to USA cheap muscle relaxer online USA and RelaxMedsUSA buy Zanaflex online USA
Сайт о новорожденных детях http://www.malishi.online .
ivermectin 1 ivermectin cream before and after IverCare Pharmacy
1xbat 1xbat .
IverCare Pharmacy: ivermectin 3 mg dose – IverCare Pharmacy
lasix furosemide 40 mg lasix 40 mg or lasix medication
https://toolbarqueries.google.com.eg/url?sa=t&url=https://fluidcarepharmacy.com furosemide
furosemide furosemida and furosemida buy lasix online
cele mai bune cazinouri portofele electronice cele mai bune cazinouri portofele electronice
ivermectin side effects scabies ivermectin for scabies dosage or ivermectin side effects in dogs
http://maps.google.fm/url?q=https://ivercarepharmacy.com ivermectin 1% cream generic
how expensive is ivermectin stromectol tab price and ivermectin protocol ivermectin dosage cats oral
ivermectin and coronavirus: IverCare Pharmacy – IverCare Pharmacy
https://relaxmedsusa.shop/# Tizanidine tablets shipped to USA
AsthmaFree Pharmacy ventolin 4mg price ventolin cream
chiterskiy.ru http://www.chiterskiy.ru .
data-vyhoda.online data-vyhoda.online .
IverCare Pharmacy: IverCare Pharmacy – IverCare Pharmacy
ventolin brand name: AsthmaFree Pharmacy – AsthmaFree Pharmacy
RelaxMeds USA Tizanidine 2mg 4mg tablets for sale or safe online source for Tizanidine
https://client.paltalk.com/client/webapp/client/External.wmt?url=https://relaxmedsusa.com muscle relaxants online no Rx
RelaxMedsUSA RelaxMedsUSA and Tizanidine 2mg 4mg tablets for sale RelaxMedsUSA
AsthmaFree Pharmacy semaglutide nyc semaglutide maintenance dose every other week
FluidCare Pharmacy: lasix 100mg – FluidCare Pharmacy
proedy https://proedy.online/ .
does semaglutide stop working: how much does rybelsus cost – AsthmaFree Pharmacy
pelenku.ru http://www.pelenku.ru .
imalishka.ru http://www.imalishka.ru .
pamyatniki-kultury.ru http://pamyatniki-kultury.ru .
furosemida 40 mg furosemida or lasix 20 mg
https://www.google.co.ck/url?q=https://fluidcarepharmacy.com lasix 20 mg
lasix 20 mg furosemide 40mg and furosemide 40mg lasix for sale
rybelsus commercial rybelsus oral semaglutide or rybelsusВ®
http://www.javlibrary.com/en/redirect.php?url=http://glucosmartrx.com rybelsus trial
does semaglutide give you energy semaglutide hers and how does semaglutide work to lose weight rybelsus indication
lasix generic FluidCare Pharmacy FluidCare Pharmacy
AsthmaFree Pharmacy: AsthmaFree Pharmacy – ventolin 2.5 mg
http://ivercarepharmacy.com/# stromectol ivermectin
cost of ivermectin lotion: buy stromectol online – IverCare Pharmacy
নমস্কার!
রিয়েল ক্যাসিনো
এই লিঙ্কটি পড়ুন – https://digitalpokerclub.cfd
অনলাইন ক্যাসিনো অ্যাপ
অনলাইন ক্যাসিনো গেম
রিয়েল ক্যাসিনো
শুভকামনা!
নমস্কার!
ক্যাসিনো টাকা ডিপোজিট
এই লিঙ্কটি দেখুন – https://jackpotslotsonline.cfd
অনলাইন জোয়া
ক্যাসিনো টাকা ডিপোজিট
অনলাইন ক্যাসিনো খেলা
শুভকামনা!
кашпо оригинальное купить http://dizaynerskie-kashpo-rnd.ru .
AsthmaFree Pharmacy AsthmaFree Pharmacy can i buy ventolin over the counter in canada
Tizanidine 2mg 4mg tablets for sale: buy Zanaflex online USA – Tizanidine 2mg 4mg tablets for sale
relief from muscle spasms online: prescription-free muscle relaxants – RelaxMeds USA
reckey http://www.reckey.ru .
автоматические шторы на окна http://rulonnye-shtory-s-elektroprivodom11.ru .
рулонные шторы автоматические рулонные шторы автоматические .
электрические рулонные шторы купить elektricheskie-rulonnye-shtory90.ru .
шторы роллы на окна шторы роллы на окна .
электрические рулонные шторы электрические рулонные шторы .
lasix 40mg lasix furosemide 40 mg or lasix furosemide 40 mg
https://images.google.ms/url?q=https://fluidcarepharmacy.com lasix generic
lasix pills lasix generic and buy furosemide online furosemide 40mg
Привет!
10 лучших казино онлайн казахстан
Переходи: – https://clasicslotsonline.cfd/
казино онлайн в казахстане с бонусом за регистрацию
пин ап казино онлайн казахстан
онлайн казино казахстана
Бывай!
rybelsus 3 mg precio rybelsus cost without insurance or semaglutide brand name
http://www.soshu.cc/book/BookTran.aspx?url=https://glucosmartrx.com/ is semaglutide fda approved
compound semaglutide near me how much is rybelsus a month and what is rybelsus prescribed for can rybelsus cause constipation
ventolin 4mg uk ventolin 100 mg AsthmaFree Pharmacy
IverCare Pharmacy: IverCare Pharmacy – IverCare Pharmacy
rybelsus and farxiga: ozempic vs rybelsus vs wegovy – semaglutide weight loss
http://relaxmedsusa.com/# Tizanidine 2mg 4mg tablets for sale
ivermectin gel ivermectin tablets price buy ivermectin pills
rozhau http://rozhau.ru .
IverCare Pharmacy: how to buy ivermectin – IverCare Pharmacy
semaglutide stomach pain relief: drinking alcohol on semaglutide – semaglutide withdrawal
1 win baixar http://1win40005.ru
melbet ставки http://melbet1039.ru
melbet account [url=http://melbet1040.ru]http://melbet1040.ru[/url]
Ca cu?c tr?c tuy?n GK88: Ca cu?c tr?c tuy?n GK88 – GK88
jollibet casino: 1winphili – Online betting Philippines
¡Qué tal!!
juegos de casino en lГnea con dinero real ecuador
Lee este enlace – https://digitalbetting.cfd
cassino dando giros gratis ecuador
casino online dinero real ecuador
casino con dinero real ecuador
¡Buena suerte!
Jiliko bonus: Jiliko bonus – Jiliko login
Swerte99 casino walang deposit bonus para sa Pinoy Swerte99 online gaming Pilipinas Swerte99 app
автоматические рулонные шторы на окна rulonnye-shtory-s-elektroprivodom11.ru .
рулонные шторы с электроприводом на окна http://www.elektricheskie-rulonnye-shtory.ru/ .
¡Hola!
como jugar casino en linea con dinero real bolivia
Lee el enlace – https://livedealers.cfd/
300 reales a bolivianos
casino en lГnea dinero real bolivia
400 reales a bolivianos
¡Buena suerte!
купить рольшторы цены https://elektricheskie-rulonnye-shtory90.ru .
https://pinwinaz.pro/# Yuks?k RTP slotlar
автоматические рулонные шторы на створку http://www.avtomaticheskie-rulonnye-shtory50.ru .
¡Hola, amigo!!
casino real online chile
Lee el enlace – https://livecasinogames.cfd
tu casino en casa chile
casino en lГnea chile
casino real online chile
¡Buena suerte!
Bandar togel resmi Indonesia: Situs togel online terpercaya – Link alternatif Abutogel
jollibet app: jollibet casino – jollibet casino
Promo slot gacor hari ini: Login Beta138 – Promo slot gacor hari ini
Swerte99 bonus Swerte99 bonus Swerte99 login
Etibarli onlayn kazino Az?rbaycanda: Pinco il? real pul qazan – Pinco kazino
Ca cu?c tr?c tuy?n GK88: Slot game d?i thu?ng – Dang ky GK88
Jiliko: Jiliko casino – Jiliko bonus
Ðang ký GK88: Slot game d?i thu?ng – Nhà cái uy tín Vi?t Nam
Pinco casino mobil t?tbiq: Yuks?k RTP slotlar – Onlayn rulet v? blackjack
Qeydiyyat bonusu Pinco casino Pinco kazino Pinco kazino
Bonus new member 100% Beta138: Slot gacor Beta138 – Link alternatif Beta138
¡Saludos!
juegos de casino con dinero real chile
Lee este enlace – https://onlinepokerroom.cfd/
juegos de casino con dinero real chile
1xbet casino chile
casino en lГnea chile
¡Buena suerte!
https://gkwinviet.company/# Link vao GK88 m?i nh?t
Здарова!
проверенные онлайн казино с выводом денег казахстан
По ссылке: – https://pokerstrategyhub.cfd
казахстан онлайн казино
казино онлайн в казахстане с бонусом за регистрацию
онлайн казино кз
Пока!
lucky jet телеграмм lucky jet телеграмм
Situs judi resmi berlisensi Login Beta138 or Login Beta138
http://www.oxfordeye.co.uk/redirect.aspx?url=//betawinindo.top/ Situs judi resmi berlisensi
Situs judi resmi berlisensi Bandar bola resmi and Login Beta138 Slot gacor Beta138
Slot jackpot terbesar Indonesia: Judi online deposit pulsa – Slot jackpot terbesar Indonesia
Swerte99 casino walang deposit bonus para sa Pinoy: Swerte99 app – Swerte99 slots
Online casino Jollibet Philippines: 1winphili – jollibet casino
শুভেচ্ছা!
অনলাইন ক্যাসিনো অ্যাপ
এই লিঙ্কটি পড়ুন – https://europeanroulette.cfd/
অনলাইন ক্যাসিনো গেম
ক্যাসিনো টাকা ইনকাম
অনলাইন জোয়া
শুভকামনা!
Swerte99 app Swerte99 bonus Swerte99 casino walang deposit bonus para sa Pinoy
оригинальные цветочные горшки оригинальные цветочные горшки .
¡Hola!
400 reales a bolivianos casino
Lee este enlace – https://casinogamesonline.cfd
como jugar casino en linea con dinero real bolivia
casino con dinero real bolivia
juegos de casino en linea con dinero real bolivia
¡Buena suerte!
Hi friend!
Save money and boost your bankroll with our exclusive live online gaming casino promo codes offering special discounts and bonuses. These limited-time live online gaming casino promo codes provide extra value on deposits, free spins, and cashback rewards. canadian real money casino Stay updated with the latest live online gaming casino promo codes and never miss an opportunity to maximize your gaming budget.
Check out this link – https://livegamingonline.cfd/
casino apps for real money
real money casino online canada
online casino real money no deposit canada
Good luck!
Jiliko Jiliko app or Jiliko casino walang deposit bonus para sa Pinoy
https://www.google.tg/url?sa=t&url=https://jilwin.pro Jiliko
Jiliko Jiliko and jilwin Jiliko bonus
jollibet casino jollibet casino or Jollibet online sabong
http://clients1.google.co.ao/url?q=https://1winphili.company Jollibet online sabong
1winphili jollibet login and 1winphili jollibet login
Etibarli onlayn kazino Az?rbaycanda: Pinco casino mobil t?tbiq – Qeydiyyat bonusu Pinco casino
Swerte99 app: Swerte99 login – Swerte99
Beta138: Promo slot gacor hari ini – Beta138
Slot game d?i thu?ng Slot game d?i thu?ng Dang ky GK88
1 win.com.ci https://www.1win40013.ru
https://swertewin.life/# Swerte99
maglaro ng Jiliko online sa Pilipinas: jilwin – Jiliko casino walang deposit bonus para sa Pinoy
Slot oyunlar? Pinco-da Yeni az?rbaycan kazino sayt? or Slot oyunlar? Pinco-da
https://images.google.bt/url?sa=t&url=https://pinwinaz.pro Etibarl? onlayn kazino Az?rbaycanda
Yuks?k RTP slotlar Kazino bonuslar? 2025 Az?rbaycan and Pinco il? real pul qazan Pinco kazino
Bandar bola resmi Withdraw cepat Beta138 or Login Beta138
https://maps.google.lk/url?sa=t&url=https://betawinindo.top Bandar bola resmi
Withdraw cepat Beta138 Promo slot gacor hari ini and Withdraw cepat Beta138 Login Beta138
Pinco casino mobil t?tbiq: Yuks?k RTP slotlar – Pinco r?smi sayt
Хай!
Казино онлайн Узбекистан набирает популярность. онлайн казино ташкент РРіСЂРѕРєРё выбирают удобные платформы.
Написал: – https://casinostrategies.cfd/
казино онлайн узбекистан
онлайн казино uz
онлайн казино ташкент
Удачи!
Yo!
Best online casino games in India pay well. online casino india app download Discover your favorite games.
Check out this link – https://blackjackpro.cfd/
online casino india legal
online casino india real money
indian online casino
Best of luck!
Jiliko casino Jiliko bonus or Jiliko casino walang deposit bonus para sa Pinoy
https://www.google.fi/url?q=https://jilwin.pro Jiliko app
Jiliko app Jiliko casino and Jiliko casino Jiliko app
plinko игра на деньги скачать http://1win1162.ru/
Bandar bola resmi Bandar bola resmi Bandar bola resmi
Abutogel: Abutogel – Situs togel online terpercaya
Dang ky GK88: Rut ti?n nhanh GK88 – GK88
Online casino Jollibet Philippines Online gambling platform Jollibet or Online betting Philippines
http://www.albert-schweitzer-haus-bonn.de/umleitung.php?link=1winphili.company 1winphili
jollibet login jollibet and 1winphili jollibet login
Abutogel: Link alternatif Abutogel – Abutogel login
jocuri ruleta jocuri ruleta
бонусы спорт 1win как пользоваться https://1win1162.ru
1win bahis https://www.1win40012.ru
1вин мобильная версия сайта 1вин мобильная версия сайта
jollibet login: jollibet app – jollibet login
Приветствую!
Vavada казино онлайн Казахстан вход через официальный сайт. онлайн казино кз Регистрация занимает две минуты.
Написал: – https://mobilecasinogames.cfd
онлайн казино казахстана
казахстан онлайн казино
казино онлайн в казахстане с бонусом за регистрацию
Бывай!
apple store moldova 1win40008.ru
Good day!!
Best online casino in Nigeria awaits. online casino nigeria Claim your welcome bonus now.
Check this example resource – https://livedealeronline.cfd
best casino app in nigeria
nigeria online casino
best online casino in nigeria
Best of luck!
Swerte99 online gaming Pilipinas Swerte99 casino Swerte99 login
Yuks?k RTP slotlar: Slot oyunlar? Pinco-da – Kazino bonuslar? 2025 Az?rbaycan
¡Buen día!
Un casino en lГnea confiable garantiza seguridad total. juego casino real Juega con tranquilidad y confianza.
Lee este enlace – https://smartphonecasino.cfd/
casino en lГnea confiable
casino en lГnea dinero real
casino real en linea
¡Buena suerte!
1win yükle https://www.1win40011.ru
https://swertewin.life/# Swerte99 online gaming Pilipinas
Link alternatif Abutogel: Bandar togel resmi Indonesia – Abutogel
Bandar bola resmi Promo slot gacor hari ini or Withdraw cepat Beta138
https://www.google.am/url?q=https://betawinindo.top Slot gacor Beta138
Situs judi resmi berlisensi Link alternatif Beta138 and Bandar bola resmi Bandar bola resmi
1win сайт 1win сайт
maglaro ng Jiliko online sa Pilipinas Jiliko login or Jiliko casino walang deposit bonus para sa Pinoy
http://www.openlaw.com.pl/wikka.php?wakka=jilwin.pro Jiliko app
Jiliko casino walang deposit bonus para sa Pinoy Jiliko slots and Jiliko maglaro ng Jiliko online sa Pilipinas
электрокарнизы москва http://elektrokarniz11.ru/ .
jocuri poker online jocuri poker online
jilwin: Jiliko slots – Jiliko login
проект перепланировки квартиры для согласования http://proekt-pereplanirovki-kvartiry4.ru/ .
1win казино http://www.1win1163.ru
Ca cu?c tr?c tuy?n GK88: Ca cu?c tr?c tuy?n GK88 – Rut ti?n nhanh GK88
проект по перепланировке квартиры proekt-pereplanirovki-kvartiry4.ru .
1вин верификация http://1win1163.ru
Swerte99 casino walang deposit bonus para sa Pinoy Swerte99 login Swerte99 app
1win букмекерская контора скачать http://1win1161.ru
Online betting Philippines: jollibet – jollibet
электрокарнизы москва http://elektrokarnizy-dlya-shtor150.ru .
¡Bienvenido!
Los juegos de casino ecuador han ganado popularidad por su diversidad y calidad grГЎfica excepcional. cassino dando giros gratis ecuador Explora la amplia gama de juegos de casino ecuador y descubre nuevas formas de entretenimiento.
Lee este enlace – https://bestslotmachines.shop/
casino en linea ecuador
¡Buena suerte!
Jollibet online sabong Online casino Jollibet Philippines or Jollibet online sabong
https://images.google.sn/url?sa=t&url=https://1winphili.company jollibet app
jollibet login jollibet and jollibet Jollibet online sabong
Swerte99: Swerte99 casino – Swerte99 casino walang deposit bonus para sa Pinoy
¡Qué tal!
Los juegos de casino en linea con dinero real ofrecen la combinaciГіn perfecta de entretenimiento y oportunidades de ganancia. casino online dinero real chile Explora toda la variedad de juegos de casino en linea con dinero real y encuentra tu juego perfecto para ganar en grande.
Lee este enlace – https://jackpotwins.shop/
1xbet casino chile
¡Buena suerte!
Live casino Indonesia: Situs judi resmi berlisensi – Link alternatif Beta138
прикольные горшки https://dizaynerskie-kashpo-nsk.ru/ .
Situs judi online terpercaya Indonesia Mandiribet login Mandiribet
https://abutowin.icu/# Situs togel online terpercaya
GK88: Ca cu?c tr?c tuy?n GK88 – Ca cu?c tr?c tuy?n GK88
Jiliko app Jiliko slots or Jiliko bonus
https://cse.google.com.cu/url?sa=t&url=https://jilwin.pro Jiliko
Jiliko slots Jiliko casino walang deposit bonus para sa Pinoy and Jiliko casino Jiliko casino
Withdraw cepat Beta138 Link alternatif Beta138 or Bonus new member 100% Beta138
https://images.google.com.na/url?q=https://betawinindo.top Withdraw cepat Beta138
Link alternatif Beta138 Beta138 and Link alternatif Beta138 Bonus new member 100% Beta138
mexican mail order pharmacies: medicine in mexico pharmacies – Mexican Pharmacy Hub
Mexican Pharmacy Hub: Mexican Pharmacy Hub – legit mexican pharmacy for hair loss pills
indian pharmacy Indian Meds One indian pharmacy paypal
как вывести деньги с 1win http://1win1164.ru/
бот lucky jet скачать https://www.1win1169.ru
trusted mexico pharmacy with US shipping: Mexican Pharmacy Hub – Mexican Pharmacy Hub
1win вывод средств http://1win1168.ru/
Good day!!
Master the art of live online gaming roulette casino strategy with our comprehensive guides and expert tips. online casino real money no deposit canada Learn proven live online gaming roulette casino strategy techniques from professional players and start playing smarter today.
Check this out – https://mobilecasinoplay.shop
free cash bonus no deposit casino canada real money
Enjoy your study session!
Glad to see you!
Online casino India app download takes just minutes. best online casino india Start gaming right away.
Check this out – https://newcasinosites.shop
best online casino games in india
is online casino legal in india
Best of luck!
1win бонус за установку приложения http://1win1169.ru/
промокод 1вин http://1win1170.ru
Indian Meds One: indian pharmacy paypal – Indian Meds One
https://mexicanpharmacyhub.com/# Mexican Pharmacy Hub
¡Buen día!
Un casino real en lГnea brinda emociГіn autГ©ntica. casino en lГnea confiable Vive la experiencia Las Vegas.
Lee este enlace – https://playonlinecasino.shop/
casino en lГnea dinero real
casino real en linea
juego casino real
¡Buena suerte!
Привет!
Топ онлайн казино Узбекистан обновляется ежемесячно. казино онлайн узбекистан Рейтинги помогают выбрать площадку.
По ссылке: – https://realmoneycasino.shop/
топ онлайн казино узбекистан
онлайн казино ташкент
Удачи!
Mexican Pharmacy Hub: Mexican Pharmacy Hub – Mexican Pharmacy Hub
¡Buenas!
Trending online casino games represent the cutting edge of digital entertainment with innovative features and stunning graphics. casino online dinero real bolivia Discover what makes these trending online casino games so popular among players and critics alike.
Lee este enlace – https://onlinecasinoreview.shop/
casino online bolivia
¡Buena suerte!
pharmacy rx one legit: MediDirect USA – MediDirect USA
1вин сайт официальный вход https://www.1win1167.ru
buy antibiotics from mexico buy viagra from mexican pharmacy generic drugs mexican pharmacy
pharmacy cialis no prescription: pharmacy at home viagra – MediDirect USA
1вин ракета 1win1165.ru
acyclovir cream pharmacy: Ponstel – MediDirect USA
pharmacy website india: Indian Meds One – top 10 pharmacies in india
гидроизоляция цена http://www.gidroizolyaciya-cena-3.ru .
электрические рулонные шторы купить москва http://elektricheskie-zhalyuzi.ru/ .
вход в 1win http://1win1165.ru
где купить аттестат за 10 11 класс где купить аттестат за 10 11 класс .
диплом ссср купить недорого диплом ссср купить недорого .
mexico drug stores pharmacies: Mexican Pharmacy Hub – buying prescription drugs in mexico
купить учебный диплом в одессе купить учебный диплом в одессе .
купить аттестаты за 11 класс с занесением купить аттестаты за 11 класс с занесением .
можно ли купить диплом в реестре можно ли купить диплом в реестре .
Мы предлагаем документы ВУЗов, расположенных в любом регионе России. Приобрести диплом о высшем образовании:
купить аттестат за 11 класс омск
купить аттестат 11 класса отзывы http://arus-diplom23.ru/ .
купить аттестат за 10 11 https://arus-diplom24.ru .
https://mexicanpharmacyhub.shop/# Mexican Pharmacy Hub
купить проведенный диплом всеми купить проведенный диплом всеми .
купил аттестат за 11 класс и поступил в омон купил аттестат за 11 класс и поступил в омон .
где купить диплом с реестром где купить диплом с реестром .
Выгодно приобрести диплом любого ВУЗа!
Мы изготавливаем дипломы любой профессии по приятным ценам— study-lingvo.ru
Mexican Pharmacy Hub Mexican Pharmacy Hub Mexican Pharmacy Hub
купить диплом ижевск с занесением в реестр купить диплом ижевск с занесением в реестр .
Indian Meds One: buy medicines online in india – indian pharmacies safe
Indian Meds One: buy prescription drugs from india – Indian Meds One
скачать казино 1win https://www.1win1166.ru
jocuri de noroc moldova 1win40014.ru
1win букмекерская зеркало 1win букмекерская зеркало
официальный сайт 1win ставки на спорт 1win1171.ru
1вин ракета https://1win1166.ru/
1вин оф http://1win1164.ru/
1win skachat 1win skachat
Online medicine home delivery: Indian Meds One – top 10 pharmacies in india
активные ваучеры 1win http://1win1170.ru
скачать казино 1win http://1win1167.ru/
Online medicine order: reputable indian online pharmacy – Indian Meds One
moldova casino https://1win40014.ru
гидроизоляция цена http://gidroizolyaciya-cena-1.ru/ .
гидроизоляция цена gidroizolyaciya-cena-2.ru .
semaglutide mexico price: order kamagra from mexican pharmacy – best mexican pharmacy online
1win login http://1win40015.ru/
MediDirect USA help rx pharmacy discount card rite aid store hours pharmacy
What’s up!
Enjoy peace of mind with our secure login live online gaming casino system that protects your personal information and gaming activities. real money casinos canada Trust in our secure login live online gaming casino infrastructure for a worry-free gaming experience every time you play.
Check this example resource – https://top10casinos.shop/
top 6 online real money casino canada
online casino canada real money jackpot city
Have a great day!
Здравствуйте!
Онлайн казино РљР— работает круглосуточно. казино онлайн РІ Казахстане СЃ Р±РѕРЅСѓСЃРѕРј Р·Р° регистрацию Рграйте РІ любимые слоты онлайн.
Здесь подробней: – https://freeplaycasino.shop/
онлайн казино Казахстана
пин ап казино онлайн Казахстан
Пока!
1win ставки на спорт официальный сайт http://1win1168.ru/
Indian Meds One: Indian Meds One – india pharmacy
¡Hola amigo!
Los casinos online Bolivia ofrecen una experiencia de juego emocionante desde la comodidad de tu hogar. casino en Bolivia Descubre las ventajas de jugar en casinos online Bolivia con seguridad y transparencia garantizadas.
Lee este enlace – https://realcasinogames.shop/
Casino en Bolivia
Casino online Bolivia
Casino con dinero real Bolivia
¡Buena suerte!
https://indianmedsone.shop/# п»їlegitimate online pharmacies india
tesco pharmacy sildenafil: india rx pharmacy – MediDirect USA
проект перепланировки в Москве проект перепланировки в Москве .
автоматический горшок автоматический горшок .
blink online pharmacy viagra asda pharmacy or publix pharmacy online ordering
https://images.google.gy/url?sa=t&url=https://medidirectusa.com Precose
express rx pharmacy and medical supplies online pharmacy denmark and safeway pharmacy store 1818 meijer pharmacy free atorvastatin
гидроизоляция цена https://www.gidroizolyaciya-cena-3.ru .
স্বাগতম!
অনলাইন ক্যাসিনো সাইট
এই লিঙ্কটি পড়ুন – https://onlinecasinospins.shop
ক্যাসিনো টাকা ইনকাম
অনলাইন ক্যাসিনো খেলার নিয়ম
অনলাইন ক্যাসিনো গেম
শুভকামনা!
Indian Meds One reputable indian online pharmacy Indian Meds One
mexican mail order pharmacies pharmacies in mexico that ship to usa or mexican border pharmacies shipping to usa
https://maps.google.com.om/url?sa=t&url=https://mexicanpharmacyhub.com pharmacies in mexico that ship to usa
[url=http://rosieanimaladoption.ca/?URL=http://mexicanpharmacyhub.com::]mexican rx online[/url] mexican online pharmacies prescription drugs and [url=https://dongzong.my/forum/home.php?mod=space&uid=37896]mexican online pharmacies prescription drugs[/url] mexican rx online
MediDirect USA: MediDirect USA – asda pharmacy ventolin
автоматика somfy http://www.avtomatika-somfy77.ru/ .
сколько стоит проект перепланировки квартиры сколько стоит проект перепланировки квартиры .
reputable indian online pharmacy pharmacy website india or pharmacy website india
https://www.google.com.vn/url?q=https://indianmedsone.com indian pharmacy online
top 10 pharmacies in india india pharmacy mail order and indian pharmacy top 10 pharmacies in india
buy from mexico pharmacy: Mexican Pharmacy Hub – Mexican Pharmacy Hub
1вин верификация https://1win1172.ru
diovan pharmacy card: MediDirect USA – MediDirect USA
www mostbet com https://mostbet11062.ru/
mostbet kg регистрация http://mostbet11061.ru/
аттестат 11 класс купить аттестат 11 класс купить .
Заказать диплом на заказ вы можете через сайт компании. igrosoft.getbb.ru/viewtopic.php?f=11&t=4965
купить аттестат за 11 класс рязань http://www.arus-diplom23.ru .
как купить диплом с проводкой как купить диплом с проводкой .
вход мостбет https://mostbet11062.ru/
купить аттестаты за 11 класс г облучье https://arus-diplom22.ru .
мостбеь https://mostbet11063.ru/
купить проведенный диплом одно купить проведенный диплом одно .
купить аттестат об образовании 11 классов https://arus-diplom25.ru .
диплом с проводкой купить диплом с проводкой купить .
купить диплом украины с занесением в реестр http://www.arus-diplom35.ru/ .
диплом о высшем образовании купить с занесением в реестр диплом о высшем образовании купить с занесением в реестр .
Albenza: MediDirect USA – seroquel pharmacy assistance
Hello there!
Online casino India legal sites follow strict rules. online gambling in india Play with complete confidence.
Check this out – https://vipcasinooffers.shop/
Online casino in India is legal
Online casino India real money
Best online casino India
Have a great day!
Mexican Pharmacy Hub Mexican Pharmacy Hub safe place to buy semaglutide online mexico
reputable indian pharmacies: online shopping pharmacy india – indian pharmacy paypal
купить диплом в ровно купить диплом в ровно .
купить диплом о техническом образовании с занесением в реестр купить диплом о техническом образовании с занесением в реестр .
можно ли купить диплом о среднем образовании можно ли купить диплом о среднем образовании .
¡Saludos!
Blackjack en vivo disponible ahora. cassino dando giros gratis ecuador Juegos de casino Ecuador con crupieres reales esperan.
Lee este enlace – https://bestonlineslots.shop/
Casino con giros gratis Ecuador
Como jugar casino en linea con dinero real Ecuador
¡Buena suerte!
аттестат о среднем образовании 9 классов купить аттестат о среднем образовании 9 классов купить .
https://indianmedsone.shop/# Indian Meds One
24 7 pharmacy online: MediDirect USA – MediDirect USA
lucky jet игра скачать lucky jet игра скачать
aviator 1win download http://www.1win1173.ru
Mexican Pharmacy Hub: buying prescription drugs in mexico online – Mexican Pharmacy Hub
mexico pharmacies prescription drugs mexico drug stores pharmacies or purple pharmacy mexico price list
https://maps.google.com.pr/url?sa=t&url=https://mexicanpharmacyhub.com mexican online pharmacies prescription drugs
mexico drug stores pharmacies medicine in mexico pharmacies and buying prescription drugs in mexico best online pharmacies in mexico
online shopping pharmacy india: reputable online pharmacy no prescription – viagra apollo pharmacy
купить аттестат за 11 класс тайшет купить аттестат за 11 класс тайшет .
all med pharmacy buy viagra pharmacy 100mg or pharmacy rx one viagra
http://nou-rau.uem.br/nou-rau/zeus/auth.php?back=http://medidirectusa.com&go=x&code=x&unit=x viagra pharmacy us
online pharmacy vardenafil adipex pharmacy coupon and levitra us pharmacy viagra pharmacy malaysia
Mexican Pharmacy Hub Mexican Pharmacy Hub Mexican Pharmacy Hub
купить диплом внесенный в реестр купить диплом внесенный в реестр .
диплом реестр купить диплом реестр купить .
MediDirect USA: cialis cost pharmacy – MediDirect USA
sportandbets http://sportbets32.ru .
автоматика somfy https://www.avtomatika-somfy.ru .
1-win 1win1174.ru
1win app https://1win1173.ru
скачать мостбет на телефон скачать мостбет на телефон
1win скачать на ios https://www.1win1174.ru
¡Hola!
Un casino real en lГnea brinda emociГіn autГ©ntica. casino real en linea Vive la experiencia Las Vegas.
Lee este enlace – https://slotgamereview.shop
casino en lГnea confiable
casino en lГnea dinero real
casino online dinero real mГ©xico
¡Buena suerte!
¡Buen día!
juegos de casino en linea con dinero real chile
Lee este enlace – https://casinowheel.shop/
Juego de casino con dinero real Chile
Juegos de casino en linea con dinero real Chile
Juegos de casino con dinero real Chile
¡Buena suerte!
Здарова!
Рнформация можно ли играть РІ онлайн казино РІ Узбекистане. онлайн казино uz Следите Р·Р° новостями.
Здесь подробней: – https://casinowithjackpot.shop/
Онлайн казино Ташкент
Лучшие онлайн казино в Узбекистане
Онлайн казино uz
Покеда!
Indian Meds One: pharmacy website india – Indian Meds One
mostbet казино скачать mostbet казино скачать
Indian Meds One: online pharmacy india – Indian Meds One
mostbet casino mostbet11063.ru
купить аттестат об окончании 11 классов в барнауле купить аттестат об окончании 11 классов в барнауле .
id mostbet com https://mostbet11064.ru/
аттестат за 11 класс 2006 купить аттестат за 11 класс 2006 купить .
купить диплом с проводкой одно купить диплом с проводкой одно .
рольшторы заказать http://www.elektricheskie-zhalyuzi.ru/ .
indian pharmacies safe Online medicine home delivery or best online pharmacy india
https://cse.google.tl/url?sa=t&url=https://indianmedsone.com cheapest online pharmacy india
best india pharmacy buy medicines online in india and india pharmacy cheapest online pharmacy india
мос бет https://mostbet11065.ru
Indian Meds One: п»їlegitimate online pharmacies india – top 10 online pharmacy in india
https://indianmedsone.shop/# Indian Meds One
ставки на спорт мостбет http://www.mostbet11061.ru
rybelsus from mexican pharmacy isotretinoin from mexico Mexican Pharmacy Hub
спортивные новости http://novosti-sporta-3.ru/ .
новости спорта футбол novosti-sporta-2.ru .
прогноз на теннис на сегодня от профессионалов prognozy-ot-professionalov.ru .
win 1 win 1
1win приложение ios http://1win1175.ru/
is tadalafil available in generic form: Tadalify – Tadalify
Hi friend!
Online gambling in India requires responsible gaming habits. indian online casino Set limits before playing.
Check this out – https://bestcasinoplay.cfd/
Top 10 online casino in India
Online casino games in India
Online casino India app download
Enjoy your study session!
новости спорта футбол http://www.novosti-sporta-2.ru/ .
নমস্কার!
অনলাইন ক্যাসিনো সাইট
এই লিঙ্কটি পড়ুন – https://digitalblackjack.cfd
অনলাইন ক্যাসিনো গেম
শুভকামনা!
SildenaPeak: SildenaPeak – SildenaPeak
спортивные новости http://www.novosti-sporta-1.ru .
SildenaPeak: SildenaPeak – SildenaPeak
SildenaPeak: generic viagra price uk – sildenafil without prescription
KamaMeds Sildenafil oral jelly fast absorption effect Compare Kamagra with branded alternatives
приводы somfy http://www.avtomatika-somfy.ru/ .
https://sildenapeak.com/# buying viagra on line
cialis 30 mg dose: sildalis sildenafil tadalafil – Tadalify
order generic cialis online 20 mg 20 pills us pharmacy prices for cialis or cheap cialis 20mg
http://www.spiritualforums.com/vb/redir.php?link=http://tadalify.com/ tadalafil and voice problems
cialis free sample cialis canada online and generic cialis online pharmacy how long before sex should you take cialis
sportandbets http://www.sportbets31.ru/ .
Tadalify: cialis 5mg price comparison – mantra 10 tadalafil tablets
¡Hola!
El casino en lГnea dinero real ofrece premios reales. juego casino real Gana desde tu casa hoy.
Lee este enlace – https://pokerplayersonline.cfd/
casino online mГ©xico dinero real
juego casino real
casino en lГnea dinero real
¡Buena suerte!
Приветствую!
РџРёРЅ РђРї казино онлайн Казахстан предлагает тысячи РёРіСЂ. топ онлайн казино Казахстан Рспытайте удачу РІ слотах.
Перейди по ссылке: – https://1-win-2025.com/
онлайн казино Казахстана
онлайн казино КЗ
Бывай!
Tadalify Tadalify buy cialis 20mg
Safe access to generic ED medication: Affordable sildenafil citrate tablets for men – Men’s sexual health solutions online
купить аттестат об окончании 11 классов с занесением в реестр купить аттестат об окончании 11 классов с занесением в реестр .
otc viagra pills cheap generic viagra uk or how to get viagra over the counter
https://www.google.com.pa/url?q=https://sildenapeak.com buy sildenafil 50mg
where to get sildenafil online generic sildenafil otc and viagra generic viagra where can i buy cheap viagra
Купить диплом можно через сайт компании. hl2forever.ru/member.php?u=266
Fast-acting ED solution with discreet packaging Non-prescription ED tablets discreetly shipped or KamaMeds
https://sofortindenurlaub.de/redirect/index.asp?url=http://kamameds.com Sildenafil oral jelly fast absorption effect
KamaMeds Men’s sexual health solutions online and KamaMeds Kamagra oral jelly USA availability
lowest price generic viagra: female viagra medication – can i buy viagra over the counter australia
спортивные новости http://www.novosti-sporta-3.ru .
кто купил диплом с занесением в реестр кто купил диплом с занесением в реестр .
прогнозы на теннис го спорт http://www.prognozy-ot-professionalov.ru .
высшее образование купить диплом с занесением в реестр высшее образование купить диплом с занесением в реестр .
аттестат за 11 класс 2006 купить аттестат за 11 класс 2006 купить .
Kamagra oral jelly USA availability: Online sources for Kamagra in the United States – Safe access to generic ED medication
Non-prescription ED tablets discreetly shipped: Kamagra oral jelly USA availability – Affordable sildenafil citrate tablets for men
купить диплом о среднем специальном купить диплом о среднем специальном .
Non-prescription ED tablets discreetly shipped Non-prescription ED tablets discreetly shipped Affordable sildenafil citrate tablets for men
купить диплом института высшего образования купить диплом института высшего образования .
cialis 20 mg how long does it take to work: cialis dosage for bph – Tadalify
http://kamameds.com/# Sildenafil oral jelly fast absorption effect
Выгодно купить диплом любого университета!
Мы готовы предложить дипломы любой профессии по доступным ценам— diplommy.ru
прогноз на футбольный матч прогноз на футбольный матч .
cialis commercial bathtub cialis dose or tadalafil eli lilly
http://www.ohashi-co.com/w3a/redirect.php?redirect=http://tadalify.com how long before sex should you take cialis
cialis experience forum cialis tablets for sell and cialis pharmacy cialis or levitra
точные прогнозы на футбол от аналитиков https://kompyuternye-prognozy-na-futbol13.ru .
Tadalify: best place to get cialis without pesricption – Tadalify
SildenaPeak: SildenaPeak – SildenaPeak
Tadalify: buying cialis online safely – Tadalify
buy canadian sildenafil buy viagra cheap online uk or viagra sildenafil 100mg
https://cse.google.com.my/url?sa=t&url=https://sildenapeak.com where to purchase female viagra
viagra cheap how to get cheap viagra online and prescription viagra cheap over the counter viagra substitute
generic tadalafil in us Tadalify cialis dapoxetine overnight shipment
мосбет скачат mostbet11067.ru
ED treatment without doctor visits Sildenafil oral jelly fast absorption effect or Compare Kamagra with branded alternatives
https://clients1.google.com.ng/url?q=https://kamameds.com Men’s sexual health solutions online
Affordable sildenafil citrate tablets for men Affordable sildenafil citrate tablets for men and Safe access to generic ED medication Kamagra reviews from US customers
скачать мостбет с официального сайта https://mostbet11072.ru
промокод мостбет промокод мостбет
generic viagra online fast delivery: SildenaPeak – sildenafil rx drugstore online
mostbet история компании mostbet история компании
диплом купить проведенный диплом купить проведенный .
мостбет com https://www.mostbet11073.ru
Safe access to generic ED medication: Non-prescription ED tablets discreetly shipped – Online sources for Kamagra in the United States
прогнозы на хоккей сегодня прогнозы на хоккей сегодня .
Safe access to generic ED medication: Sildenafil oral jelly fast absorption effect – KamaMeds
Welcome aboard!
Online casino games in India include live dealers. online casino in india is legal Experience real casino action.
Read the link – https://win-win25.com
Online casino India app download
Best online casino India
Best online casino app in India
Have a great day!
https://tadalify.shop/# cialis manufacturer coupon
Здарова!
Подробно можно ли играть в онлайн казино в Узбекистане. топ онлайн казино узбекистан Юридический аспект.
По ссылке: – https://25-win-25.com/
Онлайн казино ташкент
Лучшие онлайн казино в Узбекистане
Топ онлайн казино Узбекистан
До встречи!
Купить диплом возможно используя сайт компании. rrsclub.ru/member.php?u=1164
Tadalify buy cialis 20 mg online order cialis soft tabs
купить диплом об образовании с занесением в реестр купить диплом об образовании с занесением в реестр .
Современный автопортал https://automobile.kyiv.ua свежие новости, сравнительные обзоры, тесты, автострахование и обслуживание. Полезная информация для водителей и покупателей.
Строительный сайт https://vitamax.dp.ua с полезными материалами о ремонте, дизайне и современных технологиях. Обзоры стройматериалов, инструкции по монтажу, проекты домов и советы экспертов.
горшки с автополивом для комнатных растений купить http://kashpo-s-avtopolivom-kazan.ru .
купить ванну гидромассажную купить ванну гидромассажную .
Мы готовы предложить дипломы любой профессии по приятным тарифам. Купить диплом в Нижнекамске — kyc-diplom.com/geography/nizhnekamsk.html
cialis free 30 day trial buy cialis by paypal or cialis over the counter at walmart
https://cse.google.tk/url?sa=t&url=https://tadalify.com where can i buy cialis online in australia
cialis online with no prescription best price on cialis and sublingual cialis vardenafil and tadalafil
best place to get cialis without pesricption: Tadalify – buying cialis internet
Мы предлагаем документы институтов, которые находятся на территории всей Российской Федерации. Заказать диплом ВУЗа:
купить аттестат за 11 классов с занесением в реестр в москве
мосбет https://www.mostbet11070.ru
Non-prescription ED tablets discreetly shipped: KamaMeds – Safe access to generic ED medication
купить диплом ижевск с занесением в реестр купить диплом ижевск с занесением в реестр .
купить диплом легальный купить диплом легальный .
SildenaPeak: sildenafil 100 mg tablets coupon – SildenaPeak
купить аттестат за 11 класс в самаре купить аттестат за 11 класс в самаре .
мостбет кж mostbet11068.ru
как купить аттестат за 11 как купить аттестат за 11 .
купить аттестат об окончании 11 классов в новосибирске купить аттестат об окончании 11 классов в новосибирске .
viagra 2018 cheap sildenafil online or sildenafil tablets where to buy
https://www.adminer.org/redirect/?url=http://sildenapeak.com how to buy genuine viagra online
where to buy cheap viagra in uk sildenafil mexico cheapest and cheap generic viagra canadian pharmacy buy viagra online price
Заказать диплом любого университета поможем. Купить диплом техникума, колледжа в Волгограде – [url=http://diplomybox.com/kupit-diplom-tekhnikuma-kolledzha-v-volgograde/]diplomybox.com/kupit-diplom-tekhnikuma-kolledzha-v-volgograde[/url]
купить аттестат за 11 класс вечерняя школа купить аттестат за 11 класс вечерняя школа .
Men’s sexual health solutions online ED treatment without doctor visits Fast-acting ED solution with discreet packaging
мост бет букмекерская контора https://mostbet11069.ru/
Kamagra oral jelly USA availability: Kamagra oral jelly USA availability – Safe access to generic ED medication
гидромассаж купить http://www.vanna-s-gidromassazhem.ru/ .
KamaMeds: Compare Kamagra with branded alternatives – Affordable sildenafil citrate tablets for men
Здарова!
В топ онлайн казино Узбекистан честно. можно ли играть в онлайн казино в узбекистане Гарантия выплат.
Читай тут: – https://1win-2025.shop
Лучшие онлайн казино в Узбекистане
Онлайн казино ташкент
Онлайн казино uz
До встречи!
¡Hola!
EncriptaciГіn SSL protege datos personales. casino en lГnea confiable TecnologГa avanzada garantiza mГЎxima privacidad.
Lee este enlace – https://1win25.shop/
Juego casino real
Casino en lГnea confiable
Casino online dinero real MГ©xico
¡Buena suerte!
?Saludos!
juego de casino con dinero real chile
Lee este enlace – https://25win25.shop
1xbet casino Chile
Casino real online Chile
Casino online dinero real Chile
?Buena suerte!
ставки мостбет https://www.mostbet11069.ru
Online sources for Kamagra in the United States ED treatment without doctor visits or Non-prescription ED tablets discreetly shipped
http://maps.google.co.zw/url?q=http://kamameds.com Online sources for Kamagra in the United States
Kamagra oral jelly USA availability Safe access to generic ED medication and Compare Kamagra with branded alternatives Non-prescription ED tablets discreetly shipped
Sildenafil oral jelly fast absorption effect: Fast-acting ED solution with discreet packaging – Fast-acting ED solution with discreet packaging
https://kamameds.shop/# Compare Kamagra with branded alternatives
vjcn,tn https://www.mostbet11068.ru
мостбет зеркало http://www.mostbet11074.ru
ставки на спорт прогнозы хоккей http://luchshie-prognozy-na-khokkej13.ru .
delivery in new york city shipping company new york city
mostbet.com казино скачать mostbet.com казино скачать
http://www.mostbet http://www.mostbet11073.ru
новости футбольных клубов https://www.novosti-sporta-12.ru .
¡Saludos!
Apuesta con dinero real ahora. casino en linea ecuador ecuador Casino con dinero real Ecuador paga premios increГbles.
Lee este enlace – https://1win-25.com/
Juegos de casino en linea con dinero real Ecuador
Casino en linea Ecuador
Juegos de casino Ecuador
¡Buena suerte!
Здравствуй!
Пин ап казино онлайн Казахстан дарит фриспины. казино онлайн в Казахстане с бонусом за регистрацию Получите бесплатные вращения.
Читай тут: – https://25win-25.shop
Онлайн казино в Казахстане
Топ онлайн казино Казахстан
Vavada казино онлайн Казахстан вход
Бывай!
мостеб мостеб
Safe access to generic ED medication: Compare Kamagra with branded alternatives – Men’s sexual health solutions online
ED treatment without doctor visits Men’s sexual health solutions online Affordable sildenafil citrate tablets for men
viagra purchase canada: SildenaPeak – viagra online pills
cialis tadalafil 20mg tablets cialis canada online or what is the generic for cialis
https://maps.google.com.uy/url?q=https://tadalify.com cialis uses
best place to buy tadalafil online cialis online pharmacy australia and cialis same as tadalafil buy cialis from canada
mostbet casino http://www.mostbet11075.ru
ED treatment without doctor visits: Compare Kamagra with branded alternatives – Men’s sexual health solutions online
mostbet мостбет https://mostbet11071.ru/
id mostbet com id mostbet com
купить диплом занесением реестр отзывы купить диплом занесением реестр отзывы .
buy viagra online in canada how to get viagra tablets or viagra uk fast delivery
https://maps.google.ht/url?sa=t&url=https://sildenapeak.com canada generic viagra price
where to purchase viagra pills viagra 40 mg and online pharmacy viagra australia viagra 100 mg generic
para que sirve las tabletas cialis tadalafil de 5mg: Tadalify – where to buy cialis
KamaMeds: Sildenafil oral jelly fast absorption effect – KamaMeds
gessi продукция http://www.gessi-santehnika-5.ru .
диплом с внесением в реестр купить диплом с внесением в реестр купить .
https://tadalify.shop/# Tadalify
купить диплом об образовании купить диплом об образовании .
Tadalify: cialis ingredients – Tadalify
Tadalify buy cialis on line cialis canada pharmacy no prescription required
купить аттестат за 11 класс петрозаводск купить аттестат за 11 класс петрозаводск .
как купить диплом с проводкой как купить диплом с проводкой .
купить аттестат за 11 классов в ростове купить аттестат за 11 классов в ростове .
купить чистый аттестат за 11 класс купить чистый аттестат за 11 класс .
где можно купить аттестаты за 11 класс https://arus-diplom9.ru/ – где можно купить аттестаты за 11 класс .
Compare Kamagra with branded alternatives ED treatment without doctor visits or Compare Kamagra with branded alternatives
https://cse.google.com.cu/url?sa=t&url=https://kamameds.com Sildenafil oral jelly fast absorption effect
Sildenafil oral jelly fast absorption effect Online sources for Kamagra in the United States and Online sources for Kamagra in the United States Men’s sexual health solutions online
SildenaPeak: viagra super active – best price viagra 50 mg
новости мирового спорта http://www.novosti-sporta-12.ru .
где можно купить аттестат за 11 класс сколько стоит красноярск где можно купить аттестат за 11 класс сколько стоит красноярск .
Online sources for Kamagra in the United States: ED treatment without doctor visits – Safe access to generic ED medication
прогнозы на спорт от профессионалов на сегодня https://www.prognozy-na-sport-7.ru .
Stavki Prognozy https://stavki-prognozy-2.ru/ .
Kamagra oral jelly USA availability Online sources for Kamagra in the United States Fast-acting ED solution with discreet packaging
how to get viagra united states buy viagra canada or sildenafil 25 mg daily
http://www.extrasmallworld.de/forward.php?to=https://sildenapeak.com brand viagra online canadian pharmacy
viagra online prescription uk prescription viagra 100mg and sildenafil 20 mg can you order viagra online
купить проведенный диплом всеми купить проведенный диплом всеми .
sildenafil generic 50 mg viagra for women 2017 or order no prescription viagra
https://www.google.gl/url?q=https://sildenapeak.com where to buy sildenafil canada
viagra online buy usa viagra 20 mg online and where can you buy viagra uk sildenafil citrate generic
buy generic viagra online free shipping: sildenafil drug coupon – viagra kaufen
Tadalify: Tadalify – cialis slogan
http://tadalify.com/# Tadalify
generic viagra pills cheap: SildenaPeak – buy sildenafil paypal
плинко плинко
ставки 1win https://1win22097.ru/
Tadalify Tadalify Tadalify
горшок для растений с автополивом https://www.kashpo-s-avtopolivom-spb.ru .
плинко кз плинко кз
Men’s sexual health solutions online: Affordable sildenafil citrate tablets for men – KamaMeds
Affordable sildenafil citrate tablets for men Compare Kamagra with branded alternatives or Kamagra oral jelly USA availability
https://clients1.google.com.vc/url?q=https://kamameds.com Men’s sexual health solutions online
Online sources for Kamagra in the United States Kamagra reviews from US customers and Sildenafil oral jelly fast absorption effect Safe access to generic ED medication
ED treatment without doctor visits: Non-prescription ED tablets discreetly shipped – Kamagra oral jelly USA availability
купить аттестат в школе за 11 класс купить аттестат в школе за 11 класс .
Spot on with this write-up, I truly believe this website requirements a lot much more consideration. I’ll probably be once more to read much much more, thanks for that info.
cialis reviews photos: Tadalify – Tadalify
прогноз на футбол сегодня прогноз на футбол сегодня .
ставки на футбол сегодня 100 процентный https://www.prognozy-na-futbol-6.ru .
cialis ingredients what does a cialis pill look like or cialis free samples
https://maps.google.co.tz/url?sa=t&url=https://tadalify.com tadalafil cheapest price
tadalafil review forum cialis san diego and cialis generic release date cialis dose
Safe access to generic ED medication: Non-prescription ED tablets discreetly shipped – KamaMeds
You ma’am have a way with words. Thank you very much!
Sildenafil oral jelly fast absorption effect Non-prescription ED tablets discreetly shipped Kamagra oral jelly USA availability
SildenaPeak: buy generic viagra online – where to get generic viagra online
where to buy viagra in india female viagra for sale uk or viagra cream price in india
https://maps.google.ne/url?q=https://sildenapeak.com brand viagra 50 mg
viagra online canada no prescription sildenafil pills from mexico and can you buy viagra online without a prescription how do i get viagra online
ED treatment without doctor visits: Sildenafil oral jelly fast absorption effect – Fast-acting ED solution with discreet packaging
Мы можем предложить документы институтов, расположенных на территории всей РФ. Приобрести диплом любого университета:
купить аттестат за 11 классов в молдове
generic viagra online usa: SildenaPeak – buy viagra online with paypal
купить аттестаты 11 класс цена купить аттестаты 11 класс цена .
купить диплом пту с занесением в реестр купить диплом пту с занесением в реестр .
Tadalify: tadalafil 20mg (generic equivalent to cialis) – cialis headache
Как сам!
Делюсь полезным: 8 способов найти деньги, не влезая в кредиты. Срочный займ на карту без отказа с плохой кредитной историей
Здесь подробней: – https://economica-2025.ru
Где взять деньги срочно без возврата
Срочный займ на карту без отказа с плохой кредитной историей
Займ на карту без отказа без проверки мгновенно
Будь здоров!
plinko slot https://www.plinko3001.ru
melbet зеркало на ios http://melbet3006.com/
Fast-acting ED solution with discreet packaging Safe access to generic ED medication or Safe access to generic ED medication
https://www.google.tg/url?q=https://kamameds.com Kamagra reviews from US customers
KamaMeds Kamagra reviews from US customers and Sildenafil oral jelly fast absorption effect Online sources for Kamagra in the United States
прогноз ставок на хоккей http://prognozy-na-khokkej.ru .
cialis price achats produit tadalafil pour femme en ligne or does cialis lowers blood pressure
https://www.gamekiller.net/proxy.php?link=https://tadalify.com mint pharmaceuticals tadalafil
buy cialis online reddit cialis efectos secundarios and order cialis online what is cialis used to treat
plinko kz http://plinko3001.ru
Kamagra reviews from US customers: Men’s sexual health solutions online – KamaMeds
melbet казино слоты melbet казино слоты
1win.com официальный сайт https://1win22097.ru
https://kamameds.shop/# Men’s sexual health solutions online
Tadalify: cialis 5 mg price – Tadalify
купить диплом украина с занесением в реестр http://www.arus-diplom32.ru/ .
СтавкиПрогнозы https://www.stavki-prognozy-two.ru .
sildenafil 10mg tablets purchase genuine viagra online or brand viagra from canada
http://www.esquiremediakit.com/r5/emaillink.asp?link=https://sildenapeak.com:: viagra india online pharmacy
viagra 4 sale sildenafil 50mg coupon and sildenafil 50 mg price purchase viagra online cheap
Stavki Prognozy http://www.stavki-prognozy-2.ru/ .
ED treatment without doctor visits: Online sources for Kamagra in the United States – Sildenafil oral jelly fast absorption effect
купить диплом в кривом роге недорого купить диплом в кривом роге недорого .
cheap viagra generic canada order viagra without prescription or sildenafil 100mg generic mexico
https://www.google.mu/url?q=https://sildenapeak.com buy cheap viagra
buy viagra pharmacy uk viagra average cost and sildenafil sale in india sildenafil 50 mg mexico
Fast-acting ED solution with discreet packaging: Non-prescription ED tablets discreetly shipped – Kamagra oral jelly USA availability
оценка аренды Москва услуга оценки
аттестат за 11 класс купить цена arus-diplom21.ru .
купить аттестаты за 11 класс с отличием https://arus-diplom21.ru .
Заказать диплом на заказ в столице можно используя сайт компании. psp-wp-test.objectsdev.com/kupit-diplom-oficialno-i-bez-riska-92
KamaMeds: Online sources for Kamagra in the United States – Fast-acting ED solution with discreet packaging
купить диплом образца ссср купить диплом образца ссср .
купить диплом о высшем с занесением в реестр купить диплом о высшем с занесением в реестр .
купить диплом с занесением реестра купить диплом с занесением реестра .
KamaMeds: Kamagra oral jelly USA availability – Online sources for Kamagra in the United States
ставки на хоккей сегодня прогнозы ставки на хоккей сегодня прогнозы .
IverGrove IverGrove IverGrove
комплектная трансформаторная подстанция цена http://transformatornye-podstancii-kupit.ru/ .
SteroidCare Pharmacy: SteroidCare Pharmacy – prednisone canada pharmacy
Приветствую!
Цена решает всё, или почему скупой платит дважды. Серый телефон как проверить?
Написал: – https://pro-telefony.ru/
Что значит серый телефон
До встречи!
IverGrove: IverGrove – IverGrove
injectable ivermectin for humans: ivermectin for mice – ivermectin for horses tractor supply
трансформаторная подстанция ква https://www.transformatornye-podstancii-kupit1.ru .
умный горшок для растений умный горшок для растений .
купить свидетельство о заключении брака http://educ-ua5.ru/ .
SteroidCare Pharmacy: SteroidCare Pharmacy – cost of prednisone 5mg tablets
хоккей сегодня прогноз https://prognozy-na-khokkej.ru .
диплом о среднем профессиональном образовании с занесением в реестр купить диплом о среднем профессиональном образовании с занесением в реестр купить .
купить обложку аттестата за 11 класс купить обложку аттестата за 11 класс .
как купить диплом о высшем образовании с занесением в реестр как купить диплом о высшем образовании с занесением в реестр .
купить аттестат за 11 классов купить аттестат за 11 классов .
where buy clomid without a prescription can i get cheap clomid no prescription FertiCare Online
TrustedMeds Direct: TrustedMeds Direct – amoxicillin 500 mg tablets
купить аттестат школы за 9 11 классы купить аттестат школы за 9 11 классы .
where to buy amoxicillin pharmacy antibiotic amoxicillin or amoxicillin over the counter in canada
http://images.google.be/url?q=https://trustedmedsdirect.com buy amoxicillin from canada
amoxicillin for sale buy amoxicillin over the counter uk and amoxacillian without a percription cost of amoxicillin 30 capsules
mostbet sayt mostbet sayt
IverGrove: п»їorder stromectol online – IverGrove
FertiCare Online: FertiCare Online – FertiCare Online
скачать казино мостбет скачать казино мостбет
mostbet casino скачать на андроид http://mostbet4150.ru
Мы предлагаем документы любых учебных заведений, расположенных в любом регионе России. Заказать диплом ВУЗа:
купить аттестат за 11 классов в екатеринбурге
http://ferticareonline.com/# can you buy cheap clomid prices
купить легальный диплом техникума купить легальный диплом техникума .
mostbet com вход mostbet com вход
скачать мостбет на андроид бесплатно старая версия mostbet4147.ru
CardioMeds Express: CardioMeds Express – furosemide 40mg
brand prednisone 54 prednisone or buy prednisone with paypal canada
https://vatikan.pennergame.de/redirect/?site=https://steroidcarepharmacy.com how to buy prednisone
[url=http://images.google.gp/url?q=https://steroidcarepharmacy.com]prednisone cost in india[/url] generic prednisone cost and [url=https://lifnest.site/user/wbzvpxowmbwbzvpxowmb/?um_action=edit]prednisone[/url] order prednisone 100g online without prescription
fast shipping prednisone: prednisone 0.5 mg – prednisone tablets 2.5 mg
CardioMeds Express: lasix 100mg – lasix side effects
прогноз хоккей на сегодня прогноз хоккей на сегодня .
CardioMeds Express: CardioMeds Express – lasix generic
mostbet uz https://mostbet4105.ru
vps hosting windows vps hosting europe
купить аттестат за 11 класс купить аттестат за 11 класс .
mostbet официальный сайт регистрация http://mostbet4148.ru
Привет!
Пора разобраться в теме дженериков. Дженерики что это такое
Написал: – https://generik-info.ru/chto-takoe-dzheneriki-prostymi-slovami/
Дженерики что это
Дженерики для чего они нужны
Что такое дженерики лекарства
Бывай!
where to buy amoxicillin pharmacy amoxicillin buy no prescription or amoxicillin 500 mg tablets
http://www.wittstock.chemie.uni-oldenburg.de/agef/link_extern.html?link=https://trustedmedsdirect.com amoxicillin cephalexin
amoxicillin 200 mg tablet amoxicillin script and amoxicillin 500mg price canada amoxicillin online without prescription
mostbet skachat mostbet skachat
купить аттестат за 11 класс в твери http://arus-diplom9.ru – купить аттестат за 11 класс в твери .
медицинские аппараты узи http://kupit-uzi-apparat26.ru .
mostbets https://mostbet4148.ru
FertiCare Online: FertiCare Online – can i buy clomid for sale
стул мастера педикюра тележка для косметолога
lasix medication: CardioMeds Express – CardioMeds Express
где купить аттестат за 11 класс в красноярске где купить аттестат за 11 класс в красноярске .
mostbet online uz https://mostbet4104.ru/
купить аттестат за 11 класс в бишкеке купить аттестат за 11 класс в бишкеке .
Получить диплом университета можем помочь. Купить диплом техникума, колледжа в Омске – diplomybox.com/kupit-diplom-tekhnikuma-kolledzha-v-omske
IverGrove: IverGrove – IverGrove
mostbet uz skachat android mostbet uz skachat android
http://cardiomedsexpress.com/# furosemide 40mg
mostbet promo bilan ro‘yxatdan o‘tish https://mostbet4103.ru/
Мы можем предложить дипломы любой профессии по доступным тарифам. Купить диплом доктора наук — kyc-diplom.com/diplom-doktora-nauk.html
can you buy prednisone prednisone buy without prescription or prednisone 10 mg tablet
https://images.google.cat/url?sa=t&url=https://steroidcarepharmacy.com where to buy prednisone without prescription
can you buy prednisone online uk prednisone buy online nz and where can i buy prednisone online without a prescription prednisone 20mg by mail order
SteroidCare Pharmacy: can you buy prednisone without a prescription – prednisone 4 mg daily
mostbet скачат http://mostbet4149.ru/
rosacea ivermectin: IverGrove – buy ivermectin stromectol
mostbet.com что это https://mostbet4147.ru
ivermectin otc ivermectin amazon or topical ivermectin cost
http://www.agrolandis.de/24.html?&no_cache=1&tipUrl=http://ivergrove.com how long does it take ivermectin to work
stromectol pills ivermectin paste 1.87 dosage for dogs and ivermectin injection ivermectin covid studies
lasix furosemide: buy furosemide online – CardioMeds Express
как купить диплом занесенный в реестр как купить диплом занесенный в реестр .
mostbet казино mostbet казино
мостбет скачать казино https://mostbet4149.ru/
мел мел .
amoxicillin 30 capsules price TrustedMeds Direct order amoxicillin uk
over the counter amoxicillin canada where can you get amoxicillin or how to get amoxicillin
http://leadertoday.org/topframe2014.php?goto=https://trustedmedsdirect.com amoxicillin without a doctors prescription
amoxicillin 875 125 mg tab amoxicillin generic and amoxicillin 30 capsules price amoxicillin 500mg no prescription
lasix online lasix side effects or buy furosemide online
https://images.google.com.kh/url?q=https://cardiomedsexpress.com lasix generic
furosemida 40 mg furosemida 40 mg and lasix generic name furosemide
mostbet sayti mostbet sayti
уличные цветочные горшки больших размеров https://www.ulichnye-kashpo-kazan.ru .
ivermectin pour on tractor supply: IverGrove – IverGrove
20 mg of prednisone: SteroidCare Pharmacy – SteroidCare Pharmacy
TrustedMeds Direct: TrustedMeds Direct – TrustedMeds Direct
https://trustedmedsdirect.shop/# TrustedMeds Direct
CardioMeds Express CardioMeds Express lasix online
бетон м3 стоимость бетона
купить аттестат 11 классов ставрополь купить аттестат 11 классов ставрополь .
как легально купить диплом о как легально купить диплом о .
Приобрести диплом университета!
Наши специалисты предлагаютвыгодно приобрести диплом, который выполнен на оригинальном бланке и заверен мокрыми печатями, штампами, подписями должностных лиц. Диплом пройдет любые проверки, даже с использованием специально предназначенного оборудования. Решайте свои задачи быстро с нашей компанией- ralphouensanga.com/read-blog/27499_gde-kupit-v-moskve-diplom.html
купить диплом с занесением в реестр цена купить диплом с занесением в реестр цена .
FertiCare Online: where can i get generic clomid pills – FertiCare Online
IverGrove: IverGrove – ivermectin study
prednisone 5093 non prescription prednisone 20mg or buying prednisone mexico
http://www.mozakin.com/bbs-link.php?tno=&url=steroidcarepharmacy.com/ prednisone 20mg online pharmacy
prednisone cream rx prednisone without rx and buy prednisone canadian pharmacy where can i get prednisone
Farmacia online migliore: kamagra online Italia – farmacie online sicure
мостбет бонус без депозита уз http://mostbet4109.ru
мостбет кыргызстан скачать мостбет кыргызстан скачать
farmacia online piГ№ conveniente: trattamenti per la salute sessuale senza ricetta – farmacia online piГ№ conveniente
мостбет уз кириш мостбет уз кириш
mostbet.com uz https://mostbet4102.ru
mostbet com android mostbet com android
https://forzaintima.shop/# kamagra originale e generico online
comprare farmaci online all’estero kamagra oral jelly spedizione discreta top farmacia online
sports bet sportbets31.ru .
рекламное агентство seo http://sites.google.com/view/reklamnoe-agenstvo-seo .
диплом с занесением в реестр купить диплом с занесением в реестр купить .
купить диплом украина с занесением в реестр http://arus-diplom33.ru .
gessi продукция gessi-santehnika-5.ru .
купить легальный диплом техникума купить легальный диплом техникума .
как купить аттестат 11 класса как купить аттестат 11 класса .
comprare farmaci online con ricetta: cialis online Italia – top farmacia online
мостбет узбекистон мостбет узбекистон
viagra generico in farmacia costo: PotenzaFacile – viagra originale in 24 ore contrassegno
п»їFarmacia online migliore: farmaci senza ricetta online – acquisto farmaci con ricetta
most bet uz http://mostbet4108.ru
sayt mostbet mostbet4111.ru
купить диплом вуза в киеве купить диплом вуза в киеве .
viagra naturale acquistare viagra generico online cialis farmacia senza ricetta
Мы предлагаем дипломы любых профессий по приятным ценам. Приобретение документа, который подтверждает обучение в университете, – это грамотное решение. Заказать диплом о высшем образовании: 1.kupitiblog.ru/10/?post_type=topic&p=17346
стоит купить диплом о высшем образовании стоит купить диплом о высшем образовании .
mostbet o‘zbekcha versiya http://mostbet4106.ru/
http://pillolesubito.com/# Farmacia online miglior prezzo
mostbet uz shikoyatlar https://www.mostbet4107.ru
купить диплом о средне специальном образовании реестр купить диплом о средне специальном образовании реестр .
купить диплом техникума в реестре цена arus-diplom33.ru .
viagra cosa serve: sildenafil senza ricetta – viagra generico in farmacia costo
Откройте для себя мир азартных игр на 888старз россия.
888starz — это популярная платформа для азартных игр, предоставляющая разнообразие возможностей для игроков. На сайте можно найти различные игры, включая слоты и настольные игры.
888starz предлагает удобный интерфейс, что облегчает процесс игры. Пользователи могут быстро находить необходимые игры и информацию на сайте.
Пользователи могут быстро зарегистрироваться и начать игру. В качестве первого шага потребуется указать основные данные и пройти верификацию.
888starz радует своих игроков щедрыми бонусами и многочисленными акциями. За счет бонусов пользователи могут увеличить свои шансы на выигрыш и продлить время игры.
купить диплом с записью в реестре купить диплом с записью в реестре .
viagra generico sandoz: PotenzaFacile – viagra consegna in 24 ore pagamento alla consegna
mostbet skachat iphone http://www.mostbet4107.ru
acquistare farmaci senza ricetta: kamagra online Italia – farmacia online senza ricetta
купить диплом в кривом роге купить диплом в кривом роге .
mosrbet https://mostbet4106.ru/
купить аттестат 11 класса отзывы http://arus-diplom9.ru – купить аттестат 11 класса отзывы .
acquistare farmaci senza ricetta Farmaci Diretti comprare farmaci online all’estero
казино мосбет https://mostbet4117.ru/
купить аттестат за 11 класс в сургуте купить аттестат за 11 класс в сургуте .
farmacia online piГ№ conveniente farmacie online affidabili or Farmacia online miglior prezzo
http://goldankauf-engelskirchen.de/out.php?link=http://forzaintima.com Farmacia online miglior prezzo
Farmacia online miglior prezzo top farmacia online and top farmacia online Farmacia online miglior prezzo
войти в мостбет mostbet4147.ru
мостбет личный кабинет http://mostbet4118.ru
farmacie online affidabili: consegna rapida in tutta Italia – Farmacie online sicure
farmaci senza ricetta elenco farmacia online senza ricetta or Farmacia online miglior prezzo
http://kinderundjugendpsychotherapie.de/url?q=https://pillolesubito.com acquisto farmaci con ricetta
top farmacia online Farmacie online sicure and comprare farmaci online all’estero Farmacia online piГ№ conveniente
мостбет ставки на спорт онлайн https://www.mostbet4117.ru
диплом купить с занесением в реестр москва диплом купить с занесением в реестр москва .
farmacia online piГ№ conveniente PilloleSubito migliori farmacie online 2024
Как сам!
Давай начистоту поговорим о том, сколько сил и времени это требует на самом деле. как заработать деньги в интернете на играх без вложений
Читай тут: – https://zarabotok-na-igrah.ru/kak-zarabotat-na-igrah/
можно ли заработать на играх с выводом денег
заработок на играх
можно ли заработать на играх в телефоне
Покеда!
farmacie online autorizzate elenco: consegna rapida in tutta Italia – acquisto farmaci con ricetta
https://potenzafacile.com/# viagra online consegna rapida
мостбет киберспорт http://mostbet4112.ru/
mostbet parolni unutdingizmi http://www.mostbet4116.ru
mostbet uz com https://www.mostbet4115.ru
acquisto farmaci con ricetta: kamagra oral jelly spedizione discreta – top farmacia online
где купить аттестат за 11 классов в воронеже где купить аттестат за 11 классов в воронеже .
мостбет слоты http://mostbet4116.ru/
mostbet texniki dəstək mostbet texniki dəstək
migliori farmacie online 2024: sildenafil generico senza ricetta – Farmacia online migliore
горшки для сада большие http://www.ulichnye-kashpo-kazan.ru/ .
gel per erezione in farmacia pillole per la disfunzione erettile in Italia dove acquistare viagra in modo sicuro
farmacie online affidabili farmacia online senza ricetta or farmacie online affidabili
https://clients1.google.bi/url?sa=t&url=http://forzaintima.com farmaci senza ricetta elenco
п»їFarmacia online migliore farmacia online senza ricetta and migliori farmacie online 2024 farmacia online piГ№ conveniente
viagra consegna in 24 ore pagamento alla consegna: PotenzaFacile – viagra originale in 24 ore contrassegno
mostbet aviator strategiyasi mostbet aviator strategiyasi
Farmacia online piГ№ conveniente farmacie online affidabili or comprare farmaci online all’estero
https://wikiroutes.info/zh/away?to=https://farmacidiretti.com Farmacie on line spedizione gratuita
Farmacia online miglior prezzo farmacie online sicure and migliori farmacie online 2024 farmacie online sicure
mostbet uz apk skachat http://mostbet4113.ru
BorderMeds Express: BorderMeds Express – BorderMeds Express
диплом о среднем образовании купить легально http://www.arus-diplom31.ru/ .
indian pharmacy: BharatMeds Direct – BharatMeds Direct
https://bharatmedsdirect.shop/# BharatMeds Direct
купить аттестат за 11 классов новосибирск купить аттестат за 11 классов новосибирск .
купить аттестат 11 классов в нижнем новгороде купить аттестат 11 классов в нижнем новгороде .
Online medicine order BharatMeds Direct BharatMeds Direct
mostbet şifrə unutmuşam https://mostbet4134.ru
Добрый день!
Не знаешь, как сообщить близким об увольнении? как пережить несправедливое увольнение
Написал: – https://zhit-legche.ru/kak-perezhit-uvolnenie/
хочу уволится с работы
как пережить увольнение с работы форум
как пережить увольнение с любимой работы
Удачи!
гидромассажные ванны цена гидромассажные ванны цена .
MapleMeds Direct: good value pharmacy – viagra generic online pharmacy
mostbet app qeydiyyat https://mostbet4134.ru/
купить диплом сколько купить диплом сколько .
мостбет уз кириш мостбет уз кириш
mostbet texniki dəstək https://www.mostbet4135.ru
Заказать диплом о высшем образовании!
Мы изготавливаем дипломы психологов, юристов, экономистов и других профессий по приятным ценам— diplom-profi.ru
mostbet promo kod http://mostbet4133.ru
mostbet apk https://www.mostbet4132.ru
indian pharmacies safe: top 10 pharmacies in india – indian pharmacy paypal
можно ли купить диплом в реестре можно ли купить диплом в реестре .
online pharmacy viagra usa: sam’s club pharmacy hours – MapleMeds Direct
купить аттестат 11 классов пермь купить аттестат 11 классов пермь .
купить диплом с занесением в реестр в уфе купить диплом с занесением в реестр в уфе .
mostbet mobil tətbiqi mostbet4135.ru
купить диплом о высшем образовании с занесением в реестр купить диплом о высшем образовании с занесением в реестр .
купить аттестат за 11 класс в киеве https://arus-diplom21.ru .
дома под ключ иркутск stroitelstvo-domov-irkutsk-2.ru .
BorderMeds Express BorderMeds Express BorderMeds Express
Stavki Prognozy https://stavki-prognozy-one.ru .
BorderMeds Express: legit mexican pharmacy for hair loss pills – BorderMeds Express
mostbet mobil qeydiyyat http://www.mostbet4133.ru
http://bordermedsexpress.com/# BorderMeds Express
мостбет уз мостбет уз
купить диплом цена купить диплом цена .
купить аттестат за 11 класс в волжском https://www.arus-diplom23.ru .
mostbet bonus ishlatish http://mostbet4112.ru/
online pharmacy provigil: reliable online pharmacy – MapleMeds Direct
купить диплом в кривом роге недорого купить диплом в кривом роге недорого .
reputable indian online pharmacy: BharatMeds Direct – reputable indian online pharmacy
pin up poker uz pin up poker uz
mexican drugstore online mexico drug stores pharmacies or medication from mexico pharmacy
http://sexynews24.com/exlink.php?url=http://bordermedsexpress.com/ purple pharmacy mexico price list
mexico drug stores pharmacies buying prescription drugs in mexico and mexico drug stores pharmacies buying prescription drugs in mexico
pin up aviator demo pin up aviator demo
BorderMeds Express: buy cheap meds from a mexican pharmacy – BorderMeds Express
BharatMeds Direct buy medicines online in india india pharmacy
пин ап бонус по промокоду http://pinup5005.ru
mostbet.com skachat https://mostbet4161.ru
mostbet ruletka uz mostbet ruletka uz
Приветствую!
Выигрыш в казино – это лучшая реклама. рейтинг казино
Переходи: – http://nagny-casino.ru/kazino-s-bystrym-vyvodom/
олимп казино
казино онлайн
казино без верификации
Удачи!
buy viagra from mexican pharmacy: BorderMeds Express – buy meds from mexican pharmacy
mostbet uz qonuniymi mostbet uz qonuniymi
BorderMeds Express: medication from mexico pharmacy – BorderMeds Express
купить аттестат 11 классов в спб купить аттестат 11 классов в спб .
indian pharmacy online: pharmacy website india – india pharmacy
pin up mobil ilova pinup5004.ru
https://maplemedsdirect.shop/# MapleMeds Direct
купить диплом колледжа с занесением в реестр купить диплом колледжа с занесением в реестр .
пин ап демо авиатор http://www.pinup5002.ru
sun rx pharmacy giant pharmacy store hours or cheapest prescription pharmacy
https://toolbarqueries.google.be/url?q=https://maplemedsdirect.com us online pharmacy cialis
pharmacy usa store cheap generic viagra online pharmacy and Cardura inhouse pharmacy domperidone
mexican rx online mexican drugstore online or medication from mexico pharmacy
https://www.google.me/url?q=https://bordermedsexpress.shop mexican drugstore online
mexico drug stores pharmacies pharmacies in mexico that ship to usa and buying prescription drugs in mexico mexican drugstore online
best online pharmacy india: BharatMeds Direct – BharatMeds Direct
top 10 pharmacies in india reputable indian pharmacies or buy prescription drugs from india
http://alt1.toolbarqueries.google.ps/url?q=https://bharatmedsdirect.com reputable indian pharmacies
reputable indian pharmacies buy medicines online in india and india online pharmacy mail order pharmacy india
напольные горшки для цветов купить интернет магазин напольные горшки для цветов купить интернет магазин .
mexican online pharmacies prescription drugs: mexico pharmacies prescription drugs – mexican mail order pharmacies
BharatMeds Direct: BharatMeds Direct – BharatMeds Direct
Stavki Prognozy https://stavki-prognozy-one.ru .
пин ап как получить выигрыш https://pinup5002.ru
пин ап поддержка в телеграм http://www.pinup5003.ru
buy prescription drugs from india BharatMeds Direct BharatMeds Direct
stavkiprognozy https://stavki-prognozy-1.ru/ .
mostbet versi mobile https://mostbet4162.ru/
Мы изготавливаем дипломы психологов, юристов, экономистов и любых других профессий по приятным ценам. Приобретение документа, который подтверждает окончание ВУЗа, – это выгодное решение. Купить диплом о высшем образовании: community.viamingle.com/read-blog/57_kupit-diplom-vysshee.html
mexican online pharmacies prescription drugs pharmacies in mexico that ship to usa or mexican online pharmacies prescription drugs
http://naiyoujc.ff66.net/productshow.asp?id=30&mnid=51913&url=http://bordermedsexpress.com mexican drugstore online
mexican drugstore online pharmacies in mexico that ship to usa and mexican border pharmacies shipping to usa medication from mexico pharmacy
мосбет https://www.mostbet4161.ru
мостбет промокод 2025 уз http://www.mostbet4163.ru
mostbet com uz https://mostbet4162.ru/
MapleMeds Direct: cheap pharmacy cialis – viagra online india pharmacy
reputable indian pharmacies: best online pharmacy india – Online medicine order
BorderMeds Express: BorderMeds Express – mexican mail order pharmacies
Online medicine home delivery top online pharmacy india BharatMeds Direct
скачать mostbet uz http://mostbet4163.ru/
Добрый день!
Откровенный рассказ о том, почему официальная гарантия — это не просто бумажка. Серый телефон как проверить?
По ссылке: – https://pro-telefony.ru/chto-delat-esli-kupil-seryj-telefon/
Что значит серый телефон
Серый телефон что значит
Как зарегистрировать серый телефон
Бывай!
http://bordermedsexpress.com/# mexico pharmacies prescription drugs
pin up jonli kazino https://pinup5004.ru/
пин ап проверить баланс пин ап проверить баланс
mostbet aviator demo mostbet aviator demo
Здарова!
Составляем финансовый план для безопасного увольнения. увольнение с работы
По ссылке: – https://zhit-legche.ru/hochu-uvolitsya-no-ne-mogu-reshitsya/
как пережить увольнение с любимой работы
увольнение с работы
что делать если уволили с работы
Пока!
clotrimazole price pharmacy manor pharmacy store locator or target pharmacy celexa
https://images.google.com.ai/url?sa=t&url=https://maplemedsdirect.com online pharmacy scams
best pharmacy price cialis women’s health and cialis online pharmacy no prescription Zerit
купить аттестат 11 классов киров купить аттестат 11 классов киров .
online shopping pharmacy india: indianpharmacy com – п»їlegitimate online pharmacies india
п»їlegitimate online pharmacies india best online pharmacy india or Online medicine order
https://maps.google.ne/url?sa=t&url=https://bharatmedsdirect.com world pharmacy india
top online pharmacy india top 10 online pharmacy in india and top 10 pharmacies in india best online pharmacy india
online mexico pharmacy USA: BorderMeds Express – BorderMeds Express
купить аттестат образование купить аттестат образование .
mostbet esports mərclər mostbet esports mərclər
mostbet.com скачать mostbet.com скачать
mexican border pharmacies shipping to usa: BorderMeds Express – mexican mail order pharmacies
mostbet poker otağı https://mostbet4140.ru
top online pharmacy india cheapest online pharmacy india online pharmacy india
мостбет скачать приложение https://www.mostbet4152.ru
mostbet parolni unutdingizmi https://www.mostbet4161.ru
диплом с проводкой купить диплом с проводкой купить .
stavkiprognozy http://www.stavki-prognozy-two.ru/ .
номер наркологии http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-12.ru .
психолог нарколог http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-13.ru/ .
п»їbest mexican online pharmacies mexican online pharmacies prescription drugs or best online pharmacies in mexico
http://cse.google.ad/url?sa=t&url=http://bordermedsexpress.com mexican mail order pharmacies
medication from mexico pharmacy mexican mail order pharmacies and mexico pharmacies prescription drugs mexico drug stores pharmacies
BorderMeds Express: tadalafil mexico pharmacy – buy antibiotics over the counter in mexico
п»їlegitimate online pharmacies india: india pharmacy mail order – top online pharmacy india
как купить диплом с проведением как купить диплом с проведением .
sports bet https://sportbets32.ru .
mexican online pharmacies prescription drugs: mexican online pharmacies prescription drugs – BorderMeds Express
motion sickness pharmacy warfarin counselling pharmacy support team viagra
Мы готовы предложить документы университетов, расположенных в любом регионе Российской Федерации. Приобрести диплом любого ВУЗа:
купить аттестат 11 класс 2016 год
иркутск строительство домов под ключ http://www.stroitelstvo-domov-irkutsk-6.ru .
mostbet promo qeydiyyat mostbet promo qeydiyyat
купить аттестат об окончании 11 классов в спб http://arus-diplom21.ru/ .
mostbet az casino mostbet az casino
https://bordermedsexpress.com/# buying from online mexican pharmacy
купить диплом легально купить диплом легально .
диплом купить проведенный диплом купить проведенный .
купить аттестат цена купить аттестат цена .
buy antibiotics from mexico: BorderMeds Express – mexican pharmacy for americans
best online pharmacy wellbutrin toronto pharmacy online or advair pharmacy price
https://cse.google.ms/url?sa=t&url=https://maplemedsdirect.com Meclizine
selegiline online pharmacy pharmacy viagra now and cyclophosphamide online pharmacy sildenafil citrate
купить аттестат 11 классов в вологде купить аттестат 11 классов в вологде .
indian pharmacy online india pharmacy mail order or indian pharmacy paypal
http://www.a-31.de/url?q=https://bharatmedsdirect.com indian pharmacy online
top 10 pharmacies in india india pharmacy and indian pharmacy online best india pharmacy
п»їlegitimate online pharmacies india: BharatMeds Direct – best online pharmacy india
купить аттестат за 11 классов в волгограде купить аттестат за 11 классов в волгограде .
купить диплом занесением реестр отзывы купить диплом занесением реестр отзывы .
can you get viagra at the pharmacy MapleMeds Direct mypharmacy
mostbet az qeydiyyat mostbet az qeydiyyat
Online medicine order: BharatMeds Direct – india online pharmacy
Привет!
Дешевые таблы: лотерея или умный выбор? Дженерики для чего они нужны
Читай тут: – https://generik-info.ru/analogi-lekarstv-deshevle/
Дженерики это простыми словами
Что такое дженерики простыми словами
Дженерики для чего они нужны
Покеда!
mostbet apk 2024 http://mostbet4162.ru
купить аттестат 9 класс с реестром https://educ-ua5.ru .
mostbet aviator hack uz https://www.mostbet4161.ru
млстбет http://mostbet4163.ru/
купить кашпо напольное купить кашпо напольное .
mostbet idman mərcləri http://mostbet4140.ru
mostbet promo bilan ro‘yxatdan o‘tish https://mostbet4162.ru/
купить аттестат 11 класса в красноярске http://www.arus-diplom9.ru – купить аттестат 11 класса в красноярске .
Starburst giri gratis senza deposito: giocare da mobile a Starburst – casino online sicuri con Starburst
где можно купить аттестаты 11 класс в таджикистан в иркутске где можно купить аттестаты 11 класс в таджикистан в иркутске .
мостбет бонус за регистрацию уз мостбет бонус за регистрацию уз
наркологические клиники в москве http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-12.ru/ .
preman69 login tanpa ribet promosi dan bonus harian preman69 promosi dan bonus harian preman69
купить диплом без внесения в реестр купить диплом без внесения в реестр .
сколько стоит купить аттестат за 9 класс http://www.educ-ua3.ru .
http://1wbook.com/# migliori casino online con Book of Ra
recensioni Book of Ra Deluxe slot: migliori casino online con Book of Ra – Book of Ra Deluxe slot online Italia
mostbet bonus mostbet4136.ru
???? 888starz ????? ????? ?? ????? ?? ???? ???????? . ????? 888starz ?????? ?????? ????? ?????? ???????? .
??? ????? 888starz ??????? ????? ?????? ??? ???? ???????. ???? ??????? ??????? ?? 888starz ?? ?? ????? ???? ???????? .
????? ???? 888starz ?????? ????? ??????? . ???? 888starz ??? ????? ?????? ????????? ?? ?? ?????? .
???????? ??? ???? ???? 888starz ?????? ????? ??????? ????? . ????? ??? ???????? ?????? ????? ???????? ??? ???? 888starz .
888 africa https://888starz-africa.pro/
mostbet az mostbet az
Заказать диплом под заказ вы можете через официальный сайт компании. gspanel.net/showthread.php?tid=4351
купить аттестат за 11 класс в петрозаводске http://www.arus-diplom22.ru/ .
mostbet crypto ödənişlər mostbet crypto ödənişlər
starburst: migliori casino online con Starburst – Starburst giri gratis senza deposito
можно купить аттестат 11 классов https://www.arus-diplom24.ru .
mostbet aviator necə qazanmaq mostbet4138.ru
bonus di benvenuto per Starburst giocare da mobile a Starburst or Starburst giri gratis senza deposito
https://www.valldenuria.cat/content/comun/ajax_get_news.php?ruta=/&bk=&idioma=ca&season=1&mostviews=3&rss=http://1wstarburst.com casino online sicuri con Starburst
casino online sicuri con Starburst casino online sicuri con Starburst and Starburst slot online Italia casino online sicuri con Starburst
bonus di benvenuto per Book of Ra Italia Book of Ra Deluxe slot online Italia bonus di benvenuto per Book of Ra Italia
recensioni Book of Ra Deluxe slot: migliori casino online con Book of Ra – bonus di benvenuto per Book of Ra Italia
preman69: preman69 login tanpa ribet – preman69 login tanpa ribet
Заказать диплом университета мы поможем. Купить диплом в городах – diplomybox.com/kupit-diplom-v-gorodakh
Хай!
Процентная ставка в 292% годовых — это не шутка. Микрозайм онлайн на карту круглосуточно
Читай тут: – https://kredit-bez-slov.ru/kak-bystro-sdelat-kreditnuyu-istoriyu/
Что такое дженерики в медицине
Дженерики что это такое
Дженерики это простыми словами
Покеда!
диплом о среднем образовании купить легально http://arus-diplom31.ru .
Планируете ремонт https://remontkomand.kz в Алматы и боитесь скрытых платежей? Опубликовали полный и честный прайс-лист! Узнайте точные расценки на все виды работ — от демонтажа до чистовой отделки. Посчитайте стоимость своего ремонта заранее и убедитесь в нашей прозрачности. Никаких «сюрпризов» в итоговой смете!
https://1wstarburst.com/# casino online sicuri con Starburst
garuda888 slot online terpercaya garuda888 game slot RTP tinggi situs judi online resmi Indonesia
preman69 slot: slot gacor hari ini preman69 – preman69 login
bonaslot situs bonus terbesar Indonesia: bonaslot jackpot harian jutaan rupiah – bonaslot kasino online terpercaya
1wbona bonaslot situs bonus terbesar Indonesia or bonaslot kasino online terpercaya
http://www.bloodpressureuk.org/mediacentre/Newsreleases/SaltInMedicine?came_from=http://1wbona.com/ 1wbona
bonaslot situs bonus terbesar Indonesia bonaslot link resmi mudah diakses and bonaslot jackpot harian jutaan rupiah bonaslot
888starz هو منصة شهيرة للتسلية والمراهنات . تأسست هذه المنصة بهدف توفير تجربة فريدة للمستخدمين . يمكن للمستخدمين الاستمتاع بتجارب لعب متنوعة على 888starz.
قسم الألعاب. تتمتع الألعاب بتجربة مستخدم سلسة ومرنة . تقدم المنصة مسابقات دورية حيث يمكن للاعبين استعراض مهاراتهم .
تعتبر المراهنات الرياضية جزءًا أساسيًا من 888starz . يمكن للاعبين متابعة المباريات في الوقت الحقيقي . توفر المنصة خيارات مراهنة مباشرة أثناء المباريات .
تعتمد 888starz تقنيات متقدمة لحماية بيانات المستخدمين . يتلقى اللاعبون المساعدة السريعة لحل أي مشاكل قد تواجههم. تعمل المنصة على تطوير خدماتها بناءً على ملاحظات اللاعبين .
888 africa 888 africa.
migliori casino online con Book of Ra: Book of Ra Deluxe slot online Italia – giri gratis Book of Ra Deluxe
Купить диплом о высшем образовании!
Мы предлагаембыстро купить диплом, который выполнен на оригинальном бланке и заверен печатями, штампами, подписями официальных лиц. Наш диплом способен пройти любые проверки, даже с использованием специально предназначенного оборудования. Достигайте цели максимально быстро с нашими дипломами- freeads.sg/profile/etsukoreaves19
bonaslot jackpot harian jutaan rupiah bonaslot kasino online terpercaya bonaslot link resmi mudah diakses
migliori casino online con Book of Ra: recensioni Book of Ra Deluxe slot – Book of Ra Deluxe slot online Italia
bonus di benvenuto per Starburst: migliori casino online con Starburst – giocare da mobile a Starburst
giocare da mobile a Starburst bonus di benvenuto per Starburst or giocare da mobile a Starburst
https://toolbarqueries.google.lt/url?q=http://1wstarburst.com Starburst slot online Italia
giocare da mobile a Starburst Starburst slot online Italia and casino online sicuri con Starburst migliori casino online con Starburst
купить качественный аттестат за 11 класс купить качественный аттестат за 11 класс .
permainan slot gacor hari ini 1win888indonesia or garuda888
http://www.ruth-moschner-fanclub.de/link.php?url=http://1win888indonesia.com link alternatif garuda888 terbaru
garuda888 live casino Indonesia garuda888 game slot RTP tinggi and link alternatif garuda888 terbaru garuda888 game slot RTP tinggi
https://1wbook.com/# Book of Ra Deluxe soldi veri
bonus di benvenuto per Starburst jackpot e vincite su Starburst Italia starburst
bonaslot jackpot harian jutaan rupiah: bonaslot situs bonus terbesar Indonesia – bonaslot link resmi mudah diakses
bonaslot: bonaslot – 1wbona
giocare a Starburst gratis senza registrazione: jackpot e vincite su Starburst Italia – starburst
Мы изготавливаем дипломы любых профессий по разумным тарифам. Заказ диплома, который подтверждает обучение в университете, – это выгодное решение. Заказать диплом ВУЗа: iriflessidiluce.com/smotret-doramy-onlajn-v-horoshem-kachestve-49
купить аттестат за 11 класс с занесением в реестр отзывы спб купить аттестат за 11 класс с занесением в реестр отзывы спб .
купить аттестат 11 класс 2014 купить аттестат 11 класс 2014 .
купить диплом москва с занесением в реестр купить диплом москва с занесением в реестр .
Здарова!
Раскрываем секреты успешного заработка на играх. как заработать деньги на играх в телефоне
По ссылке: – https://zarabotok-na-igrah.ru/na-kakih-igrah-mozhno-zarabotat-realnye-dengi/
сколько можно заработать на яндекс играх
заработок в играх
можно ли заработать на играх в телефоне
Будь здоров!
купить диплом с реестром о высшем образовании купить диплом с реестром о высшем образовании .
Мы изготавливаем дипломы любой профессии по приятным ценам. Города продажи дипломов — kyc-diplom.com/geography.html
трансформаторные будки https://www.transformatornye-podstancii-kupit.ru .
bonaslot jackpot harian jutaan rupiah 1wbona or bonaslot jackpot harian jutaan rupiah
https://www.google.com.gt/url?q=https://1wbona.com bonaslot login
1wbona bonaslot jackpot harian jutaan rupiah and bonaslot login bonaslot jackpot harian jutaan rupiah
трансформаторная подстанция трансформаторная подстанция .
купить диплом легальный купить диплом легальный .
купить аттестаты за 11 класс калуга купить аттестаты за 11 класс калуга .
купить диплом института ссср купить диплом института ссср .
купить диплом колледжа с занесением в реестр в купить диплом колледжа с занесением в реестр в .
bonus di benvenuto per Book of Ra Italia: giri gratis Book of Ra Deluxe – bonus di benvenuto per Book of Ra Italia
можно ли купить аттестат об окончании 11 классов можно ли купить аттестат об окончании 11 классов .
bonaslot login 1wbona bonaslot login
preman69 login: slot gacor hari ini preman69 – preman69 situs judi online 24 jam
garuda888: 1win888indonesia – garuda888
Starburst slot online Italia Starburst slot online Italia or giocare da mobile a Starburst
https://toolbarqueries.google.hu/url?q=http://1wstarburst.shop giocare da mobile a Starburst
giocare a Starburst gratis senza registrazione jackpot e vincite su Starburst Italia and Starburst giri gratis senza deposito Starburst slot online Italia
giocare da mobile a Starburst bonus di benvenuto per Starburst or bonus di benvenuto per Starburst
http://soccertraining.net/dap/product-error.php?msg=Possibly+the+best+areas+to+get+household+leather+couches+from+is+from+this+website.+There+products+range+between+leather+couches,+chesterfield+sofas+and+fabric+recliners+to+antique+sofas+and+in+addition+they+have+good+reveiws+to+indicate+for+their+own+reasons.&request=https://1wstarburst.com giocare a Starburst gratis senza registrazione
Starburst slot online Italia migliori casino online con Starburst and Starburst slot online Italia casino online sicuri con Starburst
купить диплом с занесением в реестр в калуге купить диплом с занесением в реестр в калуге .
горшок высокий для цветов купить напольные горшок высокий для цветов купить напольные .
купить диплом с реестром спб купить диплом с реестром спб .
трансформаторная будка цена https://transformatornye-podstancii-kupit2.ru .
Купить диплом под заказ можно используя сайт компании. findnearbyjob.com/employer/education-ua
купить аттестат за 11 класс в уральске https://www.arus-diplom21.ru .
https://1win69.shop/# preman69 login
preman69 situs judi online 24 jam: preman69 – preman69 login
Купить диплом любого ВУЗа!
Мы предлагаембыстро и выгодно заказать диплом, который выполнен на оригинальной бумаге и заверен печатями, штампами, подписями. Документ пройдет лубую проверку, даже с применением специально предназначенного оборудования. Достигайте своих целей быстро и просто с нашим сервисом- znamimoga.com/?p=9301
купить аттестат за 11 класс в братске купить аттестат за 11 класс в братске .
garuda888 live casino Indonesia garuda888 or garuda888 game slot RTP tinggi
https://images.google.com.au/url?q=https://1win888indonesia.com link alternatif garuda888 terbaru
garuda888 game slot RTP tinggi situs judi online resmi Indonesia and daftar garuda888 mudah dan cepat garuda888 live casino Indonesia
preman69 preman69 situs judi online 24 jam promosi dan bonus harian preman69
garuda888 slot online terpercaya: garuda888 game slot RTP tinggi – 1win888indonesia
аттестат за 11 класс купить цена http://www.arus-diplom25.ru .
купить дипломы о высшем образовании купить дипломы о высшем образовании .
купить диплом с занесением в реестр в красноярске купить диплом с занесением в реестр в красноярске .
купить диплом о высшем образовании цена харьков купить диплом о высшем образовании цена харьков .
прогнозы бесплатные prognozy-na-sport-7.ru .
купить аттестат школы за 11 https://arus-diplom9.ru – купить аттестат школы за 11 .
Привет!
Ставки сделаны, господа. казино без депозита
По ссылке: – https://nagny-casino.ru/onlajn-kazino-bez-liczenzii/
казино на деньги
казино онлайн 777
онлайн казино без лицензии
Бывай!
TrueMeds Pharmacy: all med pharmacy – canadian discount pharmacy
купить официальный аттестат за 11 класс купить официальный аттестат за 11 класс .
antibiotics over the counter ClearMeds buy antibiotics online
https://clearmedspharm.shop/# buy antibiotics online
Выгодно заказать диплом о высшем образовании!
Мы предлагаем дипломы любых профессий по приятным ценам— cultdir.ru
аппарат ультразвуковой диагностики цена kupit-uzi-apparat25.ru .
https://vitalcorepharm.com/# VitalCore Pharmacy
TrueMeds: TrueMeds – TrueMeds
Мы готовы предложить документы университетов, которые расположены в любом регионе России. Заказать диплом о высшем образовании:
купить аттестат об окончании 11 классов в томске
good pharmacy: TrueMeds – TrueMeds
buy antibiotics online buy antibiotics online for uti cheap antibiotics
http://clearmedspharm.com/# buy antibiotics
купить диплом об образовании с реестром купить диплом об образовании с реестром .
northwest canadian pharmacy pharmacy drugs or canadian pharmacy 365
https://images.google.com.py/url?q=https://truemedspharm.com canada drug pharmacy
internet pharmacy manitoba california pharmacy and canadian pharmacy cialis 20mg cheapest pharmacy to fill prescriptions without insurance
77 canadian pharmacy: TrueMeds – TrueMeds
: cheap antibiotics – ClearMeds
https://truemedspharm.shop/# canadian pharmacy cialis 20mg
TrueMeds Pharmacy TrueMeds Pharmacy TrueMeds Pharmacy
mostbet com официальный сайт http://mostbet4119.ru
аттестат за 11 класс купить москва аттестат за 11 класс купить москва .
мостбет ставки на спорт скачать http://www.mostbet4124.ru
mostbet kg http://mostbet4123.ru
https://clearmedspharm.shop/# antibiotics over the counter
legit canadian pharmacy legal online pharmacy or canadian online pharmacy
http://performance-appraisals.org/appraisal-library/topframe2014.php?goto=https://truemedspharm.shop my canadian pharmacy rx
capsule online pharmacy canada online pharmacy and canadian pharmacy 365 best india pharmacy
купить аттестат об окончании 11 классов в екатеринбурге купить аттестат об окончании 11 классов в екатеринбурге .
купить школьный аттестат об окончании 11 классов купить школьный аттестат об окончании 11 классов .
купить диплом с реестром красноярск купить диплом с реестром красноярск .
теннесси бк скачать на андроид бесплатно теннесси бк скачать на андроид бесплатно
ed pills: VitalCore Pharmacy – online erectile dysfunction prescription
купить диплом о полном среднем образовании купить диплом о полном среднем образовании .
купить диплом в уфе с реестром http://arus-diplom31.ru .
mostbet com скачать mostbet com скачать
купить аттестат за 11 класс с занесением в http://arus-diplom24.ru .
VitalCore: VitalCore Pharmacy – ed pills
TrueMeds TrueMeds Pharmacy which pharmacy is cheaper
Как сам!
Разложили по полочкам все биржи и обменники, где не нужен паспорт. перспективные альткоины
Написал: – https://pro-kriptu.ru/gde-kupit-kriptovalyutu-bez-verifikaczii/
биржи криптовалют без верификации
новые токены 2025 купить
defi проекты с доходом
До встречи!
antibiotics over the counter ClearMeds Pharmacy or ClearMeds Pharmacy
https://www.google.gm/url?q=https://clearmedspharm.com ClearMeds
antibiotics over the counter and ClearMeds
кашпо напольное высокое кашпо напольное высокое .
http://clearmedspharm.com/# ClearMeds Pharmacy
купить аттестаты за 11 класс с егэ купить аттестаты за 11 класс с егэ .
buy antibiotics online: – ClearMeds
mostbet скачать на андроид https://www.mostbet4122.ru
escrow pharmacy online canadian pharmacy sildenafil or us pharmacy
https://hjn.secure-dbprimary.com/service/util/logout/CookiePolicy.action?backto=https://truemedspharm.com www canadianonlinepharmacy
discount pharmacy mexico pharmacy rx one and vipps approved canadian online pharmacy list of online pharmacies
http://www.mostbet https://mostbet4120.ru
комплектная трансформаторная подстанция цена комплектная трансформаторная подстанция цена .
купить диплом с занесением в реестр самара https://arus-diplom33.ru/ .
Купить диплом о высшем образовании!
Наша компания предлагаетвыгодно и быстро заказать диплом, который выполнен на оригинальной бумаге и заверен печатями, штампами, подписями официальных лиц. Документ способен пройти лубую проверку, даже при использовании профессионального оборудования. Решите свои задачи быстро и просто с нашими дипломами- avto.rx22.ru/viewtopic.php?f=2&t=1666
купить аттестат в школе за 11 класс купить аттестат в школе за 11 класс .
купить диплом врача с занесением в реестр купить диплом врача с занесением в реестр .
купить аттестат за 11 класс дешево в москве купить аттестат за 11 класс дешево в москве .
VitalCore: ed pills – VitalCore Pharmacy
VitalCore Pharmacy ed pills VitalCore
https://vitalcorepharm.shop/# ed pills
поисковое продвижение москва профессиональное продвижение сайтов http://poiskovoe-prodvizhenie-moskva-professionalnoe.ru .
мостбет бк вход http://www.mostbet4121.ru
скачать мостбет на андроид бесплатно скачать мостбет на андроид бесплатно
купить аттестат за 11 класс в тюмени купить аттестат за 11 класс в тюмени .
https://vitalcorepharm.com/# VitalCore Pharmacy
rx pharmacy coupons canadian pharmacy cialis reviews or indian pharmacy paypal
https://www.printwhatyoulike.com/get_page?topic=59750.100&url=https://truemedspharm.shop/ medical mall pharmacy
canada online pharmacy online pharmacy 365 pills and best canadian pharmacy online online pharmacy drop shipping
мостбет скачать казино https://www.mostbet4121.ru
VitalCore Pharmacy: ed online prescription – ed pills
как купить диплом занесенный в реестр как купить диплом занесенный в реестр .
купить аттестат за 11 класс в спб купить аттестат за 11 класс в спб .
mostbet.kg https://mostbet4126.ru
Купить диплом на заказ вы сможете используя сайт компании. bn.tobase.ru/posting.php?mode=post&f=30&sid=d0eacdf74b595a7dfe65ba4106516af2
pharmacie en ligne france: commander médicaments livraison rapide – acheter médicament en ligne sans ordonnance
mostbet kyrgyzstan mostbet kyrgyzstan
скачать мостбет с официального сайта mostbet4127.ru
mostbet скачать бесплатно http://mostbet4123.ru/
купить настоящий диплом о высшем образовании купить настоящий диплом о высшем образовании .
viagra en ligne France sans ordonnance: viagra femme – viagra 100 mg prix abordable France
купить диплом о техническом образовании купить диплом о техническом образовании .
download mostbet download mostbet
диплом высшего образования проведенный купить диплом высшего образования проведенный купить .
купить техникум диплом купить техникум диплом .
mostbet app login mostbet app login
IntimaPharma France: tadalafil prix – pharmacie en ligne
https://pharmalibrefrance.shop/# acheter kamagra pas cher livraison rapide
диплом о высшем образовании купить в киеве http://www.educ-ua18.ru .
сколько стоит купить аттестат 11 класса сколько стоит купить аттестат 11 класса .
Приветствую!
Не попадись на удочку мошенников при анонимном обмене. где купить криптовалюту без верификации
Здесь подробней: – https://pro-kriptu.ru/birzhi-kriptovalyut-bez-verifikaczii/
крипта без kyc
куда вложить крипту без верификации
где можно купить криптовалюту без верификации
Пока!
mostbet for pc https://www.mostbet4122.ru
www mostbet com http://www.mostbet4119.ru
купить диплом в киеве купить диплом в киеве .
pharmacie en ligne sans ordonnance acheter medicaments en ligne pas cher Achat mГ©dicament en ligne fiable
acheter kamagra pas cher livraison rapide: PharmaLibre – kamagra
Clear, concise and easy to access.
трансформаторные подстанции купить трансформаторные подстанции купить .
viagra generique efficace livraison rapide et confidentielle or pilule bleue en ligne
https://toolbarqueries.google.com.ni/url?sa=i&url=http://bluepharmafrance.com Viagra en france livraison rapide
BluePharma viagra homme and viagra en ligne France sans ordonnance viagra femme
http://pharmalibrefrance.com/# acheter kamagra pas cher livraison rapide
мостбет официальный сайт вход mostbet4128.ru
mostbet uz shikoyatlar mostbet uz shikoyatlar
мостбет бонус https://mostbet4165.ru/
купить диплом о высшем образовании легально https://www.educ-ua11.ru .
http://pharmaexpressfrance.com/# pharmacie en ligne livraison europe
купить диплом колледжа в украине купить диплом колледжа в украине .
купить диплом высшем образовании занесением реестр купить диплом высшем образовании занесением реестр .
mostbet uzcard skachat mostbet uzcard skachat
IntimaPharma tadalafil 20 mg en ligne tadalafil sans ordonnance
mostbet uz skachat android http://mostbet4166.ru/
купить аттестат цена купить аттестат цена .
kamagra gel oral livraison discrete France: kamagra 100 mg prix competitif en ligne – PharmaLibre France
где купить диплом среднем где купить диплом среднем .
Хай!
Как получить адреналин, не потеряв голову и последние сбережения. [url=https://nagny-casino.ru/igry-na-dengi/]казино онлайн[/url]
Здесь подробней: – https://nagny-casino.ru/igry-na-dengi/
номад казино
казино с быстрым выводом
игры на деньги без паспорта
Бывай!
Добрый день!
Все, что ты хотел знать о заработке на играх, но боялся спросить. на каких играх можно заработать на телефоне
Читай тут: – https://zarabotok-na-igrah.ru/na-kakih-igrah-mozhno-zarabotat-bez-vlozhenij/
на каких играх можно заработать деньги без вложений
можно ли заработать на играх в телефоне
заработать на играх с выводом денег
Удачи!
Pharma Libre PharmaLibre or Pharma Libre
https://www.keepandshare.com/business/tell_keepandshare_support_reportcontent.php?url=http://pharmalibrefrance.com PharmaLibre
PharmaLibre France Pharma Libre and commander kamagra en toute confidentialite kamagra en ligne France sans ordonnance
аудит продвижения сайта аудит продвижения сайта .
Приобрести диплом о высшем образовании!
Наша компания предлагаетбыстро и выгодно заказать диплом, который выполнен на оригинальной бумаге и заверен печатями, штампами, подписями должностных лиц. Документ способен пройти любые проверки, даже с применением специально предназначенного оборудования. Достигайте свои цели быстро с нашей компанией- bbhsoba.com.ng/read-blog/9909_kupit-attestaty-za-11.html
PharmaExpress France: pharmacie digitale francaise fiable – Pharmacie Internationale en ligne
https://intimapharmafrance.shop/# cialis generique pas cher
мостбет контакты мостбет контакты
viagra femme Viagra vente libre allemagne or sildenafil citrate 100 mg
https://www.steinhaus-gmbh.de/redirect.php?lang=en&url=https://bluepharmafrance.com livraison rapide et confidentielle
viagra homme pilule bleue en ligne and BluePharma France livraison rapide et confidentielle
mostbet com официальный сайт mostbet com официальный сайт
https://pharmaexpressfrance.shop/# pharmacie en ligne france livraison belgique
скачать бесплатно мостбет http://www.mostbet4130.ru
купить диплом в ужгороде educ-ua2.ru .
cialis generique pas cher IntimaPharma France pharmacie en ligne france livraison belgique
cialis original et generique livraison rapide: cialis generique pas cher – cialis sans ordonnance
мостбет онлайн чат http://www.mostbet4167.ru
Pharmacie Internationale en ligne pharmacie en ligne avec ordonnance or Pharmacie sans ordonnance
https://www.google.com.np/url?q=https://pharmaexpressfrance.com pharmacie en ligne france fiable
pharmacie en ligne avec ordonnance Pharmacie Internationale en ligne and pharmacie en ligne pas cher pharmacie en ligne france pas cher
купить диплом о среднем купить диплом о среднем .
mostbet aviator skachat mostbet aviator skachat
мостбет apk скачать http://mostbet4168.ru/
mosbet.uz skachat http://mostbet4165.ru/
как купить диплом с занесением в реестр в екатеринбурге http://arus-diplom33.ru/ .
mostbet aviator yuklab olish mostbet aviator yuklab olish
купить диплом с реестром о высшем образовании купить диплом с реестром о высшем образовании .
mostbet apk 2024 mostbet4168.ru
мостбет кз скачать mostbet4131.ru
Как сам!
Электроника с Алиэкспресс и не только: реальный опыт. электроника китай
Читай тут: – https://pro-telefony.ru/elektronika-iz-kitaya-napryamuyu/
телефон с алиэкспресс
телефоны оптом из китая
телефон из китая
Пока!
kratonbet login: kratonbet login – kratonbet link
hargatoto hargatoto slot hargatoto login
Хай!
Индийские препараты в Россию — без нарушений закона. таблетки индия Полный гайд по оформлению и таможенным нюансам.
По ссылке: – https://generik-info.ru/gde-zakazat-tabletki-napryamuyu-iz-indii/
таблетки от давления производство индия
таблетки индия
какие таблетки привезти из индии
Бывай!
Хай!
DeFi без воды и маркетинга: только рабочие схемы. как заработать деньги на инвестициях в defi Как зарабатывать 5-50% годовых на кредитовании и пулах ликвидности.
Переходи: – https://pro-kriptu.ru/defi-proekty-s-dohodom/
что такое defi и как на этом заработать
как заработать на defi
как заработать деньги на инвестициях в defi
Будь здоров!
мостбет. регистрация. http://www.mostbet4128.ru
Купить диплом любого университета!
Наша компания предлагаетвыгодно приобрести диплом, который выполнен на оригинальной бумаге и заверен печатями, водяными знаками, подписями официальных лиц. Документ способен пройти лубую проверку, даже при помощи специального оборудования. Решите свои задачи быстро и просто с нашей компанией- helpcenter.logintrade.pl/index.php/2025/08/08/gde-kupit-diplom-v-2025-godu-bez-riska-92
betawi 77 slot betawi77
https://www.google.com.gi/url?q=https://linkr.bio/betawi777 betawi 77
betawi77 login betawi 77 slot
kratonbet kratonbet link
https://maps.google.bi/url?q=https://linklist.bio/kratonbet777 kratonbet alternatif
kratonbet kratonbet login
kratonbet alternatif: kratonbet alternatif – kratonbet alternatif
INA TOGEL Daftar Situs Togel Terpercaya Dan Bandar Daftar InaTogel Login Link Alternatif Terbaru
диплом купить техникум диплом купить техникум .
bataraslot alternatif bataraslot
http://www.northeastfwb.org/System/Login.asp?id=54595&Referer=http://bluepharmafrance.com bataraslot
batara88 bataraslot alternatif
диплом о высшем образовании купить в киеве educ-ua19.ru .
Мы изготавливаем дипломы любой профессии по приятным тарифам. Покупка диплома, подтверждающего окончание института, – это разумное решение. Купить диплом любого ВУЗа: sg.getbb.ru/viewtopic.php?f=8&t=5344
купить диплом нового образца купить диплом нового образца .
toto slot hargatoto hargatoto alternatif hargatoto slot
https://tap.bio/@hargatoto# hargatoto alternatif
купить диплом института образования купить диплом института образования .
Looking for second-hand? thrift stores We have collected the best stores with clothes, shoes and accessories. Large selection, unique finds, brands at low prices. Convenient catalog and up-to-date contacts.
Заказать диплом под заказ возможно используя официальный сайт компании. scientistsufo.ru/bezopasno-kupit-diplom-pryamo-seychas
betawi77: betawi 777 – betawi77 link alternatif
купить диплом техникума с занесением в реестр купить диплом техникума с занесением в реестр .
http://www.mostbet https://mostbet4153.ru/
mostbet bet mostbet4158.ru
мосбет мосбет
bataraslot login batara88
http://images.google.ee/url?q=https://linktr.ee/bataraslot777 situs slot batara88
bataraslot login bataraslot login
Купить диплом ВУЗа можем помочь. Значимость аттестата и диплома – diplomybox.com/kupit-diplomy-attestaty
Login Alternatif Togel Official Link Situs Toto Togel
https://cse.google.co.vi/url?q=https://linklist.bio/inatogelbrand Daftar InaTogel Login Link Alternatif Terbaru
inatogel 4D Situs Togel Terpercaya Dan Bandar
скачать мостбет официальный сайт http://www.mostbet4158.ru
mostbet скачать на телефон mostbet4159.ru
Мы предлагаем документы институтов, которые находятся в любом регионе Российской Федерации. Купить диплом о высшем образовании:
купить аттестат за 11 классов вечерней школы
Most often since i look for a blog Document realize that the vast majority of blog pages happen to be amateurish. Not so,We can honestly claim for which you writen is definitely great and then your webpage rock solid.
купить аттестат о среднем образовании купить аттестат о среднем образовании .
блог агентства интернет-маркетинга https://www.statyi-o-marketinge1.ru .
mawartoto: mawartoto link – mawartoto link
купить диплом о средне специальном образовании реестр купить диплом о средне специальном образовании реестр .
mawartoto slot mawartoto mawartoto alternatif
Хай!
Покер как профессия: превращаем увлечение в бизнес. как играть покер Все необходимые знания для стабильного заработка за столом.
Написал: – https://nagny-casino.ru/kak-vyigrat-v-poker/
покер как играть
как играть в покер онлайн
как заработать в покере
Будь здоров!
купить дипломы техникума цена купить дипломы техникума цена .
купить легально диплом купить легально диплом .
https://linktr.ee/mawartotol# mawartoto slot
купить диплом высшем образовании занесением реестр купить диплом высшем образовании занесением реестр .
kratonbet link <a href=" http://www.economia.unical.it/prova.php?a=buy+viagra “>kratonbet link
http://maps.google.to/url?q=http://pharmalibrefrance.com kratonbet link
kratonbet kratonbet login
купить диплом училища в киеве купить диплом училища в киеве .
Приветствую!
Телефоны для пожилых людей: вся правда без прикрас. телефон для пожилых сенсорный Что реально работает, а что только деньги на ветер.
Читай тут: – https://pro-telefony.ru/telefon-dlya-pozhilyh-lyudej/
мобильный телефон для пожилых людей купить
кнопочный телефон для пожилых
Удачи!
вход мостбет вход мостбет
вход в мостбет http://www.mostbet4154.ru
купить диплом с проводкой купить диплом с проводкой .
https://tap.bio/@hargatoto# hargatoto login
kratonbet alternatif: kratonbet login – kratonbet
Купить диплом техникума в Киев Купить диплом техникума в Киев .
купить аттестат за 11 классов 1998 купить аттестат за 11 классов 1998 .
mostbet com официальный сайт https://mostbet4155.ru/
мостбет вход в личный кабинет http://mostbet4154.ru
Daftar InaTogel Login Link Alternatif Terbaru Official Link Situs Toto Togel
https://www.google.com.jm/url?q=https://linklist.bio/inatogelbrand Official Link Situs Toto Togel
Official Link Situs Toto Togel INA TOGEL Daftar
букмекерские конторы бишкек mostbet4155.ru
купить диплом для иностранцев купить диплом для иностранцев .
сколько стоит купить аттестат 11 класса сколько стоит купить аттестат 11 класса .
hargatoto slot: hargatoto login – toto slot hargatoto
скачать mostbet https://mostbet4160.ru/
диплом настоящий купить с занесением в реестр https://www.arus-diplom34.ru .
мостбет казино зеркало https://mostbet4159.ru
купить проведенный диплом вуза https://www.arus-diplom31.ru .
mostbet link mostbet link
скачать мостбет казино http://www.mostbet4157.ru
купить техникум диплом купить техникум диплом .
Have you always been concerned about these issues?
мостбет казино войти mostbet4160.ru
kratonbet: kratonbet – kratonbet link
batara88 bataraslot bataraslot 88
купить диплом сколько купить диплом сколько .
seo и реклама блог http://www.blog-o-marketinge.ru .
Здравствуйте!
Резюме 2025: как не пролететь мимо работы мечты. Как создать cv Пошаговая инструкция создания резюме, которое пробьет любые ATS-системы и зацепит работодателя.
Читай тут: – https://tvoya-sila-vnutri.ru/kak-sdelat-rezyume-na-rabotu/
Как сделать резюме на hh
Покеда!
mostbet virtual sport uz mostbet virtual sport uz
inatogel 4D INA TOGEL Daftar
https://www.blickle.cn/цпФхЕЛхКЫф?зхУБ/ф?зхУБцЯецЙ?хЩи/ч?УцЮЬ?ReturnStep3=https://linklist.bio/inatogelbrand Situs Togel Toto 4D
Situs Togel Toto 4D INA TOGEL Daftar
Приобрести диплом о высшем образовании!
Наша компания предлагаетвыгодно и быстро заказать диплом, который выполнен на бланке ГОЗНАКа и заверен печатями, штампами, подписями. Документ пройдет лубую проверку, даже с использованием специально предназначенного оборудования. Достигайте цели максимально быстро с нашими дипломами- dliavas.listbb.ru/viewtopic.php?f=19&t=8779
https://linktr.ee/bataraslot777# bataraslot login
mostbwt mostbet4156.ru
mostbet личный кабинет http://mostbet4153.ru
купить диплом занесением реестр киев купить диплом занесением реестр киев .
купить диплом специалиста купить диплом специалиста .
hargatoto hargatoto login hargatoto slot
купить диплом украина с занесением в реестр https://arus-diplom33.ru .
mawartoto login: mawartoto slot – mawartoto
mawartoto slot mawartoto mawartoto slot
Мы изготавливаем дипломы любых профессий по доступным ценам. Купить диплом бакалавра — kyc-diplom.com/diplom-bakalavra.html
как купить диплом с реестром как купить диплом с реестром .
mostbet qeydiyyat zamanı bonus http://mostbet4140.ru
mostbet qeydiyyat zamanı bonus mostbet qeydiyyat zamanı bonus
mostbet az giriş https://mostbet4144.ru/
mostbet ruletka https://mostbet4145.ru
мостбеи мостбеи
how long does cialis last 20 mg: EverGreenRx USA – EverGreenRx USA
https://evergreenrxusas.com/# EverGreenRx USA
cheap cialis dapoxitine cheap online what happens if a woman takes cialis
https://clipperfund.com/?URL=https://evergreenrxusas.com:: cialis side effects forum
order cialis online cialis medicare
Как сам!
Потерял работу и не знаешь с чего начать? если вас уволили с работы Рассказываю без соплей, что делать в первую очередь.
Написал: – https://zhit-legche.ru/chto-delat-esli-uvolili-s-raboty/
как пережить увольнение с работы
как пережить несправедливое увольнение
как пережить увольнение с работы форум
Пока!
Здравствуйте!
Твоя квартира как залог: миллионы рублей даже с черным списком в БКИ. кредит 24 7 на карту с плохой кредитной историей Реальные условия и способы минимизации рисков.
По ссылке: – https://kredit-bez-slov.ru/kredit-s-plohoj-istoriej-pod-zalog-nedvizhimosti/
в каком банке можно взять кредит с плохой кредитной историей
Пока!
Мы готовы предложить документы университетов, расположенных в любом регионе РФ. Заказать диплом ВУЗа:
купить аттестат за 11 классов цена
cialis next day delivery cialis discount card
https://www.tauschbu.de/goto.php?link=http://bluepharmafrance.com cialis 20 mg from united kingdom
tadalafil cialis why is cialis so expensive
It’s the best time to make some plans for the future and it is time to be happy. I’ve read this post and if I could I wish to suggest you some interesting things or tips. Maybe you can write next articles referring to this article. I wish to read even more things about it!
cialis 5 mg for sale where to buy generic cialis
https://thecoxteam.com/?URL=https://evergreenrxusas.shop cialis how does it work
generic tadalafil 40 mg cheap generic cialis
mostbet futbol mərcləri https://mostbet4141.ru/
mostbet aviator təlimat https://mostbet4143.ru
cialis overnight shipping: EverGreenRx USA – EverGreenRx USA
Приобрести диплом вы можете используя официальный портал компании. krugozorov.ru/forum/user/11286
wettstrategie doppelte chance
Look into my web blog; Virtuelle Basketball-Wetten
what possible side effect should a patient taking tadalafil report to a physician quizlet: EverGreenRx USA – cialis payment with paypal
https://evergreenrxusas.shop/# printable cialis coupon
mostbet tətbiqi mostbet tətbiqi
Мы изготавливаем дипломы любой профессии по разумным тарифам. Заказ документа, подтверждающего обучение в университете, – это выгодное решение. Приобрести диплом ВУЗа: fremontrp.listbb.ru/viewtopic.php?f=18&t=1937
купить школьный аттестат об окончании 11 классов купить школьный аттестат об окончании 11 классов .
mostbet qanunidirmi mostbet qanunidirmi
http://evergreenrxusas.com/# EverGreenRx USA
Приобрести диплом любого ВУЗа мы поможем. Купить диплом магистра в Магнитогорске – diplomybox.com/kupit-diplom-magistra-v-magnitogorske
диплом кулинарного техникума купить http://www.educ-ua10.ru/ .
купить диплом высшем образовании занесением реестр купить диплом высшем образовании занесением реестр .
mostbet pul yatırmaq mostbet4142.ru
купить диплом об образовании с реестром купить диплом об образовании с реестром .
cialis available in walgreens over counter??: EverGreenRx USA – EverGreenRx USA
купить диплом в херсоне http://educ-ua2.ru .
EverGreenRx USA: EverGreenRx USA – EverGreenRx USA
купить диплом проведенный купить диплом проведенный .
mostbet aviator təlimat http://mostbet4144.ru
мостбет регистрация узбекистан http://www.mostbet4173.ru
mostbet uz ishonchlimi https://www.mostbet4172.ru
диплом автодорожного техникума купить в https://www.educ-ua9.ru .
mostbet apk 2025 https://mostbet4171.ru/
https://evergreenrxusas.com/# buy cialis online overnight shipping
купить старый диплом техникума http://www.educ-ua8.ru/ – купить старый диплом техникума .
cialis coupon code buy a kilo of tadalafil powder
https://www.keepandshare.com/business/tell_keepandshare_support_reportcontent.php?url=http://pharmalibrefrance.com cialis 20mg side effects
cialis black cialis and grapefruit enhance
cialis com free sample viagara cialis levitra
https://www.google.bs/url?q=https://evergreenrxusas.shop cialis dose
cialis samples cialis 10mg
buy cialis usa tadalafil generic headache nausea
https://www.google.mn/url?sa=t&url=https://evergreenrxusas.shop cialis no prescription
cialis super active real online store tadalafil prescribing information
можно купить аттестат можно купить аттестат .
мостбет узбекистан http://mostbet4173.ru
BluePill UK https://mediquickuk.shop/# cheap UK online pharmacy
Здарова!
Steam-аккаунты: от покупки до перепродажи пошагово. продать аккаунт в стим Детальная инструкция для тех, кто хочет попробовать этот заработок.
Здесь подробней: – https://zarabotok-na-igrah.ru/prodat-akkaunt-stim/
продать аккаунт в стим
как продать стим аккаунт
До встречи!
mostbet şikayətlər http://mostbet4143.ru
Приветствую!
RWA-токены: когда недвижимость становится криптой. альткоины которые дадут иксы Почему BlackRock и другие гиганты массово входят в сектор.
Переходи: – https://pro-kriptu.ru/altkoiny-kotorye-dadut-iksy/
как заработать на своем токене
альткоины которые дадут иксы
альткоины которые вырастут
Покеда!
https://intimacareuk.com/# weekend pill UK online pharmacy
https://bluepilluk.shop/# viagra discreet delivery UK
pharmacy online fast delivery UK: order medicines online discreetly – MediQuick UK
Здарова!
Смартфоны с лучшими камерами 2025 года по версии экспертов. телефон с 4 камерами Китайцы захватили топ, Apple держится в тройке, Samsung провалился.
По ссылке: – https://pro-telefony.ru/telefon-s-horoshej-kameroj/
смартфоны с хорошей камерой до 20000
Будь здоров!
viagra discreet delivery UK http://mediquickuk.com/# MediQuickUK
Купить диплом колледжа в Чернигов Купить диплом колледжа в Чернигов .
https://meditrustuk.com/# MediTrust
discreet ivermectin shipping UK: safe ivermectin pharmacy UK – trusted online pharmacy ivermectin UK
купить диплом техникума с занесением в реестр купить диплом техникума с занесением в реестр .
диплом о высшем образовании с проводкой купить диплом о высшем образовании с проводкой купить .
сколько стоит купить аттестат за 11 http://www.arus-diplom25.ru .
купить диплом специалиста недорого купить диплом специалиста недорого .
где можно купить аттестат где можно купить аттестат .
generic sildenafil UK pharmacy https://meditrustuk.com/# ivermectin without prescription UK
Мы готовы предложить документы институтов, которые находятся в любом регионе РФ. Приобрести диплом ВУЗа:
как купить аттестаты за 11 класс
http://meditrustuk.com/# trusted online pharmacy ivermectin UK
купить диплом украины цена купить диплом украины цена .
купить легально диплом купить легально диплом .
https://mediquickuk.com/# generic and branded medications UK
диплом об образовании купить диплом об образовании купить .
купить дипломы о высшем в киеве купить дипломы о высшем в киеве .
игра авиатор в 1xbet игра авиатор в 1xbet .
купить легально диплом купить легально диплом .
sildenafil tablets online order UK https://meditrustuk.com/# ivermectin tablets UK online pharmacy
ivermectin tablets UK online pharmacy ivermectin tablets UK online pharmacy discreet ivermectin shipping UK
Здравствуйте!
Твоя девушка жалуется, что ты стал другим человеком? как понять что у тебя выгорание Возможно, дело в эмоциональном выгорании.
Написал: – https://zhit-legche.ru/emoczionalnoe-vygoranie/
тест на эмоциональное выгорание
что такое выгорание у человека
эмоциональное выгорание
До встречи!
1win телефон официальное приложение https://1win12005.ru/
Хай!
Машина в кредит 2025: гайд для нормальных пацанов. машина в кредит купить Без банковской лапши на уши и маркетинговых трюков.
По ссылке: – https://kredit-bez-slov.ru/mashina-v-kredit/
машина в кредит без первоначального взноса
Бывай!
weekend pill UK online pharmacy: confidential delivery cialis UK – cialis cheap price UK delivery
мостьет http://mostbet12001.ru
купить диплом с занесением в реестр в архангельске https://kuzu.ru/forum/?PAGE_NAME=profile_view&UID=11257/ .
купить диплом техникума украина https://www.educ-ua2.ru .
online pharmacy UK no prescription MediQuickUK and pharmacy online fast delivery UK UK pharmacy home delivery
https://docs.whirlpool.eu/?brand=bk&locale=de&linkreg=https://mediquickuk.com MediQuickUK and https://sierraseo.com/user/tznfbkyvqg/?um_action=edit MediQuick UK
online pharmacy UK no prescription confidential delivery pharmacy UK and online pharmacy UK no prescription generic and branded medications UK
mostbet sitio oficial mostbet sitio oficial
BluePill UK https://meditrustuk.com/# MediTrust
viagra discreet delivery UK viagra online UK no prescription order viagra online safely UK
купить учебный диплом купить учебный диплом .
Приветствую!
Как не стать жертвой рулетки: практический гайд. стратегия фибоначчи рулетка Стратегии, лимиты, психология и главные ошибки игроков.
Написал: – https://nagny-casino.ru/kak-vyigrat-v-poker/
казино рулетка стратегия
как обыграть рулетку беспроигрышная стратегия игры
Бывай!
купить диплом о среднем купить диплом о среднем .
https://meditrustuk.com/# MediTrust UK
MediTrust: MediTrust UK – MediTrust
игра авиатор на деньги игра авиатор на деньги .
купить диплом с занесением в реестр в спб http://www.arus-diplom34.ru .
1вин официальный сайт вход http://www.1win12001.ru
1win ваучер http://1win12003.ru/
Эта разъяснительная статья содержит простые и доступные разъяснения по актуальным вопросам. Мы стремимся сделать информацию понятной для широкой аудитории, чтобы каждый смог разобраться в предмете и извлечь из него максимум пользы.
Выяснить больше – https://quick-vyvod-iz-zapoya-1.ru/
купить диплом о высшем образовании бакалавр купить диплом о высшем образовании бакалавр .
plane crash money game http://www.aviator-igra-5.ru .
куплю диплом в киеве украина https://educ-ua17.ru .
IntimaCareUK buy ED pills online discreetly UK or IntimaCareUK IntimaCare
https://www.google.com.cy/url?q=https://intimacareuk.com confidential delivery cialis UK or http://nidobirmingham.com/user/xbfpiclxhm/ tadalafil generic alternative UK
IntimaCare weekend pill UK online pharmacy or buy ED pills online discreetly UK IntimaCare
order viagra online safely UK https://meditrustuk.com/# stromectol pills home delivery UK
купить дипломы о высшем в киеве купить дипломы о высшем в киеве .
свидетельство о браке купить недорого http://educ-ua4.ru .
купить диплом техникума ссср купить диплом техникума ссср .
как использовать бонусы 1win казино [url=https://1win12001.ru]https://1win12001.ru[/url]
confidential delivery cialis UK: cialis online UK no prescription – IntimaCareUK
диплом купить реестр диплом купить реестр .
1win casino официальный сайт скачать https://1win12002.ru
Мы можем предложить дипломы любой профессии по приятным ценам. Покупка диплома, который подтверждает окончание университета, – это грамотное решение. Заказать диплом любого университета: pinksandblues.com/read-blog/65_diplom-o-vysshem-obrazovanii-kupit.html
купить диплом жд техникума купить диплом жд техникума .
aviator игра http://1win12002.ru
fast delivery viagra UK online http://meditrustuk.com/# MediTrust UK
asiatische handicap wette schweiz frankreich – Kasha,
Хай!
Контрацепция без паники: что делать, когда все пошло не по плану. что такое контрацепция Разбираем гормоны, барьеры и хирургию простым языком.
Переходи: – https://net-tabletok.ru/ekstrennaya-kontraczepcziya/
экстренная контрацепция таблетки
контрацепция диафрагма
Удачи!
Приобрести диплом ВУЗа!
Наша компания предлагаетвыгодно купить диплом, который выполняется на оригинальном бланке и заверен печатями, водяными знаками, подписями официальных лиц. Документ способен пройти лубую проверку, даже с применением профессионального оборудования. Решайте свои задачи быстро с нашим сервисом- electricmotorjobs.in/employer/aurus-diplomany
Transform your interiors with copper effect tiles, the perfect blend of style and durability. Our copper effect bathroom tiles bring spa-like warmth and elegance to wet areas, while the robust copper effect floor tiles add an industrial yet luxurious touch to living spaces. Crafted from premium porcelain, these copper look porcelain tiles capture the rich, oxidised beauty of real metal with all the benefits of easy maintenance, stain resistance, and long-lasting performance. Available in a striking 60×120 copper floor tiles format, they create a seamless, contemporary look with minimal grout lines, making them an ideal choice for modern homes and commercial projects alike.
I loved your idea there, I tell you blogs are so exciting sometimes like looking into people’s private life’s and work. Every new remark wonderful in its own right.
buy ED pills online discreetly UK: confidential delivery cialis UK – branded and generic tadalafil UK pharmacy
электрокарнизы для штор цена elektrokarnizy5.ru .
mostbet kz скачать http://www.mostbet12001.ru
скачать mostbet http://www.mostbet12002.ru
мостбет сайт бк мостбет сайт бк
диплом с проведением купить диплом с проведением купить .
купить срочно диплом о высшем образовании вуза купить срочно диплом о высшем образовании вуза .
http://mediquickuk.com/# order medicines online discreetly
Приветствую!
Скальпинг на фондовом и криптовалютном рынке. что такое скальпинг Полный разбор техник от стакана до кластерного анализа.
По ссылке: – https://pro-kriptu.ru/skalping-kriptovalyut/
стратегия скальпинг
трейдинг скальпинг
скальпинг в трейдинге
Будь здоров!
pharmacy online fast delivery UK MediQuick confidential delivery pharmacy UK
mostbet kg скачать на андроид https://mostbet12004.ru/
диплом с занесением в реестр купить диплом с занесением в реестр купить .
Купить диплом под заказ возможно используя официальный портал компании. admithel.com/employer/education-ua
branded and generic tadalafil UK pharmacy: branded and generic tadalafil UK pharmacy – IntimaCareUK
1win регистрация скачать 1win12005.ru
1win bet скачать https://www.1win12003.ru
купить диплом об образовании в запорожье купить диплом об образовании в запорожье .
cheap UK online pharmacy MediQuickUK or confidential delivery pharmacy UK UK pharmacy home delivery
https://cse.google.jo/url?sa=t&url=https://mediquickuk.com order medicines online discreetly and https://voicebyjosh.com/user/zdhlasqtjd/ trusted UK digital pharmacy
trusted UK digital pharmacy cheap UK online pharmacy or online pharmacy UK no prescription generic and branded medications UK
Добрый день!
Купейная кухня: готовим в дороге правильно. еда в поезд лайфхак Как организовать питание в поезде без вреда для здоровья.
Здесь подробней: – https://tvoya-sila-vnutri.ru/eda-v-poezde/
еда в дорогу на поезде
Бывай!
Приветствую!
CS2 скины как бизнес: от новичка до профи. продать скины кс 2 с выводом на карту Разбираем все нюансы торговли цифровыми активами.
Написал: – https://zarabotok-na-igrah.ru/prodat-skiny/
продать скины кс го
продать скины кс
где продать скины кс 2
Покеда!
купить диплом о среднем купить диплом о среднем .
купить диплом образование киеве https://www.educ-ua16.ru .
купить диплом в виннице http://www.educ-ua2.ru .
бот lucky jet скачать 1win12005.ru
промокод в 1вин казино 1win12004.ru
MediTrustUK: MediTrust UK – safe ivermectin pharmacy UK
мостбет лицензия http://mostbet12009.ru
купить медицинский диплом с занесением в реестр купить медицинский диплом с занесением в реестр .
купить аттестат образование купить аттестат образование .
1win ставки официальный сайт https://www.1win12004.ru
1win официальный сайт войти онлайн бесплатно https://www.1win12006.ru
http://meditrustuk.com/# stromectol pills home delivery UK
Приобрести диплом ВУЗа!
Мы предлагаемвыгодно купить диплом, который выполняется на оригинальном бланке и заверен мокрыми печатями, штампами, подписями. Данный документ пройдет лубую проверку, даже с применением профессионального оборудования. Решите свои задачи максимально быстро с нашими дипломами- quickad.0ok0.com/profile/glenh385476970
купить диплом о среднем специальном образовании с занесением в реестр купить диплом о среднем специальном образовании с занесением в реестр .
I just sent this post to a bunch of my friends as I agree with most of what you’re saying here and the way you’ve presented it is awesome.
I Am Going To have to come back again when my course load lets up – however I am taking your Rss feed so i can go through your site offline. Thanks.
Как сам!
Выбор спортивных наушников без воды и PR – только факты. лучшие наушники для бега Какие технологии реально нужны а на что можно забить при покупке.
По ссылке: – https://pro-telefony.ru/naushniki-dlya-sporta/
накладные наушники для спорта
купить наушники для спорта
лучшие наушники для бега
Покеда!
These are some of the most important issues we’ll face over the next few decades.
Could not disagree with the main ideas. Wonder how things will develop over the coming years.
phentermine in mexico pharmacy: SaludFrontera – mexico pharmacy price list
сайт mostbet сайт mostbet
мостбет. https://www.mostbet12008.ru
CuraBharat USA: CuraBharat USA – get medicines from india
Как сам!
Как я решил проблемы со сном с помощью мелатонина. вита мелатонин Практические советы, работающие схемы приема и разбор популярных брендов.
Здесь подробней: – https://generik-info.ru/melatonin-dlya-sna/
мелатонин цена
как принимать мелатонин
Пока!
как купить диплом с занесением в реестр [url=www.educ-ua12.ru]как купить диплом с занесением в реестр[/url] .
диплом с внесением в реестр купить диплом с внесением в реестр купить .
https://truenorthpharm.shop/# TrueNorth Pharm
sportwette tipps
Also visit my web-site – esc Wetten Schweiz
скачать мостбет на андроид mostbet12006.ru
https://truenorthpharm.com/# canadian pharmacy 365
mostbet com http://mostbet12003.ru/
купить аттестат об окончании 11 классов купить аттестат об окончании 11 классов .
промокод мостбет промокод мостбет
SaludFrontera: mexican farmacia – mexican medicine
mexi pharmacy: pharmacy in mexico that ships to us – SaludFrontera
купить диплом о образовании недорого купить диплом о образовании недорого .
Купить диплом техникума в Севастополь [url=http://www.educ-ua7.ru]Купить диплом техникума в Севастополь[/url] .
мостбет сайт бк мостбет сайт бк
1win букмекерская контора 1win букмекерская контора
купить диплом с занесением в реестр в кемерово купить диплом с занесением в реестр в кемерово .
Приветствую!
Секретное оружие успешных людей, о котором не говорят в школе. эмоциональный интеллект книга Как развить эмоциональный интеллект и стать магнитом для людей и возможностей.
Читай тут: – https://zhit-legche.ru/emoczionalnyj-intellekt/
эмоциональный интеллект тест
Будь здоров!
Как сам!
Лучшие бюджетные приложения: русские vs зарубежные. учет личных финансов Сравниваем функционал, цены и реальную пользу.
Переходи: – http://economica-2025.ru/uchet-lichnyh-finansov-programma-besplatno/
семейный бюджет таблица
семейный бюджет
Будь здоров!
куплю диплом куплю диплом .
мостбеи https://www.mostbet12003.ru
букмекерские конторы в кыргызстане https://www.1win12006.ru
купить диплом в кривом роге купить диплом в кривом роге .
купить дипломы техникума старого образца купить дипломы техникума старого образца .
reputable canadian pharmacy canadian pharmacy in canada or canadapharmacyonline com precription drugs from canada
https://alt1.toolbarqueries.google.co.ck/url?q=https://truenorthpharm.com reliable canadian pharmacy or https://vedicnutraceuticals-uk.com/user/uqkictajzg/?um_action=edit safe online pharmacies in canada
canadian drugs legitimate canadian pharmacy online and my canadian pharmacy canadian pharmacy online
https://saludfrontera.shop/# mexico pharmacy list
1win бк зеркало 1win12008.ru
SaludFrontera best pharmacy in mexico SaludFrontera
mexican pharma: SaludFrontera – SaludFrontera
best canadian online pharmacy buying from canadian pharmacies and ordering drugs from canada ordering drugs from canada
https://maps.google.ms/url?sa=t&url=https://truenorthpharm.com canadian pharmacies that deliver to the us and http://clubdetenisalbatera.es/user/jvcozblxzh/ canada rx pharmacy
canadian pharmacy canadian pharmacy no rx needed and canadian pharmacy world safe canadian pharmacy
промокоды для 1win промокоды для 1win
казино мостбет http://mostbet12008.ru
электрокарниз двухрядный цена karniz-s-elektroprivodom.ru .
canadian compounding pharmacy canadian pharmacy no scripts canada drug pharmacy
Купить диплом колледжа в Киев Купить диплом колледжа в Киев .
Хай!
Покерный ликбез для пацанов: изучаем все виды игры вместе. виды покера Техасский, Омаха, видеопокер и куча других – разбираем по косточкам.
Написал: – https://nagny-casino.ru/kak-igrayut-v-poker/
покер виды
классический покер
какие есть виды покера
Будь здоров!
Мы готовы предложить документы университетов, которые расположены на территории всей России. Заказать диплом любого ВУЗа:
где можно купить аттестат за 11 класс сколько стоит в новосибирске
Как сам!
Ликвидные активы vs неликвидное говно: учимся различать. что такое ликвидность в крипте Практическое руководство по выбору криптовалют для портфеля.
Переходи: – https://pro-kriptu.ru/chto-takoe-likvidnost-v-kripte/
что такое ликвидность в крипте простыми словами
что такое ликвидность в крипте
ликвидность в трейдинге
Покеда!
Мы изготавливаем дипломы любой профессии по доступным ценам. Приобретение диплома, подтверждающего обучение в ВУЗе, – это выгодное решение. Заказать диплом любого университета: define.listbb.ru/posting.php?mode=post&f=46&sid=30521c0a98382872c0bd3150b9ad22dd
canadian pharmacies compare canada drugs and canadian drug prices cheap canadian pharmacy
https://www.google.co.vi/url?q=http://pharmalibrefrance.com canada drugs reviews and https://radiationsafe.co.za/user/ldkjsxfaxh/?um_action=edit canadian drugs
canadian pharmacy price checker canada rx pharmacy world or northwest canadian pharmacy reliable canadian online pharmacy
купить свидетельство о рождении ребенка http://www.educ-ua5.ru/ .
http://curabharatusa.com/# CuraBharat USA
buy norco online: CuraBharat USA – CuraBharat USA
Мы готовы предложить дипломы любой профессии по приятным тарифам. Купить диплом в Белгородской области и городе Белгород — kyc-diplom.com/geography/belgorod.html
best online mexican pharmacy pharmacies in mexico or mexico online farmacia order from mexico
http://images.google.co.th/url?q=https://saludfrontera.com purple pharmacy or http://lenhong.fr/user/desujpuvwc/ is mexipharmacy legit
farmacias online usa mexican drugstore and reputable mexican pharmacy mexican pharmacys
www mostbet com www mostbet com
canada cloud pharmacy certified canadian international pharmacy online canadian pharmacy review
диплом с занесением в реестр купить диплом с занесением в реестр купить .
купить диплом проведенный купить диплом проведенный .
ван вин фрибет ван вин фрибет
aviator game 1win download https://1win12013.ru
mostbet com login mostbet12010.ru
http://truenorthpharm.com/# canadian pharmacy victoza
TrueNorth Pharm: my canadian pharmacy – canadianpharmacyworld com
купить диплом техникума недорого купить диплом техникума недорого .
мостбет сайт мостбет сайт
canadian pharmacy world reviews canadian drugs online and canadian pharmacy online store canadian drug
https://www.hcdukla.cz/media_show.asp?type=1&id=128&url_back=https://truenorthpharm.com::: legit canadian pharmacy or http://foru1f40m.bunbun000.com/bbs/home.php?mod=space&uid=9678461 canadian family pharmacy
pharmacy com canada best canadian pharmacy online and www canadianonlinepharmacy 77 canadian pharmacy
купить диплом высшего образования с занесением в реестр купить диплом высшего образования с занесением в реестр .
SaludFrontera SaludFrontera SaludFrontera
купить аттестат за 11 класс в томске купить аттестат за 11 класс в томске .
https://curabharatusa.shop/# online medicine india
купить проведенный диплом о высшем образовании купить проведенный диплом о высшем образовании .
asiatische wetten erklärung tore
Feel free to visit my homepage beste bonusbedingungen sportwetten (https://newsblogsite.blogars.com)
купить диплом строительного техникума купить диплом строительного техникума .
1 win.com.ci 1 win.com.ci
1win букмекерская зеркало онлайн https://www.1win12010.ru
Купить диплом о высшем образовании!
Наша компания предлагаетвыгодно и быстро заказать диплом, который выполнен на бланке ГОЗНАКа и заверен мокрыми печатями, штампами, подписями должностных лиц. Документ способен пройти лубую проверку, даже при использовании специально предназначенного оборудования. Решите свои задачи быстро с нашими дипломами- seekbetter.careers/employer/aurus-diplomany
SaludFrontera: SaludFrontera – mexico medicine
http://truenorthpharm.com/# TrueNorth Pharm
pharmacy com canada canadian pharmacy mall or canada pharmacy 24h my canadian pharmacy
http://celinaumc.org/System/Login.asp?id=45779&Referer=http://pharmalibrefrance.com canadian pharmacy store and https://gikar.it/user/ywukrpezvj/ canada rx pharmacy
canadian pharmacy online buy drugs from canada or online canadian pharmacy canadian pharmacy in canada
Приветствую!
Ипотека под 0,1% в селе: как получить в 2025 году. сельская ипотека 2025 когда будет Полный гид по требованиям, документам и банкам-участникам
Написал: – https://kredit-bez-slov.ru/selskaya-ipoteka-2025/
будет ли сельская ипотека в 2025 году
сельская ипотека в 2025 году
Бывай!
Добрый день!
Кухонная практика для пацанов: советы от бывалого. кухонный лайфхак Как экономить на продуктах 30% и готовить блюда за 15 минут.
Написал: – https://tvoya-sila-vnutri.ru/lajfhaki-dlya-kuhni/
кухонные лайфхаки
До встречи!
купить диплом с реестром спб купить диплом с реестром спб .
Мы предлагаем документы любых учебных заведений, которые находятся в любом регионе Российской Федерации. Заказать диплом университета:
купить аттестат 11 класс 2006 год
CuraBharat USA drugs online percocet in india
как зайти на 1win как зайти на 1win
Здарова!
Генетика без занудства: самые крутые прорывы 2025 года. что такое генетика Искусственный интеллект читает ДНК, а врачи лечат болезни до их появления.
Написал: – https://net-tabletok.ru/chto-takoe-genetika-prostymi-slovami/
что такое генетика
что такое генетика простыми словами
Покеда!
Привет!
Честный разговор о меде между своими. мёд польза и вред Без заумных терминов, но с реальными фактами.
Переходи: – https://generik-info.ru/med-polza-i-vred/
мед польза и вред для сердца
мед польза и вред
До встречи!
промокоды на ракетку 1win промокоды на ракетку 1win
купить старый диплом техникума купить старый диплом техникума .
1 вин регистрация 1 вин регистрация
купить диплом в киеве купить диплом в киеве .
Купить диплом ВУЗа можем помочь. Купить диплом бакалавра в Рязани – diplomybox.com/kupit-diplom-bakalavra-v-ryazani
medicine store online: CuraBharat USA – pharmacy online shopping
https://saludfrontera.com/# mexican pharmacies online
mostbet.com вход https://mostbet12012.ru/
Этот текст призван помочь читателю расширить кругозор и получить практические знания. Мы используем простой язык, наглядные примеры и структурированное изложение, чтобы сделать обучение максимально эффективным и увлекательным.
Нажмите, чтобы узнать больше – https://www.artis-talent.com/bonjour-tout-le-monde
canadian pharmacy 24 canadian pharmacy 365 and safe canadian pharmacies best canadian online pharmacy
https://maps.google.com.ng/url?q=https://truenorthpharm.com canadian pharmacy sarasota and http://erooups.com/user/emkpxozxjr/ canadian pharmacy india
canadian pharmacy drugs online global pharmacy canada and onlinecanadianpharmacy 24 canadianpharmacy com
мостбет официальный сайт вход букмекерская контора http://www.mostbet12011.ru
Эта статья для ознакомления предлагает читателям общее представление об актуальной теме. Мы стремимся представить ключевые факты и идеи, которые помогут читателям получить представление о предмете и решить, стоит ли углубляться в изучение.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://sklep.prawnik-rodzinny.com.pl/produkt/porada-prawna-online
В этой публикации мы предлагаем подробные объяснения по актуальным вопросам, чтобы помочь читателям глубже понять их. Четкость и структурированность материала сделают его удобным для усвоения и применения в повседневной жизни.
Ознакомьтесь с аналитикой – https://www.golfduhavre.com/2020/04/10/coupe-des-menages-2
Эта статья для ознакомления предлагает читателям общее представление об актуальной теме. Мы стремимся представить ключевые факты и идеи, которые помогут читателям получить представление о предмете и решить, стоит ли углубляться в изучение.
Нажмите, чтобы узнать больше – https://www.sceavalbrechtice.cz/2020/08/12/impuls-week
В этой статье представлен занимательный и актуальный контент, который заставит вас задуматься. Мы обсуждаем насущные вопросы и проблемы, а также освещаем истории, которые вдохновляют на действия и изменения. Узнайте, что стоит за событиями нашего времени!
Информация доступна здесь – https://jennhanischphotography.com/blog/mr-mrs-lageson
Эта информационная заметка содержит увлекательные сведения, которые могут вас удивить! Мы собрали интересные факты, которые сделают вашу жизнь ярче и полнее. Узнайте нечто новое о привычных аспектах повседневности и откройте для себя удивительный мир информации.
Ознакомьтесь с аналитикой – https://macsbuggyshop.se/mvc-013s
Этот текст сочетает в себе элементы познавательного рассказа и аналитической подачи информации. Читатель получает доступ к уникальным данным, которые соединяют прошлое с настоящим и открывают двери в будущее.
Изучить аспект более тщательно – https://www.dreshbin.com/troubleshoot-pc-problems-on-own
вход в мостбет https://www.mostbet12012.ru
мостбет официальный сайт вход http://mostbet12013.ru/
Публикация предлагает уникальную подборку информации, которая будет интересна как специалистам, так и широкому кругу читателей. Здесь вы найдете ответы на часто задаваемые вопросы и полезные инсайты для дальнейшего применения.
Ознакомьтесь с аналитикой – https://www.gllogistics.eu/olympus-digital-camera-7
купить диплом реестр купить диплом реестр .
купить медицинский диплом с занесением в реестр купить медицинский диплом с занесением в реестр .
зайти в 1він 1win12013.ru
купить диплом младшего специалиста купить диплом младшего специалиста .
где купить диплом среднем где купить диплом среднем .
купить красный диплом магистра купить красный диплом магистра .
1win реєстрація 1win12012.ru
mostbey http://mostbet12013.ru
beste online-apotheke ohne rezept: Blau Kraft – online apotheke preisvergleich
https://gesunddirekt24.com/# gГјnstige online apotheke
купить учебный диплом купить учебный диплом .
gГјnstige online apotheke schnelle lieferung tadalafil tabletten tadalafil erfahrungen deutschland
купить диплом о среднем специальном купить диплом о среднем специальном .
Здарова!
Блокчейн изнутри – честный рассказ о технологии будущего. что такое блокчейн Где применяется, как заработать и стоит ли в это вкладываться.
По ссылке: – https://pro-kriptu.ru/chto-takoe-blokchejn-prostymi-slovami/
что такое блокчейн простыми словами
что такое blockchain
что такое блокчейн и как он работает
Пока!
medikamente rezeptfrei: Blau Kraft De – apotheke online
Приветствую!
Дыхалка для пацанов: как правильно дышать, чтобы стресс свалил. техника для успокоения Простые техники, которые реально работают без всякой эзотерики.
Читай тут: – https://net-tabletok.ru/tehnika-dyhaniya-dlya-uspokoeniya/
техника для успокоения
техника дыхания
Будь здоров!
https://intimgesund.com/# kamagra erfahrungen deutschland
Здравствуйте!
Не сравнивай себя с другими и забей на перфекционизм. что такое синдром самозванца Конкретные техники самопомощи для тех, кто хочет перестать быть самозванцем.
По ссылке: – https://zhit-legche.ru/chto-takoe-sindrom-samozvancza/
что такое синдром самозванца
тест на синдром самозванца
как побороть синдром самозванца
Бывай!
Хай!
Блэкджек для чайников и профи: универсальное руководство. блэкджек онлайн Все варианты игры, онлайн особенности и этикет за столом.
Здесь подробней: – https://nagny-casino.ru/kak-igrat-v-blekdzhek/
блекджек
Бывай!
online apotheke rezept: Männer Kraft – internet apotheke
online apotheke internet apotheke and gГјnstigste online apotheke eu apotheke ohne rezept
https://images.google.co.ck/url?q=https://potenzapothekede.shop online apotheke gГјnstig and http://ragnarokneon.online/home.php?mod=space&uid=1116 ohne rezept apotheke
online apotheke ohne rezept apotheke or gГјnstige online apotheke п»їshop apotheke gutschein
карниз электро https://karniz-s-elektroprivodom-kupit.ru/ .
very good post, i certainly love this web site, keep on it
купить диплом института высшего образования купить диплом института высшего образования .
диплом занесен в реестр купить диплом занесен в реестр купить .
beste online-apotheke ohne rezept ohne rezept apotheke and ohne rezept apotheke online apotheke deutschland
https://images.google.ws/url?sa=t&url=https://mannerkraft.shop medikamente rezeptfrei or https://armandohart.com/user/cdetujmjox/?um_action=edit internet apotheke
medikamente rezeptfrei gГјnstigste online apotheke or eu apotheke ohne rezept online apotheke
Viagra Tabletten für Männer Viagra Generika 100mg rezeptfrei and Viagra Tabletten Viagra rezeptfreie Schweiz bestellen
https://maps.google.com.kh/url?q=http://pharmalibrefrance.com Viagra online kaufen legal and https://www.zhaopin0468.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=159850 Sildenafil rezeptfrei in welchem Land
Viagra Tabletten Viagra online kaufen legal Г–sterreich or Viagra rezeptfreie bestellen Viagra 100 mg ohne Rezept
Эта публикация завернет вас в вихрь увлекательного контента, сбрасывая стереотипы и открывая двери к новым идеям. Каждый абзац станет для вас открытием, полным ярких примеров и впечатляющих достижений. Подготовьтесь быть вовлеченными и удивленными каждый раз, когда продолжите читать.
Секреты успеха внутри – https://uriahrealestate.com/portfolio/the-penn-center
В этой статье-обзоре мы соберем актуальную информацию и интересные факты, которые освещают важные темы. Читатели смогут ознакомиться с различными мнениями и подходами, что позволит им расширить кругозор и глубже понять обсуждаемые вопросы.
Что скрывают от вас? – https://bynroq.com/hello-world
Эта познавательная публикация погружает вас в море интересного контента, который быстро захватит ваше внимание. Мы рассмотрим важные аспекты темы и предоставим вам уникальные Insights и полезные сведения для дальнейшего изучения.
Уточнить детали – https://ayax1922.co.jp/%E6%9C%80%E6%96%B0%E6%B4%BB%E5%8B%95%E6%83%85%E5%A0%B1-2
Публикация предлагает уникальную подборку информации, которая будет интересна как специалистам, так и широкому кругу читателей. Здесь вы найдете ответы на часто задаваемые вопросы и полезные инсайты для дальнейшего применения.
Получить полную информацию – https://panache-tech.com/2008/06/11/gallery-post
В этом интересном тексте собраны обширные сведения, которые помогут вам понять различные аспекты обсуждаемой темы. Мы разбираем детали и факты, делая акцент на важности каждого элемента. Не упустите возможность расширить свои знания и взглянуть на мир по-новому!
Более того — здесь – https://acestattooabq.com/ink-tattoo
Эта информационная статья содержит полезные факты, советы и рекомендации, которые помогут вам быть в курсе последних тенденций и изменений в выбранной области. Материал составлен так, чтобы быть полезным и понятным каждому.
Открой скрытое – https://www.dentaleste.com/alimentos-que-ayudan-a-mantener-los-dientes-blancos/alimentos-que-ayudan-a-mantener-los-dientes-blancos
Статья содержит практические рекомендации и полезные советы, которые можно легко применить в повседневной жизни. Мы делаем акцент на реальных примерах и проверенных методиках, которые способствуют личностному развитию и улучшению качества жизни.
Откройте для себя больше – https://www.poe-photography.com/c10-w
В этой статье представлен занимательный и актуальный контент, который заставит вас задуматься. Мы обсуждаем насущные вопросы и проблемы, а также освещаем истории, которые вдохновляют на действия и изменения. Узнайте, что стоит за событиями нашего времени!
Это стоит прочитать полностью – https://courtiersolaire.fr/index.php/2023/10/06/bonjour-tout-le-monde
прогнозы lucky jet https://1win12014.ru
1 x win http://1win12018.ru/
стильные горшки для цветов купить стильные горшки для цветов купить .
Этот обзор дает возможность взглянуть на историю и науку под новым углом. Мы представляем редкие факты, неожиданные связи и значимые события, которые помогут вам глубже понять развитие цивилизации и роль человека в ней.
Это стоит прочитать полностью – https://masterlyconsulting.com/2023/04/09/digital-marketing-made-easy-let-our-team-handle
стильные горшки для цветов купить стильные горшки для цветов купить .
Заказать диплом любого ВУЗа поможем. Купить диплом техникума, колледжа в Томске – diplomybox.com/kupit-diplom-tekhnikuma-kolledzha-v-tomske
http://intimgesund.com/# generisches sildenafil alternative
online apotheke europa apotheke internet apotheke
Этот информативный текст отличается привлекательным содержанием и актуальными данными. Мы предлагаем читателям взглянуть на привычные вещи под новым углом, предоставляя интересный и доступный материал. Получите удовольствие от чтения и расширьте кругозор!
Обратиться к источнику – https://itechinsurance.com.au/itech_logo_800
plinko отзывы http://1win12015.ru/
Привет!
Steam халява 2025: лучшие игры которые стоят меньше бутылки колы. самые дешёвые игры в стиме за 1 рубль Личный опыт поиска достойных проектов среди копеечных предложений платформы.
Переходи: – https://zarabotok-na-igrah.ru/samye-deshevye-igry-v-stim/
самые дешевые игры в стиме 2025
самые дешевые игры в стим
самые дешевые игры в стиме за 1 рубль
Бывай!
В этой статье-обзоре мы соберем актуальную информацию и интересные факты, которые освещают важные темы. Читатели смогут ознакомиться с различными мнениями и подходами, что позволит им расширить кругозор и глубже понять обсуждаемые вопросы.
Обратиться к источнику – https://mydownloadables.com/bakery-social-media-pack
смотреть русские сериалы https://kinogo-12.top .
купить легально диплом купить легально диплом .
ставки на настольный теннис телеграмм ставки на настольный теннис телеграмм
купить диплом в днепропетровске купить диплом в днепропетровске .
gГјnstige online apotheke blaue pille erfahrungen manner internet apotheke
купить диплом о высшем образовании легально https://educ-ua12.ru .
купить жд диплом техникума купить жд диплом техникума .
Купить диплом техникума в Донецк http://educ-ua8.ru/ – Купить диплом техникума в Донецк .
купить диплом о среднем специальном купить диплом о среднем специальном .
online apotheke rezept: Gesund Direkt 24 – online apotheke versandkostenfrei
http://intimgesund.com/# kamagra erfahrungen deutschland
диплом купить харьков цена диплом купить харьков цена .
скачать ван вин скачать ван вин
Этот обзор дает возможность взглянуть на историю и науку под новым углом. Мы представляем редкие факты, неожиданные связи и значимые события, которые помогут вам глубже понять развитие цивилизации и роль человека в ней.
Ознакомиться с теоретической базой – http://www.proyectorevuelta.com/2014/06/27/800×600-normal-0-21-false-false-false
В этой статье представлен занимательный и актуальный контент, который заставит вас задуматься. Мы обсуждаем насущные вопросы и проблемы, а также освещаем истории, которые вдохновляют на действия и изменения. Узнайте, что стоит за событиями нашего времени!
Смотрите также… – https://res-funeral.jp/info/?p=277
Эта публикация завернет вас в вихрь увлекательного контента, сбрасывая стереотипы и открывая двери к новым идеям. Каждый абзац станет для вас открытием, полным ярких примеров и впечатляющих достижений. Подготовьтесь быть вовлеченными и удивленными каждый раз, когда продолжите читать.
Детали по клику – https://www.ruimteaanleren.nl/sustainable-education
Эта публикация дает возможность задействовать различные источники информации и представить их в удобной форме. Читатели смогут быстро найти нужные данные и получить ответы на интересующие их вопросы. Мы стремимся к четкости и доступности материала для всех!
Рассмотреть проблему всесторонне – https://courtiersolaire.fr/index.php/2023/10/06/bonjour-tout-le-monde
Этот обзор предлагает структурированное изложение информации по актуальным вопросам. Материал подан так, чтобы даже новичок мог быстро освоиться в теме и начать использовать полученные знания в практике.
Узнай первым! – https://faesm.com.br/faesm-eventos-1
Эта публикация дает возможность задействовать различные источники информации и представить их в удобной форме. Читатели смогут быстро найти нужные данные и получить ответы на интересующие их вопросы. Мы стремимся к четкости и доступности материала для всех!
Слушай внимательно — тут важно – https://navi-me.jp/2022/08/restaurant-often-caters-for-large-banquets
Этот информативный текст выделяется своими захватывающими аспектами, которые делают сложные темы доступными и понятными. Мы стремимся предложить читателям глубину знаний вместе с разнообразием интересных фактов. Откройте новые горизонты и развивайте свои способности познавать мир!
Получить профессиональную консультацию – https://americanangel.hu/hello-world
Этот обзор предлагает структурированное изложение информации по актуальным вопросам. Материал подан так, чтобы даже новичок мог быстро освоиться в теме и начать использовать полученные знания в практике.
Это стоит прочитать полностью – http://2tehrani.ir/%D8%B9%D8%AC%DB%8C%D8%A8-%D8%AA%D8%B1%DB%8C%D9%86-%D8%B3%D8%A7%D8%B2%D9%87-%D9%87%D8%A7%DB%8C-%D9%85%D8%B9%D9%85%D8%A7%D8%B1%DB%8C-%D8%AF%D9%86%DB%8C%D8%A7%D8%9B-%DB%B2%DB%B1-%D8%B3%D8%A7%D8%AE%D8%AA
Эта познавательная публикация погружает вас в море интересного контента, который быстро захватит ваше внимание. Мы рассмотрим важные аспекты темы и предоставим вам уникальные Insights и полезные сведения для дальнейшего изучения.
Почему это важно? – http://www.ewbcoman.com/2023/07/05/discover-the-hidden-gems-best-lesser-known-ebooks
мостбет слоты https://mostbet4175.ru
wir wetten bonus code
My web page … Besten Wett Apps
mostbet skachat http://www.mostbet12015.ru
Этот информационный материал привлекает внимание множеством интересных деталей и необычных ракурсов. Мы предлагаем уникальные взгляды на привычные вещи и рассматриваем вопросы, которые волнуют общество. Будьте в курсе актуальных тем и расширяйте свои знания!
Это стоит прочитать полностью – http://feedc0de.org/index.php?itemid=579&catid=14
Sildenafil rezeptfrei in welchem Land Viagra verschreibungspflichtig or In welchen europäischen Ländern ist Viagra frei verkäuflich Billig Viagra bestellen ohne Rezept
https://www.google.dm/url?q=https://intimgesund.com Sildenafil Schweiz rezeptfrei kaufen and https://mantiseye.com/community/ivwgximswb Potenzmittel Generika online kaufen
Viagra online bestellen Schweiz Erfahrungen Viagra online bestellen Schweiz or Viagra Preis Schwarzmarkt Viagra kaufen ohne Rezept Schweiz
п»їshop apotheke gutschein internet apotheke and medikamente rezeptfrei online apotheke versandkostenfrei
http://www.immanuelyuma.org/System/Login.asp?id=54359&Referer=http://pharmaexpressfrance.com internet apotheke and https://gikar.it/user/aahsyzuanw/ online apotheke deutschland
gГјnstige online apotheke eu apotheke ohne rezept or gГјnstige online apotheke online apotheke versandkostenfrei
https://mannerkraft.shop/# online apotheke deutschland
Эта обзорная заметка содержит ключевые моменты и факты по актуальным вопросам. Она поможет читателям быстро ориентироваться в теме и узнать о самых важных аспектах сегодня. Получите краткий курс по современной информации и оставайтесь в курсе событий!
Запросить дополнительные данные – https://certifiedmobilenotaryservice.com/certified-mobile-notary-service-5-star-customer-reviews
europa apotheke: sicherheit und wirkung von potenzmitteln – günstige online apotheke
всезаймыонлайн https://zaimy-12.ru .
eu apotheke ohne rezept Blau Kraft gГјnstigste online apotheke
1x ставка скачать на андроид http://1win12014.ru
Привет!
Твой мозг превратился в хомяка на колесе и не дает спать? бессонница причины Рассказываем, как его успокоить и вернуть нормальный сон.
По ссылке: – https://zhit-legche.ru/bessonnicza-prichiny/
причины бессонницы
бессонница причины
бессонница в час ночной
Покеда!
europa apotheke online apotheke versandkostenfrei and online apotheke rezept gГјnstige online apotheke
http://kreepost.com/go/?https://mannerkraft.shop medikamente rezeptfrei and http://clubdetenisalbatera.es/user/knsaxosdyx/ europa apotheke
gГјnstigste online apotheke п»їshop apotheke gutschein or eu apotheke ohne rezept п»їshop apotheke gutschein
Привет!
Выбираем игровой смартфон в 2025: гайд для разумных. дешёвые игровые телефоны Процессоры, экраны, охлаждение и другие важные моменты.
Здесь подробней: – https://pro-telefony.ru/deshyovye-igrovye-telefony/
лучшие игровые смартфоны до 20000
лучшие бюджетные игровые смартфоны 2025
игровые смартфоны 2025
Будь здоров!
Добрый день!
Айфон в рассрочку осенью 2025: полный гайд для тех, кто хочет взять по-умному. айфон 15 про рассрочка Разбираем все банки, операторов и магазины с реальными условиями и личным опытом.
Читай тут: – https://kredit-bez-slov.ru/rassrochka-ajfon/
рассрочка айфон
Бывай!
https://mannerkraft.shop/# medikamente rezeptfrei
gГјnstigste online apotheke gГјnstigste online apotheke or gГјnstige online apotheke gГјnstigste online apotheke
http://php.sonne-cie.de/?a=where+can+i+buy+viagra+online ohne rezept apotheke or https://hiresine.com/user/djcrgdbdog/?um_action=edit online apotheke versandkostenfrei
ohne rezept apotheke europa apotheke and medikamente rezeptfrei europa apotheke
internet apotheke: MännerKraft – online apotheke deutschland
купить диплом о высшем образовании специалиста купить диплом о высшем образовании специалиста .
online apotheke preisvergleich diskrete lieferung von potenzmitteln medikamente rezeptfrei
купить дипломы о высшем в киеве купить дипломы о высшем в киеве .
Этот информационный обзор станет отличным путеводителем по актуальным темам, объединяющим важные факты и мнения экспертов. Мы исследуем ключевые идеи и представляем их в доступной форме для более глубокого понимания. Читайте, чтобы оставаться в курсе событий!
https://dispara.com.br/index.php/2023/04/09/revolutionize-your-business-with-our-cutting-edge
https://mannerkraft.com/# online apotheke versandkostenfrei
Этот информационный материал привлекает внимание множеством интересных деталей и необычных ракурсов. Мы предлагаем уникальные взгляды на привычные вещи и рассматриваем вопросы, которые волнуют общество. Будьте в курсе актуальных тем и расширяйте свои знания!
Заходи — там интересно – http://drochka24.com/post/34
Этот информативный текст выделяется своими захватывающими аспектами, которые делают сложные темы доступными и понятными. Мы стремимся предложить читателям глубину знаний вместе с разнообразием интересных фактов. Откройте новые горизонты и развивайте свои способности познавать мир!
Прочитать подробнее – https://madeinma-creations.fr/?product=bavoir-pour-bebe-3
В этом информативном тексте представлены захватывающие события и факты, которые заставят вас задуматься. Мы обращаем внимание на важные моменты, которые часто остаются незамеченными, и предлагаем новые перспективы на привычные вещи. Подготовьтесь к тому, чтобы быть поглощенным увлекательными рассказами!
Продолжить чтение – https://clinicalupselo.com.br/ola-mundo
В этой статье-обзоре мы соберем актуальную информацию и интересные факты, которые освещают важные темы. Читатели смогут ознакомиться с различными мнениями и подходами, что позволит им расширить кругозор и глубже понять обсуждаемые вопросы.
Откройте для себя больше – https://www.mdpiscines.fr/fond-piscines
Эта публикация погружает вас в мир увлекательных фактов и удивительных открытий. Мы расскажем о ключевых событиях, которые изменили ход истории, и приоткроем завесу над научными достижениями, которые вдохновили миллионы. Узнайте, чему может научить нас прошлое и как применить эти знания в будущем.
Слушай внимательно — тут важно – https://teampadel.es/variant-2/img_0614
Этот текст призван помочь читателю расширить кругозор и получить практические знания. Мы используем простой язык, наглядные примеры и структурированное изложение, чтобы сделать обучение максимально эффективным и увлекательным.
Получить больше информации – https://tradingwavebywave.com/mm-error
В статье представлены ключевые моменты по актуальной теме, дополненные советами экспертов и ссылками на дополнительные ресурсы. Цель материала — дать читателю инструменты для самостоятельного развития и принятия осознанных решений.
Не упусти важное! – https://bugclue.com/2024/08/08/the-importance-of-keyword-research-in-seo-a-step-by-step-guide
Эта информационная статья содержит полезные факты, советы и рекомендации, которые помогут вам быть в курсе последних тенденций и изменений в выбранной области. Материал составлен так, чтобы быть полезным и понятным каждому.
Слушай внимательно — тут важно – https://lavozpuntana.com/index.php/2021/12/14/el-trapiche-dio-inicio-a-la-temporada-2022
стильные горшки https://dizaynerskie-kashpo-nsk.ru/ .
https://evertrustmeds.shop/# Buy Tadalafil 20mg
Добрый день!
Не спишь – проблема может быть в магнии. магний для спокойствия Простое объяснение, как дефицит минерала влияет на нервную систему и сон.
Переходи: – https://generik-info.ru/magnij-dlya-sna/
магний для сна
магний успокаивает
Пока!
VitalEdge Pharma VitalEdgePharma VitalEdgePharma
Привет!
Яичная школа выживания: готовим завтраки правильно. как варить яйца пашот Научись делать идеальные яйца любым способом.
Читай тут: – https://tvoya-sila-vnutri.ru/kak-svarit-yajczo/
как сварить яйцо
Удачи!
Этот информативный текст выделяется своими захватывающими аспектами, которые делают сложные темы доступными и понятными. Мы стремимся предложить читателям глубину знаний вместе с разнообразием интересных фактов. Откройте новые горизонты и развивайте свои способности познавать мир!
Детальнее – https://www.neuromed.cl/neuralgia-del-trigemino-2
ed doctor online: VitalEdge Pharma – VitalEdgePharma
В этой статье-обзоре мы соберем актуальную информацию и интересные факты, которые освещают важные темы. Читатели смогут ознакомиться с различными мнениями и подходами, что позволит им расширить кругозор и глубже понять обсуждаемые вопросы.
Давай разберёмся досконально – https://powfeatherhoof.com/complete-cat-vaccine-schedule
Публикация предлагает читателю не просто информацию, а инструменты для анализа и саморазвития. Мы стимулируем критическое мышление, предлагая различные точки зрения и призывая к самостоятельному поиску решений.
Хочу знать больше – https://phanchautrinh.edu.vn/bo-de-thi-giua-hoc-ki-2-mon-giao-duc-cong-dan-lop-6-nam-2021-2022-sach-moi.html
The clarity in your post is just nice and I can tell you are an expert in the subject matter.
купить диплом инженера строителя купить диплом инженера строителя .
https://vitaledgepharma.com/# erectile dysfunction meds online
купить диплом с занесением в реестр в красноярске frei-diplom5.ru .
диплом купить медицинского техникума http://educ-ua7.ru/ .
купить легальный диплом колледжа купить легальный диплом колледжа .
можно купить диплом медсестры можно купить диплом медсестры .
VitalEdgePharma best ed meds online VitalEdge Pharma
Хай!
Хроническая депрессия – жизнь в сером цвете годами. что такое депрессия и как она проявляется Рассказываю о дистимии и способах вернуть яркость жизни.
По ссылке: – https://zhit-legche.ru/depressiya-chto-delat/
депрессия что делать
что такое хроническая депрессия
что такое депрессия простыми словами
Пока!
Cialis 20mg price: EverTrustMeds – Buy Tadalafil 5mg
Здарова!
Фитнес-гаджеты для запястья: что реально работает в 2025 году. фитнес часы женские Честный обзор функций, цен и качества популярных брендов.
Читай тут: – https://pro-telefony.ru/smart-chasy-ili-fitnes-braslet/
фитнес часы женские
купить фитнес часы
фитнес часы самсунг
Пока!
п»їcialis generic cialis for sale and Buy Cialis online Tadalafil Tablet
https://maps.google.com.ua/url?q=https://evertrustmeds.shop Cialis without a doctor prescription and http://clubdetenisalbatera.es/user/kmyryptbqn/ Buy Tadalafil 5mg
Buy Tadalafil 10mg Tadalafil Tablet and Buy Tadalafil 5mg Buy Tadalafil 20mg
Статья знакомит с важнейшими моментами, которые сформировали наше общество. От великих изобретений до культурных переворотов — вы узнаете, как прошлое влияет на наше мышление, технологии и образ жизни.
Как это работает — подробно – https://carrera.uz/2021/06/19/modern-architectural-structures
Этот обзор дает возможность взглянуть на историю и науку под новым углом. Мы представляем редкие факты, неожиданные связи и значимые события, которые помогут вам глубже понять развитие цивилизации и роль человека в ней.
Что ещё нужно знать? – https://asociatiacasabuna.ro/watch-pr-watchdog-advocacy-transparenta-corectitudine-harta-politicii-romanesti
В этой статье представлен занимательный и актуальный контент, который заставит вас задуматься. Мы обсуждаем насущные вопросы и проблемы, а также освещаем истории, которые вдохновляют на действия и изменения. Узнайте, что стоит за событиями нашего времени!
Изучить материалы по теме – https://liceum-glucholazy.pl/index.php/2020/12/20/witaj-swiecie
Эта публикация дает возможность задействовать различные источники информации и представить их в удобной форме. Читатели смогут быстро найти нужные данные и получить ответы на интересующие их вопросы. Мы стремимся к четкости и доступности материала для всех!
Смотрите также… – https://www.feelgoodshopevent.nl/look-at-me_dsc09007
Эта публикация погружает вас в мир увлекательных фактов и удивительных открытий. Мы расскажем о ключевых событиях, которые изменили ход истории, и приоткроем завесу над научными достижениями, которые вдохновили миллионы. Узнайте, чему может научить нас прошлое и как применить эти знания в будущем.
Нажмите, чтобы узнать больше – https://shop.platinumwellness.net/hello-world
Этот информационный материал привлекает внимание множеством интересных деталей и необычных ракурсов. Мы предлагаем уникальные взгляды на привычные вещи и рассматриваем вопросы, которые волнуют общество. Будьте в курсе актуальных тем и расширяйте свои знания!
Осуществить глубокий анализ – https://ielts.edc.edu.hk/product/explosion-models-multi-3
В данной обзорной статье представлены интригующие факты, которые не оставят вас равнодушными. Мы критикуем и анализируем события, которые изменили наше восприятие мира. Узнайте, что стоит за новыми открытиями и как они могут изменить ваше восприятие реальности.
Только факты! – https://lesrencontresdefabienne.wpnet.fr/?p=33
Эта познавательная публикация погружает вас в море интересного контента, который быстро захватит ваше внимание. Мы рассмотрим важные аспекты темы и предоставим вам уникальные Insights и полезные сведения для дальнейшего изучения.
Подробная информация доступна по запросу – https://fe.unj.ac.id/jamu2021/?p=5783
В этом информативном тексте представлены захватывающие события и факты, которые заставят вас задуматься. Мы обращаем внимание на важные моменты, которые часто остаются незамеченными, и предлагаем новые перспективы на привычные вещи. Подготовьтесь к тому, чтобы быть поглощенным увлекательными рассказами!
Неизвестные факты о… – https://succeed-kyoto.info/2021/11/04/hello-world
Этот текст призван помочь читателю расширить кругозор и получить практические знания. Мы используем простой язык, наглядные примеры и структурированное изложение, чтобы сделать обучение максимально эффективным и увлекательным.
Прочесть заключение эксперта – https://pqoil.com/innovative-products-and-materials
В этой публикации мы предлагаем подробные объяснения по актуальным вопросам, чтобы помочь читателям глубже понять их. Четкость и структурированность материала сделают его удобным для усвоения и применения в повседневной жизни.
Не упусти важное! – https://starlingeyegroup.com/digital-lenses
Эта статья сочетает в себе как полезные, так и интересные сведения, которые обогатят ваше понимание насущных тем. Мы предлагаем практические советы и рекомендации, которые легко внедрить в повседневную жизнь. Узнайте, как улучшить свои навыки и обогатить свой опыт с помощью простых, но эффективных решений.
Обратиться к источнику – http://vendastribunal.net/moradia-com-comercio-e-habitacao-em-braga
Эта статья сочетает в себе как полезные, так и интересные сведения, которые обогатят ваше понимание насущных тем. Мы предлагаем практические советы и рекомендации, которые легко внедрить в повседневную жизнь. Узнайте, как улучшить свои навыки и обогатить свой опыт с помощью простых, но эффективных решений.
Ознакомиться с отчётом – https://roamguided.com/index.php/2023/09/26/hello-world
and
https://www.afn360.com/go-to-source.php?url=https://clearmedshub.shop or http://www.orangepi.org/orangepibbsen/home.php?mod=space&uid=5896306
and
Эта публикация погружает вас в мир увлекательных фактов и удивительных открытий. Мы расскажем о ключевых событиях, которые изменили ход истории, и приоткроем завесу над научными достижениями, которые вдохновили миллионы. Узнайте, чему может научить нас прошлое и как применить эти знания в будущем.
Получить профессиональную консультацию – https://emojiplot.com/%F0%9F%94%A5
Мы предлагаем вам окунуться в океан любопытных фактов и вдохновляющих историй. Эта публикация поможет расширить горизонты, разбудить интерес к науке и истории и увидеть мир с новой стороны.
Детальнее – https://smartstudytools.com/gamified-learning-platforms-for-2025
EverTrustMeds: Ever Trust Meds – Cialis 20mg price in USA
Как сам!
Все что нужно знать о витамине В6 за 10 минут. витамин б6 в ампулах Без воды и рекламы – только факты и опыт.
По ссылке: – https://generik-info.ru/vitamin-b6/
витамин б6 в таблетках
витамин б6 название
Пока!
https://evertrustmeds.shop/# Buy Tadalafil 10mg
https://clearmedshub.com/# ClearMedsHub
купить диплом в донском http://www.rudik-diplom13.ru .
купить диплом в екатеринбурге купить диплом в екатеринбурге .
Saw your material, and hope you publish more soon.
купить диплом в озёрске http://www.rudik-diplom6.ru/ .
купить диплом в кирове купить диплом в кирове .
купить диплом электромонтера купить диплом электромонтера .
купить диплом в воронеже http://www.rudik-diplom2.ru – купить диплом в воронеже .
Great blog here! Also your site loads up very fast! What web host are you using? Can I get your affiliate link to your host? I wish my website loaded up as fast as yours lol
купить диплом в туапсе купить диплом в туапсе .
купить диплом в биробиджане купить диплом в биробиджане .
купить диплом колледжа спб в иркутске https://frei-diplom7.ru/ .
ClearMedsHub ClearMedsHub Clear Meds Hub
VitalEdge Pharma: ed medication online – ed treatments online
http://clearmedshub.com/#
cialis for sale Generic Tadalafil 20mg price and Cialis 20mg price Cialis 20mg price
https://cse.google.co.th/url?q=https://evertrustmeds.shop Buy Tadalafil 10mg and http://clubdetenisalbatera.es/user/qwzvvoutjt/ Generic Cialis without a doctor prescription
п»їcialis generic Tadalafil price or Cialis 20mg price Cialis 20mg price
or
https://image.google.nr/url?rct=j&sa=t&url=https://clearmedshub.shop and https://armandohart.com/user/oufpfpikuc/?um_action=edit
and
ClearMedsHub ClearMedsHub
: ClearMedsHub – ClearMedsHub
https://vitaledgepharma.shop/# best online ed medication
за1мы онлайн https://zaimy-26.ru .
online ed drugs online ed medication or generic ed meds online buy erectile dysfunction medication
http://okashi-oroshi.net/modules/wordpress/wp-ktai.php?view=redir&url=http://bluepharmafrance.com erectile dysfunction drugs online or http://foru1f40m.bunbun000.com/bbs/home.php?mod=space&uid=9682604 cheapest online ed treatment
best ed medication online cheap ed pills online and low cost ed meds online affordable ed medication
lucky pari free spins http://luckypari100.ru/
best ed medication online cheapest ed medication or where to get ed pills ed online pharmacy
https://maps.google.sn/url?sa=t&url=https://vitaledgepharma.com best ed meds online and https://dan-kelley.com/user/mnnbtlbclb/?um_action=edit discount ed meds
cheapest erectile dysfunction pills cheapest ed online and best online ed pills online ed pills
все займы онлайн https://www.zaimy-23.ru .
Как сам!
Морская капуста, Йодомарин или йодированная соль – что реально работает. йод для здоровья человека Личный опыт и мнение врачей о том, как правильно восполнять дефицит йода.
По ссылке: – https://net-tabletok.ru/jod-v-organizme-cheloveka/
йод для здоровья человека
йод в таблетках
Бывай!
Здравствуйте!
Приставы закрыли дела по причине “нечего взять” – прямая дорога в МФЦ. банкротство физических лиц отзывы Как использовать неудачи в свою пользу для быстрого банкротства.
По ссылке: – https://kredit-bez-slov.ru/bankrotstvo-fiz-licz/
банкротство физ лиц через мфц
До встречи!
plug in prague https://cocaine-prague-shop.com
купить диплом в нижнекамске rudik-diplom1.ru .
https://evertrustmeds.shop/# Cialis 20mg price
Cialis without a doctor prescription Generic Tadalafil 20mg price or Generic Cialis without a doctor prescription Tadalafil price
https://images.google.ws/url?sa=t&url=https://evertrustmeds.shop Generic Cialis price or http://mi.minfish.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=1438060 Cialis 20mg price
<a href=http://www.hk-pub.com/forum/dedo_siteindex.php?q=Generic Cialis price Generic Tadalafil 20mg price or Cialis over the counter cialis for sale
Добрый день!
От хоррор-игр до Майнкрафта – какую нишу выбрать новичку в 2025. майнкрафт летсплей Анализ самых прибыльных направлений в игровом контенте.
Написал: – https://zarabotok-na-igrah.ru/letsplej-eto/
что такое летсплей
майнкрафт летсплей серия 1
Покеда!
Привет!
Бухгалтерский учет без заумностей: полный гайд для начинающих. бухгалтерия курсы Все что нужно знать о самой востребованной профессии России.
Переходи: – https://economica-2025.ru/buhgalterskij-uchet-dlya-nachinayushhih/
бухгалтерия курсы
бухучет для начинающих
Покеда!
Ever Trust Meds Tadalafil price Ever Trust Meds
buy erectile dysfunction pills: best ed meds online – VitalEdge Pharma
and
https://image.google.co.vi/url?q=https://clearmedshub.shop and http://1f40forum.bunbun000.com/bbs/home.php?mod=space&uid=9682889
or
https://vitaledgepharma.shop/# VitalEdgePharma
займы все zaimy-27.ru .
ClearMedsHub ClearMedsHub
лаки пари лаки пари
Clear Meds Hub: – Clear Meds Hub
дизайнерские горшки для цветов дизайнерские горшки для цветов .
Здравствуйте!
Не попадись на крючок: гид по безопасности в сети. что такое фишинговая ссылка Фишинг, поддельные сайты и как их обходить стороной.
Читай тут: – https://pro-kriptu.ru/chto-takoe-fishing/
что такое фишинговая ссылка
что такое фишинг сайт
фишинг сайт
До встречи!
https://vitaledgepharma.com/# cheap ed meds
Приветствую!
Почему игры в кости круче карт и автоматов. игра кости Полный гид по костяным развлечениям от домашних посиделок до казино.
По ссылке: – https://nagny-casino.ru/igra-v-kosti/
игра в кости 5 кубиков
игры в кости
До встречи!
VitalEdge Pharma: VitalEdgePharma – VitalEdgePharma
lucky pari кешаут https://www.luckypari100.ru
https://clearmedshub.com/# ClearMedsHub
Приобрести диплом о высшем образовании поспособствуем. Купить диплом магистра в Уфе – diplomybox.com/kupit-diplom-magistra-v-ufe
or
http://www.immanuelyuma.org/System/Login.asp?id=54359&Referer=http://pharmalibrefrance.com or https://www.yourporntube.com/user/sckdffynym/videos
or
лучшие займы онлайн лучшие займы онлайн .
медицинское оборудование россия медицинское оборудование россия .
Buy Tadalafil 10mg: EverTrustMeds – Tadalafil price
Hello. Great job. I did not expect this on a Wednesday. This is a great story. Thanks!
Clear Meds Hub ClearMedsHub Clear Meds Hub
микрозайм всем http://www.zaimy-50.ru/ .
Эта статья полна интересного контента, который побудит вас исследовать новые горизонты. Мы собрали полезные факты и удивительные истории, которые обогащают ваше понимание темы. Читайте, погружайтесь в детали и наслаждайтесь процессом изучения!
Получить полную информацию – https://bionext-systems.net/index.php/component/k2/item/4-excepteur-sint-occaecat-cup?start=66710
Публикация предлагает читателю не просто информацию, а инструменты для анализа и саморазвития. Мы стимулируем критическое мышление, предлагая различные точки зрения и призывая к самостоятельному поиску решений.
Обратиться к источнику – https://cas.edu.vn/khoa-hoc-digital-marketing-tai-cas-viet-nam
MapleCareRx: canadian pharmacy com – Pharmacies in Canada that ship to the US
В этом интересном тексте собраны обширные сведения, которые помогут вам понять различные аспекты обсуждаемой темы. Мы разбираем детали и факты, делая акцент на важности каждого элемента. Не упустите возможность расширить свои знания и взглянуть на мир по-новому!
Осуществить глубокий анализ – https://tamilnenjam.com/?p=5185
Эта публикация дает возможность задействовать различные источники информации и представить их в удобной форме. Читатели смогут быстро найти нужные данные и получить ответы на интересующие их вопросы. Мы стремимся к четкости и доступности материала для всех!
https://www.lavacapurpura.com/madrids-photographer-marathon
luckypari вход http://luckypari102.ru/
Этот текст призван помочь читателю расширить кругозор и получить практические знания. Мы используем простой язык, наглядные примеры и структурированное изложение, чтобы сделать обучение максимально эффективным и увлекательным.
Продолжить чтение – https://beritakhusus.com/bandar-togel
Эта обзорная заметка содержит ключевые моменты и факты по актуальным вопросам. Она поможет читателям быстро ориентироваться в теме и узнать о самых важных аспектах сегодня. Получите краткий курс по современной информации и оставайтесь в курсе событий!
Ознакомиться с теоретической базой – https://magneticafilms.com/cropped-favicon-magnetica-png
В этом обзорном материале представлены увлекательные детали, которые находят отражение в различных аспектах жизни. Мы исследуем непонятные и интересные моменты, позволяя читателю увидеть картину целиком. Погрузитесь в мир знаний и удивительных открытий!
Что ещё нужно знать? – https://news.mangalayatan.in/2022/08/10/group-b-wins-in-debate-competition
В этой публикации мы предлагаем подробные объяснения по актуальным вопросам, чтобы помочь читателям глубже понять их. Четкость и структурированность материала сделают его удобным для усвоения и применения в повседневной жизни.
ТОП-5 причин узнать больше – https://professionalsealers.com/10-reason-why-roofing-are-factmake-easier-9
Мы предлагаем вам окунуться в океан любопытных фактов и вдохновляющих историй. Эта публикация поможет расширить горизонты, разбудить интерес к науке и истории и увидеть мир с новой стороны.
Узнать больше > – http://entreprise-de-nettoyage-versailles-78-yvelines.fr/solar-power-in-developing-nations-brightening-lives
Этот текст призван помочь читателю расширить кругозор и получить практические знания. Мы используем простой язык, наглядные примеры и структурированное изложение, чтобы сделать обучение максимально эффективным и увлекательным.
Откройте для себя больше – https://p3-plus.com/5-elements-that-build-a-roster-of-terrific-clients
Статья знакомит с важнейшими моментами, которые сформировали наше общество. От великих изобретений до культурных переворотов — вы узнаете, как прошлое влияет на наше мышление, технологии и образ жизни.
Расширить кругозор по теме – https://cefacilinas.com/where-does-it-come-fromwhat-is-api-formulation-and-why-it-matters-in-pharmaceutical-industrywhere-does-it-come-from
Этот интересный отчет представляет собой сборник полезных фактов, касающихся актуальных тем. Мы проанализируем данные, чтобы вы могли сделать обоснованные выводы. Читайте, чтобы узнать больше о последних трендах и значимых событиях!
Посмотреть всё – https://cryvora.club/hello-world
В этой статье вы найдете уникальные исторические пересечения с научными открытиями. Каждый абзац — это шаг к пониманию того, как наука и события прошлого создают основу для технологического будущего.
Посмотреть всё – https://jabirjalali.com/think-positive
В этом информативном тексте представлены захватывающие события и факты, которые заставят вас задуматься. Мы обращаем внимание на важные моменты, которые часто остаются незамеченными, и предлагаем новые перспективы на привычные вещи. Подготовьтесь к тому, чтобы быть поглощенным увлекательными рассказами!
Хочу знать больше – https://stomatologweterynaryjny.pl/zdjecie1-15-of-15
Эта обзорная заметка содержит ключевые моменты и факты по актуальным вопросам. Она поможет читателям быстро ориентироваться в теме и узнать о самых важных аспектах сегодня. Получите краткий курс по современной информации и оставайтесь в курсе событий!
Это стоит прочитать полностью – https://studentssolution.com.pk/left-sidebar
Эта обзорная заметка содержит ключевые моменты и факты по актуальным вопросам. Она поможет читателям быстро ориентироваться в теме и узнать о самых важных аспектах сегодня. Получите краткий курс по современной информации и оставайтесь в курсе событий!
Узнать напрямую – https://agenciasmart.digital/o-que-e-seo
BajaMedsDirect: phentermine in mexico pharmacy – Best Mexican pharmacy online
Этот обзор предлагает структурированное изложение информации по актуальным вопросам. Материал подан так, чтобы даже новичок мог быстро освоиться в теме и начать использовать полученные знания в практике.
Не упусти важное! – https://bebote.com.br/2015/07/18/ter-coragem-e-ser-gentil
В этой статье вы найдете уникальные исторические пересечения с научными открытиями. Каждый абзац — это шаг к пониманию того, как наука и события прошлого создают основу для технологического будущего.
Смотрите также… – https://smartifysol.com/unveiling-the-power-of-our-level-4-ietm-delivery-package
Публикация предлагает читателю не просто информацию, а инструменты для анализа и саморазвития. Мы стимулируем критическое мышление, предлагая различные точки зрения и призывая к самостоятельному поиску решений.
Читать далее > – https://worldcryptoupdate.com/tetraguard-the-financial-safe
Этот информационный обзор станет отличным путеводителем по актуальным темам, объединяющим важные факты и мнения экспертов. Мы исследуем ключевые идеи и представляем их в доступной форме для более глубокого понимания. Читайте, чтобы оставаться в курсе событий!
Как это работает — подробно – https://monopoly-dice.com/best-strategies-to-dominate-monopoly-go-leaderboards
Best Indian pharmacy online medical order indian pharmacy
Mexican pharmacy price list: mexican pharmacy – Online Mexican pharmacy
https://maplecarerx.shop/# Pharmacies in Canada that ship to the US
Как сам!
H2O в деле: как вода работает в нашем организме. как движется вода в организме человека Подробный разбор всех процессов с водой от поступления до выведения.
Читай тут: – https://net-tabletok.ru/voda-v-organizme-cheloveka/
что будет с организмом если пить только воду
как движется вода в организме человека
До встречи!
Как сам!
Твой мозг можно прокачать за 8 недель: секреты осознанности. как развить осознанность Научно доказанные способы улучшить память, снизить стресс и стать спокойнее.
Написал: – https://tvoya-sila-vnutri.ru/chto-takoe-osoznannost/
осознанность это
Пока!
Слив курсов sliv.fun .
Здарова!
Молодым семьям без детей: как взять ипотеку выгоднее всех. ипотека-банк онлайн кредит Сравнение программ, банков и реальные отзывы участников.
Здесь подробней: – https://economica-2025.ru/gosudarstvennaya-ipotechnaya-kompaniya/
ипотека для молодой семьи без детей
государственная ипотечная компания
Бывай!
Хай!
Покупка аккаунтов CR – русская рулетка для геймеров. аккаунт клеш рояль продать Разбираем все способы как тебя могут развести.
Здесь подробней: – https://zarabotok-na-igrah.ru/prodazha-akkauntov-klesh-royal/
аккаунт клеш рояль продать
аккаунты клеш рояль продать
До встречи!
регистрация в 1вин http://1win12017.ru/
It sounds like you’re creating problems yourself by defining this as such a comprehensive, almost unknowable problem. Isn’t that self-defeating?
Public policy is key here, and our states need to develop some strategies – – soon.
CuraMedsIndia: CuraMedsIndia – Best online Indian pharmacy
Публикация предлагает уникальную подборку информации, которая будет интересна как специалистам, так и широкому кругу читателей. Здесь вы найдете ответы на часто задаваемые вопросы и полезные инсайты для дальнейшего применения.
Открыть полностью – https://zevainnovations.com/about_img-2-1-jpeg
Этот обзор дает возможность взглянуть на историю и науку под новым углом. Мы представляем редкие факты, неожиданные связи и значимые события, которые помогут вам глубже понять развитие цивилизации и роль человека в ней.
А есть ли продолжение? – https://rahulartsindia.com/blog/aluminium-building-coating-options-available-today
Эта информационная статья содержит полезные факты, советы и рекомендации, которые помогут вам быть в курсе последних тенденций и изменений в выбранной области. Материал составлен так, чтобы быть полезным и понятным каждому.
Хочешь знать всё? – https://synclik.com/index.php/content-writing
the purple pharmacy mexico Best Mexican pharmacy online mexican drugstore
Эта статья предлагает уникальную подборку занимательных фактов и необычных историй, которые вы, возможно, не знали. Мы постараемся вдохновить ваше воображение и разнообразить ваш кругозор, погружая вас в мир, полный интересных открытий. Читайте и открывайте для себя новое!
Получить больше информации – https://vinhoatevoce.com.br/strategies-for-writing-a-successful-custom-essay
lucky pari mirror http://www.luckypari102.ru
BajaMedsDirect: Online Mexican pharmacy – Online Mexican pharmacy
можно ли в колледже купить диплом можно ли в колледже купить диплом .
Canadian pharmacy prices: Pharmacies in Canada that ship to the US – Canadian pharmacy online
как купить диплом техникума в красноярске как купить диплом техникума в красноярске .
купить диплом вуза купить диплом вуза .
Эта публикация завернет вас в вихрь увлекательного контента, сбрасывая стереотипы и открывая двери к новым идеям. Каждый абзац станет для вас открытием, полным ярких примеров и впечатляющих достижений. Подготовьтесь быть вовлеченными и удивленными каждый раз, когда продолжите читать.
Детальнее – https://besturduquotes.net/90-best-good-morning-quotes-to-brighten-your
Публикация предлагает читателю не просто информацию, а инструменты для анализа и саморазвития. Мы стимулируем критическое мышление, предлагая различные точки зрения и призывая к самостоятельному поиску решений.
Всё, что нужно знать – https://wakaresaseya-ceo.jp/%E3%83%8F%E3%82%B0
Эта информационная заметка содержит увлекательные сведения, которые могут вас удивить! Мы собрали интересные факты, которые сделают вашу жизнь ярче и полнее. Узнайте нечто новое о привычных аспектах повседневности и откройте для себя удивительный мир информации.
Нажмите, чтобы узнать больше – https://arthistorysurvey.com/art_history_survey_logo-02
Эта публикация погружает вас в мир увлекательных фактов и удивительных открытий. Мы расскажем о ключевых событиях, которые изменили ход истории, и приоткроем завесу над научными достижениями, которые вдохновили миллионы. Узнайте, чему может научить нас прошлое и как применить эти знания в будущем.
Продолжить чтение – https://elcongmbh.de/prgjos-de-ce-gtudier-prenne-place-un-glgment-en-7
Эта информационная заметка содержит увлекательные сведения, которые могут вас удивить! Мы собрали интересные факты, которые сделают вашу жизнь ярче и полнее. Узнайте нечто новое о привычных аспектах повседневности и откройте для себя удивительный мир информации.
Откройте для себя больше – https://investigacion.politicas.unam.mx/racomunicacion/?p=8980
В данной обзорной статье представлены интригующие факты, которые не оставят вас равнодушными. Мы критикуем и анализируем события, которые изменили наше восприятие мира. Узнайте, что стоит за новыми открытиями и как они могут изменить ваше восприятие реальности.
Не упусти шанс – https://marcrodenberg.biz/sevilla-drachenboot-em-6
В этой статье-обзоре мы соберем актуальную информацию и интересные факты, которые освещают важные темы. Читатели смогут ознакомиться с различными мнениями и подходами, что позволит им расширить кругозор и глубже понять обсуждаемые вопросы.
Что скрывают от вас? – https://www.agriturismoilmurello.it/portfolio/spacebound-2
Эта информационная заметка содержит увлекательные сведения, которые могут вас удивить! Мы собрали интересные факты, которые сделают вашу жизнь ярче и полнее. Узнайте нечто новое о привычных аспектах повседневности и откройте для себя удивительный мир информации.
Продолжить чтение – https://milwaukeeexpress.com/trump-in-milwaukee
В этой публикации мы сосредоточимся на интересных аспектах одной из самых актуальных тем современности. Совмещая факты и мнения экспертов, мы создадим полное представление о предмете, которое будет полезно как новичкам, так и тем, кто глубоко изучает вопрос.
Переходите по ссылке ниже – https://chellemeuniformes.com.br/the-greatest-moments-in-travel-history
Этот информационный материал собраны данные, которые помогут лучше понять текущие тенденции и процессы в различных сферах жизни. Мы предоставляем четкий анализ, графики и примеры, чтобы информация была не только понятной, но и практичной для принятия решений.
Все материалы собраны здесь – https://www.qvccert.com/logo
Публикация предлагает уникальную подборку информации, которая будет интересна как специалистам, так и широкому кругу читателей. Здесь вы найдете ответы на часто задаваемые вопросы и полезные инсайты для дальнейшего применения.
Практические советы ждут тебя – https://arescell.com/index.php/2020/11/01/spring-wine-festival-at-a-vintage-vineyard-3
Публикация предлагает уникальную подборку информации, которая будет интересна как специалистам, так и широкому кругу читателей. Здесь вы найдете ответы на часто задаваемые вопросы и полезные инсайты для дальнейшего применения.
Читать дальше – https://atermit.nl/tech-products-that-makes-its-easier-to-stay-at-home
Публикация предлагает читателю не просто информацию, а инструменты для анализа и саморазвития. Мы стимулируем критическое мышление, предлагая различные точки зрения и призывая к самостоятельному поиску решений.
Давай разберёмся досконально – https://www.robynson.cz/graficke-prace-a-proc-jsou-nezbytne-pro-uspech-vaseho-podnikani
Indian pharmacy online Best Indian pharmacy Indian pharmacy to USA
купить диплом в ачинске купить диплом в ачинске .
canadian family pharmacy canada online pharmacy or canadian pharmacy near me canada pharmacy online
http://www.google.sr/url?q=https://maplecarerx.com canadian pharmacy ed medications and https://bold-kw.com/user/yinyurizom/?um_action=edit safe canadian pharmacies
reputable canadian pharmacy canadian 24 hour pharmacy and canadian pharmacy antibiotics online canadian pharmacy
купить диплом в миассе купить диплом в миассе .
Хай!
Вся правда о таурине: польза для сердца, мозгов и мышц. таурин польза Личный опыт применения и советы по выбору добавок.
Переходи: – https://net-tabletok.ru/taurin/
таурин это простыми словами
таурин польза
Пока!
Хай!
К2 менахинон полный гайд для тех кто не любит заумные статьи. витамин к2 для чего Дозировки цены и где купить без развода
Читай тут: – https://generik-info.ru/vitamin-k2/
витамин к2 где содержится
витамин к2
Удачи!
купить диплом инженера https://rudik-diplom2.ru – купить диплом инженера .
apotek utan receptkrav: apotek utan receptkrav – europa apotheke
Эта познавательная публикация погружает вас в море интересного контента, который быстро захватит ваше внимание. Мы рассмотрим важные аспекты темы и предоставим вам уникальные Insights и полезные сведения для дальнейшего изучения.
Почему это важно? – https://ccvni.de/pc-20192
Этот информационный обзор станет отличным путеводителем по актуальным темам, объединяющим важные факты и мнения экспертов. Мы исследуем ключевые идеи и представляем их в доступной форме для более глубокого понимания. Читайте, чтобы оставаться в курсе событий!
Детальнее – https://ejv.co.nz/hello-world
medicaments sans ordonnance livraison rapide: PharmaRapide – п»їpharmacie en ligne france
В этой статье представлен занимательный и актуальный контент, который заставит вас задуматься. Мы обсуждаем насущные вопросы и проблемы, а также освещаем истории, которые вдохновляют на действия и изменения. Узнайте, что стоит за событиями нашего времени!
Ознакомиться с отчётом – http://www.nejlevnejsi-filtry.cz/logo_nf
Этот информативный материал предлагает содержательную информацию по множеству задач и вопросов. Мы призываем вас исследовать различные идеи и факты, обобщая их для более глубокого понимания. Наша цель — сделать обучение доступным и увлекательным.
https://www.smkbuanainsan.sch.id/172
Публикация предлагает читателю не просто информацию, а инструменты для анализа и саморазвития. Мы стимулируем критическое мышление, предлагая различные точки зрения и призывая к самостоятельному поиску решений.
Только факты! – https://avocats-narbonne-am.fr/hello-world
Эта публикация дает возможность задействовать различные источники информации и представить их в удобной форме. Читатели смогут быстро найти нужные данные и получить ответы на интересующие их вопросы. Мы стремимся к четкости и доступности материала для всех!
Рассмотреть проблему всесторонне – https://pharmacy.ishan.ac/news-and-events/celebration-of-world-pharmacist-day
В этом информативном тексте представлены захватывающие события и факты, которые заставят вас задуматься. Мы обращаем внимание на важные моменты, которые часто остаются незамеченными, и предлагаем новые перспективы на привычные вещи. Подготовьтесь к тому, чтобы быть поглощенным увлекательными рассказами!
Получить полную информацию – https://limabatido.com.br/high-blood-pressure-the-silent-awesome
Эта информационная заметка предлагает лаконичное и четкое освещение актуальных вопросов. Здесь вы найдете ключевые факты и основную информацию по теме, которые помогут вам сформировать собственное мнение и повысить уровень осведомленности.
Выяснить больше – https://cleaningbypinkladies.co.uk/home/the-top-3-germiest-places-in-your-office
Публикация предлагает уникальную подборку информации, которая будет интересна как специалистам, так и широкому кругу читателей. Здесь вы найдете ответы на часто задаваемые вопросы и полезные инсайты для дальнейшего применения.
Это стоит прочитать полностью – https://hook.ng/best-way-to-redeem-amazon-gift-cards-for-naira-online
В этом информативном тексте представлены захватывающие события и факты, которые заставят вас задуматься. Мы обращаем внимание на важные моменты, которые часто остаются незамеченными, и предлагаем новые перспективы на привычные вещи. Подготовьтесь к тому, чтобы быть поглощенным увлекательными рассказами!
Хочу знать больше – https://sepidsanat.com/%D9%86%D8%B5%D8%A8-%D8%B3%DB%8C%D9%86%DB%8C-%D9%87%D8%A7%DB%8C-%DA%A9%D8%A7%D8%A8%D9%84
Как сам!
Производные инструменты криптобирж: полный обзор. фьючерсы это простыми словами Сравниваем условия Binance и Bybit, изучаем комиссии и функционал.
Написал: – https://pro-kriptu.ru/chto-takoe-fyuchersy/
что такое фьючерсы в крипте
как работают фьючерсы
фьючерсы бинанс
Будь здоров!
Enjoyed reading through this, very good material. Thanks!
médicaments sans ordonnance livraison rapide: commande discrète médicaments France – pharmacie en ligne france pas cher
online apotheke versandkostenfrei apotheke online and apotheke online gГјnstigste online apotheke
https://www.google.com.ua/url?q=https://vitalapotheke24.com online apotheke rezept and https://www.packadvisory.com/user/hayoxngxjg/ online apotheke rezept
beste online-apotheke ohne rezept online apotheke rezept and internet apotheke online apotheke gГјnstig
Здарова!
Налоги с инвестиций и как их минимизировать законно. книги про инвестиции для начинающих ИИС, льготы и все способы платить государству меньше.
Переходи: – https://economica-2025.ru/investiczii-dlya-nachinayushhih/
инвестиции для начинающих
инвестиции для начинающих куда
Бывай!
Здравствуйте!
Домино без розовых очков: жесткий разбор для серьезных игроков. правила игры в домино вдвоем Математика, вероятности и холодный расчет вместо удачи.
Переходи: – https://nagny-casino.ru/pravila-igry-v-domino/
правила игры в домино
Бывай!
pharmacie en ligne france livraison belgique pharmacie en ligne France fiable pharmacie en ligne France fiable
Эта информационная заметка содержит увлекательные сведения, которые могут вас удивить! Мы собрали интересные факты, которые сделают вашу жизнь ярче и полнее. Узнайте нечто новое о привычных аспектах повседневности и откройте для себя удивительный мир информации.
Смотри, что ещё есть – https://www.ricsfeet.com/2023/11/25/white-with-stripes
Статья содержит практические рекомендации и полезные советы, которые можно легко применить в повседневной жизни. Мы делаем акцент на реальных примерах и проверенных методиках, которые способствуют личностному развитию и улучшению качества жизни.
Перейти к полной версии – https://www.balademusicale-rixensart.be/travel_472868326
Публикация предлагает читателю не просто информацию, а инструменты для анализа и саморазвития. Мы стимулируем критическое мышление, предлагая различные точки зрения и призывая к самостоятельному поиску решений.
Ознакомиться с теоретической базой – https://xyz.norwestcomputing.com.au/2020/07/14/recollections-of-a-conversation-with-antoine-mariadassou
pharmacie française livraison à domicile: solution santé en ligne sécurisée – Pharmacie Internationale en ligne
Этот текст призван помочь читателю расширить кругозор и получить практические знания. Мы используем простой язык, наглядные примеры и структурированное изложение, чтобы сделать обучение максимально эффективным и увлекательным.
Всё, что нужно знать – https://www.poeselhof.be/placeholder-png
Публикация предлагает уникальную подборку информации, которая будет интересна как специалистам, так и широкому кругу читателей. Здесь вы найдете ответы на часто задаваемые вопросы и полезные инсайты для дальнейшего применения.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://cinemovel.tv/sic/2020/la-mafia-e-lo-sport
Публикация предлагает читателю не просто информацию, а инструменты для анализа и саморазвития. Мы стимулируем критическое мышление, предлагая различные точки зрения и призывая к самостоятельному поиску решений.
Неизвестные факты о… – https://torcidadofuracao.com.br/2022/11/08/agenda-de-jogos-de-hoje-e-amanha-quarta-09-11-onde-assistir
Эта обзорная заметка содержит ключевые моменты и факты по актуальным вопросам. Она поможет читателям быстро ориентироваться в теме и узнать о самых важных аспектах сегодня. Получите краткий курс по современной информации и оставайтесь в курсе событий!
Смотрите также… – https://www.res.cmb.ac.lk/humanities.education/c.hathlahawaththa/index.php/pubs/reproductive-health-of-katunayake-ftz-migrant-female-workers
Эта статья предлагает уникальную подборку занимательных фактов и необычных историй, которые вы, возможно, не знали. Мы постараемся вдохновить ваше воображение и разнообразить ваш кругозор, погружая вас в мир, полный интересных открытий. Читайте и открывайте для себя новое!
Изучить материалы по теме – https://footcare-tajima.com/2021/03/29/hello-world
Публикация предлагает читателю не просто информацию, а инструменты для анализа и саморазвития. Мы стимулируем критическое мышление, предлагая различные точки зрения и призывая к самостоятельному поиску решений.
Где почитать поподробнее? – https://manhyiapalace.org/lies-are-the-root-of-land-disputes-otumfuo-tells-ahafo-peace-council
Эта познавательная публикация погружает вас в море интересного контента, который быстро захватит ваше внимание. Мы рассмотрим важные аспекты темы и предоставим вам уникальные Insights и полезные сведения для дальнейшего изучения.
Подробная информация доступна по запросу – https://ker-mer.com/en/stella-pardo
В этой статье вы найдете познавательную и занимательную информацию, которая поможет вам лучше понять мир вокруг. Мы собрали интересные данные, которые вдохновляют на размышления и побуждают к действиям. Открывайте новую информацию и получайте удовольствие от чтения!
Провести детальное исследование – https://trouver-prenom.com/prenom-retro-fille
Этот интересный отчет представляет собой сборник полезных фактов, касающихся актуальных тем. Мы проанализируем данные, чтобы вы могли сделать обоснованные выводы. Читайте, чтобы узнать больше о последних трендах и значимых событиях!
Познакомиться с результатами исследований – https://jeevanelevators.com/hello-world
Читатель отправляется в интеллектуальное путешествие по самым ярким событиям истории и важнейшим научным открытиям. Мы раскроем тайны эпох, покажем, как идеи меняли миры, и объясним, почему эти знания остаются актуальными сегодня.
Изучить аспект более тщательно – https://ofix.or.jp/2024/03/10/12382
Этот информативный текст отличается привлекательным содержанием и актуальными данными. Мы предлагаем читателям взглянуть на привычные вещи под новым углом, предоставляя интересный и доступный материал. Получите удовольствие от чтения и расширьте кругозор!
Перейти к полной версии – https://movietheme.dubdesign.net/demo1/microsoft/xbox/49
Этот увлекательный информационный материал подарит вам массу новых знаний и ярких эмоций. Мы собрали для вас интересные факты и сведения, которые обогатят ваш опыт. Откройте для себя увлекательный мир информации и насладитесь процессом изучения!
Смотрите также… – https://apelconsulting.cz/hello-world
Здарова!
Закрыть гештальт: что это значит и как это сделать правильно. гештальт психология Практические советы по работе с незавершенными ситуациями.
Переходи: – https://tvoya-sila-vnutri.ru/geshtalt-psihologiya/
что такое гештальт психология
Покеда!
электрокранизы http://www.avtomaticheskie-karnizy-dlya-shtor.ru/ .
SaludExpress: farmacias online seguras – farmacia con envío rápido y seguro
reseptfrie medisiner pa nett apotek uten resept med levering hjem apotek pa nett
горшки для цветов с поливом https://kashpo-s-avtopolivom-spb.ru/ .
купить диплом медсестры купить диплом медсестры .
http://hollandapotheeknl.com/# Holland Apotheek
Как сам!
Финансовая подушка – твоя страховка от неожиданностей судьбы. финансовая подушка безопасности размер Как накопить резерв денег и использовать его только по назначению.
Здесь подробней: – https://economica-2025.ru/finansovaya-podushka-bezopasnosti-eto/
финансовая подушка безопасности размер
как финансовая подушка безопасности защищает человека и его семью
Бывай!
Привет!
Повербанк для iPhone какой купить чтобы не жалеть. беспроводной повербанк для айфона Разбираем емкость мощность зарядки совместимость и дополнительные фишки.
Здесь подробней: – https://pro-telefony.ru/poverbank-dlya-ajfona/
лучший повербанк для айфона
беспроводной повербанк для айфона оригинал
купить повербанк для айфона
Покеда!
billige generiske legemidler Norge: apotek på nett med gode priser – nettapotek Norge trygt og pålitelig
pedir farmacos por Internet farmacia con envio rapido y seguro pedir farmacos por Internet
можно купить диплом медсестры можно купить диплом медсестры .
1win tennis tikish https://1win5502.ru
farmacia online senza ricetta acquisto farmaci con ricetta or acquisto farmaci con ricetta farmacia online piГ№ conveniente
https://www.ehso.com/ehsord.php?URL=https://farmaciafacileit.com top farmacia online and https://pramias.com/profile/tvrvciulwk/ migliori farmacie online 2024
acquisto farmaci con ricetta Farmacia online miglior prezzo or farmacie online autorizzate elenco farmacie online sicure
farmacia con envío rápido y seguro: farmacia online España fiable – medicamentos sin receta a domicilio
Здарова!
Дешевые игры без обмана: честный обзор всех площадок от человека с опытом. распродажа игр Три года покупок, косяки продавцов и способы поднять бабки на ключах.
Читай тут: – https://zarabotok-na-igrah.ru/skidki-na-igry/
где можно купить игры на пк
где купить дешевые игры
скидки на игры
До встречи!
bestille medisiner online diskret apotek uten resept med levering hjem or bestille medisiner online diskret nettapotek Norge trygt og pålitelig
http://101.43.178.182/sell/email.asp?d=pharmalibrefrance.com&on=tb nettapotek Norge trygt og pålitelig or http://dnp-malinovka.ru/user/dwcizpqwxh/?um_action=edit apotek uten resept med levering hjem
apotek på nett med gode priser kundevurderinger av nettapotek and apotek uten resept med levering hjem apotek på nett billigst
farmacia online Espana fiable: SaludExpress – medicamentos sin receta a domicilio
farmacia online Italia affidabile: medicinali generici a basso costo – FarmaciaFacile
Farmacia online piГ№ conveniente medicinali generici a basso costo spedizione rapida farmaci Italia
farmacia online barcelona farmacia barata or farmacia barata farmacia online envГo gratis
http://maps.google.com.na/url?q=https://saludexpresses.shop farmacia online madrid or http://orbita-3.ru/forum/index.php?PAGE_NAME=profile_view&UID=30663 farmacia online barcelona
farmacia online envГo gratis farmacia en casa online descuento or farmacia online madrid farmacia online madrid
1win slot o‘yinlari 1win slot o‘yinlari
veilig online apotheek NL: online apotheek – Holland Apotheek
Хай!
Конный спорт и ставки в России: традиции и инновации. скачки лошади От царских скачек до цифровых платформ.
Здесь подробней: – https://nagny-casino.ru/konnye-skachki/
конские скачки
конные скачки
До встречи!
Здравствуйте!
Кровь восстанавливается за 8 недель, нервы могут болеть до 6 месяцев. витамина в12 Сроки восстановления после лечения дефицита B12.
По ссылке: – https://generik-info.ru/vitamin-b12/
недостаток витамина в12 и фолиевой кислоты симптомы
нехватка витамина в12 симптомы у взрослых
Будь здоров!
apotek pa nett: apotek pa nett med gode priser – reseptfrie medisiner pa nett
farmacie online sicure Farmacie on line spedizione gratuita or Farmacie on line spedizione gratuita farmacia online
http://notice.iptv.by/nomoney.php?host=pharmaexpressfrance.com&n=lizyukovyh7_913&nm=Ralink¶ms=redirect=/forum/tracker.php&reason=3&url=/forum/index.php migliori farmacie online 2024 and https://istinastroitelstva.xyz/user/trcvjwiakx/ Farmacie on line spedizione gratuita
farmacia online piГ№ conveniente acquistare farmaci senza ricetta and п»їFarmacia online migliore farmacie online affidabili
online apotheek: discrete levering van medicijnen – veilig online apotheek NL
купить диплом вуза диплом техникума пять плюс купить диплом вуза диплом техникума пять плюс .
уличное кашпо для цветов напольное уличное кашпо для цветов напольное .
apotek pa nett billigst apotek pa nett med gode priser reseptfrie medisiner pa nett
Привет!
Краудфандинг – это не попрошайничество, а цивилизованный способ найти деньги на проект. [url=https://economica-2025.ru/kraudfanding/]краудфандинга что это[/url] Как работать с толпой и получать от нее финансирование.
Написал: – https://economica-2025.ru/kraudfanding/
краудфандинг это простыми словами
краудфандинг это
Будь здоров!
1win aviator yuklab olish 1win aviator yuklab olish
Привет!
Игровые планшеты 2025 которые не подведут в решающий момент. игровой планшет 120 герц Честный обзор топового железа с примерами реального использования.
Здесь подробней: – https://pro-telefony.ru/igrovoj-planshet/
игровой планшет
купить игровой планшет
игровой планшет 120 фпс
Будь здоров!
pedir fármacos por Internet: farmacia con envío rápido y seguro – comprar medicinas online sin receta médica
cầu 3 càng chuẩn nhất việt nam
Этот текст призван помочь читателю расширить кругозор и получить практические знания. Мы используем простой язык, наглядные примеры и структурированное изложение, чтобы сделать обучение максимально эффективным и увлекательным.
Это стоит прочитать полностью – https://template136.webekspor.com/sculpted-elegance-aston-martins-artistry-on-wheels
В обзорной статье вы найдете собрание важных фактов и аналитики по самым разнообразным темам. Мы рассматриваем как современные исследования, так и исторические контексты, чтобы вы могли получить полное представление о предмете. Погрузитесь в мир знаний и сделайте шаг к пониманию!
Интересует подробная информация – https://graficosenrecorte.com/2017/01/18/some-amazing-buildings
В этой статье представлен занимательный и актуальный контент, который заставит вас задуматься. Мы обсуждаем насущные вопросы и проблемы, а также освещаем истории, которые вдохновляют на действия и изменения. Узнайте, что стоит за событиями нашего времени!
Узнать больше – https://blackbritishbookfestival.com/2024/11/19/ya-writing-workshop-success
FarmaciaFacile: farmaci senza prescrizione disponibili online – spedizione rapida farmaci Italia
Farmacia online miglior prezzo farmacie online autorizzate elenco or farmacia online acquistare farmaci senza ricetta
https://toolbarqueries.google.co.ug/url?sa=t&url=https://farmaciafacileit.com farmacia online and http://ussher.org.uk/user/xunncejlly/?um_action=edit Farmacia online miglior prezzo
farmacia online farmacie online affidabili or acquistare farmaci senza ricetta farmacie online sicure
1вин uzcard пополнение https://1win5503.ru/
Хай!
Братан, твои кости требуют кальция: полный расклад. какой кальций лучше усваивается Что есть, что пить и как не переборщить с дозировками.
Переходи: – https://net-tabletok.ru/kakoj-kalczij-luchshe-usvaivaetsya/
кальций
какой кальций лучше усваивается
Бывай!
https://chickenroadslotindia.shop/# Chicken Road slot game India
Chicken Road slot UK: UK players free spins Chicken Road – play Chicken Road casino online UK
vincite e bonus gioco Chicken Road: slot a tema fattoria Italia – vincite e bonus gioco Chicken Road
play Chicken Road casino online UK casino promotions Chicken Road game licensed UK casino sites Chicken Road
Эта информационная заметка содержит увлекательные сведения, которые могут вас удивить! Мы собрали интересные факты, которые сделают вашу жизнь ярче и полнее. Узнайте нечто новое о привычных аспектах повседневности и откройте для себя удивительный мир информации.
Всё, что нужно знать – https://www.happydive.net/2024/04/29/losin-october
В данной обзорной статье представлены интригующие факты, которые не оставят вас равнодушными. Мы критикуем и анализируем события, которые изменили наше восприятие мира. Узнайте, что стоит за новыми открытиями и как они могут изменить ваше восприятие реальности.
Уникальные данные только сегодня – https://www.jeromechapuis.com/show-wheels-fest-festival
Эта публикация погружает вас в мир увлекательных фактов и удивительных открытий. Мы расскажем о ключевых событиях, которые изменили ход истории, и приоткроем завесу над научными достижениями, которые вдохновили миллионы. Узнайте, чему может научить нас прошлое и как применить эти знания в будущем.
Эксклюзивная информация – https://securedata.systems/index.php/2024/01/09/hello-world
В этом информативном тексте представлены захватывающие события и факты, которые заставят вас задуматься. Мы обращаем внимание на важные моменты, которые часто остаются незамеченными, и предлагаем новые перспективы на привычные вещи. Подготовьтесь к тому, чтобы быть поглощенным увлекательными рассказами!
Что ещё нужно знать? – https://pixelperfect360.in/protfolio/conventions/shreekrishnaconvention
Эта публикация дает возможность задействовать различные источники информации и представить их в удобной форме. Читатели смогут быстро найти нужные данные и получить ответы на интересующие их вопросы. Мы стремимся к четкости и доступности материала для всех!
Детали по клику – https://assignmentmastershq.com/product/communication-studies
Эта публикация погружает вас в мир увлекательных фактов и удивительных открытий. Мы расскажем о ключевых событиях, которые изменили ход истории, и приоткроем завесу над научными достижениями, которые вдохновили миллионы. Узнайте, чему может научить нас прошлое и как применить эти знания в будущем.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://www.sixcleversisters.com/how-to-make-a-genuine-greek-frappe
Эта статья сочетает в себе как полезные, так и интересные сведения, которые обогатят ваше понимание насущных тем. Мы предлагаем практические советы и рекомендации, которые легко внедрить в повседневную жизнь. Узнайте, как улучшить свои навыки и обогатить свой опыт с помощью простых, но эффективных решений.
ТОП-5 причин узнать больше – https://clizak.com/revolutionize-your-business-with-our-cutting-edge
В этом информативном тексте представлены захватывающие события и факты, которые заставят вас задуматься. Мы обращаем внимание на важные моменты, которые часто остаются незамеченными, и предлагаем новые перспективы на привычные вещи. Подготовьтесь к тому, чтобы быть поглощенным увлекательными рассказами!
Не упусти важное! – https://terekamjejak.com/jelajah-waktu-jejak-melawan-voc
Этот обзор предлагает структурированное изложение информации по актуальным вопросам. Материал подан так, чтобы даже новичок мог быстро освоиться в теме и начать использовать полученные знания в практике.
Дополнительно читайте здесь – https://debbyconrad.com/my-chihuahua-bites
Этот информационный материал собраны данные, которые помогут лучше понять текущие тенденции и процессы в различных сферах жизни. Мы предоставляем четкий анализ, графики и примеры, чтобы информация была не только понятной, но и практичной для принятия решений.
Всё, что нужно знать – https://markaparket.com/%D8%A7%D8%B3%D8%AA%D8%B9%D9%84%D8%A7%D9%85-%D9%82%DB%8C%D9%85%D8%AA-%D9%BE%D8%A7%D8%B1%DA%A9%D8%AA-%D8%A7%D8%AF%D9%88%D9%86%D8%B3-%D8%A2%D9%84%D9%85%D8%A7%D9%86
Статья знакомит с важнейшими моментами, которые сформировали наше общество. От великих изобретений до культурных переворотов — вы узнаете, как прошлое влияет на наше мышление, технологии и образ жизни.
Подробнее тут – https://mybestbox.shop/index.php/2023/04/09/boost-your-online-presence-our-top-digital-marketing
Публикация предлагает читателю не просто информацию, а инструменты для анализа и саморазвития. Мы стимулируем критическое мышление, предлагая различные точки зрения и призывая к самостоятельному поиску решений.
Посмотреть всё – https://wicp.network/manual-guide
recensione Chicken Road slot: giocare Chicken Road gratis o con soldi veri – giri gratis Chicken Road casino Italia
1вин слоты https://www.1win5505.ru
licensed UK casino sites Chicken Road Chicken Road slot UK British online casinos with Chicken Road
https://chickenroadslotitalia.shop/# vincite e bonus gioco Chicken Road
Хай!
Твоя кредитка испорчена и банки не дают денег? как исправить кредитную историю после банкротства Узнай, как исправить ситуацию законно и без переплат мошенникам.
Написал: – https://kredit-bez-slov.ru/kak-ispravit-kreditnuyu-istoriyu/
как исправить кредитную историю после банкротства
как исправить кредитную историю
как исправить кредитную историю после просрочки
Покеда!
Хай!
От героя до нуля за счет гормонов стресса. гормоны стресса Кортизол и компания портят жизнь 24/7 – пора дать отпор.
Читай тут: – https://tvoya-sila-vnutri.ru/gormony-stressa/
кортизол это гормон стресса
Пока!
В этой статье представлен занимательный и актуальный контент, который заставит вас задуматься. Мы обсуждаем насущные вопросы и проблемы, а также освещаем истории, которые вдохновляют на действия и изменения. Узнайте, что стоит за событиями нашего времени!
Подробнее тут – https://quick-vyvod-iz-zapoya-1.ru/
secure online gambling India free demo Chicken Road game and best Indian casinos with Chicken Road how to win Chicken Road slot game
http://newagestyle.net/forum/away.php?s=https://chickenroadslotindia.com bonus spins Chicken Road casino India or http://sotoycasal.com/user/aeyihysscj/ secure online gambling India
how to win Chicken Road slot game how to win Chicken Road slot game and Chicken Road slot game India Chicken Road slot game India
1win uz kirish 1win uz kirish
Plinko casinò online Italia: Plinko casinò online Italia – giocare Plinko con soldi veri
В этой статье вы найдете познавательную и занимательную информацию, которая поможет вам лучше понять мир вокруг. Мы собрали интересные данные, которые вдохновляют на размышления и побуждают к действиям. Открывайте новую информацию и получайте удовольствие от чтения!
Что ещё? Расскажи всё! – https://cardyz.in/product/bmw-metal-nfc-card
В данной статье вы найдете комплексный подход к изучению насущных тем. Мы комбинируем теоретические сведения с практическими советами, чтобы читатель мог не только понять проблему, но и найти пути её решения.
Открыть полностью – https://datsumask.com/wp/?p=69
Этот обзор предлагает структурированное изложение информации по актуальным вопросам. Материал подан так, чтобы даже новичок мог быстро освоиться в теме и начать использовать полученные знания в практике.
Где можно узнать подробнее? – https://www.rordrom.se/produkt/rrdrm001
Публикация предлагает уникальную подборку информации, которая будет интересна как специалистам, так и широкому кругу читателей. Здесь вы найдете ответы на часто задаваемые вопросы и полезные инсайты для дальнейшего применения.
Осуществить глубокий анализ – https://training-grc.com/pelatihan-telemarketing-skills
В данной статье вы найдете комплексный подход к изучению насущных тем. Мы комбинируем теоретические сведения с практическими советами, чтобы читатель мог не только понять проблему, но и найти пути её решения.
Более того — здесь – https://vandien.info/product/go-ghep-tram-bc-10-x-1220-x-2440
Эта информационная заметка содержит увлекательные сведения, которые могут вас удивить! Мы собрали интересные факты, которые сделают вашу жизнь ярче и полнее. Узнайте нечто новое о привычных аспектах повседневности и откройте для себя удивительный мир информации.
Только факты! – https://telegra.ph/Interesnye-sajty-s-poleznymi-materialami-09-18
Эта статья сочетает в себе как полезные, так и интересные сведения, которые обогатят ваше понимание насущных тем. Мы предлагаем практические советы и рекомендации, которые легко внедрить в повседневную жизнь. Узнайте, как улучшить свои навыки и обогатить свой опыт с помощью простых, но эффективных решений.
Тыкай сюда — узнаешь много интересного – https://dental-art-ke.de/home_image_1
Эта информационная заметка содержит увлекательные сведения, которые могут вас удивить! Мы собрали интересные факты, которые сделают вашу жизнь ярче и полнее. Узнайте нечто новое о привычных аспектах повседневности и откройте для себя удивительный мир информации.
Что скрывают от вас? – https://tomnassal.com/2016/02/24/supernatural-showreel
real money slot Chicken Road UK UK players free spins Chicken Road and UK players free spins Chicken Road Chicken Road slot UK
http://images.google.com.mm/url?q=https://chickenroadslotuk.com Chicken Road slot UK or http://lzdsxxb.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=5212989 casino promotions Chicken Road game
Chicken Road play Chicken Road casino online UK or play Chicken Road casino online UK casino promotions Chicken Road game
vincite e bonus gioco Chicken Road: giri gratis Chicken Road casino Italia – slot a tema fattoria Italia
1вин мобильная версия https://1win5505.ru
http://medicexpressmx.com/# MedicExpress MX
sildenafil: Sildenafil 100mg price – Sildenafil 100mg price
Buy Tadalafil online Generic Cialis without a doctor prescription Buy Tadalafil 20mg
http://truevitalmeds.com/# Sildenafil 100mg
https://medicexpressmx.com/# MedicExpress MX
buying prescription drugs in mexico: Online Mexican pharmacy – MedicExpress MX
buy generic tadalafil 20mg tadalafil brand name in india Buy Tadalafil online
купить диплом в новом уренгое http://www.rudik-diplom15.ru/ .
В обзорной статье вы найдете собрание важных фактов и аналитики по самым разнообразным темам. Мы рассматриваем как современные исследования, так и исторические контексты, чтобы вы могли получить полное представление о предмете. Погрузитесь в мир знаний и сделайте шаг к пониманию!
Хочешь знать всё? – https://spaceeyenews.com/after-deepseek-china-unveils-manus-ai-worlds-first-autonomous-ai-agent-video
Этот информационный материал собраны данные, которые помогут лучше понять текущие тенденции и процессы в различных сферах жизни. Мы предоставляем четкий анализ, графики и примеры, чтобы информация была не только понятной, но и практичной для принятия решений.
Слушай внимательно — тут важно – http://vipjetbet.online/post/34
Эта публикация погружает вас в мир увлекательных фактов и удивительных открытий. Мы расскажем о ключевых событиях, которые изменили ход истории, и приоткроем завесу над научными достижениями, которые вдохновили миллионы. Узнайте, чему может научить нас прошлое и как применить эти знания в будущем.
Перейти к полной версии – http://www.paluansejati.com/single-product
Эта статья сочетает в себе как полезные, так и интересные сведения, которые обогатят ваше понимание насущных тем. Мы предлагаем практические советы и рекомендации, которые легко внедрить в повседневную жизнь. Узнайте, как улучшить свои навыки и обогатить свой опыт с помощью простых, но эффективных решений.
Тыкай сюда — узнаешь много интересного – https://hoppinghawks.com/hello-world
Этот обзор дает возможность взглянуть на историю и науку под новым углом. Мы представляем редкие факты, неожиданные связи и значимые события, которые помогут вам глубже понять развитие цивилизации и роль человека в ней.
Это стоит прочитать полностью – https://marathi.deccanquest.com/?p=31
Статья содержит практические рекомендации и полезные советы, которые можно легко применить в повседневной жизни. Мы делаем акцент на реальных примерах и проверенных методиках, которые способствуют личностному развитию и улучшению качества жизни.
Слушай внимательно — тут важно – https://crbank.com.br/the-art-of-negotiation-tips-for-successful-business-deals
В этой статье представлен занимательный и актуальный контент, который заставит вас задуматься. Мы обсуждаем насущные вопросы и проблемы, а также освещаем истории, которые вдохновляют на действия и изменения. Узнайте, что стоит за событиями нашего времени!
Это стоит прочитать полностью – https://vistoweekly.com/silaverdaddies
Публикация приглашает вас исследовать неизведанное — от древних тайн до современных достижений науки. Вы узнаете, как случайные находки превращались в революции, а смелые мысли — в новые эры человеческого прогресса.
Как это работает — подробно – https://brighthomecareinc.com/2017/09/27/lab-priority-services-delivered
Читатель отправляется в интеллектуальное путешествие по самым ярким событиям истории и важнейшим научным открытиям. Мы раскроем тайны эпох, покажем, как идеи меняли миры, и объясним, почему эти знания остаются актуальными сегодня.
ТОП-5 причин узнать больше – https://ghmgf.com/celebrating-our-one-year-anniversary
Legit online Mexican pharmacy Best online Mexican pharmacy Best online Mexican pharmacy
Эта публикация погружает вас в мир увлекательных фактов и удивительных открытий. Мы расскажем о ключевых событиях, которые изменили ход истории, и приоткроем завесу над научными достижениями, которые вдохновили миллионы. Узнайте, чему может научить нас прошлое и как применить эти знания в будущем.
Не упусти важное! – https://parsacode.com/%D8%B3%D8%A6%D9%88-%DA%A9%D9%84%D8%A7%D9%87-%D8%B3%DB%8C%D8%A7%D9%87-%D8%B3%D9%81%DB%8C%D8%AF-%D8%AA%D9%81%D8%A7%D9%88%D8%AA-%D8%A2%D9%86%D9%87%D8%A7
купить диплом медсестры купить диплом медсестры .
I am glad to talk with you and you give me great help
http://tadalmedspharmacy.com/# buy tadalafil 5mg
Buy sildenafil online usa: sildenafil – sildenafil
диплом техникума купить самара диплом техникума купить самара .
Эта обзорная заметка содержит ключевые моменты и факты по актуальным вопросам. Она поможет читателям быстро ориентироваться в теме и узнать о самых важных аспектах сегодня. Получите краткий курс по современной информации и оставайтесь в курсе событий!
Посмотреть всё – https://eazycomms.com/2017/09/30/three-ways-to-optimize-your-pricing-strategy
В этой статье представлен занимательный и актуальный контент, который заставит вас задуматься. Мы обсуждаем насущные вопросы и проблемы, а также освещаем истории, которые вдохновляют на действия и изменения. Узнайте, что стоит за событиями нашего времени!
Не пропусти важное – https://www.envisio360.com/hidden-benefits-of-3d-true-view-real-estate-walkthroughs
Эта публикация завернет вас в вихрь увлекательного контента, сбрасывая стереотипы и открывая двери к новым идеям. Каждый абзац станет для вас открытием, полным ярких примеров и впечатляющих достижений. Подготовьтесь быть вовлеченными и удивленными каждый раз, когда продолжите читать.
Детали по клику – http://profumia.net/prodotto/acqua-profumata-corpo-della-felicita-collistar
sildenafil purchase india sildenafil price australia or sildenafil 100 mg tablets coupon cheap rx sildenafil
http://yoshio.noizm.com/jump.php?u=http://pharmalibrefrance.com 20 mg sildenafil 30 tablets cost and https://bold-kw.com/user/ymbmpxfbmc/?um_action=edit sildenafil citrate 100 mg
sildenafil 2 buy sildenafil no prescription and sildenafil citrate tablets 100 mg buying sildenafil citrate online
В данной статье вы найдете комплексный подход к изучению насущных тем. Мы комбинируем теоретические сведения с практическими советами, чтобы читатель мог не только понять проблему, но и найти пути её решения.
Более того — здесь – http://bethanyfamilyinstitute.com/high-quality-da-dr-backlinks-high-tf-backlinks-high-traffic-guest-post-website-available-ahrefs-domain-rating-70-moz-domain-authority-2541
Статья знакомит с важнейшими моментами, которые сформировали наше общество. От великих изобретений до культурных переворотов — вы узнаете, как прошлое влияет на наше мышление, технологии и образ жизни.
Почему это важно? – https://www.absautoservisas.lt/naujienos/jusu-automobilio-paruosimas-ziemai
Эта информационная статья содержит полезные факты, советы и рекомендации, которые помогут вам быть в курсе последних тенденций и изменений в выбранной области. Материал составлен так, чтобы быть полезным и понятным каждому.
Посмотреть всё – https://exactarrow.com/5-reasons-to-consider-an-it-risk-assessment
sildenafil: Buy sildenafil – sildenafil
Эта информационная статья содержит полезные факты, советы и рекомендации, которые помогут вам быть в курсе последних тенденций и изменений в выбранной области. Материал составлен так, чтобы быть полезным и понятным каждому.
Эксклюзивная информация – https://vcelynastrechach.cz/en/career-we-are-looking-for-a-new-team-member
https://truevitalmeds.com/# true vital meds
купить диплом техникума казахстана купить диплом техникума казахстана .
Buy Tadalafil 20mg Buy Tadalafil 20mg Generic Cialis without a doctor prescription
Buy Tadalafil online: Generic Cialis without a doctor prescription – Generic Cialis without a doctor prescription
купить диплом фарм колледжа http://www.frei-diplom10.ru .
купить диплом в рыбинске http://rudik-diplom13.ru/ .
https://amoxdirectusa.com/# AmoxDirect USA
buy amoxicillin: buy amoxil – Purchase amoxicillin online
https://zithromedsonline.shop/# cheap zithromax
купить диплом в бору https://www.rudik-diplom10.ru .
купить диплом в кирове купить диплом в кирове .
1win kg скачать 1win kg скачать
buying cheap propecia without a prescription propecia tablets and order generic propecia no prescription cost propecia without rx
https://www.google.com/url?q=https://regrowrxonline.com cost propecia for sale and https://www.bsnconnect.co.uk/profile/ouwipdeakq/ propecia without dr prescription
buy propecia no prescription home and propecia buy cheap propecia without insurance
buy generic clomid no prescription Generic Clomid Clomid fertility
buy propecia: Best place to buy propecia – buy finasteride
generic zithromax ZithroMeds Online cheap zithromax
buy amoxicillin online no prescription amoxicillin medicine over the counter or amoxicillin 1000 mg capsule amoxicillin order online no prescription
http://alt1.toolbarqueries.google.co.id/url?q=https://amoxdirectusa.com buying amoxicillin in mexico and https://www.packadvisory.com/user/rjxbfyqlec/ amoxicillin 250 mg capsule
buy amoxicillin over the counter uk buy cheap amoxicillin online or amoxicillin 500mg for sale uk amoxicillin 500mg price canada
zithromax 500 mg lowest price online zithromax coupon or zithromax z-pak price without insurance buy zithromax
http://lupo.jp/gl7.php?g_url=bluepharmafrance.com buy generic zithromax no prescription and https://www.ipixels.com/profile/168627/jiqujslywj zithromax for sale usa
zithromax 500mg over the counter zithromax without prescription and zithromax 500 purchase zithromax z-pak
AmoxDirect USA: Amoxicillin 500mg buy online – Purchase amoxicillin online
can i order generic clomid tablets where can i buy cheap clomid without insurance and cost cheap clomid now can you buy cheap clomid without insurance
https://tvtropes.org/pmwiki/no_outbounds.php?o=https://clomicareusa.com can i purchase generic clomid without dr prescription or http://www.psicologiasaludable.es/user/vfdlymblql/ where can i get cheap clomid pill
clomid otc how to get clomid for sale or how to buy clomid without rx buying generic clomid without prescription
Best place to buy propecia Propecia prescription Propecia 1mg price
cost of generic propecia without rx cost of generic propecia without rx and cost of propecia without rx cost of cheap propecia pill
http://images.google.ps/url?q=https://regrowrxonline.com buy propecia without prescription or https://vintage-car.eu/user/jzwqidomfc/ cost of cheap propecia online
cost of propecia online buy generic propecia without a prescription or generic propecia no prescription get propecia without insurance
http://amoxdirectusa.com/# buy amoxicillin
В этом обзорном материале представлены увлекательные детали, которые находят отражение в различных аспектах жизни. Мы исследуем непонятные и интересные моменты, позволяя читателю увидеть картину целиком. Погрузитесь в мир знаний и удивительных открытий!
Ознакомьтесь с аналитикой – http://cultureregions-manouba.gov.tn/?attachment_id=8&cpage=1
Эта публикация дает возможность задействовать различные источники информации и представить их в удобной форме. Читатели смогут быстро найти нужные данные и получить ответы на интересующие их вопросы. Мы стремимся к четкости и доступности материала для всех!
Секреты успеха внутри – https://popcornradio.be/physiological-responses-to-rock-climbing-in-young-climbers
pin up poker uz pin up poker uz
RegrowRx Online: Best place to buy propecia – Propecia prescription
order cheap clomid pills where to get clomid pills Generic Clomid
If you are looking to post free classifieds in India online, we highly recommend Xpdea Classifieds. Xpdea is India’s leading free online ads posting site.
If you are looking to post free classifieds in India online, we highly recommend Xpdea Classifieds. Xpdea is India’s leading free online ads posting site.
We’re developing some community services to respond to this, and your blog is helpful.
https://clomicareusa.shop/# Buy Clomid online
If you are looking to post free classifieds in India online, we highly recommend Xpdea Classifieds. Xpdea is India’s leading free online ads posting site.
pin up litsenziya http://pinup5006.ru
where can i buy amoxicillin over the counter amoxicillin pharmacy price and generic amoxicillin cost generic amoxicillin cost
https://www.google.nl/url?sa=t&url=https://amoxdirectusa.com amoxicillin 500mg pill or http://la-maison-des-amis.com/user/udkmzbeihv/ buy amoxicillin online without prescription
amoxicillin 875 mg tablet amoxicillin for sale online and buy amoxicillin 500mg uk amoxicillin 500 mg brand name
Эта статья предлагает уникальную подборку занимательных фактов и необычных историй, которые вы, возможно, не знали. Мы постараемся вдохновить ваше воображение и разнообразить ваш кругозор, погружая вас в мир, полный интересных открытий. Читайте и открывайте для себя новое!
Более того — здесь – https://sportowagdynia.eu/index.php/2020/10/05/na-koniec-sezonu-zwyciestwo-w-tarnowie
В этом интересном тексте собраны обширные сведения, которые помогут вам понять различные аспекты обсуждаемой темы. Мы разбираем детали и факты, делая акцент на важности каждого элемента. Не упустите возможность расширить свои знания и взглянуть на мир по-новому!
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://freihardt.com/component/k2/item/1-if-you-can-dream-it-do-it?start=966070
В этой статье вы найдете уникальные исторические пересечения с научными открытиями. Каждый абзац — это шаг к пониманию того, как наука и события прошлого создают основу для технологического будущего.
Интересует подробная информация – http://bukimi.site/?p=46
Эта статья предлагает уникальную подборку занимательных фактов и необычных историй, которые вы, возможно, не знали. Мы постараемся вдохновить ваше воображение и разнообразить ваш кругозор, погружая вас в мир, полный интересных открытий. Читайте и открывайте для себя новое!
Получить больше информации – http://alchimie-des-montagnes.com/cropped-septembre-jpg
В этом информативном тексте представлены захватывающие события и факты, которые заставят вас задуматься. Мы обращаем внимание на важные моменты, которые часто остаются незамеченными, и предлагаем новые перспективы на привычные вещи. Подготовьтесь к тому, чтобы быть поглощенным увлекательными рассказами!
Узнать из первых рук – https://clickbot.site/savvy-vinyl-flooring-perth
Этот информационный обзор станет отличным путеводителем по актуальным темам, объединяющим важные факты и мнения экспертов. Мы исследуем ключевые идеи и представляем их в доступной форме для более глубокого понимания. Читайте, чтобы оставаться в курсе событий!
Открой скрытое – https://bulle-perpignan.fr/education-positive-et-communication-bienveillante
buy clomid can you get generic clomid Generic Clomid
купить медицинский диплом медсестры купить медицинский диплом медсестры .
We absolutely love your blog and find the majority of your post’s to be exactly what I’m looking for. Do you offer guest writers to write content to suit your needs? I wouldn’t mind composing a post or elaborating on a number of the subjects you write about here. Again, awesome weblog!
I cannot thank you more than enough for the blogposts on your website. I know you set a lot of time and energy into these and truly hope you know how deeply I appreciate it. I hope I’ll do a similar thing person sooner or later.
https://everlastrx.com/# Tadalafil tablets
Thanks , I’ve recently been searching for info about this topic for ages and yours is the best I have discovered so far. But, what concerning the bottom line? Are you certain concerning the source?
Prednisone tablets online USA: how to get Prednisone legally online – prednisone 20mg prices
online pokies gambling and social costs (Jeannie)
australia, free pokies in united states and best free slots united states,
or online casino not in uk
Эта обзорная заметка содержит ключевые моменты и факты по актуальным вопросам. Она поможет читателям быстро ориентироваться в теме и узнать о самых важных аспектах сегодня. Получите краткий курс по современной информации и оставайтесь в курсе событий!
Читать далее > – https://galernaresidencial.com/2019/10/18/advertising-relationships-vs-business-decisions
В этой статье представлен занимательный и актуальный контент, который заставит вас задуматься. Мы обсуждаем насущные вопросы и проблемы, а также освещаем истории, которые вдохновляют на действия и изменения. Узнайте, что стоит за событиями нашего времени!
Смотрите также… – http://devilcupido.com/post/34
Публикация предлагает уникальную подборку информации, которая будет интересна как специалистам, так и широкому кругу читателей. Здесь вы найдете ответы на часто задаваемые вопросы и полезные инсайты для дальнейшего применения.
Получить полную информацию – https://raymarketsound.com.br/selecting-a-matchmaking-company
Glad to be one of several visitors on this awful internet site : D.
I absolutely adore your site! You aggressive me as able-bodied as all the others actuality and your broiled PS is absolutely great!
prednisone canada purchase prednisone or india buy prednisone online drug prices prednisone
https://mclast.de/redirect/?url=http://pharmalibrefrance.com ordering prednisone and https://gikar.it/user/epjdcnyjol/ prednisone price south africa
prednisone brand name us prednisone online pharmacy and prednisone 5093 prednisone buy canada
1win daxil ol http://1win5001.com/
купить диплом слесаря купить диплом слесаря .
бонусы в 1 win бонусы в 1 win
диплом техникума с отличием купить диплом техникума с отличием купить .
https://neurocaredirect.shop/# gabapentin trade name australia
1win az virtual oyunlar 1win5001.com
https://neurocaredirect.shop/# order gabapentin discreetly
generic gabapentin pharmacy USA: order gabapentin discreetly – neuropathic pain relief treatment online
Эта публикация погружает вас в мир увлекательных фактов и удивительных открытий. Мы расскажем о ключевых событиях, которые изменили ход истории, и приоткроем завесу над научными достижениями, которые вдохновили миллионы. Узнайте, чему может научить нас прошлое и как применить эти знания в будущем.
Хочешь знать всё? – https://jose-de-san-martin.ch/logo-san-martin
В этой статье-обзоре мы соберем актуальную информацию и интересные факты, которые освещают важные темы. Читатели смогут ознакомиться с различными мнениями и подходами, что позволит им расширить кругозор и глубже понять обсуждаемые вопросы.
Что ещё? Расскажи всё! – https://citysupport.com/screen-shot-2019-04-03-at-10-31-02-am
В этой статье вы найдете уникальные исторические пересечения с научными открытиями. Каждый абзац — это шаг к пониманию того, как наука и события прошлого создают основу для технологического будущего.
Хочешь знать всё? – https://sariyermimar.com/sihhi-tesisat-isleri
Публикация предлагает уникальную подборку информации, которая будет интересна как специалистам, так и широкому кругу читателей. Здесь вы найдете ответы на часто задаваемые вопросы и полезные инсайты для дальнейшего применения.
Посмотреть всё – https://iartfivas.it/5-amazing-glitter-artists-to-find-at-a-festival
В этой статье вы найдете уникальные исторические пересечения с научными открытиями. Каждый абзац — это шаг к пониманию того, как наука и события прошлого создают основу для технологического будущего.
Смотрите также… – http://mrshade.com/events/under-the-skin
Статья знакомит с важнейшими моментами, которые сформировали наше общество. От великих изобретений до культурных переворотов — вы узнаете, как прошлое влияет на наше мышление, технологии и образ жизни.
Смотрите также – https://kiddycodes.com/post-format-gallery/2
Эта публикация погружает вас в мир увлекательных фактов и удивительных открытий. Мы расскажем о ключевых событиях, которые изменили ход истории, и приоткроем завесу над научными достижениями, которые вдохновили миллионы. Узнайте, чему может научить нас прошлое и как применить эти знания в будущем.
Наши рекомендации — тут – https://louisvilledailyjournal.com/regina-kings-son-ian-alexander-jr-has-died-by-suicide-he-cared-so-deeply-about-the-happiness-of-others
Эта информационная заметка содержит увлекательные сведения, которые могут вас удивить! Мы собрали интересные факты, которые сделают вашу жизнь ярче и полнее. Узнайте нечто новое о привычных аспектах повседневности и откройте для себя удивительный мир информации.
Что скрывают от вас? – https://pure-fm.de/qtvideo/blue-world
prednisone cream brand name how to get Prednisone legally online PredniWell Online
Эта публикация дает возможность задействовать различные источники информации и представить их в удобной форме. Читатели смогут быстро найти нужные данные и получить ответы на интересующие их вопросы. Мы стремимся к четкости и доступности материала для всех!
Уточнить детали – https://rankva.com/increase-da-dr-and-tf-with-refill-guarantee-1654
Эта публикация дает возможность задействовать различные источники информации и представить их в удобной форме. Читатели смогут быстро найти нужные данные и получить ответы на интересующие их вопросы. Мы стремимся к четкости и доступности материала для всех!
Детальнее – https://numberlina.com/5-interesting-facts-about-venus-for-kids
FDA-approved gabapentin alternative generic gabapentin pharmacy USA neuropathic pain relief treatment online
generic gabapentin pharmacy USA order gabapentin discreetly neuropathic pain relief treatment online
Публикация предлагает читателю не просто информацию, а инструменты для анализа и саморазвития. Мы стимулируем критическое мышление, предлагая различные точки зрения и призывая к самостоятельному поиску решений.
Ссылка на источник – https://marcrodenberg.biz/sevilla-drachenboot-em-6
Эта информационная заметка содержит увлекательные сведения, которые могут вас удивить! Мы собрали интересные факты, которые сделают вашу жизнь ярче и полнее. Узнайте нечто новое о привычных аспектах повседневности и откройте для себя удивительный мир информации.
Перейти к полной версии – https://www.marionjouclas.fr/teilhard-de-chardin-2
диплом колледжа купить с занесением в реестр диплом колледжа купить с занесением в реестр .
Эта информационная статья охватывает широкий спектр актуальных тем и вопросов. Мы стремимся осветить ключевые факты и события с ясностью и простотой, чтобы каждый читатель мог извлечь из нее полезные знания и полезные инсайты.
Детали по клику – https://drabhinavjaiswal.com/blog/2023/03/18/retrograde-intrarenal-surgery-rirs
buy tadalafil online without a prescription tadalafil online canada or canadian pharmacy generic tadalafil tadalafil soft gel capsule
http://atoo.su/redirect.php?url=http://pharmaexpressfrance.com tadalafil – generic or https://cv.devat.net/user/fgmqpszsjz/?um_action=edit tadalafil cheap
tadalafil 20mg online canada online pharmacy tadalafil 20mg and generic tadalafil united states tadalafil pills for sale
buchmacher us wahl
my blog post – euroleague basketball wett tipps
super bowl wetten deutschland
my page … wette schweiz frankreich
https://medivermonline.shop/# Stromectol ivermectin tablets for humans USA
generic ivermectin online pharmacy
1win az müsbət rəylər 1win az müsbət rəylər
Tadalafil tablets safe online pharmacy for ED pills Tadalafil tablets
Mediverm Online order Stromectol discreet shipping USA Stromectol ivermectin tablets for humans USA
1win qeydiyyat yoxlaması http://www.1win5002.com
cost of tadalafil in canada tadalafil soft or cheap tadalafil tablets tadalafil 20mg uk
https://www.google.com.na/url?q=https://everlastrx.com tadalafil capsules 20mg and http://www.88moli.top/home.php?mod=space&uid=775 tadalafil united states
cheap generic tadalafil tadalafil 2.5 mg tablets and buy tadalafil 100mg tadalafil cheap
https://medreliefuk.com/# cheap prednisolone in UK
https://medreliefuk.shop/# Prednisolone tablets UK online
кто нибудь работает медсестрой по купленному диплому http://www.frei-diplom14.ru .
Unquestionably believe that which you said. Your favorite reason seemed to be on the net the easiest thing to be aware of. I say to you, I certainly get annoyed while people consider worries that they plainly don’t know about. You managed to hit the nail on the head. Will probably be back to get more. Thanks
iffezheim pferderennen wetten
Take a look at my webpage – Besten Quoten Wettanbieter (Mcgatgjer.Oaknash.Ch)
Amoxicillin online UK: UK online antibiotic service – buy amoxicillin
buy viagra online viagra or order ED pills online UK Viagra online UK
https://clients1.google.gg/url?sa=t&source=web&rct=j&url=https://britpharmonline.com BritPharm Online and http://mbuild.store/user/agckzsfpzy/?um_action=edit viagra
viagra uk viagra and Viagra online UK BritPharm Online
generic Amoxicillin pharmacy UK amoxicillin uk or generic amoxicillin UK online antibiotic service
https://www.ferienhaus-privat.de/backend/externerlink/frameset.php?url=http://bluepharmafrance.com generic amoxicillin or https://www.ipixels.com/profile/170956/iwvwgxodee buy amoxicillin
buy penicillin alternative online amoxicillin uk and buy penicillin alternative online buy penicillin alternative online
buy prednisolone UK chemist Prednisolone delivery and Prednisolone tablets UK online UK chemist Prednisolone delivery
https://toolbarqueries.google.co.il/url?q=https://medreliefuk.com best UK online chemist for Prednisolone or https://virtualchemicalsales.ca/user/ixxcqpivjw/?um_action=edit best UK online chemist for Prednisolone
cheap prednisolone in UK buy prednisolone or buy corticosteroids without prescription UK UK chemist Prednisolone delivery
Prednisolone tablets UK online: cheap prednisolone in UK – cheap prednisolone in UK
купить диплом в сургуте купить диплом в сургуте .
купить диплом массажиста купить диплом массажиста .
купить рулонные шторы москва купить рулонные шторы москва .
Amoxicillin online UK: buy amoxicillin – Amoxicillin online UK
где купить диплом техникума старая пять плюс где купить диплом техникума старая пять плюс .
amoxicillin uk UK online antibiotic service or amoxicillin uk generic amoxicillin
https://www.google.vu/url?q=https://amoxicareonline.com generic Amoxicillin pharmacy UK or https://mantiseye.com/community/rvtejfdawe Amoxicillin online UK
UK online antibiotic service Amoxicillin online UK or amoxicillin uk buy penicillin alternative online
online pharmacy: Brit Meds Direct – order medication online legally in the UK
где можно купить диплом техникума где можно купить диплом техникума .
buy corticosteroids without prescription UK Prednisolone tablets UK online and order steroid medication safely online buy corticosteroids without prescription UK
http://maps.google.cf/url?q=http://pharmalibrefrance.com cheap prednisolone in UK or http://ragnarokneon.online/home.php?mod=space&uid=4478 cheap prednisolone in UK
order steroid medication safely online buy prednisolone and UK chemist Prednisolone delivery UK chemist Prednisolone delivery
тканевый натяжной потолок самара тканевый натяжной потолок самара .
order medication online legally in the UK: online pharmacy – order medication online legally in the UK
sportwetten online bonus Vergleich wetten
MedRelief UK: cheap prednisolone in UK – cheap prednisolone in UK
https://britpharmonline.shop/# British online pharmacy Viagra
order ED pills online UK: BritPharm Online – Viagra online UK
cheap prednisolone in UK buy prednisolone and UK chemist Prednisolone delivery MedRelief UK
https://www.google.fm/url?sa=t&url=https://medreliefuk.com best UK online chemist for Prednisolone and https://dan-kelley.com/user/simwtvduqe/?um_action=edit buy corticosteroids without prescription UK
buy corticosteroids without prescription UK cheap prednisolone in UK and order steroid medication safely online UK chemist Prednisolone delivery
cheap amoxicillin: cheap amoxicillin – UK online antibiotic service
buy viagra online: BritPharm Online – buy viagra
viagra uk: Viagra online UK – order ED pills online UK
neue wettanbieter
Look into my web blog; wetten vorhersage heute
диплом об окончании педагогического колледжа купить http://frei-diplom7.ru .
back und lay wetten anbieter
my blog; wett tipps heute telegram (Odell)
online pharmacy: UK online pharmacy without prescription – BritMeds Direct
buy corticosteroids without prescription UK Prednisolone tablets UK online or MedRelief UK buy corticosteroids without prescription UK
https://maps.google.gl/url?q=https://medreliefuk.com buy prednisolone and https://bbs.hy2001.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=668213 Prednisolone tablets UK online
Prednisolone tablets UK online best UK online chemist for Prednisolone and buy prednisolone best UK online chemist for Prednisolone
Amoxicillin online UK: generic amoxicillin – Amoxicillin online UK
MedRelief UK buy prednisolone buy prednisolone
аренда грузоподъемной техники аренда грузоподъемной техники .
sportwetten neukundenbonus ohne einzahlung
Stop by my blog post … value wetten strategie
http://tadalifepharmacy.com/# safe online pharmacy for Cialis
online pharmacy: buy amoxil – online pharmacy
https://medicosur.shop/# MedicoSur
sportwetten bonus ohne einzahlung österreich
Check out my web page … Bester Wimbledon wettanbieter
affordable Cialis with fast delivery: cialis – Cialis online USA
MedicoSur: MedicoSur – mexico medication
1win az casino 1win az casino
cialis trusted online pharmacy for ED meds cialis
Thanks for sharing the information. I found the information very useful. That’s a awesome story you posted. I will come back to scan some more.
vorhersagen sportwetten
Check out my web page; Das WettbüRo Gewinnt Immer
mexico pharmacy: MedicoSur – pharmacy mexico city
pharmacy in mexico the purple pharmacy mexico and farmacias mexicanas farmacia mexicana online
http://www.eloiseplease.com/?URL=bluepharmafrance.com meds from mexico or https://virtualchemicalsales.ca/user/remtozpsnc/?um_action=edit progreso mexico pharmacy online
п»їmexican pharmacy mexico pharmacy list and mexico prescriptions mexico online pharmacy
affordable online pharmacy for Americans: ZenCare Meds com – buy amoxil
tadalafil tablets without prescription affordable Cialis with fast delivery and affordable Cialis with fast delivery cialis
https://www.google.is/url?q=https://tadalifepharmacy.com affordable Cialis with fast delivery and http://foru1f40m.bunbun000.com/bbs/home.php?mod=space&uid=9702969 buy cialis online
Cialis online USA tadalafil tablets without prescription and tadalafil tablets without prescription affordable Cialis with fast delivery
https://medicosur.shop/# MedicoSur
Cialis online USA: tadalafil tablets without prescription – buy cialis online
Приветствую!
Здесь подробней:
Как заработать деньги в роблоксе Как заработать деньги в роблоксе http://m.shopinlincoln.com/redirect.aspx?url=http://zarabotok-na-igrah.ru/kak-zarabotat-dengi-v-roblokse/
Будь здоров!
sportwetten bonus code
My web page buchmacher lübeck – Lovie,
MedicoSur: mexico pharmacy – MedicoSur
мостбет бонус https://mostbet4182.ru/
http://tadalifepharmacy.com/# trusted online pharmacy for ED meds
mexican pharmacy pharmacy mexico tijuana pharmacy online
купить диплом машиниста купить диплом машиниста .
mexican pharmacy: mexican pharmacy – mexican pharmacy
Здарова!
Переходи:
Что такое осознанность Что такое осознанность https://maps.google.kz/url?q=https://tvoya-sila-vnutri.ru/chto-takoe-osoznannost/
До встречи!
купить диплом в ноябрьске купить диплом в ноябрьске .
https://potenzvital.shop/# potenzmittel cialis
купить диплом колледжа отзывы https://frei-diplom11.ru/ .
https://intimisante.com/# cialis prix
Intimi Santé: achat discret de Cialis 20mg – tadalafil sans ordonnance
cialis 20 mg achat en ligne: cialis generique – cialis prix
Tadalafil 20mg Bestellung online cialis generika Tadalafil 20mg Bestellung online
https://tadalafiloexpress.com/# cialis precio
где и как купить диплом колледжа https://frei-diplom10.ru/ .
https://tadalafiloexpress.com/# tadalafilo sin receta
comprar cialis: farmacia online fiable en España – tadalafilo sin receta
Potenz Vital Cialis Preisvergleich Deutschland cialis kaufen ohne rezept
Of course, what a great site and informative posts, I will add backlink – bookmark this site? Regards, Reader
There is perceptibly a lot to identify about this. I consider you made some good points in features also.
potenzmittel cialis: cialis generika – Potenz Vital
http://pilloleverdi.com/# cialis generico
сколько стоит проект перепланировки сколько стоит проект перепланировки .
https://pilloleverdi.shop/# cialis generico
PilloleVerdi: acquistare Cialis online Italia – compresse per disfunzione erettile
где купить диплом колледжа в смоленске https://frei-diplom9.ru/ .
москва купить диплом о высшем образовании с занесением в реестр москва купить диплом о высшем образовании с занесением в реестр .
https://intimisante.shop/# tadalafil sans ordonnance
cialis generico: dove comprare Cialis in Italia – cialis
pillole verdi: cialis – PilloleVerdi
Cialis generika günstig kaufen: Cialis generika günstig kaufen – tadalafil 20 mg preis
п»їshop apotheke gutschein online apotheke deutschland and gГјnstigste online apotheke medikamente rezeptfrei
http://www.dvdmania.ru/eshop/search.php?search_query=%3Ca+href%3Dhttps://potenzvital.com%2Fusers%2F1495316%2F%3E%EE%F2%E5%EB%E8+%CF%E5%F2%E5%F0%E1%F3%F0%E3%E0%3C%2Fa%3E+%97+%EC%FB%F1%EB%E8%2C+%ED%E0%E1%EB%FE%E4%E5%ED%E8%FF online apotheke deutschland and http://georgiantheatre.ge/user/himekwqcbn/ internet apotheke
online apotheke apotheke online or internet apotheke beste online-apotheke ohne rezept
cialis generika: internet apotheke – Tadalafil 20mg Bestellung online
Заказать диплом университета поспособствуем. Купить диплом техникума, колледжа в Омске – diplomybox.com/kupit-diplom-tekhnikuma-kolledzha-v-omske
купить диплом в астрахани купить диплом в астрахани .
http://pilloleverdi.com/# dove comprare Cialis in Italia
https://pilloleverdi.com/# tadalafil italiano approvato AIFA
top 10 seo reiting-seo-agentstv.ru .
https://intimisante.shop/# livraison rapide et confidentielle
internet apotheke online apotheke preisvergleich and online apotheke deutschland ohne rezept apotheke
http://performance-appraisals.org/appraisal-library/topframe2014.php?goto=https://potenzvital.shop apotheke online and https://www.soumoli.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=901496 beste online-apotheke ohne rezept
internet apotheke п»їshop apotheke gutschein or internet apotheke online apotheke rezept
Tadalafil 20mg Bestellung online PotenzVital Tadalafil 20mg Bestellung online
Cialis Preisvergleich Deutschland: PotenzVital – PotenzVital
online apotheke online apotheke rezept and medikamente rezeptfrei online apotheke deutschland
https://images.google.ee/url?sa=t&url=https://potenzvital.com eu apotheke ohne rezept and https://voicebyjosh.com/user/ehuhyiaggr/ medikament ohne rezept notfall
internet apotheke online apotheke gГјnstig and online apotheke deutschland online apotheke versandkostenfrei
Tips and tools you offer are so helpful to agencies in our community.
п»їfarmacia online espaГ±a farmacia online barata y fiable and farmacia online madrid farmacia online madrid
http://www.ixawiki.com/link.php?url=https://tadalafiloexpress.com farmacias online seguras and https://allchoicesmatter.org/user/fwzunwcxvt/?um_action=edit farmacia barata
farmacias online seguras en espaГ±a farmacia online barata or farmacia online barata y fiable farmacias online seguras en espaГ±a
tadalafil senza ricetta: farmacia online italiana Cialis – farmacia online italiana Cialis
https://pilloleverdi.shop/# PilloleVerdi
https://intimisante.shop/# acheter Cialis en ligne France
dove comprare Cialis in Italia cialis prezzo tadalafil italiano approvato AIFA
купить диплом юриста http://rudik-diplom2.ru/ – купить диплом юриста .
farmacia online italiana Cialis: acquistare Cialis online Italia – miglior prezzo Cialis originale
pharmacie en ligne france fiable п»їpharmacie en ligne france and trouver un mГ©dicament en pharmacie pharmacie en ligne france livraison belgique
http://images.google.ad/url?q=https://intimisante.com acheter mГ©dicament en ligne sans ordonnance and https://gikar.it/user/oitjthznzi/ acheter mГ©dicament en ligne sans ordonnance
pharmacie en ligne france fiable pharmacie en ligne france pas cher or Pharmacie en ligne livraison Europe Pharmacie Internationale en ligne
ED medication online UK: order Viagra discreetly – trusted British pharmacy
Sometimes, the sheer magnitude of the information seems overwhelming.
The clarity in your post is just nice and I can tell you are an expert in the subject matter.
Sildenafil Wirkung und Dosierung: Sildenafil ohne Rezept – Viagra Generika 100mg rezeptfrei
This is an awesome entry. Thank you very much for the supreme post provided! I was looking for this entry for a long time, but I wasn’t able to find a honest source.
Viagra kaufen Apotheke Preis Viagra online bestellen Schweiz or Billig Viagra bestellen ohne Rezept Viagra Generika kaufen Schweiz
https://www.google.im/url?q=https://medivertraut.shop Sildenafil 100mg online bestellen and https://kherkun.com/user/uvmxiotfvr/?um_action=edit Viagra Alternative rezeptfrei
Viagra kaufen Apotheke Preis Viagra Generika 100mg rezeptfrei or Viagra 100 mg ohne Rezept Viagra verschreibungspflichtig
Viagra online UK: order Viagra discreetly – affordable potency tablets
Viagra online UK affordable potency tablets and NHS Viagra cost alternatives trusted British pharmacy
https://www.google.com.et/url?q=https://britmedsuk.shop order Viagra discreetly or http://www.88moli.top/home.php?mod=space&uid=2608 Viagra online UK
Viagra online UK order Viagra discreetly and licensed online pharmacy UK Brit Meds Uk
How come you do not have your website viewable in mobile format? cant see anything in my Droid.
диплом колледжа купить в уфе диплом колледжа купить в уфе .
Good site! I truly love how it is easy on my eyes it is. I am wondering how I might be notified when a new post has been made. I’ve subscribed to your RSS which may do the trick? Have a great day!
Medi Uomo: trattamento ED online Italia – Viagra generico con pagamento sicuro
https://herengezondheid.shop/# online apotheek zonder recept
Heren Gezondheid Sildenafil zonder recept bestellen HerenGezondheid
MediUomo: Viagra generico con pagamento sicuro – Viagra generico con pagamento sicuro
köp receptfria potensmedel online billig Viagra Sverige Sildenafil utan recept
officiële Sildenafil webshop: Sildenafil zonder recept bestellen – online apotheek zonder recept
farmacia con entrega rápida: Confia Farmacia – comprar Sildenafilo sin receta
Simply wish to say the frankness in your article is surprising.
online apotheek zonder recept online apotheek zonder recept and HerenGezondheid officiële Sildenafil webshop
https://images.google.gm/url?sa=t&url=https://herengezondheid.com erectiepillen discreet bestellen or https://mantiseye.com/community/gphneamkqh HerenGezondheid
online apotheek zonder recept officiële Sildenafil webshop and online apotheek zonder recept betrouwbare online apotheek
https://confiafarmacia.com/# Confia Farmacia
http://confiafarmacia.com/# Viagra sin prescripcion medica
MediUomo Medi Uomo Viagra generico online Italia
internet Wetten quoten erklärung vergleich
Sildenafil utan recept mannens apotek and mannens apotek erektionspiller på nätet
https://www.google.co.bw/url?sa=t&url=https://mannensapotek.com MannensApotek or https://mantiseye.com/community/mwpiqxdfxr köpa Viagra online Sverige
Viagra utan läkarbesök erektionspiller på nätet or onlineapotek för män MannensApotek
farmacia con entrega rápida: farmacia online para hombres – Viagra sin prescripción médica
http://herengezondheid.com/# online apotheek zonder recept
farmaci per potenza maschile: comprare Sildenafil senza ricetta – farmaci per potenza maschile
I really like your writing style, excellent info , thanks for putting up : D.
farmaci per potenza maschile farmaci per potenza maschile or Viagra generico con pagamento sicuro trattamento ED online Italia
https://www.zyteq.com.au/?URL=https://mediuomo.com MediUomo and https://pramias.com/profile/ojjjdewalw/ Medi Uomo
comprare Sildenafil senza ricetta Medi Uomo and trattamento ED online Italia Viagra generico con pagamento sicuro
Viagra online kopen Nederland: online apotheek zonder recept – erectiepillen discreet bestellen
ordinare Viagra generico in modo sicuro: Viagra generico online Italia – pillole per disfunzione erettile
наркология анонимно narkologicheskaya-klinika-25.ru .
гидроизоляция цена москва http://www.gidroizolyaciya-cena-7.ru/ .
erektionspiller på nätet Viagra utan läkarbesök mannens apotek
comprare Sildenafil senza ricetta: pillole per disfunzione erettile – comprare Sildenafil senza ricetta
pillole per disfunzione erettile: Medi Uomo – ordinare Viagra generico in modo sicuro
гидроизоляция подвала снаружи цены http://www.gidroizolyaciya-podvala-cena.ru/ .
https://mannensapotek.com/# MannensApotek
beste wetter-app österreich
my web page – sportwetten paysafecard ohne oasis (Mira)
http://mannensapotek.com/# erektionspiller pa natet
http://vitalpharma24.com/# Kamagra 100mg bestellen
Sildenafil uten resept billig Viagra Norge nettapotek for menn
ereksjonspiller på nett viagra reseptfri and Sildenafil tabletter pris ereksjonspiller på nett
https://congnghebitcoin.com/proxy.php?link=https://mannvital.com generisk Viagra 50mg / 100mg or https://istinastroitelstva.xyz/user/jmofrdqiup/ Mann Vital
viagra reseptfri nettapotek for menn or billig Viagra Norge billig Viagra Norge
Potenzmittel ohne ärztliches Rezept: vitalpharma24 – Kamagra Oral Jelly Deutschland
seo специалист seo специалист .
Avanafil senza ricetta: acquistare Spedra online – Spedra
viagra reseptfri: billig Viagra Norge – Sildenafil uten resept
купить диплом в россоши купить диплом в россоши .
купить диплом техникума 1997 года купить диплом техникума 1997 года .
электронный карниз для штор электронный карниз для штор .
диплом купить колледжа http://frei-diplom9.ru .
Have you given any kind of thought at all with converting your current web-site into French? I know a couple of of translaters here that will would certainly help you do it for no cost if you want to get in touch with me personally.
seo продвижение рейтинг компаний seo продвижение рейтинг компаний .
куплю диплом младшей медсестры https://www.frei-diplom14.ru .
диплом об окончании техникума купить диплом об окончании техникума купить .
купить диплом в гуково купить диплом в гуково .
A friend of mine advised me to review this site. And yes. it has some useful pieces of info and I enjoyed reading it.
купить диплом маркетолога купить диплом маркетолога .
услуги сео http://reiting-kompanii-po-prodvizheniyu-sajtov.ru .
1xbet resmi giri? https://1xbet-giris-2.com/ .
сайт школы английского языка http://www.by-moscow777.ru/forum/topic/5493// .
Amazing article, cheers, I will bookmark you now.
можно ли купить диплом медсестры можно ли купить диплом медсестры .
сайт школы английского языка https://asbest.name/forum/31-14770-1 .
согласование перепланировки в нежилом помещении http://pereplanirovka-nezhilogo-pomeshcheniya16.ru .
согласование проекта перепланировки нежилого помещения pereplanirovka-nezhilogo-pomeshcheniya17.ru .
аренда экскаватора смена https://www.arenda-ekskavatora-pogruzchika-1.ru .
согласование перепланировки нежилого помещения в нежилом здании http://www.pereplanirovka-nezhilogo-pomeshcheniya18.ru/ .
ооо смартвэй http://sajt-smart-way.ru .
купить диплом бурильщика https://rudik-diplom9.ru .
диплом техникума торгового купить диплом техникума торгового купить .
купить диплом в озёрске http://www.rudik-diplom12.ru/ .
легальный диплом купить легальный диплом купить .
Spot on with this write-up, I truly believe this website requirements a lot much more consideration. I’ll probably be once more to read much much more, thanks for that info.
купить диплом маи http://www.r-diploma7.ru/ .
whoah this weblog is great i really like studying your articles. Stay up the great work! You already know, lots of persons are looking round for this information, you can aid them greatly.
купить диплом проводник пассажирского вагона купить диплом проводник пассажирского вагона .
Thank you for this great piece of content. Best Regards
I have to disagree with most of the comments here, but maybe I’m just a contrarian.
Our community leaders need to read this, and look at developing some of your recommendations.
наркологическая клиника город http://www.narkologicheskaya-klinika-28.ru .
экстренное вытрезвление http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-23.ru .
1xbwt giri? http://1xbet-17.com/ .
аттестат купить 9 класс аттестат купить 9 класс .
купить диплом николаев купить диплом николаев .
оценочный лист к диплому купить оценочный лист к диплому купить .
A wholly agreeable point of view, I think primarily based on my own experience with this that your points are well made, and your analysis on target.
электрокарниз недорого [url=www.elektrokarniz499.ru]www.elektrokarniz499.ru[/url] .
Thanks for another great post. Where else may anybody get that type of info in such an ideal way of writing? I have a presentation next week, and I’m at the search for such information.
электрокарнизы для штор купить в москве https://elektrokarniz499.ru/ .
торкретирование стен цена за м2 http://www.torkretirovanie-1.ru .
рулонные жалюзи с электроприводом рулонные жалюзи с электроприводом .
электрический карниз для штор купить http://www.elektrokarniz777.ru .
купить диплом ссср в спб купить диплом ссср в спб .
купить диплом в астане купить диплом в астане .
купил ташкентский диплом купил ташкентский диплом .
Simply wish to say the frankness in your article is surprising.
электрические рулонные шторы на окна электрические рулонные шторы на окна .
1xbet lite https://1xbet-giris-5.com .
поставка медоборудования http://medoborudovanie-postavka.ru/ .
вебинарная студия https://studiya-podkastov-spb4.ru .
рулонные шторы это https://www.avtomaticheskie-rulonnye-shtory1.ru .
1xbet mobi http://1xbet-giris-2.com .
Glad to be one of many visitants on this amazing site : D.
I’m impressed, I need to say. Really rarely do I encounter a blog that’s both educational and entertaining, and let me tell you, you have hit the nail on the head.
перепланировка офиса согласование https://pereplanirovka-nezhilogo-pomeshcheniya17.ru/ .
смартвэй официальный сайт смвэй http://www.sajt-smart-way.ru .
согласование перепланировки нежилого помещения в жилом доме http://www.pereplanirovka-nezhilogo-pomeshcheniya18.ru .
разрешение на перепланировку нежилого помещения не требуется https://pereplanirovka-nezhilogo-pomeshcheniya18.ru .
перепланировка нежилого помещения в нежилом здании законодательство https://pereplanirovka-nezhilogo-pomeshcheniya17.ru .
Please let us know when you plan to publish your book!
I want to see your book when it comes out.
have already been reading ur blog for a couple of days. really enjoy what you posted. btw i will be doing a report about this topic. do you happen to know any great websites or forums that I can find out more? thanks a lot.
Way cool! Some very valid points! I appreciate
you writing this write-up plus the rest of the site is very good.
Feel free to surf to my web-site; apuestas gratis con premios; Mercatdolot.cat,
Thanks pertaining to discussing the following superb written content on your site. I ran into it on the search engines. I will check back again if you publish extra aricles.
I dont think Ive caught all the angles of this subject the way youve pointed them out. Youre a true star, a rock star man. Youve got so much to say and know so much about the subject that I think you should just teach a class about it
newsky88 asia newsky-online.com .
I will share you blog with my sis.
There most be a solution for this problem, some people think there will be now solutions, but i think there wil be one.
Sometimes, the sheer magnitude of the information seems overwhelming.
That is really fascinating, You’re an excessively skilled blogger. I’ve joined your rss feed and look forward to in the hunt for extra of your magnificent post. Additionally, I’ve shared your website in my social networks!
Nevertheless, it’s all carried out with tongues rooted solidly in cheeks, and everybody has got nothing but absolutely love for their friendly neighborhood scapegoat. In reality, he is not merely a pushover. He is simply that extraordinary breed of person solid enough to take all that good natured ribbing for what it really is.
I am glad to be a visitor on this website!, regards for this rare information!
Woah this is just an insane amount of information, must of taken ages to compile so thanx so much for just sharing it with all of us. If your ever in any need of related information, just check out my own site!
сколько стоит согласование перепланировки квартиры сколько стоит согласование перепланировки квартиры .
Some truly nice stuff on this website , I like it.
Just wanna admit that this is extremely helpful, Thanks for taking your time to write this.
We absolutely love your blog and find the majority of your post’s to be exactly what I’m looking for. Do you offer guest writers to write content to suit your needs? I wouldn’t mind composing a post or elaborating on a number of the subjects you write about here. Again, awesome weblog!
hey thanks for the info. appreciate the good work
Lovely just what I was looking for. Thanks to the author for taking his clock time on this one.
ganabet app http://www.ganabet-online.com .
good day 4 play login good day 4 play login .
newsky login newsky-online.com .
1xbet 1xbet .
согласование перепланировки квартиры согласование перепланировки квартиры .
ganabet betting ganabet-online.com .
Thanks pertaining to discussing the following superb written content on your site. I ran into it on the search engines. I will check back again if you publish extra aricles.
jp99 slot online http://www.jp99-online.com/ .
сколько стоит оформление перепланировки сколько стоит оформление перепланировки .
beep casino http://beepbeepcasino-online.com/ .
surewin http://surewin-online.com .
jp 99 slot http://jp99-online.com/ .
стоимость согласования перепланировки стоимость согласования перепланировки .
1xbet mobil giri? http://www.1xbet-7.com .
перепланировка и согласование http://www.soglasovanie-pereplanirovki-1.ru/ .
casino beep beep beepbeepcasino-online.com .
nicee content keep writing
918kiss test id 918kiss test id .
кухни на заказ в санкт-петербурге http://www.kuhni-spb-10.ru/ .
goliath casino http://www.goliath-casino.com .
заказать кухню в спб по индивидуальному проекту http://www.kuhni-spb-12.ru/ .
топ seo компаний топ seo компаний .
xbet giri? 1xbet-14.com .
goliath casino online casino http://www.goliath-casino.com .
icebet casino no deposit http://icebet-online.com .
устный перевод +по скайпу teletype.in/@alexd78/D1bRUvZKB7G .
seo бесплатно seo бесплатно .
юридический перевод услуги юридический перевод услуги .
синхронный переводчик услуги dzen.ru/a/aRDuRn3LkCngCegS .
устный перевод заказать teletype.in/@alexd78/D1bRUvZKB7G .
юридический переводчик услуги юридический переводчик услуги .
seo курсы seo курсы .
Our local network of agencies has found your research so helpful.
battery aviator game apk battery aviator game apk .
aviator bonus game http://www.aviator-game-cash.com .
aviator bonus game http://aviator-game-best.com .
Took me time to read all the comments, but I really enjoyed the article. It proved to be Very helpful to me and I am sure to all the commenters here It’s always nice when you can not only be informed, but also entertained I’m sure you had fun writing this article.
it переводчик в москве telegra.ph/Oshibka-lokalizacii-pochemu-vash-IT-produkt-ne-ponimayut-za-granicej-11-09 .
I dont think Ive caught all the angles of this subject the way youve pointed them out. Youre a true star, a rock star man. Youve got so much to say and know so much about the subject that I think you should just teach a class about it
I do not even know how I ended up here, but I thought this post was good. I do not know who you are but certainly you are going to a famous blogger if you are not already 😉 Cheers!
You certainly deserve a round of applause for your post and more specifically, your blog in general. Very high quality material!
it переводчик заказать telegra.ph/Oshibka-lokalizacii-pochemu-vash-IT-produkt-ne-ponimayut-za-granicej-11-09 .
синхронный перевод в москве dzen.ru/a/aRDuRn3LkCngCegS .
You ma’am have a way with words. Thank you very much!
Amazing article, cheers, I will bookmark you now.
of course like your web-site however you have to check the spelling on several of your posts. Many of them are rife with spelling problems and I find it very troublesome to tell the reality then again I will surely come back again.
I like to spend my free time by scanning various internet resources. Today I came across your website and I found it has some of the most practical and helpful information I’ve seen.
I appreciate, cause I found just what I was looking for. You’ve ended my four day long hunt! God Bless you man. Have a great day. Bye -.
With this issue, it’s important to have someone like you with something to say that really matters.
I imagine so. Very good stuff, I agree totally.
Appreciation for taking the time to discuss this topic, I would love to discover more on this topic. If viable, as you gain expertise, would you object to updating the website with further information? It is tremendously beneficial for me.
you may have an ideal blog here! would you prefer to make some invite posts on my blog?
The post is absolutely fantastic! Lots of great info and inspiration, both of which we all need! Also like to admire the time and effort you put into your website and detailed info you offer! I will bookmark your website!
jet game money http://www.aviator-game-deposit.com/ .
airplane money game https://aviator-game-predict.com/ .
электрокарниз двухрядный https://prokarniz36.ru/ .
Beneficial Blog! I had been simply just debating that there are plenty of screwy results at this issue you now purely replaced my personal belief. Thank you an excellent write-up.
электрокарнизы для штор купить в москве http://elektrokarniz-dlya-shtor11.ru .
Your posts provide a clear, concise description of the issues.
электрокарниз недорого https://elektrokarniz-dlya-shtor499.ru/ .
электрические рулонные шторы купить электрические рулонные шторы купить .
I like your quality that you put into your writing . Please do continue with more like this.
купить диплом для первоклассника купить диплом для первоклассника .
Admiring the time and effort you put into your site and detailed info you offer!
I believe this web site has some really wonderful info for everyone : D.
диплом купить новгород великий диплом купить новгород великий .
рулонные шторы автоматические купить http://rulonnye-shtory-s-elektroprivodom177.ru .
купить диплом о высшем образовании заполненный купить диплом о высшем образовании заполненный .
диплом в братске купить диплом в братске купить .
Does it look like we’re in for a big ride here?
A colleague in the field told me to check out your website.
birxbet giri? http://1xbet-12.com .
Great blog right here! You seem to put a significant amount of material on the site rather quickly.
диплом мастера маникюра купить диплом мастера маникюра купить .
When we look at these issues, we know that they are the key ones for our time.
заказать курсовой проект заказать курсовой проект .
Glad to be one of several visitors on this awful internet site : D.
Simply wish to say the frankness in your article is surprising.
как доказать виновника залива ekspertiza-zaliva-kvartiry-2.ru .
download metatrader 5 download metatrader 5 .
mt5 mac download http://metatrader-5-downloads.com .
вызвать эксперта после залива http://www.ekspertiza-zaliva-kvartiry-2.ru .
meta trader 5 download https://metatrader-5-sync.com/ .
mt5 download mt5 download .
диплом настоящий купить диплом настоящий купить .
купить диплом санкт петербург купить диплом санкт петербург .
купить вкладыш с оценками к аттестату https://www.r-diploma19.ru .
купить курсовая работа http://www.kupit-kursovuyu-2.ru .
купить курсовая работа купить курсовая работа .
курсовые под заказ курсовые под заказ .
горизонтальные жалюзи с электроприводом горизонтальные жалюзи с электроприводом .
I believe you have remarked on some very interesting points , thankyou for the post.
автоматический карниз для штор http://www.elektrokarniz-dlya-shtor11.ru .
электронный карниз для штор электронный карниз для штор .
Some truly interesting info , well written and broadly user genial .
I think I will become a great follower.Just want to say your post is striking. The clarity in your post is simply striking and i can take for granted you are an expert on this subject.
наркологическая клиника москва http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-34.ru .
Great write-up, I am a big believer in placing comments on sites to inform the blog writers know that they’ve added something advantageous to the world wide web!
купить реальный диплом о высшем образовании купить реальный диплом о высшем образовании .
управление шторами с телефона управление шторами с телефона .
купить диплом екатеринбурга купить диплом екатеринбурга .
бамбуковые электрожалюзи https://prokarniz23.ru/ .
This information is very important and you’ll need to know this when you constructor your own photo voltaic panel.
диплом горного мастера купить диплом горного мастера купить .
I’ve thought about posting something about this before. Good job! Can I use part of your post in my blog?
I know this is not exactly on topic, but i have a blog using the blogengine platform as well and i’m having issues with my comments displaying. is there a setting i am forgetting? maybe you could help me out? thank you.
инъекционная гидроизоляция инъекционная гидроизоляция .
I like your blog. It sounds every informative.
шторы умный дом шторы умный дом .
технология инъекционной гидроизоляции технология инъекционной гидроизоляции .
услуги аренда экскаватора погрузчика услуги аренда экскаватора погрузчика .
автосервис vag спб автосервис vag спб .
технология инъекционной гидроизоляции технология инъекционной гидроизоляции .
гидроизоляция подвала влажность http://gidroizolyacziya-podvala-samara.ru .
купить аттестаты за 11 класс москва купить аттестаты за 11 класс москва .
купить диплом нархоза иркутск купить диплом нархоза иркутск .
you may have an ideal blog here! would you prefer to make some invite posts on my blog?
Simply want to say your article is as amazing. The clarity in your post is just great and i can assume you’re an expert on this subject. Fine with your permission allow me to grab your feed to keep up to date with forthcoming post. Thanks a million and please keep up the gratifying work.
Top 10 Nhà cái uy tín với dịch vụ chuyên nghiệp hàng đầu năm 2025 · 1. VIN88 · 2. ZO88 · 3. 86BET · 4. FO88 · 5. VIVU88 · 6. DOM88 · 7. SUNWIN · 8. GO88 …
Just a quick note to express my appreciation. Take care
Your posts provide a clear, concise description of the issues.
Simply wish to say the frankness in your article is surprising.
This is valuable stuff.In my opinion, if all website owners and bloggers developed their content they way you have, the internet will be a lot more useful than ever before.
It’s time for communities to rally.
Wow, amazing blog layout! How long have you been blogging for? you make blogging look easy. The overall look of your site is wonderful, let alone the content!
This will be helpful for my family.
We can see that we need to develop policies to deal with this trend.
I am very happy to look your post. Thanks a lot and i am taking a look ahead to touch you.
I just couldn’t leave your web site prior to suggesting that I really enjoyed the standard info an individual supply to your guests? Is going to be again continuously in order to inspect new posts
OK, you outline what is a big issue. But, can’t we develop more answers in the private sector?
This is really interesting, You’re a very skilled blogger. I have joined your feed and look forward to seeking more of your fantastic post. Also, I have shared your website in my social networks!
Hi my family member! I want to say that this article is amazing, great written and include approximately all important infos. I’d like to see more posts like this .
I really love this article.
Aw, this was a very nice post. In idea I wish to put in writing like this moreover taking time and precise effort to make an excellent article! I procrastinate alot and by no means seem to get something done.
Great post. Just a heads up – I am running Ubuntu with the beta of Firefox and the navigation of your blog is kind of broken for me.
Thank you a lot for sharing this with all folks you actually recognize what you’re speaking about! Bookmarked. Please additionally visit my site =). We can have a hyperlink trade contract among us!
Just a quick note to express my appreciation. Take care
Wish I’d thought of this. Am in the field, but I procrastinate alot and haven’t written as much as I’d like. Thanks.
Hello, I think your blog might be having browser compatibility issues. When I look at your website in Chrome, it looks fine but when opening in Internet Explorer, it has some overlapping. I just wanted to give you a quick heads up! Other than that, awesome blog!
I love your blog. It looks every informative.
Wish I’d thought of this. Am in the field, but I procrastinate alot and haven’t written as much as I’d like. Thanks.
Our communities really need to deal with this.
Our community leaders need to read this, and look at developing some of your recommendations.
you’re in reality a just right webmaster. The web site loading velocity is incredible. It sort of feels that you’re doing any distinctive trick. In addition, The contents are masterpiece. you’ve performed a great process on this topic!
Thank you a lot for sharing this with all folks you actually recognize what you’re speaking about! Bookmarked. Please additionally visit my site =). We can have a hyperlink trade contract among us!
The post is absolutely great! Lots of great info and inspiration, both of which we all need! Also like to admire the time and effort you put into your blog and detailed information you offer! I will bookmark your website!
Hi, do have a e-newsletter? In the event you don’t definately should get on that piece…this web site is pure gold!
I like your quality that you put into your writing . Please do continue with more like this.
I like the helpful information you provide in your articles. I’ll bookmark your blog and check again here frequently. I am quite certain I’ll learn many new stuff right here! Best of luck for the next!
I think I might disagree with some of your analysis. Are the figures solid?
This contained some excellent tips and tools. Great blog publication.
Like the way you’ve outlined things. Easy to follow. Not cluttered.
Excellent read, I just passed this onto a colleague who was doing a little research on that. And he actually bought me lunch because I found it for him smile So let me rephrase that.|
I am glad to be one of the visitors on this great site (:, appreciate it for putting up.
Peculiar this blog is totaly unrelated to what I was searching for – – interesting to see you’re well indexed in the search engines.
It’s clear you’re passionate about the issues.
Crypto Real Money Online Casino Australia Quiet Real Big Wins
My brother suggested I might like this websiteHe was once totally rightThis post truly made my dayYou can not imagine simply how a lot time I had spent for this information! Thanks!
I am glad to talk with you and you give me great help
I like meeting utile info, this post has got me even more info!
I do not even know how I ended up here, but I thought this post was good. I do not know who you are but certainly you are going to a famous blogger if you are not already 😉 Cheers!
Im impressed. I dont think Ive met anyone who knows as much about this subject as you do. Youre truly well informed and very intelligent. You wrote something that people could understand and made the subject intriguing for everyone. Really, great blog youve got here.
My brother suggested I might like this websiteHe was once totally rightThis post truly made my dayYou can not imagine simply how a lot time I had spent for this information! Thanks!
Thanks a bunch for sharing this with all people you really recognize what you are talking about! Bookmarked. Kindly also seek advice from my web site =). We can have a link alternate contract between us!
真实的人类第一季高清完整版,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
Hi, possibly i’m being a little off topic here, but I was browsing your site and it looks stimulating. I’m writing a blog and trying to make it look neat, but everytime I touch it I mess something up. Did you design the blog yourself?
Καθώς τα χρόνια περνούν, η βιομηχανία του τζόγου συνεχώς εξελίσσεται, προσφέροντας ολοένα και περισσότερες επιλογές διασκέδασης. Τα καζίνο δεν αποτελούν απλώς χώρους παιχνιδιού, αλλά και εμπειρίες γεμάτες ένταση, όπου οι παίκτες αναζητούν τόσο τη διασκέδαση όσο και την πιθανότητα μεγάλων κερδών. Ειδικά στην Ελλάδα, όπου το πάθος για τα τυχερά παιχνίδια είναι βαθιά ριζωμένο, η δημοτικότητα του διαδικτυακού τζόγου αυξάνεται σταθερά.
It’s time for communities to rally.
Unquestionably believe that which you said. Your favorite reason seemed to be on the net the easiest thing to be aware of. I say to you, I certainly get annoyed while people consider worries that they plainly don’t know about. You managed to hit the nail on the head. Will probably be back to get more. Thanks
Just what I needed to know thank you for this.
Just stumble upon your blog from from time to time. nice article
I have been curious about these trends, and you have really helped me. I have just told a few of my friends about this on FaceBook and they love your content just as much as I do.
I’ve been surfing online more than 3 hours today, yet I never found any interesting article like yours. It’s pretty worth enough for me. In my view, if all web owners and bloggers made good content as you did, the net will be much more useful than ever before.
Przejrzyj nasz aktualny ranking i przeczytaj szczegółowe opisy, aby dowiedzieć się, gdzie znaleźć najlepsze bonusy bez depozytu na luty 2026 roku. Wyjaśniamy, na czym polega bonus bez depozytu, jak otrzymać darmowe środki lub spiny, oraz które oferty są naprawdę warte uwagi! Serwisy hazardowe proponują atrakcyjne bonusy bez depozytu za rejestrację. Przeanalizowaliśmy rynek, sprawdzając, które polskie kasyno online oferuje najkorzystniejsze warunki dla nowych graczy. Prezentujemy najlepsze oferty bonusów bez depozytu na luty 2026, w tym propozycje od NV Casino oraz Roman Casino.
You have some helpful ideas! Maybe I should consider doing this by myself.
I saw a similar post on another website but the points were not as well articulated.
Simply wish to say the frankness in your article is surprising.
How long does it take you to write an article like this?
Europe Readr ist mehr als nur eine digitale Bibliothek – es ist ein kulturelles und demokratisches Projekt, das Literatur, Bildung und gesellschaftliches Engagement miteinander verbindet. Initiiert im Rahmen der slowenischen EU-Ratspräsidentschaft im Jahr 2021, bietet Europe Readr eine kostenlose, mehrsprachige Sammlung literarischer Werke aus ganz Europa, die aktuelle gesellschaftliche Themen aufgreifen und zur aktiven Auseinandersetzung anregen.
Woah this is just an insane amount of information, must of taken ages to compile so thanx so much for just sharing it with all of us. If your ever in any need of related information, just check out my own site!
Took me time to read all the comments, but I really enjoyed the article. It proved to be Very helpful to me and I am sure to all the commenters here It’s always nice when you can not only be informed, but also entertained I’m sure you had fun writing this article.
I am glad to be a visitor on this website!, regards for this rare information!
hey thanks for the info. appreciate the good work
Thanks , I’ve recently been searching for info about this topic for ages and yours is the best I have discovered so far. But, what concerning the bottom line? Are you certain concerning the source?
双轨2026 高清都市情感 海外华人专属平台 AI智能推荐高清
I want to see your book when it comes out.
Thank you for this great piece of content. Best Regards
You need to really control the comments listed here
I will share you blog with my sis.
What’s Happening i’m new to this, I stumbled upon this I’ve found It positively useful and it has aided me out loads. I hope to contribute & help other users like its aided me. Great job.
We’re developing a conference, and it looks like you would be a great speaker.
This website has lots of really useful stuff on it. Thanks for informing me.
I am glad to be one of the visitors on this great site (:, appreciate it for putting up.
I will share you blog with my sis.
Thanks for posting this. Looking for these resources 😀
Thanks , I’ve recently been searching for info about this topic for ages and yours is the best I have discovered so far. But, what concerning the bottom line? Are you certain concerning the source?
Thanks for sharing the information. I found the information very useful. That’s a awesome story you posted. I will come back to scan some more.
Our community leaders need to read this, and look at developing some of your recommendations.
Platforma Slottica to miejsce, w którym pasja do hazardu spotyka się z technologią najwyższej klasy. Od momentu uruchomienia w 2019 roku kierujemy się zasadami fair play, ochrony danych osobowych oraz ciągłego rozwoju oferty. Posiadamy ważną licencję międzynarodową Curaçao eGaming (nr 8048/JAZ2018-040), co potwierdza naszą wiarygodność i zgodność z regulacjami branżowymi. Tysiące aktywnych użytkowników z Polski wybiera nas każdego dnia.
Easily, the post is really the greatest on this laudable topic. I concur with your conclusions and will thirstily look forward to your future updates. Saying thank will not just be sufficient, for the wonderful c lucidity in your writing. I will instantly grab your rss feed to stay privy of any updates. Solid work and much success in your business enterprise!
I simply could not leave your site before suggesting that I actually enjoyed the usual info a person supply in your visitors? Is going to be back often to inspect new posts
Im impressed. I dont think Ive met anyone who knows as much about this subject as you do. Youre truly well informed and very intelligent. You wrote something that people could understand and made the subject intriguing for everyone. Really, great blog youve got here.
Hiya, I am really glad I have found this information. Nowadays bloggers publish only about gossip and net stuff and this is actually frustrating.
I came across an article that talks about the same thing but even more and when you go deeper.
I simply could not leave your site before suggesting that I actually enjoyed the usual info a person supply in your visitors? Is going to be back often to inspect new posts
I appreciate, cause I found just what I was looking for. You’ve ended my four day long hunt! God Bless you man. Have a great day. Bye -.
you may have an ideal blog here! would you prefer to make some invite posts on my blog?