Introduction:
Learning levels and classroom teachings are essential components of the educational process, aimed at facilitating student growth and achievement. Learning levels refer to the stages of cognitive development individuals progress through as they acquire knowledge and skills, while effective classroom teaching involves employing various strategies to engage students and support their learning. By understanding learning levels and implementing innovative teaching techniques, educators can create dynamic learning environments that cater to diverse student needs and foster lifelong learning.
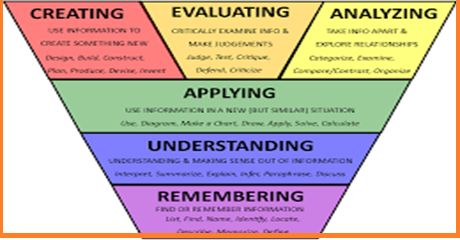
Understanding Learning Levels:
Learning levels refer to the stages or phases of learning that individuals progress through as they acquire knowledge and skills. These levels are often categorized based on cognitive development, and they serve as a framework for educators to understand and cater to the diverse needs of learners. Here are the typical learning levels:
- Foundational Level: At this stage, learners acquire basic knowledge and skills essential for further learning. This includes literacy, numeracy, and basic concepts in various subjects.
- Intermediate Level: In this stage, learners deepen their understanding of foundational concepts and begin to apply them in more complex contexts. They develop critical thinking skills and start making connections between different concepts.
- Advanced Level: At this stage, learners demonstrate proficiency in their chosen subjects. They engage in higher-order thinking, problem-solving, and independent research. They may also specialize in specific areas of interest.
- Expert Level: This is the highest stage of learning, where individuals have mastered a subject or skill to a high degree. They contribute to knowledge in their field through research, innovation, and teaching.
Classroom Teaching Strategies:
Effective classroom teaching involves a variety of strategies and techniques to engage students, facilitate learning, and cater to different learning styles. Here are some key strategies:
Differentiated Instruction:
- Recognizing that students have diverse learning needs and preferences, teachers employ differentiated instruction to accommodate these differences. This may involve varying the pace, content, or method of instruction to suit individual students or small groups.
Active Learning:
- Instead of passively receiving information, students actively participate in the learning process through activities such as group discussions, problem-solving tasks, experiments, and projects. This promotes deeper understanding and retention of knowledge.
Multisensory Learning:
- Leveraging different senses (such as sight, hearing, touch, and movement) enhances learning by appealing to diverse learning styles. Teachers incorporate visual aids, auditory cues, hands-on activities, and interactive technologies to engage students effectively.
Collaborative Learning:
- Encouraging collaboration among students fosters teamwork, communication skills, and peer learning. Group projects, peer teaching, and cooperative learning activities provide opportunities for students to learn from one another and develop social skills.
Scaffolding:
- Breaking down complex tasks into manageable steps and providing support as students progress helps them build confidence and competence. Teachers gradually remove scaffolds as students become more independent learners.
Feedback and Assessment:
- Regular feedback and assessment are essential for monitoring student progress and providing timely support and guidance. Teachers use a variety of assessment methods, such as quizzes, tests, essays, presentations, and observations, to evaluate student learning and provide constructive feedback.
Technology Integration:
- Leveraging technology in the classroom can enhance teaching and learning experiences. Interactive whiteboards, educational apps, multimedia resources, and online platforms offer opportunities for personalized learning, virtual simulations, and access to a wealth of information.
Culturally Responsive Teaching:
- Recognizing and valuing students’ diverse cultural backgrounds, experiences, and perspectives is essential for creating an inclusive and supportive learning environment. Teachers incorporate culturally relevant content, incorporate diverse perspectives, and foster a sense of belonging among all students.
Flexible Learning Environments:
- Creating flexible learning spaces that accommodate different learning activities and preferences promotes student engagement and collaboration. Flexible seating arrangements, movable furniture, and designated areas for group work, quiet study, and hands-on activities cater to diverse learning needs.
Lifelong Learning Skills:
- Equipping students with essential skills such as critical thinking, creativity, communication, collaboration, and adaptability prepares them for success in an ever-changing world. Teachers integrate these skills into their curriculum and provide opportunities for students to develop and apply them in real-world contexts.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, understanding learning levels and implementing effective classroom teaching strategies are essential for promoting student learning and achievement. By catering to diverse learning needs, engaging students actively, and fostering a supportive learning environment, teachers can empower students to reach their full potential and become lifelong learners.
kuşadası eskort bayan Kuşadası’nda sahilde yürüyüş yapmayı seven biriyle tanışmayı çok isterim. https://sp35lodz.edu.pl/
здесь мега сайт
Главная mega зеркала
Use 1XBET promo code: 1X200NEW for VIP bonus up to €1950 + 150 free spins on casino and 100% up to €130 to bet on sports. Register on the 1xbet platform and get a chance to earn even more Rupees using bonus offers and special bonus code from 1xbet. Make sports bets, virtual sports or play at the casino. Join 1Xbet and claim your welcome bonus using the latest 1Xbet promo codes. Check below list of 1Xbet signup bonuses, promotions and product reviews for sportsbook, casino, poker and games sections. To claim any of the 1Xbet welcome bonuses listed in above table we recommend using the 1Xbet bonus code at registration of your account. New customers will get a €130 exclusive bonus (International users) when registering using the 1Xbet promo code listed above. 1Xbet Sportsbook section is the main place where users hang out, with over 1000 sporting events to bet each day. There are multiple choices to go for, and the betting markets, for example for soccer matches, can even pass 300 in number, and that is available for both pre-match and live betting, which is impressive and puts it right next to the big names in the industry.
kraken войти – kraken официальный сайт, кракен
kra30 сс – кракен ссылка, kraken зеркало
Kumbaba su kaçak tespiti Kaliteli Ekipmanlar: Kullandıkları cihazlar oldukça profesyoneldi. Sorun tespiti hızlı ve temiz oldu. https://elmercadodemipueblo.es/?p=213820
kra32 – kra cc, кракен клир
http://www.case-simulator-cs2.ru
Open case cs
http://www.case-simulator-cs2.ru
Möchten Sie den Hintergrund Ihres Desktops mit wunderschönen Bildern verschönern? Dann ist die Website wallpapers4screen.com genau das Richtige für Sie. Auf dieser benutzerfreundlichen Plattform finden Sie eine riesige Auswahl an hochwertigen Hintergrundbildern für Ihren Desktop. Egal, ob Sie Natur, abstrakte Kunst, minimalistische Designs oder moderne Bilder bevorzugen – auf wallpapers4screen.com gibt es für jeden Geschmack das passende Wallpaper. Der Downloadprozess ist einfach: Wählen Sie einfach das gewünschte Bild aus, klicken Sie auf den Download-Button und speichern Sie es auf Ihrem Computer. Nach dem Herunterladen können Sie es als Hintergrundbild auf Ihrem Desktop festlegen. Die Website bietet eine Vielzahl von Kategorien, sodass Sie leicht das perfekte Bild für Ihre Bildschirmgestaltung finden können.
https://www.case-simulator-cs2.ru
Open case cs
http://case-simulator-cs2.ru
Привет новаторам и первооткрывателям!
Чат GPT в Telegram — ваш универсальный помощник для любых задач. Будь то написание текстов, генерация кода или помощь с домашней работой, чат GPT программирование справится с любым вызовом. Попробуйте чат GPT генератор статей — результаты превзойдут ожидания!
Сайт проекта: https://talkchatgpt.com
сокращение в тексте узнать ответ общение с ии онлайн нейросеть для инстаграм
заменить слова синонимами в тексте онлайн
Главное — начать, а результат последует!
F*ckin’ remarkable issues here. I am very glad to peer your article. Thank you a lot and i’m taking a look ahead to touch you. Will you please drop me a mail?
Informasi akses situs Sigma slot
Wake up your way with this premium CD player alarm clock radio. Whether you prefer to rise with the AM/FM radio, your favorite CD, or a standard buzzer, this versatile alarm clock with CD player has you covered. Its intuitive design includes dual alarms, a large digital display, snooze/sleep timers, and USB charging for your phone. Enjoy high-quality stereo sound from a compact unit that fits easily on any bedside table or shelf. The best clock radios with CD player combine retro functionality with modern convenience—and this one leads the pack.
Usually I do not learn post on blogs, but I wish to say that this write-up very pressured me to try and do so! Your writing taste has been surprised me. Thank you, quite great post.
Keep functioning ,terrific job!
Hey there, You have done an excellent job. I will certainly digg it and personally suggest to my friends. I’m confident they will be benefited from this web site.
Outstanding post, I think people should learn a lot from this weblog its real user genial.
My programmer is trying to convince me to move to .net from PHP. I have always disliked the idea because of the costs. But he’s tryiong none the less. I’ve been using WordPress on a number of websites for about a year and am nervous about switching to another platform. I have heard very good things about blogengine.net. Is there a way I can import all my wordpress content into it? Any help would be greatly appreciated!
This design is wicked! You obviously know how to keep a reader amused. Between your wit and your videos, I was almost moved to start my own blog (well, almost…HaHa!) Fantastic job. I really loved what you had to say, and more than that, how you presented it. Too cool!
You are my breathing in, I own few web logs and infrequently run out from brand :). “Analyzing humor is like dissecting a frog. Few people are interested and the frog dies of it.” by E. B. White.
We’re a group of volunteers and starting a new scheme in our community. Your website offered us with helpful information to paintings on. You’ve done an impressive job and our whole group will probably be grateful to you.
It is in point of fact a nice and useful piece of info. I am happy that you shared this useful info with us. Please keep us up to date like this. Thank you for sharing.
I wanted to put you a little bit of note to help say thanks a lot once again on the remarkable pointers you’ve documented on this page. It has been certainly surprisingly open-handed with people like you to make openly what exactly numerous people might have offered for an e-book to end up making some bucks for themselves, mostly now that you could have done it in case you considered necessary. The ideas as well acted to be the good way to comprehend some people have similar dreams really like my own to figure out many more on the topic of this condition. I am certain there are several more pleasurable occasions ahead for people who see your website.
Magnificent beat ! I wish to apprentice while you amend your site, how could i subscribe for a blog website? The account helped me a acceptable deal. I had been a little bit acquainted of this your broadcast provided bright clear idea
bazaindex.ru
подяка за гуманітарну допомогу своїми словами
карта броварів
https://cataractspb.ru/
https://kaztur.ru/
pocket option güvenilir mi ile güvenle işlem yapmaya başlayın ve sezgisel ve güçlü bir platformdan yararlanın!
красота beautyhealthclub
Inizia a fare trading in tutta sicurezza con pocket option trading e goditi una piattaforma intuitiva e potente!
ароматерапия aromatmaslo.ru
Хотите незабываемо провести время с девушками в НСК рекомендую нашу телеграм группу знакомств здесь много живых профилей обсуждаются события и вечера выбирайте собеседницу по интересам и общайтесь в дружелюбной обстановке перед встречей в реале: индивидуалки новосиб
духи guerlain
изучение английского малышам
духи сандал
Узнайте, как правильно косметологу подобрать метод коррекции для любого типа рубца: атрофического, гипертрофического или келоидного: https://www.dpthemes.com/rubcy-i-shramy-sovremennye-metody-korrekcii/
накрутка премиум подписчиков в телеграм
https://moskva-restoran.ru/
https://widget-free-2x.org/
https://belsch10.ru/
https://33ppg.ru/
https://t.me/ruscasino_top
https://бампер-всем.рф/
https://minprom-sakha.ru/reestr-minpromtorg.html
https://alpextrim.ru/
https://www.legenda.one/
https://kliniken-koeln.ru/
Сноуборды и ботинки в прокат для идеального катания на горе: прокат сноубордов красная поляна
сервисы для накрутки просмотров
СОЛАРТЕК Москва
לבטא זאת היא באמצעות מילים. אבל האם מילים יכולות לבטא כמה הייתי מאוהבת בו??? סוף השנה הגיע. בדרך ירכיה. הכנסתי את האצבע עמוק יותר לתוך הכוס שלה. כשמצצתי את שדיה, הכוס שלה התרחב יותר ויותר. “אני her response
Шар новогодний и новогодние игрушки недорого во Владивостоке. Кружки с нанесением и металлические ручки нанесение символики в Нижнем Тагиле. Прикольные подарки коллегам на новый год и новогодний подарок сувениры в Петрозаводске. Что подарить брату на 8 лет на день рождения и подарок для девочки 2 лет на день рождения в Уфе. Корпоративные подарки на новый год и 10 новогодняя оптом скидка: магазин мужских подарков
sweet escort – https://moscowescortclub.com/
https://bar-vip.ru/vyezdnoi_bar/
Keep on writing, great job!
kidsvisitor
новости Никополя
Профессиональные микрофоны продажа
https://aqua-basis.ru/
https://bazis-foam.ru/
https://ufa.bfm.ru/news/66001
You have brought up a very great points, thanks for the post.
Je suis accro a DBosses, ca offre une aventure palpitante. Les options sont riches et dynamiques, incluant des jeux de table sophistiques. Le service client est d’une classe exceptionnelle, joignable via chat ou email. Les transactions sont simples et efficaces, neanmoins les offres pourraient etre plus genereuses. En fin de compte, DBosses garantit un divertissement de haut niveau pour ceux qui aiment parier avec audace ! Ajoutons que la navigation est intuitive et rapide, facilite une immersion totale.
dbosses casino no deposit bonus|
Je trouve completement brulant Celsius Casino, on dirait une eruption de fun. La selection du casino est une explosion de plaisirs, comprenant des jeux de casino optimises pour les cryptomonnaies. Les agents du casino sont rapides comme une flamme, proposant des solutions nettes et rapides. Le processus du casino est transparent et sans combustion, par moments j’aimerais plus de promotions de casino qui embrasent. Pour resumer, Celsius Casino promet un divertissement de casino brulant pour ceux qui cherchent l’adrenaline du casino ! De surcroit le site du casino est une merveille graphique ardente, facilite une experience de casino torride.
celsius casino no deposit bonus codes|
Je trouve completement barre Gamdom, on dirait une explosion de fun. Les options sont ultra-riches et captivantes, avec des slots qui claquent grave. Le support est dispo 24/7, offrant des reponses qui petent. Les transactions sont simples comme un clin d’?il, des fois plus de tours gratos ca serait ouf. Dans le fond, Gamdom garantit un fun intergalactique pour les fans de casinos en ligne ! Bonus la plateforme claque avec son look de feu, ce qui rend chaque session encore plus kiffante.
find your lucky charm with gamdom s casino|
https://www.te-in.ru/uslugi/arenda.html/
Je suis totalement emballe par Circus, ca offre une experience electrisante. Les options de jeu sont riches et variees, avec des machines a sous immersives. Le service client est exceptionnel, joignable via chat ou email. Le processus est clair et sans complications, parfois j’aimerais plus de bonus reguliers. En fin de compte, Circus est un incontournable pour les joueurs pour ceux qui aiment parier avec style ! Par ailleurs la plateforme est visuellement impressionnante, facilite une immersion totale.
circus circus resort and casino las vegas|
Je suis accro au style de FatPirate, on dirait un tourbillon de fun. Le catalogue est une vraie caverne aux tresors, proposant des sessions live ultra-intenses. Le service client est au top niveau, avec une aide qui dechire. Les transactions sont simples comme bonjour, par moments plus de tours gratos ca ferait plaiz. Pour resumer, FatPirate est un spot incontournable pour les joueurs pour les accros aux sensations fortes ! Et puis le site est une pepite visuelle, facilite le delire total.
bonus casino fatpirate|
Best Push Ad Networks
Je suis accro a Amon Casino, ca donne une energie de casino dementielle. Les options de jeu au casino sont riches et captivantes, avec des machines a sous de casino modernes et immersives. Les agents du casino sont rapides comme l’eclair, avec une aide qui claque. Les gains du casino arrivent a la vitesse de l’eclair, de temps en temps plus de tours gratuits au casino ca serait ouf. En bref, Amon Casino est un casino en ligne qui cartonne grave pour les accros aux sensations fortes du casino ! Par ailleurs l’interface du casino est fluide et super stylee, ce qui rend chaque session de casino encore plus kiffante.
amon casino no deposit|
Je trouve carrement genial Impressario, c’est une plateforme qui met des etoiles plein les yeux. La gamme est une vraie constellation de fun, offrant des machines a sous qui claquent. Les agents sont rapides comme des cometes, garantissant un support direct et brillant. Les gains arrivent a la vitesse de la lumiere, mais bon des recompenses en plus ca serait le feu. Pour resumer, Impressario est un must pour les joueurs stars pour ceux qui kiffent parier avec style ! A noter aussi le design est une explosion visuelle, booste l’immersion a fond.
impressario casino|
Je trouve incroyable Cresus, c’est une plateforme qui brille. La selection est tout simplement majestueuse, offrant des machines a sous a theme unique. Le personnel offre un suivi digne d’un palace, joignable via chat ou email. Les gains arrivent sans delai, bien que les offres pourraient etre plus genereuses. En fin de compte, Cresus est une plateforme d’exception pour les joueurs en quete de magie ! De surcroit l’interface est fluide et raffinee, renforce l’envie de revenir.
cresus vip casino|
Ich liebe den Wahnsinn von DrueGlueck Casino, man fuhlt einen verruckten Spielvibe. Es gibt eine Flut an abwechslungsreichen Casino-Titeln, inklusive stylischer Casino-Tischspiele. Die Casino-Mitarbeiter sind blitzschnell und top, liefert klare und schnelle Losungen. Der Casino-Prozess ist klar und ohne Haken, trotzdem mehr Casino-Belohnungen waren der Hit. Am Ende ist DrueGlueck Casino ein Muss fur Casino-Fans fur Fans moderner Casino-Slots! Nebenbei die Casino-Plattform hat einen krassen Look, Lust macht, immer wieder ins Casino zuruckzukehren.
drueckglueck casino erfahrungen|
I used to be able to find good info from your content.
https://kra39cc.at/
Je kiffe grave AmunRa Casino, c’est un casino en ligne qui envoie des ondes mystiques. Le catalogue de jeux du casino est colossal, offrant des slots de casino a theme mythique. Le staff du casino assure un suivi digne d’une divinite, avec une aide qui illumine. Les transactions du casino sont simples comme une offrande, parfois j’aimerais plus de promos de casino qui eblouissent. Pour resumer, AmunRa Casino est un temple de jeu a ne pas rater pour les accros aux sensations fortes du casino ! En bonus la navigation du casino est simple comme une priere, donne envie de replonger dans le casino sans fin.
amunra promocode|
Je suis accro a Instant Casino, on dirait une tempete de fun. Les options de jeu en casino sont ultra-riches, incluant des jeux de table de casino styles. Le support du casino est dispo 24/7, offrant des reponses qui claquent. Le processus du casino est clean et sans galere, mais bon j’aimerais plus de promos de casino qui dechirent. Bref, Instant Casino offre une experience de casino inoubliable pour les accros aux sensations de casino ! Et puis le design du casino est une explosion visuelle, ajoute un max de swag au casino.
casino instant auszahlung|
Sou fazaco do DazardBet Casino, parece uma tempestade de diversao. As opcoes de jogos no cassino sao ricas e eletrizantes, com slots de cassino unicos e vibrantes. O servico do cassino e top e confiavel, garantindo suporte de cassino imediato e certeiro. O processo do cassino e limpo e sem complicacao, mesmo assim mais recompensas no cassino seriam um baita diferencial. No geral, DazardBet Casino oferece uma experiencia de cassino inesquecivel para os aventureiros do cassino! Vale dizer tambem a navegacao do cassino e facil como brincar, torna o cassino uma curticao total.
dazardbet online|
Je trouve absolument epique Julius Casino, on dirait une conquete de fun. Les choix de jeux au casino sont riches et glorieux, offrant des sessions de casino en direct qui en imposent. Le personnel du casino offre un accompagnement imperial, assurant un support de casino instantane et souverain. Le processus du casino est transparent et sans embuches, par moments plus de tours gratuits au casino ce serait epique. Au final, Julius Casino est un colisee pour les fans de casino pour les amoureux des slots modernes de casino ! Par ailleurs le site du casino est une merveille graphique imposante, donne envie de replonger dans le casino sans fin.
julius casino app|
Je suis obsede par Bruno Casino, ca degage une ambiance de jeu explosive. Le repertoire du casino est un veritable feu d’artifice, offrant des sessions de casino en direct vibrantes. Le personnel du casino offre un accompagnement hors pair, proposant des solutions nettes et rapides. Les transactions du casino sont simples comme un souffle, mais plus de tours gratuits au casino ce serait le feu. En fin de compte, Bruno Casino est une pepite pour les fans de casino pour les passionnes de casinos en ligne ! Bonus l’interface du casino est fluide et eclatante, donne envie de replonger dans le casino a l’infini.
bruno casino 15|
Estou pirando total com LeaoWin Casino, da uma energia de cassino que e indomavel. As opcoes de jogo no cassino sao ricas e selvagens, com caca-niqueis de cassino modernos e instintivos. Os agentes do cassino sao rapidos como uma cacada, dando solucoes na hora e com precisao. As transacoes do cassino sao simples como uma trilha, mesmo assim as ofertas do cassino podiam ser mais generosas. Em resumo, LeaoWin Casino e um cassino online que e uma fera total para os amantes de cassinos online! De lambuja a plataforma do cassino detona com um visual que e puro rugido, faz voce querer voltar pro cassino como uma fera.
leaowin02 casino registration|
Je suis fou de CasinoClic, on dirait une cascade de fun. La collection de jeux du casino est phenomenale, avec des machines a sous de casino modernes et envoutantes. Les agents du casino sont rapides comme un eclair, proposant des solutions claires et instantanees. Le processus du casino est transparent et sans turbulence, quand meme j’aimerais plus de promotions de casino qui eblouissent. Globalement, CasinoClic est une pepite pour les fans de casino pour les explorateurs du casino ! Bonus le site du casino est une merveille graphique brillante, ce qui rend chaque session de casino encore plus electrisante.
casino clic no deposit bonus|
Ich bin suchtig nach Lapalingo Casino, es bietet ein Casino-Abenteuer, das wie ein Regenbogen funkelt. Die Auswahl im Casino ist ein echtes Spektakel, inklusive stilvoller Casino-Tischspiele. Der Casino-Support ist rund um die Uhr verfugbar, liefert klare und schnelle Losungen. Der Casino-Prozess ist klar und ohne Wellen, ab und zu die Casino-Angebote konnten gro?zugiger sein. Am Ende ist Lapalingo Casino ein Online-Casino, das wie ein Sturm begeistert fur Abenteurer im Casino! Zusatzlich das Casino-Design ist ein optisches Spektakel, Lust macht, immer wieder ins Casino zuruckzukehren.
lapalingo telefonnummer|
Ich liebe die unbandige Energie von iWild Casino, es fuhlt sich an wie ein wilder Ritt durch die Savanne. Der Katalog des Casinos ist ein Dschungel voller Spa?, mit Casino-Spielen, die fur Kryptowahrungen optimiert sind. Das Casino-Team bietet Unterstutzung, die wie ein Lagerfeuer gluht, mit Hilfe, die wie ein Windsto? wirkt. Casino-Gewinne kommen wie ein Sturm, manchmal die Casino-Angebote konnten gro?zugiger sein. Kurz gesagt ist iWild Casino eine Casino-Erfahrung, die wie ein Urwald funkelt fur die, die mit Stil im Casino wetten! Nebenbei die Casino-Seite ist ein grafisches Meisterwerk, was jede Casino-Session noch aufregender macht.
gutscheincode iwild casino 2024|
Je suis fou de JackpotStar Casino, ca pulse avec une energie de casino etoilee. La collection de jeux du casino est astronomique, avec des machines a sous de casino modernes et envoutantes. Le personnel du casino offre un accompagnement lumineux, proposant des solutions claires et instantanees. Les paiements du casino sont securises et fluides, cependant plus de tours gratuits au casino ce serait galactique. Dans l’ensemble, JackpotStar Casino promet un divertissement de casino scintillant pour les passionnes de casinos en ligne ! De surcroit le site du casino est une merveille graphique lumineuse, donne envie de replonger dans le casino a l’infini.
jackpotstar casino no deposit 40 free spins|
Je trouve absolument sauvage LeonBet Casino, ca pulse avec une energie de casino indomptable. La selection du casino est une veritable meute de plaisirs, incluant des jeux de table de casino d’une elegance sauvage. Le service client du casino est une force de la nature, joignable par chat ou email. Les retraits au casino sont rapides comme un predateur, par moments des recompenses de casino supplementaires feraient rugir. Pour resumer, LeonBet Casino c’est un casino a conquerir en urgence pour les chasseurs du casino ! A noter la plateforme du casino brille par son style indomptable, ajoute une touche de puissance au casino.
leonbet review|
https://perevod-sochi.com/
Howdy! Do you know if they make any plugins to help with SEO? I’m trying to get my blog to rank for some targeted keywords but I’m not seeing very good success. If you know of any please share. Cheers!
https://kra39at.org/
drgn
https://mykredit-online.ru/
Acho simplesmente insano JabiBet Casino, da uma energia de cassino que e uma mare alta. As opcoes de jogo no cassino sao ricas e eletrizantes, com jogos de cassino perfeitos pra criptomoedas. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e uma mare de qualidade, acessivel por chat ou e-mail. Os pagamentos do cassino sao lisos e blindados, mesmo assim mais bonus regulares no cassino seria top. Resumindo, JabiBet Casino garante uma diversao de cassino que e uma mare cheia para os cacadores de slots modernos de cassino! De lambuja a plataforma do cassino detona com um visual que e puro mar, torna o cassino uma curticao total.
jabibet login|
Ich bin vollig verzaubert von JokerStar Casino, es verstromt eine Spielstimmung, die verzaubert. Die Casino-Optionen sind bunt und mitrei?end, mit einzigartigen Casino-Slotmaschinen. Die Casino-Mitarbeiter sind schnell wie ein Zauberstab, sorgt fur sofortigen Casino-Support, der verblufft. Casino-Gewinne kommen wie ein Blitz, dennoch mehr regelma?ige Casino-Boni waren zauberhaft. Am Ende ist JokerStar Casino ein Online-Casino, das die Sterne vom Himmel holt fur Abenteurer im Casino! Und au?erdem die Casino-Navigation ist kinderleicht wie ein Zauberspruch, was jede Casino-Session noch magischer macht.
jokerstar bonus code|
Je trouve absolument grandiose LeoVegas Casino, ca degage une vibe de jeu princiere. Les choix de jeux au casino sont riches et princiers, avec des machines a sous de casino modernes et envoutantes. Le personnel du casino offre un accompagnement majestueux, assurant un support de casino instantane et souverain. Les retraits au casino sont rapides comme un couronnement, mais plus de tours gratuits au casino ce serait grandiose. En somme, LeoVegas Casino est un joyau pour les fans de casino pour les passionnes de casinos en ligne ! Bonus la navigation du casino est intuitive comme un sceptre, ce qui rend chaque session de casino encore plus majestueuse.
leovegas down|
https://antidetectbrowser.us/
J’adore la feerie de Luckland Casino, il propose une aventure de casino qui fait briller les etoiles. La selection du casino est une cascade de plaisirs, incluant des jeux de table de casino d’une elegance feerique. L’assistance du casino est chaleureuse et irreprochable, assurant un support de casino immediat et lumineux. Les retraits au casino sont rapides comme un coup de chance, mais des recompenses de casino supplementaires feraient rever. Globalement, Luckland Casino est un joyau pour les fans de casino pour les chasseurs de fortune du casino ! A noter le design du casino est une explosion visuelle feerique, ajoute une touche de feerie au casino.
luckland casino bonus code|
Ich bin vollig verzaubert von LuckyNiki Casino, es ist ein Online-Casino, das wie ein Glucksbringer leuchtet. Es gibt eine Woge an packenden Casino-Titeln, mit Live-Casino-Sessions, die wie ein Feuerwerk knistern. Der Casino-Service ist zuverlassig und strahlend, antwortet blitzschnell wie ein Gluckszauber. Der Casino-Prozess ist klar und ohne Trugbilder, dennoch mehr Casino-Belohnungen waren ein funkelnder Gewinn. Kurz gesagt ist LuckyNiki Casino ein Casino mit einem Spielspa?, der wie ein Komet leuchtet fur die, die mit Stil im Casino wetten! Und au?erdem die Casino-Oberflache ist flussig und glitzert wie ein Nordlicht, was jede Casino-Session noch magischer macht.
luckyniki casino no deposit bonus code 2017|
J’adore le charme de Luckster Casino, ca pulse avec une energie de casino envoutante. La collection de jeux du casino est un veritable grimoire, proposant des slots de casino a theme feerique. Le support du casino est disponible 24/7, assurant un support de casino immediat et ensorcelant. Les paiements du casino sont securises et fluides, parfois des recompenses de casino supplementaires feraient rever. Pour resumer, Luckster Casino promet un divertissement de casino scintillant pour ceux qui cherchent l’adrenaline enchantee du casino ! Bonus la plateforme du casino brille par son style ensorcelant, ce qui rend chaque session de casino encore plus magique.
luckster casino|
Je trouve absolument exaltant MonteCryptos Casino, c’est un casino en ligne qui grimpe comme un sommet enneige. Le repertoire du casino est une montagne de plaisirs, offrant des sessions de casino en direct qui electrisent. Les agents du casino sont rapides comme un vent de montagne, repondant en un eclair glacial. Les retraits au casino sont rapides comme une descente en luge, par moments des recompenses de casino supplementaires feraient grimper l’adrenaline. En somme, MonteCryptos Casino est un joyau pour les fans de casino pour les joueurs qui aiment parier avec panache au casino ! Par ailleurs le design du casino est une explosion visuelle alpine, donne envie de replonger dans le casino sans fin.
montecryptos free bonus|
http://110km.ru/
Центр лечения катаракты в Санкт-Петербурге
Je trouve absolument envoutant LuckyTreasure Casino, il propose une aventure de casino qui brille comme de l’or. Les choix de jeux au casino sont riches et eclatants, proposant des slots de casino a theme d’aventure. Le personnel du casino offre un accompagnement scintillant, repondant en un eclair de lumiere. Les transactions du casino sont simples comme une cle d’or, quand meme des bonus de casino plus frequents seraient precieux. Globalement, LuckyTreasure Casino promet un divertissement de casino scintillant pour les chasseurs de tresors du casino ! Par ailleurs le design du casino est une explosion visuelle precieuse, facilite une experience de casino feerique.
lucky treasure casino france|
Je trouve absolument enivrant LuckyBlock Casino, on dirait une pluie de trefles a quatre feuilles. La selection du casino est une fontaine de plaisirs, incluant des jeux de table de casino d’une elegance radieuse. Le personnel du casino offre un accompagnement lumineux, proposant des solutions claires et instantanees. Les gains du casino arrivent a une vitesse supersonique, parfois j’aimerais plus de promotions de casino qui eblouissent. Globalement, LuckyBlock Casino c’est un casino a decouvrir en urgence pour ceux qui cherchent l’adrenaline lumineuse du casino ! A noter le site du casino est une merveille graphique lumineuse, ajoute une touche de magie au casino.
minecraft luckyblock server|
Je suis accro a Lucky8 Casino, il propose une aventure de casino qui illumine comme un phare. La selection du casino est une explosion de plaisirs, offrant des sessions de casino en direct qui brillent. Le service client du casino est une etoile porte-bonheur, repondant en un eclair magique. Les retraits au casino sont rapides comme un coup de baguette, mais les offres du casino pourraient etre plus genereuses. En somme, Lucky8 Casino c’est un casino a decouvrir en urgence pour ceux qui cherchent l’adrenaline lumineuse du casino ! A noter le design du casino est une explosion visuelle feerique, amplifie l’immersion totale dans le casino.
lucky8|
Sou louco pelo role de MegaPosta Casino, e um cassino online que e uma verdadeira explosao. O catalogo de jogos do cassino e uma bomba total, com caca-niqueis de cassino modernos e eletrizantes. Os agentes do cassino sao rapidos como um estalo, acessivel por chat ou e-mail. Os ganhos do cassino chegam voando como um missil, as vezes as ofertas do cassino podiam ser mais generosas. No geral, MegaPosta Casino e um cassino online que e um vulcao de diversao para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! E mais o design do cassino e uma explosao visual braba, faz voce querer voltar pro cassino toda hora.
megaposta reclame aqui|
Je suis captive par MyStake Casino, ca degage une ambiance de jeu aussi mysterieuse qu’un clair-obscur. Le repertoire du casino est une toile d’enigmes ludiques, incluant des jeux de table de casino d’une elegance cryptique. Le personnel du casino offre un accompagnement digne d’un sage, garantissant un support de casino immediat et eclaire. Le processus du casino est transparent et sans ombres, parfois les offres du casino pourraient etre plus genereuses. Globalement, MyStake Casino est un joyau pour les fans de casino pour les amoureux des slots modernes de casino ! A noter la plateforme du casino brille par son style ensorcelant, facilite une experience de casino mystique.
mystake bonus code no deposit|
Ich bin vollig hingerissen von Pledoo Casino, es ist ein Online-Casino, das wie ein Wirbelwind tobt. Es gibt eine Woge an packenden Casino-Titeln, mit Casino-Spielen, die fur Kryptowahrungen optimiert sind. Das Casino-Team bietet Unterstutzung, die wie ein Stern funkelt, liefert klare und schnelle Losungen. Auszahlungen im Casino sind schnell wie ein Sturm, aber mehr Casino-Belohnungen waren ein funkelnder Gewinn. Insgesamt ist Pledoo Casino ein Online-Casino, das wie ein Orkan begeistert fur Abenteurer im Casino! Nebenbei die Casino-Navigation ist kinderleicht wie ein Windhauch, den Spielspa? im Casino in die Hohe treibt.
pledoo casino free spins|
Adoro o clima feroz de MonsterWin Casino, parece uma tempestade de diversao monstruosa. As opcoes de jogo no cassino sao ricas e brutais, com caca-niqueis de cassino modernos e selvagens. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e um monstro de eficiencia, acessivel por chat ou e-mail. Os pagamentos do cassino sao lisos e blindados, mas mais bonus regulares no cassino seria brabo. Em resumo, MonsterWin Casino vale demais explorar esse cassino para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! Vale falar tambem a navegacao do cassino e facil como uma trilha na selva, aumenta a imersao no cassino a mil.
monsterwin promo code|
Acho simplesmente brabissimo PagolBet Casino, parece uma tempestade de diversao. Tem uma enxurrada de jogos de cassino irados, com jogos de cassino perfeitos pra criptomoedas. A equipe do cassino entrega um atendimento que e uma voltagem alta, garantindo suporte de cassino direto e sem curto-circuito. O processo do cassino e limpo e sem turbulencia, de vez em quando queria mais promocoes de cassino que eletrizam. No fim das contas, PagolBet Casino oferece uma experiencia de cassino que e puro choque para os aventureiros do cassino! E mais o design do cassino e uma explosao visual vibrante, da um toque de voltagem braba ao cassino.
cГіdigo promocional pagolbet|
Je trouve absolument enivrant PokerStars Casino, on dirait un ciel etoile de sensations. La selection du casino est une constellation de delices, proposant des slots de casino a theme audacieux. Le support du casino est disponible 24/7, assurant un support de casino immediat et precis. Le processus du casino est transparent et sans mauvaise donne, parfois les offres du casino pourraient etre plus genereuses. Pour resumer, PokerStars Casino offre une experience de casino palpitante pour les strateges du casino ! Par ailleurs la plateforme du casino brille par son style audacieux, donne envie de replonger dans le casino sans fin.
code promo pokerstars|
Hi i am kavin, its my first occasion to commenting anyplace, when i read this paragraph i thought i could also make comment due to this sensible piece of writing.
https://lkra39.at/
Je trouve incroyablement delirant MrPlay Casino, il propose une aventure de casino qui swingue comme un orchestre. La gamme du casino est un veritable feu d’artifice, avec des machines a sous de casino modernes et entrainantes. Le personnel du casino offre un accompagnement digne d’un maestro, repondant en un clin d’?il festif. Les retraits au casino sont rapides comme un final de spectacle, par moments plus de tours gratuits au casino ce serait enivrant. Globalement, MrPlay Casino promet un divertissement de casino eclatant pour les fetards du casino ! A noter la plateforme du casino brille par son style endiable, ajoute une touche de panache au casino.
mr.play promo coce|
Estou pirando com ParamigoBet Casino, oferece uma aventura de cassino que faz tudo voar. Os titulos do cassino sao um espetaculo avassalador, com caca-niqueis de cassino modernos e eletrizantes. A equipe do cassino entrega um atendimento que e uma ventania, respondendo mais rapido que um trovao. Os pagamentos do cassino sao lisos e blindados, as vezes queria mais promocoes de cassino que arrasam. Em resumo, ParamigoBet Casino vale demais explorar esse cassino para quem curte apostar com estilo no cassino! De bonus a interface do cassino e fluida e cheia de energia tempestuosa, da um toque de forca braba ao cassino.
paramigobet betting|
Je suis accro a Posido Casino, on dirait une tempete sous-marine de fun. Il y a une maree de jeux de casino captivants, incluant des jeux de table de casino d’une elegance marine. Le support du casino est disponible 24/7, repondant en un eclat d’ecume. Le processus du casino est transparent et sans remous, par moments des recompenses de casino supplementaires feraient nager de joie. Au final, Posido Casino est un casino en ligne qui fait des vagues pour ceux qui cherchent l’adrenaline fluide du casino ! A noter la plateforme du casino brille par son style oceanique, ajoute une touche d’eclat marin au casino.
casino posido login|
Je suis accro a MrXBet Casino, on dirait une enigme pleine de surprises. Les options de jeu au casino sont riches et mysterieuses, avec des machines a sous de casino modernes et captivantes. Les agents du casino sont rapides comme une enigme resolue, joignable par chat ou email. Le processus du casino est transparent et sans zones d’ombre, parfois plus de tours gratuits au casino ce serait envoutant. Dans l’ensemble, MrXBet Casino offre une experience de casino mysterieuse pour les joueurs qui aiment parier avec flair au casino ! Bonus la navigation du casino est intuitive comme une enigme resolue, facilite une experience de casino mysterieuse.
mrxbet recensioni|
Je suis totalement envoute par ParisVegasClub, il propose une aventure de casino qui danse comme un spectacle. La selection du casino est un bouquet de plaisirs, proposant des slots de casino a theme glamour. Le personnel du casino offre un accompagnement digne d’un metteur en scene, avec une aide qui fait vibrer la salle. Les paiements du casino sont securises et fluides, cependant des recompenses de casino supplementaires feraient applaudir. Pour resumer, ParisVegasClub offre une experience de casino eclatante pour les passionnes de casinos en ligne ! Par ailleurs le design du casino est un spectacle visuel glamour, ajoute une touche de panache au casino.
bonus code paris vegas club|
Ich bin vollig begeistert von Richard Casino, es fuhlt sich an wie ein koniglicher Triumph. Die Spielauswahl im Casino ist wie ein koniglicher Schatz, mit Live-Casino-Sessions, die wie ein Festbankett leuchten. Das Casino-Team bietet Unterstutzung, die wie ein Zepter glanzt, mit Hilfe, die wie ein Thron majestatisch ist. Auszahlungen im Casino sind schnell wie ein koniglicher Marsch, dennoch mehr regelma?ige Casino-Boni waren furstlich. Alles in allem ist Richard Casino ein Casino mit einem Spielspa?, der wie ein Thron funkelt fur Fans von Online-Casinos! Ubrigens die Casino-Oberflache ist flussig und prunkvoll wie ein Thronsaal, das Casino-Erlebnis total veredelt.
richard branson james bond casino royale|
J’adore l’eclat de PlazaRoyal Casino, ca vibre avec une energie de casino majestueuse. L’assortiment de jeux du casino est un tresor couronne, offrant des sessions de casino en direct qui eblouissent. Les agents du casino sont rapides comme un decret royal, joignable par chat ou email. Les retraits au casino sont rapides comme une procession royale, mais des bonus de casino plus frequents seraient royaux. Globalement, PlazaRoyal Casino est un casino en ligne qui regne en maitre pour les amoureux des slots modernes de casino ! Bonus l’interface du casino est fluide et eclatante comme un palais, ajoute une touche de grandeur au casino.
plaza royal casino review|
Hi to every body, it’s my first pay a quick visit of this weblog; this web site consists of amazing and actually good information in favor of readers.
https://usadba.in.ua/de-kupyty-yakisne-sklo-far-v-ukrayini.html
התחיל השמיכות לצד ולעיני הגברים, הופיע גוף יפה בתחתונים ורודים. היא נמתחה במתיקות. הגברים קהים. 27, אבל מעולם לא הצלחתי לקיים יחסי מין ללא חזק. הייתה לה דמות למות למענה . התחלה סוערת עקבתי הנאה בתל אביב – חוויה שכל גבר חייב לעצמו לפחות פעם אחת בחיים
J’adore la frenesie de Spinanga Casino, il propose une aventure de casino qui spirale comme un vortex. Le repertoire du casino est un tourbillon de divertissement, comprenant des jeux de casino adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Les agents du casino sont rapides comme une rafale, avec une aide qui fait tourbillonner. Les gains du casino arrivent a une vitesse orageuse, cependant plus de tours gratuits au casino ce serait dement. Au final, Spinanga Casino offre une experience de casino virevoltante pour les joueurs qui aiment parier avec panache au casino ! En plus l’interface du casino est fluide et eclatante comme un ouragan, donne envie de replonger dans le casino sans fin.
spinanga casino login|
Je trouve absolument delirant Spinsy Casino, ca vibre avec une energie de casino electrisante. Il y a une vague de jeux de casino captivants, comprenant des jeux de casino adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. L’assistance du casino est chaleureuse et fluide, offrant des solutions claires et instantanees. Les transactions du casino sont simples comme un pas de moonwalk, quand meme j’aimerais plus de promotions de casino qui eblouissent. Dans l’ensemble, Spinsy Casino offre une experience de casino vibrante pour les danseurs du casino ! Bonus le design du casino est un spectacle visuel disco, ce qui rend chaque session de casino encore plus dansante.
spinsy casino login|
Ich bin vollig fasziniert von SlotClub Casino, es bietet ein Casino-Abenteuer, das wie ein Wirbelwind durch die Nacht rast. Der Katalog des Casinos ist ein Kaleidoskop voller Spa?, mit modernen Casino-Slots, die einen hypnotisieren. Das Casino-Team bietet Unterstutzung, die wie ein Neonlicht gluht, antwortet blitzschnell wie ein Kurzschluss. Casino-Zahlungen sind sicher und reibungslos, manchmal die Casino-Angebote konnten gro?zugiger sein. Am Ende ist SlotClub Casino ein Muss fur Casino-Fans fur Fans von Online-Casinos! Ubrigens die Casino-Plattform hat einen Look, der wie ein Laserstrahl funkelt, was jede Casino-Session noch aufregender macht.
slotclub abzocke|
Estou pirando com RioPlay Casino, da uma energia de cassino que e puro axe. A gama do cassino e simplesmente um bloco de carnaval, oferecendo sessoes de cassino ao vivo que sambam com energia. A equipe do cassino entrega um atendimento que e puro carnaval, com uma ajuda que e puro gingado. O processo do cassino e limpo e sem tropecos, mesmo assim mais recompensas no cassino seriam um diferencial brabo. Em resumo, RioPlay Casino oferece uma experiencia de cassino que e puro axe para os amantes de cassinos online! Alem disso a plataforma do cassino brilha com um visual que e puro samba, adiciona um toque de axe ao cassino.
rioplay Г© confiГЎvel|
Acho simplesmente magico SpinGenei Casino, e um cassino online que brilha como uma lampada de Aladim. O catalogo de jogos do cassino e um bau de tesouros misticos, oferecendo sessoes de cassino ao vivo que reluzem como pocoes. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e um feitico de eficiencia, acessivel por chat ou e-mail. Os ganhos do cassino chegam voando como uma lampada magica, mas as ofertas do cassino podiam ser mais generosas. No fim das contas, SpinGenei Casino e um cassino online que e um portal de diversao para os amantes de cassinos online! Alem disso a plataforma do cassino brilha com um visual que e puro feitico, eleva a imersao no cassino a um nivel magico.
spingenie|
Je suis accro a Riviera Casino, il propose une aventure de casino qui brille comme un bijou mediterraneen. Les options de jeu au casino sont riches et ensoleillees, proposant des slots de casino a theme mediterraneen. Le personnel du casino offre un accompagnement digne d’un concierge de luxe, avec une aide qui brille comme une vague. Les gains du casino arrivent a une vitesse de yacht, cependant plus de tours gratuits au casino ce serait somptueux. En somme, Riviera Casino c’est un casino a explorer sans tarder pour les amoureux des slots modernes de casino ! A noter la navigation du casino est intuitive comme une promenade cotiere, donne envie de replonger dans le casino sans fin.
casino riviera methode pour gagner|
Ich bin vollig begeistert von SportingBet Casino, es verstromt eine Spielstimmung, die wie ein Stadion tobt. Es gibt eine Welle an mitrei?enden Casino-Titeln, mit einzigartigen Casino-Slotmaschinen. Der Casino-Support ist rund um die Uhr verfugbar, ist per Chat oder E-Mail erreichbar. Casino-Zahlungen sind sicher und reibungslos, dennoch wurde ich mir mehr Casino-Promos wunschen, die wie ein Sieg jubeln. Kurz gesagt ist SportingBet Casino ein Online-Casino, das wie ein Stadion tobt fur Fans moderner Casino-Slots! Ubrigens die Casino-Oberflache ist flussig und glanzt wie ein Flutlicht, was jede Casino-Session noch spannender macht.
sportingbet apps download|
Acho simplesmente alucinante AFun Casino, oferece uma aventura de cassino que gira como um carrossel enlouquecido. As opcoes de jogo no cassino sao ricas e cheias de swing, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino com um toque de folia. O suporte do cassino ta sempre na ativa 24/7, dando solucoes na hora e com precisao. Os pagamentos do cassino sao lisos e blindados, de vez em quando mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura. No geral, AFun Casino e um cassino online que e uma explosao de alegria para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! Vale dizer tambem a interface do cassino e fluida e reluz como um desfile noturno, o que torna cada sessao de cassino ainda mais animada.
como funciona o aplicativo afun|
Sou louco pela energia de BetorSpin Casino, tem uma vibe de jogo tao vibrante quanto uma supernova dancante. A gama do cassino e simplesmente uma constelacao de prazeres, oferecendo sessoes de cassino ao vivo que reluzem como supernovas. O servico do cassino e confiavel e brilha como uma galaxia, acessivel por chat ou e-mail. As transacoes do cassino sao simples como uma orbita lunar, as vezes mais recompensas no cassino seriam um diferencial astronomico. No fim das contas, BetorSpin Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! De bonus a plataforma do cassino brilha com um visual que e puro cosmos, o que torna cada sessao de cassino ainda mais estelar.
betorspin app baixar|
Adoro o balanco de BRCasino, oferece uma aventura de cassino que pulsa como um pandeiro. A selecao de titulos do cassino e um desfile de prazeres, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino com um toque de carnaval. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e uma bateria de responsa, acessivel por chat ou e-mail. O processo do cassino e limpo e sem tropecos, mas mais recompensas no cassino seriam um diferencial festivo. No fim das contas, BRCasino oferece uma experiencia de cassino que e puro batuque para os folioes do cassino! Alem disso a plataforma do cassino brilha com um visual que e puro axe, o que torna cada sessao de cassino ainda mais animada.
br77 cassino|
Ich finde absolut magisch Trickz Casino, es fuhlt sich an wie ein magischer Trick voller Gewinne. Der Katalog des Casinos ist ein magischer Zirkus voller Action, mit einzigartigen Casino-Slotmaschinen. Der Casino-Service ist zuverlassig und verhext, ist per Chat oder E-Mail erreichbar. Der Casino-Prozess ist klar und ohne Tauschung, dennoch wurde ich mir mehr Casino-Promos wunschen, die wie Zaubertranke wirken. Zusammengefasst ist Trickz Casino eine Casino-Erfahrung, die wie ein Zaubertrick glanzt fur Spieler, die auf magische Casino-Kicks stehen! Extra die Casino-Navigation ist kinderleicht wie ein Zauberspruch, einen Hauch von Zauberei ins Casino bringt.
trickz casino no deposit|
Estou vidrado no BacanaPlay Casino, da uma energia de cassino que e pura purpurina. A gama do cassino e simplesmente um sambodromo de prazeres, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino com um toque de folia. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e uma rainha de bateria, garantindo suporte de cassino direto e sem perder o ritmo. Os pagamentos do cassino sao lisos e blindados, porem mais recompensas no cassino seriam um diferencial festivo. No fim das contas, BacanaPlay Casino oferece uma experiencia de cassino que e puro axe para os apaixonados por slots modernos de cassino! De bonus o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo carioca, eleva a imersao no cassino ao ritmo de um tamborim.
bacanaplay paga|
J’adore la fraicheur de ViggoSlots Casino, c’est un casino en ligne qui scintille comme un glacier sous l’aurore. L’eventail de jeux du casino est une toundra de delices, proposant des slots de casino a theme polaire. Les agents du casino sont rapides comme un vent de toundra, assurant un support de casino immediat et givre. Les paiements du casino sont securises et fluides, par moments j’aimerais plus de promotions de casino qui eblouissent comme l’aurore. Dans l’ensemble, ViggoSlots Casino est un casino en ligne qui brille comme une banquise pour les passionnes de casinos en ligne ! Bonus la navigation du casino est intuitive comme un chemin dans la neige, ajoute une touche de fraicheur au casino.
viggoslots casino connexion|
Sou louco pela energia de Bet4Slot Casino, e um cassino online que roda como um carrossel enlouquecido. O catalogo de jogos do cassino e um redemoinho de emocoes, oferecendo sessoes de cassino ao vivo que giram como um tornado. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e uma engrenagem de eficiencia, dando solucoes na hora e com precisao. Os ganhos do cassino chegam voando como um carrossel, porem queria mais promocoes de cassino que giram como um tornado. Resumindo, Bet4Slot Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para quem curte apostar com estilo giratorio no cassino! Vale dizer tambem o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo vibrante, adiciona um toque de adrenalina giratoria ao cassino.
bet4slot mn|
I find absolutely wild Wazamba Casino, it radiates a gaming vibe as untamed as a tropical storm. The casino’s game lineup is a rainforest of delights, including classy casino table games with a tribal flair. The casino support is available 24/7, providing clear and instant solutions. Casino withdrawals are as fast as a jungle sprint, however extra casino rewards would make hearts pound. To sum up, Wazamba Casino delivers a casino experience as wild as a safari for casino adventurers! As a bonus the casino interface is smooth and vibrant like a tropical sunrise, making you want to dive back into the casino endlessly.
wazamba casino nz|
Je suis totalement submerge par Winamax Casino, on dirait une tempete sous-marine de plaisir. Les options de jeu au casino sont riches et fluides, comprenant des jeux de casino adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Le service client du casino est une perle rare, assurant un support de casino immediat et fluide. Les paiements du casino sont securises et fluides, mais plus de tours gratuits au casino ce serait aquatique. Dans l’ensemble, Winamax Casino c’est un casino a explorer sans tarder pour les amoureux des slots modernes de casino ! Bonus la navigation du casino est intuitive comme un courant marin, amplifie l’immersion totale dans le casino.
paris sportif winamax|
Acho simplesmente epico VikingLuck Casino, tem uma vibe de jogo tao feroz quanto uma tempestade nordica. A gama do cassino e simplesmente um salao de Valhalla, com jogos de cassino perfeitos pra criptomoedas. O servico do cassino e confiavel e forte como um escudo, garantindo suporte de cassino direto e sem fraqueza. As transacoes do cassino sao simples como uma inscricao runica, de vez em quando as ofertas do cassino podiam ser mais generosas. Na real, VikingLuck Casino e um cassino online que e um Valhalla de diversao para quem curte apostar com bravura no cassino! De bonus o design do cassino e um espetaculo visual epico, adiciona um toque de gloria viking ao cassino.
viking luck casino|
Galera, preciso compartilhar minha experiencia no 4PlayBet Casino porque me pegou de surpresa. A variedade de jogos e muito completa: roletas animadas, todos bem otimizados ate no celular. O suporte foi atencioso, responderam em minutos pelo chat, algo que faz diferenca. Fiz saque em Bitcoin e o dinheiro entrou mais ligeiro do que imaginei, ponto fortissimo. Se tivesse que criticar, diria que podia ter mais promocoes semanais, mas isso nao estraga a experiencia. No geral, o 4PlayBet Casino e completo. Vale experimentar.
4play strip|
Curto demais o asfalto de F12.Bet Casino, e um cassino online que acelera como um carro de corrida. As escolhas sao vibrantes como um velocimetro. com caca-niqueis que aceleram como turbo. O time do cassino e digno de um piloto. com ajuda que ronca como um motor. Os saques aceleram como um turbo. mesmo assim mais giros gratis seriam uma loucura de pista. Em sintese, F12.Bet Casino e um motor de emocoes para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! Como extra o layout e vibrante como um velocimetro. transformando cada aposta em uma ultrapassagem.
f12 bet br|
Estou completamente vidrado por MarjoSports Casino, tem um ritmo de jogo que vibra como um apito. O leque do cassino e um estadio de delicias. com jogos adaptados para criptomoedas. Os agentes voam como jogadores. respondendo rapido como um apito. Os saques sao velozes como um sprint final. as vezes mais recompensas fariam a torcida pular. Ao final, MarjoSports Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os exploradores de jogos online! Adicionalmente o visual e uma explosao de quadras. criando uma experiencia de cassino de torcida.
marjosports do ratinho|
Sou louco pela fornalha de Fogo777 Casino, pulsa com uma forca de cassino digna de um xama. Os jogos formam uma fogueira de diversao. incluindo jogos de mesa com um toque de ritual. O atendimento e solido como carvoes. assegurando apoio sem fumaca. Os saques queimam como brasas. ocasionalmente mais bonus seriam um diferencial ardente. Resumindo, Fogo777 Casino garante um jogo que reluz como chamas para os fas de adrenalina ardente! E mais a navegacao e facil como uma labareda. dando vontade de voltar como uma labareda.
https://fogo777.com/r/xxxxxx|
Estou completamente incendiado por Verabet Casino, tem um ritmo de jogo que danca como labaredas. As escolhas sao vibrantes como chamas. com jogos adaptados para criptomoedas. Os agentes voam como chamas. respondendo veloz como uma faisca. As transacoes sao simples como uma tocha. ocasionalmente mais bonus seriam um diferencial ardente. Resumindo, Verabet Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os xamas do cassino! Adicionalmente o layout e vibrante como uma tocha. transformando cada aposta em uma aventura flamejante.
bet vera|
prague plug buy coke in prague
Sou louco pela rede de IJogo Casino, e um cassino online que enreda como uma teia de aranha gigante. As opcoes sao ricas e se entrelacam como vinhas. oferecendo lives que explodem como uma selva. Os agentes sao rapidos como uma cobra. assegurando apoio sem enredos. Os ganhos chegam rapido como uma teia rompida. porem as ofertas podiam ser mais generosas. No geral, IJogo Casino oferece uma experiencia que e puro emaranhado para os apaixonados por slots modernos! De bonus o design e um espetaculo visual enredado. elevando a imersao ao nivel de uma selva.
ijogo games|
Curto demais a vibracao de Stake Casino, e um cassino online que ressoa como um sino ancestral. Os jogos formam uma ressonancia de diversao. com jogos adaptados para criptomoedas. O atendimento e solido como uma corda. com ajuda que ressoa como um sino. Os saques vibram como harpas. porem as ofertas podiam ser mais generosas. Ao final, Stake Casino promete uma diversao que e uma onda sonora para os amantes de cassinos online! Vale dizer o design e fluido como uma onda sonora. criando uma experiencia de cassino harmonica.
stake telegram|
Je suis fou de Casinia Casino, ca vibre avec une energie de casino digne d’un roi. La selection du casino est une cour de plaisirs. offrant des lives qui pulsent comme un tournoi. offre un soutien qui protege tout. assurant un support de casino immediat et noble. Les retraits au casino sont rapides comme un assaut. mais des bonus de casino plus frequents seraient medievaux. Pour resumer, Casinia Casino resonne comme une epopee de plaisir pour ceux qui cherchent l’adrenaline royale du casino! Par ailleurs le site du casino est une merveille graphique noble. fait vibrer le jeu comme un concerto medieval.
la casinia st tropez|
plug in prague prague drugs
Je suis captive par RollBit Casino, c’est un casino en ligne qui deroule comme un ruban de pixels. La selection du casino est une chaine de plaisirs. comprenant des jeux de casino adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. offre un soutien qui deroule tout. proposant un appui qui enchante. Le processus du casino est transparent et sans glitch. mais des offres qui vibrent comme une cadence pixelisee. Dans l’ensemble, RollBit Casino est un casino en ligne qui deroule une symphonie de bits pour les passionnes de casinos en ligne! A noter offre un orchestre de couleurs cubiques. facilite une experience de casino bit par bit.
rollbit rewards|
Sou louco pela roda de XPBet Casino, parece um vortice de adrenalina giratoria. O leque do cassino e um vortice de delicias. incluindo jogos de mesa com um toque eterno. Os agentes sao rapidos como um giro. respondendo rapido como um ciclo. Os pagamentos sao seguros e fluidos. porem mais giros gratis seriam vibrantes. No fim das contas, XPBet Casino garante um jogo que gira como uma roda para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! De bonus a navegacao e facil como um loop. fazendo o cassino pulsar como uma roda.
xp bet paga mesmo|
J’adore le retour de Boomerang Casino, ca degage une ambiance de jeu aussi circulaire qu’un arc parfait. L’assortiment de jeux du casino est une courbe de delices. offrant des lives qui pulsent comme un cercle. repond comme un boomerang parfait. assurant un support de casino immediat et boomerang. Les transactions du casino sont simples comme un arc. occasionnellement les offres du casino pourraient etre plus genereuses. En conclusion, Boomerang Casino est un casino en ligne qui revient comme un boomerang pour les virtuoses des jeux! En plus la plateforme du casino brille par son style ricochet. facilite une experience de casino boomerang.
boomerang casino steun|
Estou alucinado com DonaldBet Casino, vibra com uma vibe circense eletrizante. As escolhas sao vibrantes como um palhaco. com caca-niqueis modernos que encantam como acrobacias. Os agentes sao rapidos como um malabarista. com ajuda que ilumina como um refletor. O processo e claro e sem cortinas. as vezes mais recompensas fariam o coracao saltar. Na real, DonaldBet Casino e um picadeiro de emocoes para os apaixonados por slots modernos! De lambuja a plataforma reluz com um visual circense. adicionando um toque de magia de circo ao cassino.
donaldbet com|
Why viewers still make use of to read news papers when in this technological globe all is existing on web?
online casinos
Je suis totalement seduit par 7BitCasino, ca ressemble a une aventure pleine de sensations. Le catalogue est incroyablement vaste, avec des machines a sous modernes et captivantes. Le service client est remarquable, offrant des reponses rapides et precises. Les paiements sont fluides et securises, bien que davantage de recompenses seraient appreciees, comme des offres de cashback plus avantageuses. En fin de compte, 7BitCasino ne decoit jamais pour les adeptes de sensations fortes ! Notons egalement que la navigation est intuitive et rapide, ce qui intensifie le plaisir de jouer.
7bitcasino serios|
Je suis accro a DBosses, on ressent une vibe unique. Le catalogue est d’une diversite impressionnante, proposant des sessions live vibrantes. Le support est disponible 24/7, avec une aide personnalisee. Le processus est clair et sans complications, parfois des recompenses supplementaires seraient bienvenues. Pour conclure, DBosses est une plateforme hors norme pour les fans de jeux modernes ! Notons aussi l’interface est fluide et moderne, amplifie le plaisir de jouer.
dbosses casino review|
J’apprecie enormement BetFury Casino, c’est une veritable immersion dans un univers vibrant. La selection de jeux est phenomenale, incluant des slots de derniere generation. Le service client est exceptionnel, avec un suivi exemplaire. Le processus de retrait est simple et fiable, bien que les bonus pourraient etre plus reguliers. En resume, BetFury Casino ne decoit jamais pour les joueurs en quete de sensations fortes ! Par ailleurs le site est concu avec modernite et elegance, ce qui renforce l’immersion.
betfury crypto bonus|
Je kiffe grave Gamdom, c’est une plateforme qui envoie du lourd. Il y a un tsunami de titres varies, proposant des sessions live qui tabassent. L’assistance est au top du top, repondant en mode eclair. Les paiements sont fluides et blindes, des fois des bonus plus reguliers ce serait la classe. En gros, Gamdom est une plateforme qui dechire tout pour ceux qui kiffent parier avec style ! Et puis le design est une bombe visuelle, ce qui rend chaque session encore plus kiffante.
gamdom bonus sans depot|
Je suis totalement seduit par Betify Casino, ca procure une experience de jeu captivante. Il y a une profusion de titres varies, incluant des slots de derniere generation. Le support est ultra-reactif et professionnel, offrant des reponses rapides et precises. Les paiements sont fluides et securises, occasionnellement plus de tours gratuits seraient un atout. Pour conclure, Betify Casino est une plateforme d’exception pour les adeptes de sensations fortes ! Notons egalement que l’interface est fluide et intuitive, ce qui amplifie le plaisir de jouer.
betify retrait france|
Je trouve completement fou FatPirate, c’est une plateforme qui envoie du lourd. Les jeux sont nombreux et delirants, avec des slots qui dechirent. Le service client est au top niveau, offrant des reponses claires et stylees. Le processus est clean et sans galere, par contre plus de tours gratos ca ferait plaiz. En gros, FatPirate est un spot incontournable pour les joueurs pour les accros aux sensations fortes ! Bonus le site est une pepite visuelle, booste l’immersion a fond.
bonus sans dГ©pГґt fatpirate|
https://www.monahajjar.com/apple-icon-120×120/#comment-54001
Ich finde absolut irre DrueGlueck Casino, es ist ein Casino, das richtig abgeht. Die Casino-Optionen sind super vielfaltig, inklusive stylischer Casino-Tischspiele. Der Casino-Service ist mega zuverlassig, mit Hilfe, die richtig abgeht. Der Casino-Prozess ist klar und ohne Haken, dennoch mehr Casino-Belohnungen waren der Hit. Zusammengefasst ist DrueGlueck Casino eine Casino-Erfahrung, die rockt fur Fans moderner Casino-Slots! Nebenbei die Casino-Oberflache ist flussig und mega cool, einen Hauch von Wahnsinn ins Casino bringt.
drueckglueck mobile casino|
J’adore sans reserve 1xbet Casino, ca ressemble a une plongee dans un univers palpitant. La selection de jeux est monumentale, avec des machines a sous modernes et captivantes. Le service client est exceptionnel, garantissant une aide immediate. Le processus de retrait est simple et fiable, neanmoins les bonus pourraient etre plus reguliers. Dans l’ensemble, 1xbet Casino ne decoit jamais pour les adeptes de sensations fortes ! En bonus le design est visuellement percutant, ce qui intensifie le plaisir de jouer.
1xbet casino|
Aprecio imensamente o 888 Casino, e realmente sensacao unica de cassino. A selecao de jogos e impressionante, com caca-niqueis modernos e envolventes. A equipe oferece um suporte de altissima qualidade, garantindo ajuda imediata. Os saques sao extremamente rapidos, as vezes mais rodadas gratis seriam otimas. No geral, o 888 Casino e uma plataforma excepcional para os jogadores em busca de adrenalina! Note tambem que a navegacao e simples e rapida, adiciona um toque de sofisticacao a experiencia.
888 casino app|
Estou pirando total com Flabet Casino, oferece uma aventura de cassino que detona tudo. Tem uma enxurrada de jogos de cassino irados, oferecendo sessoes de cassino ao vivo que sao um fogo. A equipe do cassino entrega um atendimento que e uma joia, com uma ajuda que e pura energia. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como um raio, mesmo assim mais giros gratis no cassino seria insano. Na real, Flabet Casino vale demais explorar esse cassino para os amantes de cassinos online! Vale falar tambem o design do cassino e uma explosao visual, faz voce querer voltar pro cassino toda hora.
flabet suspensa|
Je kiffe grave Instant Casino, on dirait une tempete de fun. La selection de titres de casino est dingue, comprenant des jeux de casino tailles pour les cryptos. Le support du casino est dispo 24/7, garantissant un support de casino direct et efficace. Les gains du casino arrivent a la vitesse lumiere, des fois j’aimerais plus de promos de casino qui dechirent. Au final, Instant Casino garantit un fun de casino supersonique pour les pirates des slots de casino modernes ! Et puis le design du casino est une explosion visuelle, donne envie de replonger dans le casino direct.
grand reef casino instant play|
https://guitarbydustin.com/2021/08/07/hello-world/#comment-36508
J’aime enormement le casino TonyBet, ca ressemble a un moment divertissant top. Les jeux sont varies, offrant des options de casino en direct. Le support est toujours la, disponible 24/7. Les paiements sont fluides, neanmoins il pourrait y avoir plus de promos. Dans l’ensemble, TonyBet vaut vraiment le coup pour ceux qui aiment parier ! En bonus, l’interface est fluide, facilitant chaque session de jeu.
tonybet ontario sportsbook|
Ich flippe aus bei JackpotPiraten Casino, es ist ein Online-Casino, das wie eine Welle kracht. Die Spielauswahl im Casino ist riesig wie ein Ozean, mit einzigartigen Casino-Slotmaschinen. Der Casino-Kundenservice ist ein echter Schatz, liefert klare und schnelle Losungen. Casino-Gewinne kommen wie ein Blitz, aber wurde ich mir mehr Casino-Promos wunschen, die funkeln. Alles in allem ist JackpotPiraten Casino ein Online-Casino, das die Meere beherrscht fur Fans von Online-Casinos! Und au?erdem die Casino-Navigation ist kinderleicht wie ein Kartenlesen, einen Hauch von Abenteuer ins Casino bringt.
jackpotpiraten login geht nicht|
Estou completamente enlouquecido por LeaoWin Casino, da uma energia de cassino que e indomavel. O catalogo de jogos do cassino e uma selva braba, com jogos de cassino perfeitos pra criptomoedas. O servico do cassino e confiavel e brabo, garantindo suporte de cassino direto e sem rugas. O processo do cassino e limpo e sem emboscada, porem mais recompensas no cassino seriam um diferencial brabo. No geral, LeaoWin Casino vale demais explorar esse cassino para os cacadores de slots modernos de cassino! De lambuja o design do cassino e uma explosao visual feroz, o que deixa cada sessao de cassino ainda mais animal.
leaowin02 mars mgm casino|
Советую https://tuvape.es/green-interior-design-inspiration/#comment-82405
Ich bin vollig hin und weg von King Billy Casino, es ist ein Online-Casino, das wie ein Konig regiert. Es gibt eine Flut an mitrei?enden Casino-Titeln, inklusive eleganter Casino-Tischspiele. Die Casino-Mitarbeiter sind schnell wie ein koniglicher Bote, ist per Chat oder E-Mail erreichbar. Casino-Gewinne kommen wie ein Triumphzug, ab und zu wurde ich mir mehr Casino-Promos wunschen, die glanzvoll sind. Kurz gesagt ist King Billy Casino ein Online-Casino, das wie ein Konigreich strahlt fur die, die mit Stil im Casino wetten! Zusatzlich die Casino-Plattform hat einen Look, der wie ein Kronungsmantel glanzt, Lust macht, immer wieder ins Casino zuruckzukehren.
king billy casino|
Je suis absolument conquis par DBosses, c’est une plateforme qui electrise. La selection de jeux est grandiose, comprenant des jeux optimises pour les cryptos. Le personnel offre un suivi irreprochable, joignable via chat ou email. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, de temps a autre plus de tours gratuits seraient top. Dans l’ensemble, DBosses vaut pleinement le detour pour les amateurs de casino en ligne ! Notons aussi le design est captivant et elegant, renforce l’envie de revenir.
dbosses|
Je kiffe grave Gamdom, on dirait une explosion de fun. Il y a un tsunami de titres varies, offrant des machines a sous ultra-cool. Le service client est une tuerie, offrant des reponses qui petent. Les retraits sont rapides comme un ninja, par contre des bonus plus reguliers ce serait la classe. Bref, Gamdom offre une experience de ouf pour les aventuriers du jeu ! Cote plus le design est une bombe visuelle, booste l’immersion a fond les ballons.
gamdom tornado|
Крайне рекомендую http://beecroftfp.com.au/2020/05/24/skin-cancer-diagnosis-and-treatment/#comment-6848
Je trouve absolument sauvage LeonBet Casino, c’est un casino en ligne qui rugit de puissance. Il y a un raz-de-maree de jeux de casino captivants, comprenant des jeux de casino optimises pour les cryptomonnaies. Le personnel du casino offre un accompagnement rugissant, assurant un support de casino immediat et puissant. Les paiements du casino sont securises et fluides, par moments les offres du casino pourraient etre plus genereuses. Pour resumer, LeonBet Casino offre une experience de casino indomptable pour les joueurs qui aiment parier avec panache au casino ! Bonus l’interface du casino est fluide et eclatante comme une savane, amplifie l’immersion totale dans le casino.
code bonus leonbet|
Крайне советую https://www.brigittelehle.de/friday-for-future-gelbwestenbewegung-der-megatrend-neo-oekologie/#comment-24141
Ich finde absolut wild Lowen Play Casino, es bietet ein Casino-Abenteuer, das wie ein Urwald leuchtet. Die Spielauswahl im Casino ist wie eine wilde Horde, mit modernen Casino-Slots, die einen in ihren Bann ziehen. Die Casino-Mitarbeiter sind schnell wie ein Gepard, mit Hilfe, die wie ein Brullen wirkt. Casino-Zahlungen sind sicher und reibungslos, dennoch mehr Freispiele im Casino waren ein wilder Triumph. Zusammengefasst ist Lowen Play Casino ein Casino mit einem Spielspa?, der wie ein Brullen donnert fur Spieler, die auf wilde Casino-Kicks stehen! Ubrigens die Casino-Oberflache ist flussig und strahlt wie ein Sonnenaufgang, was jede Casino-Session noch wilder macht.
löwen play konstanz|
Ich bin vollig verzaubert von JokerStar Casino, es bietet ein Casino-Abenteuer, das wie ein Zaubertrick funkelt. Die Casino-Optionen sind bunt und mitrei?end, mit modernen Casino-Slots, die verhexen. Der Casino-Service ist zuverlassig und magisch, liefert klare und schnelle Losungen. Casino-Gewinne kommen wie ein Blitz, ab und zu wurde ich mir mehr Casino-Promos wunschen, die funkeln. Insgesamt ist JokerStar Casino ein Casino mit einem Spielspa?, der wie Magie funkelt fur Fans moderner Casino-Slots! Und au?erdem die Casino-Seite ist ein grafisches Meisterwerk, was jede Casino-Session noch magischer macht.
jokerstar bewertung|
Je suis fou de Luckster Casino, il propose une aventure de casino qui scintille comme un sort. Le repertoire du casino est une cascade de divertissement, offrant des sessions de casino en direct qui enchantent. L’assistance du casino est chaleureuse et irreprochable, joignable par chat ou email. Les retraits au casino sont rapides comme un coup de baguette, mais des bonus de casino plus frequents seraient ensorcelants. Au final, Luckster Casino est un casino en ligne qui porte chance pour les passionnes de casinos en ligne ! En plus la navigation du casino est intuitive comme un sortilege, donne envie de replonger dans le casino sans fin.
luckster casino login|
Je trouve absolument enivrant Lucky8 Casino, ca degage une vibe de jeu petillante comme une comete. Les choix de jeux au casino sont riches et eclatants, proposant des slots de casino a theme feerique. Le support du casino est disponible 24/7, proposant des solutions claires et instantanees. Le processus du casino est transparent et sans malefice, mais des bonus de casino plus frequents seraient ensorcelants. Au final, Lucky8 Casino c’est un casino a decouvrir en urgence pour les chasseurs de fortune du casino ! De surcroit le site du casino est une merveille graphique eclatante, donne envie de replonger dans le casino sans fin.
lucky8 code promotionnel|
Shining Crown demo oyunu ilə klassik meyvə slotunu risksiz sına.
Shining crown pacanele Rumıniyada məşhurdur, Azərbaycanda da sevilir.
Shining crown online oyunu sürətli yüklənir. Shining crown demo superbet variantı real casino təcrübəsinə yaxındır. Shining Crown oyunu klassik meyvə simvollarını əhatə edir.
Shining crown jackpot oyunçuların əsas hədəfidir.
Shining crown online sadə və əlçatan platformadır.
Ətraflı məlumat burada shining crown com az.
Shining crown big win uduşları oyunçular üçün motivasiya rolunu oynayır.
Shining crown free real oyun öncəsi yaxşı sınaqdır.
Je suis fou de LuckyBlock Casino, on dirait une pluie de trefles a quatre feuilles. La collection de jeux du casino est un tresor scintillant, incluant des jeux de table de casino d’une elegance radieuse. Les agents du casino sont rapides comme un eclair de genie, assurant un support de casino immediat et eclatant. Les gains du casino arrivent a une vitesse supersonique, mais j’aimerais plus de promotions de casino qui eblouissent. Pour resumer, LuckyBlock Casino c’est un casino a decouvrir en urgence pour ceux qui cherchent l’adrenaline lumineuse du casino ! Par ailleurs le site du casino est une merveille graphique lumineuse, ajoute une touche de magie au casino.
luckyblock com|
Je suis totalement electrise par Madnix Casino, ca pulse avec une energie de casino totalement folle. Les choix de jeux au casino sont riches et dejantes, avec des machines a sous de casino modernes et delirantes. Le support du casino est disponible 24/7, avec une aide qui claque comme un coup de tonnerre. Les paiements du casino sont securises et fluides, quand meme plus de tours gratuits au casino ce serait completement fou. Dans l’ensemble, Madnix Casino est une pepite pour les fans de casino pour les amoureux des slots modernes de casino ! En plus la plateforme du casino brille par son style completement fou, ce qui rend chaque session de casino encore plus dejantee.
avis madnix casino|
J’adore la splendeur de LuckyTreasure Casino, il propose une aventure de casino qui brille comme de l’or. Le repertoire du casino est une mine de divertissement, incluant des jeux de table de casino d’une elegance precieuse. Les agents du casino sont rapides comme une fleche d’or, proposant des solutions claires et instantanees. Les paiements du casino sont securises et fluides, cependant les offres du casino pourraient etre plus genereuses. Au final, LuckyTreasure Casino c’est un casino a decouvrir en urgence pour ceux qui cherchent l’adrenaline precieuse du casino ! A noter l’interface du casino est fluide et eclatante comme un diamant, ce qui rend chaque session de casino encore plus envoutante.
coupon lucky treasure|
Советую https://www.rotary-hospiz.de/rotary/#comment-54613
Обязательно попробуйте https://carlbaldassarremusic.com/product/silent-nights-mp3/#comment-132115
Acho simplesmente insano OshCasino, da uma energia de cassino que e um terremoto. A gama do cassino e simplesmente uma lava ardente, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino cheios de fogo. A equipe do cassino entrega um atendimento que e uma labareda, respondendo mais rapido que um relampago. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como uma erupcao, as vezes as ofertas do cassino podiam ser mais generosas. No fim das contas, OshCasino vale demais explorar esse cassino para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! E mais a interface do cassino e fluida e cheia de energia ardente, o que deixa cada sessao de cassino ainda mais incendiaria.
osh android|
Ich bin total begeistert von Pledoo Casino, es bietet ein Casino-Abenteuer, das wie ein Vulkan ausbricht. Es gibt eine Woge an packenden Casino-Titeln, mit Casino-Spielen, die fur Kryptowahrungen optimiert sind. Das Casino-Team bietet Unterstutzung, die wie ein Stern funkelt, mit Hilfe, die wie ein Funke spruht. Casino-Gewinne kommen wie ein Komet, trotzdem mehr Freispiele im Casino waren ein Volltreffer. Am Ende ist Pledoo Casino ein Casino mit einem Spielspa?, der wie ein Feuerwerk knallt fur die, die mit Stil im Casino wetten! Und au?erdem die Casino-Plattform hat einen Look, der wie ein Blitz funkelt, einen Hauch von Abenteuer ins Casino bringt.
pledoo casino free spins|
Acho simplesmente brabissimo PagolBet Casino, e um cassino online que detona como um trovao. As opcoes de jogo no cassino sao ricas e vibrantes, com slots de cassino unicos e contagiantes. O servico do cassino e confiavel e brabo, acessivel por chat ou e-mail. As transacoes do cassino sao simples como uma centelha, porem queria mais promocoes de cassino que eletrizam. Em resumo, PagolBet Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os amantes de cassinos online! Vale falar tambem o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo, faz voce querer voltar pro cassino como um raio.
pagolbet casino|
Ich finde absolut verruckt PlayJango Casino, es verstromt eine Spielstimmung, die wie ein Feuerwerk explodiert. Es gibt eine Woge an packenden Casino-Titeln, mit Live-Casino-Sessions, die wie ein Gewitter knistern. Der Casino-Kundenservice ist wie ein Leuchtfeuer, sorgt fur sofortigen Casino-Support, der verblufft. Casino-Gewinne kommen wie ein Komet, ab und zu mehr regelma?ige Casino-Boni waren ein Knaller. Zusammengefasst ist PlayJango Casino ein Casino, das man nicht verpassen darf fur die, die mit Stil im Casino wetten! Und au?erdem die Casino-Plattform hat einen Look, der wie ein Blitz funkelt, was jede Casino-Session noch aufregender macht.
bono playjango|
Estou completamente hipnotizado por Bet558 Casino, da uma energia de cassino que e puro pulsar estelar. As opcoes de jogo no cassino sao ricas e brilhantes como nebulosas, oferecendo sessoes de cassino ao vivo que reluzem como supernovas. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e uma estrela-guia, acessivel por chat ou e-mail. Os pagamentos do cassino sao lisos e blindados, porem mais bonus regulares no cassino seria estelar. Na real, Bet558 Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para quem curte apostar com estilo estelar no cassino! E mais a navegacao do cassino e facil como uma orbita lunar, faz voce querer voltar ao cassino como um cometa em orbita.
{{bet558|bet558 casino|brl 222 bet558|bet558 login|bet558 analista|bet558 casino login|bet558 login entrar|bet558 cassino|bet558 jogo|bet558 win|bet558 com|bet558 paga mesmo|bet558.wim|bet558 confiavel|bet558.com login|bet558 baixar|bet558.win|bet558 codigo promocional|bet558 com br|bet558 site|bet558 download|bet558.com|bet558 app|bet558 plataforma|bet558 bonus|plataforma bet558|bet558 Г© confiГЎvel|bet558 link|bet558. com|bet558.con|bet558.com login entrar|bet558.|bet558 com login|brl222 bet558|bet558.com caГ§a niquel|bet558 paga|bet558.cim|bet558.c9m|bet558.com/home/game|bet558 caГ§a nГqueis|bet558.com-caГ§a-niqueis online casino|bet558.com caГ§a niqueis|bet558 site oficial|bet558 caГ§a-nГqueis|bet558 cadastro|bet558.cok|bet558 entrar|bet558 como sacar|bet558 com caГ§a niqueis|bet558 tigre|baixar bet558|bet558.com.br|https://bet558.com|bet558 horarios|bet558..com|bet558.net|bet558 .com|bet558 reclame aqui|bet558 com home game|bet558 pg slots|bet558.co.|bet558 game|bet558.vom}|
J’adore la ferveur de PokerStars Casino, il propose une aventure de casino qui scintille comme un tapis vert. Les options de jeu au casino sont riches et palpitantes, proposant des slots de casino a theme audacieux. L’assistance du casino est fiable et astucieuse, avec une aide qui mise juste. Les gains du casino arrivent a une vitesse fulgurante, par moments plus de tours gratuits au casino ce serait un full house. Dans l’ensemble, PokerStars Casino promet un divertissement de casino strategique pour les joueurs qui aiment parier avec flair au casino ! Bonus l’interface du casino est fluide et eclatante comme un tapis de jeu, donne envie de replonger dans le casino sans fin.
pokerstars sport|
Крайне рекомендую http://martirent.com/uncategorized/quote-2/#comment-391558
Acho simplesmente brabissimo PlayUzu Casino, e um cassino online que e uma verdadeira ventania. O catalogo de jogos do cassino e uma explosao total, com caca-niqueis de cassino modernos e contagiantes. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e uma rajada de eficiencia, com uma ajuda que e pura adrenalina. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como um furacao, mas mais bonus regulares no cassino seria top. Em resumo, PlayUzu Casino garante uma diversao de cassino que e uma tempestade para os cacadores de slots modernos de cassino! Vale falar tambem o design do cassino e uma explosao visual eletrizante, da um toque de adrenalina braba ao cassino.
codigo de sorpresa playuzu|
Estou pirando com ParamigoBet Casino, parece uma tempestade de diversao. Os titulos do cassino sao um espetaculo avassalador, com caca-niqueis de cassino modernos e eletrizantes. O servico do cassino e confiavel e brabo, acessivel por chat ou e-mail. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como um ciclone, porem mais recompensas no cassino seriam um diferencial brabo. No geral, ParamigoBet Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os aventureiros do cassino! Alem disso a interface do cassino e fluida e cheia de energia tempestuosa, o que deixa cada sessao de cassino ainda mais alucinante.
paramigobet spiele|
Acho simplesmente incendiario BetPrimeiro Casino, parece uma cratera cheia de adrenalina. Tem uma enxurrada de jogos de cassino irados, com jogos de cassino perfeitos pra criptomoedas. O servico do cassino e confiavel e ardente, respondendo mais rapido que uma explosao vulcanica. Os pagamentos do cassino sao lisos e blindados, porem as ofertas do cassino podiam ser mais generosas. Na real, BetPrimeiro Casino oferece uma experiencia de cassino que e puro magma para quem curte apostar com estilo ardente no cassino! De bonus a navegacao do cassino e facil como uma brasa ardente, eleva a imersao no cassino ao calor de um vulcao.
betprimeiro bet|
Je suis totalement emporte par Posido Casino, on dirait une tempete sous-marine de fun. L’eventail de jeux du casino est un ocean de delices, comprenant des jeux de casino adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Le service client du casino est une perle rare, repondant en un eclat d’ecume. Les retraits au casino sont rapides comme un courant marin, mais des bonus de casino plus frequents seraient marins. Dans l’ensemble, Posido Casino est un casino en ligne qui fait des vagues pour les navigateurs du casino ! De surcroit la plateforme du casino brille par son style oceanique, donne envie de replonger dans le casino sans fin.
posido casino bewertung|
Крайне рекомендую https://madeserpa.com.br/ola-mundo/#comment-21317
Je suis accro a ParisVegasClub, il propose une aventure de casino qui danse comme un spectacle. Il y a une cascade de jeux de casino captivants, offrant des sessions de casino en direct qui scintillent. Le personnel du casino offre un accompagnement digne d’un metteur en scene, offrant des solutions claires et instantanees. Les transactions du casino sont simples comme une replique, cependant les offres du casino pourraient etre plus genereuses. Au final, ParisVegasClub promet un divertissement de casino flamboyant pour les amoureux des slots modernes de casino ! En plus la plateforme du casino brille par son style eblouissant, ce qui rend chaque session de casino encore plus spectaculaire.
promotion paris vegas club|
Je suis totalement submerge par Winamax Casino, on dirait une tempete sous-marine de plaisir. Les options de jeu au casino sont riches et fluides, avec des machines a sous de casino modernes et immersives. Les agents du casino sont rapides comme une vague deferlante, assurant un support de casino immediat et fluide. Les retraits au casino sont rapides comme un courant marin, parfois des recompenses de casino supplementaires feraient nager de joie. Dans l’ensemble, Winamax Casino promet un divertissement de casino aquatique pour ceux qui cherchent l’adrenaline fluide du casino ! A noter le design du casino est un spectacle visuel aquatique, ce qui rend chaque session de casino encore plus fluide.
team winamax|
Ich bin vollig begeistert von Richard Casino, es pulsiert mit einer luxuriosen Casino-Energie. Der Katalog des Casinos ist eine Schatzkammer voller Vergnugen, mit Casino-Spielen, die fur Kryptowahrungen optimiert sind. Die Casino-Mitarbeiter sind schnell wie ein kaiserlicher Bote, antwortet blitzschnell wie ein koniglicher Erlass. Casino-Transaktionen sind simpel wie ein kaiserlicher Befehl, manchmal mehr Casino-Belohnungen waren ein koniglicher Gewinn. Insgesamt ist Richard Casino ein Casino mit einem Spielspa?, der wie ein Thron funkelt fur Fans moderner Casino-Slots! Ubrigens die Casino-Seite ist ein grafisches Meisterwerk, den Spielspa? im Casino auf ein konigliches Niveau hebt.
richard casino no deposit bonus code 2023|
Предлагаю https://lynnrichardsonradio.com/tax-knowledge/tax-tips/#comment-41324
For newest information you have to pay a quick visit the web and on world-wide-web I found this web site as a most excellent website for latest updates.
Bi-LED
Из чего состоит процесс 3D печати
Мы предлагаем полный цикл работ — от подготовки 3D модели до готового изделия, в рамках которого мы выполняем разработку или корректировку модели, выбор подходящего материала, подготовку рабочего процесса. Мы печатаем на современных принтерах, которые обеспечивают высокое качество поверхности, прочность и точность размеров. Наши клиенты заказывают у нас прототипы, макеты, функциональные детали, сувенирную продукцию, корпуса для электроники и уникальные дизайнерские элементы. По завершении печати мы можем провести постобработку — шлифовку, окраску, сборку изделия. Мы фиксируем все параметры печати, чтобы клиент был уверен в результате: https://osclass-classifieds.a2hosted.com/index.php?page=item&id=230300
prague drugstore vhq cocaine in prague
buy drugs in prague pure cocaine in prague
Je trouve absolument dement Spinanga Casino, ca degage une ambiance de jeu aussi virevoltante qu’un cyclone. L’eventail de jeux du casino est une tornade de delices, offrant des sessions de casino en direct qui tournoient. Le support du casino est disponible 24/7, assurant un support de casino immediat et dynamique. Les transactions du casino sont simples comme une brise, quand meme les offres du casino pourraient etre plus genereuses. Pour resumer, Spinanga Casino est un casino en ligne qui dechaine les elements pour les dompteurs de tempete du casino ! Bonus la plateforme du casino brille par son style dechaine, facilite une experience de casino frenetique.
spinanga live|
Acho simplesmente estelar BetorSpin Casino, oferece uma aventura de cassino que orbita como um cometa reluzente. A gama do cassino e simplesmente uma constelacao de prazeres, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino com um toque intergalactico. O servico do cassino e confiavel e brilha como uma galaxia, dando solucoes na hora e com precisao. Os pagamentos do cassino sao lisos e blindados, porem mais bonus regulares no cassino seria intergalactico. No fim das contas, BetorSpin Casino oferece uma experiencia de cassino que e puro brilho cosmico para os astronautas do cassino! De lambuja o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo estelar, faz voce querer voltar ao cassino como um cometa em orbita.
cupom betorspin|
Estou completamente encantado por Richville Casino, e um cassino online que reluz como um palacio dourado. Tem uma cascata de jogos de cassino fascinantes, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino com um toque de sofisticacao. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e um mordomo impecavel, garantindo suporte de cassino direto e sem falhas. Os ganhos do cassino chegam com a velocidade de um jato particular, porem as ofertas do cassino podiam ser mais generosas. No geral, Richville Casino e uma joia rara para os fas de cassino para os jogadores que adoram apostar com classe! De bonus a navegacao do cassino e facil como um passeio de carruagem, adiciona um toque de sofisticacao ao cassino.
renovation company richville|
Ich finde absolut elektrisierend SlotClub Casino, es ist ein Online-Casino, das wie ein Neonlicht explodiert. Die Spielauswahl im Casino ist wie ein funkelnder Regenbogen, mit Live-Casino-Sessions, die wie ein Stroboskop blinken. Der Casino-Service ist zuverlassig und strahlend, sorgt fur sofortigen Casino-Support, der verblufft. Casino-Zahlungen sind sicher und reibungslos, aber mehr Freispiele im Casino waren ein Volltreffer. Kurz gesagt ist SlotClub Casino eine Casino-Erfahrung, die wie ein Lichtspiel glitzert fur Fans von Online-Casinos! Nebenbei die Casino-Seite ist ein grafisches Meisterwerk, das Casino-Erlebnis total elektrisiert.
slotclub pro|
Estou alucinado com BetorSpin Casino, parece uma explosao cosmica de adrenalina. As opcoes de jogo no cassino sao ricas e brilhantes como estrelas, oferecendo sessoes de cassino ao vivo que reluzem como supernovas. A equipe do cassino entrega um atendimento que e puro cometa, garantindo suporte de cassino direto e sem buracos negros. As transacoes do cassino sao simples como uma orbita lunar, as vezes queria mais promocoes de cassino que explodem como supernovas. No fim das contas, BetorSpin Casino e um cassino online que e uma galaxia de diversao para quem curte apostar com estilo estelar no cassino! Alem disso a plataforma do cassino brilha com um visual que e puro cosmos, o que torna cada sessao de cassino ainda mais estelar.
betorspin levantamento|
Adoro o fervor de SpinFest Casino, parece uma festa reluzente cheia de adrenalina. A selecao de titulos do cassino e um desfile de emocoes, com caca-niqueis de cassino modernos e giratorios. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e uma bateria de eficiencia, garantindo suporte de cassino direto e sem perder o ritmo. As transacoes do cassino sao simples como um passo de maracatu, as vezes queria mais promocoes de cassino que botam pra quebrar. Resumindo, SpinFest Casino oferece uma experiencia de cassino que e puro batuque para quem curte apostar com gingado no cassino! Vale dizer tambem a navegacao do cassino e facil como um passo de danca, faz voce querer voltar ao cassino como num desfile sem fim.
spinfest casino no deposit bonus|
Acho simplesmente intergalactico SpeiCasino, e um cassino online que decola como um foguete espacial. Tem uma chuva de meteoros de jogos de cassino irados, com slots de cassino tematicos de espaco. A equipe do cassino entrega um atendimento que e puro foguete, acessivel por chat ou e-mail. As transacoes do cassino sao simples como uma orbita, as vezes as ofertas do cassino podiam ser mais generosas. Em resumo, SpeiCasino vale demais explorar esse cassino para os apaixonados por slots modernos de cassino! Vale dizer tambem a plataforma do cassino brilha com um visual que e puro cosmos, faz voce querer voltar ao cassino como um cometa em orbita.
spei chicken game|
Je suis accro a Stake Casino, il propose une aventure de casino qui pulse comme un geyser. L’eventail de jeux du casino est une eruption de delices, comprenant des jeux de casino adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Le personnel du casino offre un accompagnement digne d’un pyromane, assurant un support de casino immediat et incandescent. Les retraits au casino sont rapides comme une coulee de lave, cependant plus de tours gratuits au casino ce serait volcanique. En somme, Stake Casino offre une experience de casino incandescente pour les amoureux des slots modernes de casino ! Par ailleurs le design du casino est un spectacle visuel en fusion, ajoute une touche de feu au casino.
stake holders|
Estou completamente encantado por SpinGenei Casino, tem uma vibe de jogo tao magica quanto um tapete voador. Tem uma enxurrada de jogos de cassino fascinantes, com jogos de cassino perfeitos pra criptomoedas. Os agentes do cassino sao rapidos como um desejo concedido, acessivel por chat ou e-mail. Os pagamentos do cassino sao lisos e blindados, porem mais recompensas no cassino seriam um diferencial encantado. Em resumo, SpinGenei Casino garante uma diversao de cassino que e magica para quem curte apostar com estilo mistico no cassino! E mais a plataforma do cassino brilha com um visual que e puro feitico, eleva a imersao no cassino a um nivel magico.
spingenie casino recension|
Estou completamente enfeiticado por SpellWin Casino, tem uma vibe de jogo tao fascinante quanto um grimorio antigo. O catalogo de jogos do cassino e um bau de encantos, com slots de cassino tematicos de fantasia. Os agentes do cassino sao rapidos como um passe de varinha, respondendo mais rapido que um estalo magico. O processo do cassino e limpo e sem truques, as vezes queria mais promocoes de cassino que hipnotizam. Resumindo, SpellWin Casino vale demais explorar esse cassino para os amantes de cassinos online! E mais a plataforma do cassino reluz com um visual que e puro feitico, eleva a imersao no cassino a um nivel magico.
spellwin app|
שוב. ברחה מבעלה הרודן לדירות דיסקרטיות כל חיי הלכו מתחת לדירות דיסקרטיות, הכל היה מדכא, חשבתי חייכו. הבחור השלישי, הקטנטן ביותר אמר. המים שווים את הכסף. אתה צריך לשלם עבור מים. “יש לנו כסף, additional info
Sou louco pela energia de BetorSpin Casino, oferece uma aventura de cassino que orbita como um cometa reluzente. A gama do cassino e simplesmente uma constelacao de prazeres, com caca-niqueis de cassino modernos e hipnotizantes. O suporte do cassino ta sempre na ativa 24/7, com uma ajuda que reluz como uma aurora boreal. Os ganhos do cassino chegam voando como um asteroide, mas mais recompensas no cassino seriam um diferencial astronomico. Resumindo, BetorSpin Casino oferece uma experiencia de cassino que e puro brilho cosmico para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! De lambuja a navegacao do cassino e facil como uma orbita lunar, eleva a imersao no cassino a um nivel cosmico.
betorspin slots|
Estou completamente alucinado por SpinSala Casino, parece uma festa reluzente cheia de energia. A gama do cassino e simplesmente um palco de delicias, com slots de cassino tematicos de festa. O suporte do cassino ta sempre na ativa 24/7, acessivel por chat ou e-mail. Os ganhos do cassino chegam voando como um foguete, mas mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura. No fim das contas, SpinSala Casino garante uma diversao de cassino que e uma explosao de cores para os amantes de cassinos online! De lambuja a navegacao do cassino e facil como uma coreografia de luzes, eleva a imersao no cassino ao brilho maximo.
spinsala casino erfahrungen|
Нужна презентация? https://generator-prezentaciy.ru Создавайте убедительные презентации за минуты. Умный генератор формирует структуру, дизайн и иллюстрации из вашего текста. Библиотека шаблонов, фирстиль, графики, экспорт PPTX/PDF, совместная работа и комментарии — всё в одном сервисе.
Очень советую https://www.realm.gmbh/hallo-welt/?unapproved=97573&moderation-hash=46cf05e98f5ae4bcb83df9b5f8fd0a27
Estou completamente apaixonado por BacanaPlay Casino, e um cassino online que explode como um desfile de carnaval. A selecao de titulos do cassino e uma explosao de cores e ritmos, com jogos de cassino perfeitos pra criptomoedas. O suporte do cassino ta sempre na ativa 24/7, respondendo mais rapido que um batuque de pandeiro. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como um carro alegorico, de vez em quando queria mais promocoes de cassino que botam pra quebrar. No geral, BacanaPlay Casino e um cassino online que e uma folia sem fim para os apaixonados por slots modernos de cassino! E mais o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo carioca, eleva a imersao no cassino ao ritmo de um tamborim.
bacanaplay roulette review|
Je trouve absolument glacial ViggoSlots Casino, ca vibre avec une energie de casino digne d’un blizzard. La selection du casino est une tempete de plaisirs, incluant des jeux de table de casino d’une elegance arctique. Le support du casino est disponible 24/7, joignable par chat ou email. Les transactions du casino sont simples comme un flocon de neige, parfois j’aimerais plus de promotions de casino qui eblouissent comme l’aurore. Pour resumer, ViggoSlots Casino c’est un casino a explorer sans tarder pour les amoureux des slots modernes de casino ! De surcroit le site du casino est une merveille graphique polaire, donne envie de replonger dans le casino sans fin.
viggoslots no deposit bonus|
Right here is the right site for anyone who hopes to understand this topic. You understand a whole lot its almost tough to argue with you (not that I actually will need to…HaHa). You definitely put a new spin on a subject that has been written about for decades. Great stuff, just excellent!
kra40 cc
Обязательно попробуйте https://spotfreeroofs.com/a-journey-through-earths-natural-splendor/?unapproved=24641&moderation-hash=490f795e6de834644823350bd27962a3
Je suis accro a Unibet Casino, ca degage une ambiance de jeu aussi petillante qu’un orchestre en feu. Les options de jeu au casino sont riches et melodiques, incluant des jeux de table de casino d’une elegance musicale. Le service client du casino est un maestro virtuose, repondant en un eclair melodique. Le processus du casino est transparent et sans fausse note, parfois des recompenses de casino supplementaires feraient chanter. En somme, Unibet Casino promet un divertissement de casino vibrant pour les melomanes du casino ! A noter la navigation du casino est intuitive comme une partition, ajoute une touche de musique au casino.
bonus unibet|
Adoro o brilho de BetorSpin Casino, da uma energia de cassino que e puro pulsar galactico. A selecao de titulos do cassino e um buraco negro de diversao, com jogos de cassino perfeitos pra criptomoedas. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e uma estrela-guia, garantindo suporte de cassino direto e sem buracos negros. Os ganhos do cassino chegam voando como um asteroide, mas mais recompensas no cassino seriam um diferencial astronomico. Na real, BetorSpin Casino vale demais explorar esse cassino para os apaixonados por slots modernos de cassino! Vale dizer tambem a interface do cassino e fluida e reluz como uma constelacao, torna a experiencia de cassino uma viagem espacial.
jogos de betorspin|
Je suis totalement envoute par Tortuga Casino, il propose une aventure de casino qui navigue comme un galion au vent. Il y a une deferlante de jeux de casino captivants, comprenant des jeux de casino adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Le support du casino est disponible 24/7, avec une aide qui hisse les voiles. Les retraits au casino sont rapides comme un abordage, cependant les offres du casino pourraient etre plus genereuses. Dans l’ensemble, Tortuga Casino c’est un casino a aborder sans tarder pour les amoureux des slots modernes de casino ! Par ailleurs le site du casino est une merveille graphique pirate, facilite une experience de casino epique.
tortuga casino no deposit bonus|
изготовление значков на заказ москва москва заказать значки с логотипом недорого
значки с логотипом на заказ цена значок нагрудный с логотипом
значки на заказ с логотипом значки на заказ со своей картинкой
Hi to every body, it’s my first pay a visit of this webpage; this website contains awesome and in fact good material for visitors.
kra40 at
Обязательно попробуйте http://miamiseobitch.com/home-3/shake/
Galera, preciso compartilhar minha experiencia no 4PlayBet Casino porque me pegou de surpresa. A variedade de jogos e surreal: roletas animadas, todos bem otimizados ate no celular. O suporte foi eficiente, responderam em minutos pelo chat, algo que me deixou confiante. Fiz saque em PIX e o dinheiro entrou sem enrolacao, ponto fortissimo. Se tivesse que criticar, diria que seria legal torneios de slots, mas isso nao estraga a experiencia. No geral, o 4PlayBet Casino tem diferencial real. Com certeza vou continuar jogando.
20×10 4play wheels|
Sou viciado no brilho de BR4Bet Casino, e uma onda de diversao que cintila como um farol. Tem uma enxurrada de jogos de cassino irados. com caca-niqueis modernos que encantam como lanternas. Os agentes voam como claroes. oferecendo respostas claras como um farol. Os saques voam como um facho de luz. mas mais bonus seriam um diferencial reluzente. No fim das contas, BR4Bet Casino e um cassino online que e um farol de diversao para os fas de adrenalina brilhante! Vale dizer a navegacao e facil como um facho de luz. elevando a imersao ao nivel de uma fogueira.
br4bet com|
Обязательно попробуйте https://summitrealtor.es/10-quick-tips-about-real-estate
joszaki regisztracio joszaki.hu
Estou completamente pixelado por PlayPix Casino, explode com uma vibe de cassino retro-futurista. As escolhas sao vibrantes como um glitch. oferecendo sessoes ao vivo que processam como servidores. O suporte e um codigo preciso. disponivel por chat ou e-mail. Os saques sao velozes como um upload. em alguns momentos mais recompensas fariam o coracao pixelar. No fim das contas, PlayPix Casino garante um jogo que reluz como pixels para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! Adicionalmente a interface e fluida e reluz como um pixel. fazendo o cassino processar como um CPU.
bot playpix|
Estou alucinado com IJogo Casino, pulsa com uma forca de cassino digna de um cacador de sombras. O catalogo de jogos e uma selva de emocoes. com slots tematicos de aventuras enredadas. O servico e confiavel como uma raiz. garantindo suporte direto e sem nos. As transacoes sao faceis como um emaranhado. de vez em quando mais recompensas fariam o coracao se enrolar. No geral, IJogo Casino e um cassino online que e um labirinto de diversao para os exploradores de jogos online! De bonus a plataforma reluz com um visual labirintico. dando vontade de voltar como um cipo.
plataforma ijogo Г© confiГЎvel|
Крайне советую https://www.tanzen3000.com/2023/05/04/hello-world/
Formula 1 puan durumu daim yenilənir və oyunçular üçün əlçatandır. Formula 1 canlı izləmə şifresiz seçimləri təqdim olunur.
Ən yaxşı nəticələr və statistikalar üçün baxın ➡ formula 1 standings.
Formula 1 haqqinda melumat axtaranlar üçün faydalı mənbə. Formula 1 cars modellərinin qiymətləri və xüsusiyyətləri.
Formula 1 2025 calendar üzrə bütün yarış tarixləri. Formula 1 baku haqqinda melumat axtaranlara məsləhətlər. Formula 1 Bakı 2024 nə zaman keçiriləcək. Formula 1 drivers ilə bağlı ən son xəbərlər.
Estou alucinado com DonaldBet Casino, tem um ritmo de jogo que danca como um acrobata. O catalogo de jogos e um picadeiro de prazeres. oferecendo sessoes ao vivo que brilham como holofotes. Os agentes sao rapidos como um malabarista. garantindo suporte direto e sem quedas. Os saques voam como um acrobata. entretanto mais bonus regulares seriam circenses. No geral, DonaldBet Casino oferece uma experiencia que e puro espetaculo para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! Alem disso o visual e uma explosao de lonas. dando vontade de voltar como um trapezista.
donaldbet|
Adoro o giro de XPBet Casino, tem um ritmo de jogo que orbita como um ciclo. As escolhas sao vibrantes como um giro. oferecendo lives que explodem como vortices. Os agentes giram como rodas. assegurando apoio sem interrupcoes. As transacoes sao simples como um giro. porem mais bonus seriam um diferencial de roda. No geral, XPBet Casino e um cassino online que e um vortice de diversao para os roteiristas do cassino! Por sinal a plataforma reluz com um visual ciclico. tornando cada sessao ainda mais giratoria.
xp bet paga|
Je suis fou de Boomerang Casino, est un retour de divertissement qui boucle. Le repertoire du casino est un arc de divertissement. avec des slots qui bouclent comme des arcs. offre un soutien qui boucle tout. repondant en un ricochet circulaire. Les paiements du casino sont securises et fluides. neanmoins des bonus de casino plus frequents seraient circulaires. Pour resumer, Boomerang Casino est un joyau pour les fans de casino pour les passionnes de casinos en ligne! Bonus resonne avec une melodie graphique arque. cadence l’aventure avec une rhapsodie de ricochets.
boomerang casino einzahlungscode|
J’ai un coup de foudre pour Casombie, ca pulse comme une invasion de zombies. La selection de jeux est terrifiante de richesse, offrant des sessions live dignes d’un film d’horreur. Les agents repondent plus vite qu’un zombie affame, joignable a toute heure. Les paiements sont securises comme une tombe scellee, de temps a autre des bonus plus mordants seraient top. En somme, Casombie merite une visite dans son antre pour les amateurs de vibes gothiques ! En bonus le site est visuellement un chef-d’?uvre macabre, donne envie de revenir hanter le site.
casombie de|
Je suis totalement hypnotise par Freespin Casino, ca scintille comme une aurore boreale. Le catalogue est un kaleidoscope de delices, offrant des sessions live qui captivent l’ame. Le support est disponible 24/7, avec une aide aussi fluide qu’une brise etoilee. Les gains atterrissent a la vitesse lumiere, neanmoins plus de promos vibrantes seraient un regal. En somme, Freespin Casino promet une aventure etincelante pour les joueurs en quete de magie ludique ! De plus le design est vibrant comme une galaxie, amplifie l’immersion dans un cosmos de fun.
casino utan svensk licens free spin|
J’adore le voile de Nomini Casino, il propose une aventure de casino qui tournoie comme un voile mystique. propose un ballet de divertissement qui seduit. comprenant des jeux de casino adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. repond comme un fantome gracieux. joignable par chat ou email. Les gains du casino arrivent a une vitesse etheree. occasionnellement des recompenses de casino supplementaires feraient danser. En somme, Nomini Casino cadence comme une sonate de victoires pour les amoureux des slots modernes de casino! De surcroit le design du casino est une fresque visuelle spectrale. ce qui rend chaque session de casino encore plus etheree.
Je suis enivre par MrPacho Casino, il orchestre une symphonie de gains succulents. Le menu est un cellier de variete exuberante, integrant des live roulettes pour des tourbillons de suspense. Le service officie en continu 24/7, accessible par messagerie ou appel instantane. Les butins affluent via USDT ou fiat fluide, par intermittence plus de hors-d’?uvre bonus journaliers agrementeraient le festin. Dans l’ensemble du menu, MrPacho Casino tisse une tapisserie de divertissement gustatif pour ceux qui cuisinent leur fortune en ligne ! A souligner la trame irradie comme un plat ancestral, instille une essence de mystere culinaire.
avis mrpacho|
Очень советую https://worldpressphoto.lv/2017/10/11/6-vestures-fakti-par-fotografijam/
Je suis ebloui par Cheri Casino, ca transporte dans un tourbillon de delices. La selection est une cascade de surprises, offrant des sessions live qui hypnotisent. Le service client est d’une douceur angelique, garantissant un support d’une clarte cristalline. Les retraits sont fluides comme une riviere, de temps a autre plus de promos eclatantes seraient geniales. Au final, Cheri Casino promet une experience eclatante pour les fans de casinos en ligne ! En bonus le site est un chef-d’?uvre visuel, facilite une experience fluide et joyeuse.
cheri casino français|
J’eprouve une brillance infinie pour RubySlots Casino, ca expose un musee de defis cristallins. Le portfolio est un salon de variete lapidaire, proposant des keno pour des extractions de chance. L’assistance grave des reponses nettes, avec une expertise qui prevoit les inclusions. Les transferts coulent stables et acceleres, a l’occasion des spins gratuits supplementaires poliraient les pieces. Dans l’ensemble de l’ecrin, RubySlots Casino forge une saga de jeu lapidaire pour les collectionneurs de casinos virtuels ! Par surcroit la structure rayonne comme un rubis ancestral, infuse une essence de mystere precieux.
ruby slots casino no deposit free spins|
J’eprouve une precision infinie pour WildRobin Casino, ca tend un arc de defis legendaires. Le feuillage est un parchemin de divertissements forestiers, integrant des lives comme Blackjack pour des duels d’arcs. Les sentinelles tirent avec une acuite exemplaire, avec une visee qui anticipe les embuscades. Les retraits filent avec une velocite remarquable, occasionnellement les salves d’offres pourraient s’epaissir en densite. En decochant la derniere fleche, WildRobin Casino invite a une traque sans fin pour les bandits de casinos virtuels ! En plus la circulation est instinctive comme un tir, simplifie la traversee des sentiers ludiques.
wild la course de survie robin|
Android üçün ən yaxşı soccer tətbiqini sınayın.
Dream league soccer oyunu gənclər arasında çox məşhurdur. Mobil futbol oyunları üçün əsas ünvan soccer com az portalıdır.
World soccer champs mod apk ilə əlavə imkanlar əldə edin. Dream league soccer 2019 hələ də sevilən versiyalardandır. Soccer legends klassik futbol anlarını yaşadır.
Soccer skills champions league ilə yeni bacarıqlar öyrənin. Soccer champs apk yükləmək çox asandır. Spbo live score soccer ilə hər dəqiqə nəticələri görün. Soccer champs para hilesi ilə oyunda üstünlük qazanın.
Попробуйте https://sportsltdrentals.com/2013/08/06/business-etiquette/
Je suis enivre par MrPacho Casino, il orchestre une symphonie de gains succulents. La carte est un grimoire de divertissements savoureux, proposant des blackjack revisites pour des bouffees d’adrenaline. Le service officie en continu 24/7, avec une maestria qui anticipe les appetits. Les retraits glissent avec une souplesse remarquable, bien qu’ les menus d’offres pourraient s’etoffer en generosite. Dans l’ensemble du menu, MrPacho Casino emerge comme un pilier pour les epicuriens pour les maitres des paris crypto ! En cerise sur le gateau le parcours est instinctif comme un arome familier, pousse a prolonger le banquet infini.
mrpacho bonus|
J’eprouve une ivresse totale pour PepperMill Casino, il concocte une alchimie de gains epoustouflants. La reserve de jeux est un herbier foisonnant de plus de 5 000 essences, incluant des jackpots progressifs pour des pics d’essence. Les artisans repondent avec une acuite remarquable, mobilisant des sentiers multiples pour une extraction fulgurante. Le processus est moulu pour une onctuosite exemplaire, toutefois les bouquets d’offres pourraient s’epanouir en generosite. En apotheose epicee, PepperMill Casino convie a une exploration sans satiete pour les explorateurs de casinos virtuels ! En piment sur le gateau le visuel est une mosaique dynamique et odorante, pousse a prolonger le festin infini.
the peppermill|
Je suis fondant pour Sugar Casino, il petrit une pate de recompenses fondantes. La collection est un sirop de divertissements delicieux, integrant des lives comme Sweet Bonanza Candyland pour des eclats de sirop. Le service mijote en continu 24/7, accessible par coulis ou appel direct. Les gains fondent via Bitcoin ou portefeuilles, malgre cela des friandises de recompense additionnelles glaceraient les alliances. A la fin de cette degustation, Sugar Casino invite a une exploration sans indigestion pour les gardiens des bonbonnieres numeriques ! A savourer le graphisme est une praline dynamique et immersive, infuse une essence de mystere sucre.
sugar bingo casino sister sites|
Je suis irremediablement appate par MrPacho Casino, il orchestre une symphonie de gains succulents. Il deborde d’une plethore de mets interactifs, offrant des jackpots progressifs des fournisseurs renommes comme Pragmatic Play. Le suivi veille avec une finesse sans pareille, accessible par messagerie ou appel instantane. Les butins affluent via USDT ou fiat fluide, bien qu’ des menus promotionnels plus frequents pimenteraient la table. En apotheose culinaire, MrPacho Casino convie a une exploration sans satiete pour les chasseurs de casinos virtuels ! A souligner le visuel est une mosaique dynamique et appetissante, instille une essence de mystere culinaire.
mrpacho online|
J’eprouve une majeste infinie pour SlotsPalace Casino, on percoit un cortege de man?uvres opulentes. Les selections forment un arbre genealogique de styles innovants, incluant des roulettes pour des tours de cour. Le support client est un chambellan vigilant et perpetuel, assurant une regence fidele dans le palais. Les retraits s’executent avec une grace remarquable, malgre cela des corteges promotionnels plus frequents dynamiseraient l’empire. A la fin de cette ordonnance, SlotsPalace Casino sculpte une lignee de jeu grandiose pour les seigneurs des paris crypto ! A proclamer le graphisme est une tapisserie dynamique et immersive, amplifie l’immersion dans le royaume du jeu.
promocode slots palace 2024|
Je suis invincible face a Super Casino, il deploie une campagne de gains extraordinaires. Il vrombit d’une flotte de quetes interactives, integrant des lives comme Mega Ball pour des explosions de score. Les sentinelles reagissent avec une alerte fulgurante, accessible par alerte ou appel d’urgence. Les flux sont blindes par des boucliers crypto, a l’occasion des gadgets gratuits supplementaires rechargent les unites. En activant le mode final, Super Casino se pose comme un phare pour les vigilantes pour ceux qui survolent leur destin en ligne ! Par surcroit la circulation est instinctive comme un jetpack, amplifie l’engagement dans l’arsenal du jeu.
super casino france|
v1av8 – The interface tries to be futuristic, but clarity is missing.
Je trouve completement incroyable Betsson Casino, il offre une plongee dans un univers vibrant. Le catalogue est incroyablement vaste avec plus de 1500 titres, proposant des jeux de table classiques comme le blackjack et la roulette. Le personnel offre un accompagnement de qualite via email ou telephone, joignable a toute heure. Le processus de retrait est simple et fiable, bien que les bonus pourraient etre plus frequents. En resume, Betsson Casino ne decoit jamais pour les joueurs en quete d’adrenaline ! De plus le site est concu avec modernite et ergonomie, facilite chaque session de jeu.
betsson erbjudande|
Ich bin total begeistert von King Billy Casino, es fuhlt sich an wie ein koniglicher Triumph. Die Casino-Optionen sind vielfaltig und prachtig, mit einzigartigen Casino-Slotmaschinen. Der Casino-Kundenservice ist wie ein koniglicher Hof, mit Hilfe, die wie ein Thron majestatisch ist. Auszahlungen im Casino sind schnell wie ein koniglicher Marsch, trotzdem wurde ich mir mehr Casino-Promos wunschen, die glanzvoll sind. Insgesamt ist King Billy Casino ein Muss fur Casino-Fans fur Fans moderner Casino-Slots! Zusatzlich die Casino-Oberflache ist flussig und prunkvoll wie ein Thronsaal, Lust macht, immer wieder ins Casino zuruckzukehren.
king billy casino no deposit bonus codes 2024|
Je suis totalement seduit par 7BitCasino, il offre une experience de jeu electrisante. Il y a une profusion de titres varies, comprenant plus de 5 000 jeux, dont 4 000 adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Le service d’assistance est de premier ordre, joignable a toute heure. Le processus de retrait est simple et fiable, bien que davantage de recompenses seraient appreciees, ou des tournois avec des prix plus eleves. Dans l’ensemble, 7BitCasino est un incontournable pour les adeptes de sensations fortes ! De plus le site est concu avec style et modernite, facilite chaque session de jeu.
promo code 7bitcasino|
Обязательно попробуйте https://coachbisnisonline.com/leadmagnet-udah-gak-laku/
jekflix – I enjoyed browsing around, the interface feels very comfortable.
fhkaslfjlas – The design is simple, modern, and easy on the eyes.
93r – I’ll check back later — the idea feels interesting, needs more substance.
aabb49 – Design is minimal, straightforward, and functional.
v1av2 – The structure is well-organized, everything is easy to locate.
heyspin – Smooth performance overall, very comfortable site to explore.
v1av7 – The design is minimal and clean, pleasant to look at.
porn300 – Overall a simple, quick, and user-friendly website interaction.
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de 1win Casino, ca procure une plongee dans un univers electrisant. Le choix de jeux est absolument gigantesque, proposant des jeux de table classiques et raffines. Le personnel est professionnel et attentionne, offrant des solutions claires et efficaces. Les gains arrivent en un temps record, cependant les bonus pourraient etre plus frequents. Globalement, 1win Casino offre une experience de jeu memorable pour ceux qui aiment parier ! Par ailleurs l’interface est fluide et intuitive, renforce l’immersion totale.
1win token|
J’adore le show de Impressario, c’est une plateforme qui met des etoiles plein les yeux. La gamme est une vraie constellation de fun, comprenant des jeux parfaits pour les cryptos. Le service client est digne d’un gala, offrant des reponses qui scintillent. Les retraits sont fluides comme une choregraphie, de temps en temps j’aimerais plus de promos qui envoutent. Dans le fond, Impressario offre un spectacle de jeu inoubliable pour les fans de casinos en ligne ! Cote plus l’interface est fluide et glamour, ce qui rend chaque session encore plus eclatante.
impressario casino login|
mydiving – The information here feels clear and nicely presented overall.
zzj186 – Feels fast and reliable, definitely a smooth browsing experience.
582388360 – Reliable and easy to use, definitely a well-performing website.
5918222q.xyz – The design is minimal, but that actually works in a clean way.
sj256.cc – Overall it feels promising, I’ll revisit to see improvements.
21009.xyz – On mobile it mostly works, though some elements shift oddly.
a6def2ef910.pw – Layout is minimal, helps focus on main content without distractions.
00381.xyz – Load speed is acceptable, though some pages felt sluggish at times.
yy380.cc – Saw this site while browsing, looks promising and quite unique.
0238.org – The color palette is subtle, pleasant to look at over long sessions.
5581249.cc – The color theme is subtle but fits the site’s vibe well.
303vip.info – Found some good links here, though a few are missing images.
sodo66000.xyz – The homepage got me hooked, easy to dig deeper into content.
J’adore l’univers de Cresus, on ressent une energie magique. Les options sont vastes et envoutantes, incluant des jeux de table elegants. Les agents sont rapides et courtois, joignable via chat ou email. Les paiements sont securises et efficaces, de temps en temps plus de tours gratuits seraient un plus. Globalement, Cresus vaut largement le detour pour les joueurs en quete de magie ! Ajoutons que la plateforme est visuellement enchanteresse, amplifie le plaisir de jouer.
cresus olympe|
J’apprecie enormement 1xbet Casino, on dirait une sensation de casino unique. Il y a une profusion de titres varies, incluant des slots de pointe. Le service client est exceptionnel, offrant des reponses rapides et precises. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, occasionnellement plus de tours gratuits seraient un atout. Dans l’ensemble, 1xbet Casino offre une experience de jeu remarquable pour les joueurs en quete d’adrenaline ! En bonus le site est concu avec dynamisme, ce qui intensifie le plaisir de jouer.
1xbet 2022|
x3165.xyz – A few images failed to load, might be broken asset links.
Крайне рекомендую http://untrustworthy.website/index.php/2018/10/08/warning-we-are-coming-for-your-untruthfullnesses/?replytocom=64
sh576.xyz – On mobile layout holds up, though a few bits overlap slightly.
bestbotanicals – The layout’s clean and makes browsing herbal products super enjoyable.
3e7r – The product details are clear, I feel confident about ordering.
bitcoin-mining-news.website – Overall it’s a valuable resource for mining info, I’ll be returning often.
J’adore a fond Azur Casino, c’est une veritable sensation de casino unique. Les options de jeu sont impressionnantes, proposant du casino en direct immersif. Le personnel est hautement professionnel, avec un suivi irreprochable. Le processus de retrait est simple et efficace, cependant davantage de recompenses seraient bienvenues. Dans l’ensemble, Azur Casino vaut vraiment le detour pour les fans de casino virtuel ! En bonus la navigation est intuitive et agreable, ajoutant une touche de raffinement.
azur casino review|
J’adore le casino TonyBet, ca ressemble a un moment divertissant top. Les jeux sont varies, incluant des slots ultra-modernes. Le support est toujours la, repondant rapidement. Les retraits sont rapides, par contre j’aimerais plus de bonus. Dans l’ensemble, TonyBet est une plateforme fiable pour les amateurs de casino ! En bonus, la plateforme est intuitive, ce qui rend l’experience encore meilleure.
tonybet sign up bonus|
gqvslhwxkqnqlmjika.live – Load speed is okay, though heavier pages lag slightly on slower networks.
axjaognr – The font choice is clean, makes reading easier across pages.
formasecoarquitectonicas – The navigation menu is ok but not intuitive in certain areas.
probuis – The homepage is clean but could use more detail or visuals.
hhproduction – The header feels strong and immediately tells me what they do.
giftd – Navigation is smooth—didn’t struggle to find anything.
studydiary – I like how the content is laid out, easy to skim through.
Обязательно попробуйте http://honeyedu.kr/bbs/board.php?bo_table=qa&wr_id=2811
creadordesitios – The footer could use links to social media or contact form.
bestbotanicals – Really impressed by the quality, feels genuine and well-sourced herbs.
missouriland – The footer is minimal — contacts or links would be helpful.
Je suis carrement scotche par Gamdom, c’est une plateforme qui envoie du lourd. La gamme est une vraie pepite, comprenant des jeux parfaits pour les cryptos. Les agents sont rapides comme des fusees, garantissant un support direct et carre. Les transactions sont simples comme un clin d’?il, mais bon des recompenses en plus ca ferait kiffer. Au final, Gamdom c’est du lourd a tester direct pour les accros aux sensations extremes ! Bonus l’interface est fluide et stylee a mort, donne envie de replonger non-stop.
gamdom sikayet|
Sou louco pela energia de Brazino Casino, oferece uma aventura que flui como uma onda cristalina. A colecao e uma onda de entretenimento. com slots tematicos de aventuras marinhas. O atendimento esta sempre ativo 24/7. com ajuda que ilumina como uma perola. As transacoes sao simples como uma bolha. ocasionalmente queria promocoes que explodem como geiseres. No fim das contas, Brazino Casino e um cassino online que e um oceano de diversao para os mergulhadores do cassino! Por sinal o visual e uma explosao de corais. amplificando o jogo com vibracao aquatica.
xvideo brazino777|
Regards for helping out, excellent info .
zonaflix – Really impressed by the variety here, looks well organized and clean.
chinh-sua-anh.online – Love the gallery examples, gives confidence in their image skills.
22ee.top – Navigation looks intuitive, even without many menu items.
tanyapoker.online – The colors and layout feel modern, fits well for gaming site.
Estou seduzido por Flabet Casino, e uma experiencia vibrante. O escolha de titulos e enorme, incluindo jogos de mesa dinamicos. A assistencia e rapida e profissional, oferecendo solucoes precisas. As transacoes sao confiaveis, mesmo que promocoes mais frequentes seriam legais. No geral, Flabet Casino vale realmente a pena para os amantes de adrenalina ! Notemos tambem a plataforma e visualmente top, reforca o desejo de voltar.
bГґnus flabet|
Je kiffe a fond Impressario, ca donne une energie de star absolue. Les options sont variees et eblouissantes, incluant des jeux de table pleins de panache. Le support est dispo 24/7, joignable par chat ou email. Les paiements sont securises et eclatants, quand meme j’aimerais plus de promos qui envoutent. En gros, Impressario garantit un show de fun epique pour les artistes du jeu ! Bonus la plateforme claque avec son look de star, ajoute un max de charisme.
impressario casino login|
Estou completamente fissurado em FSWin Casino, e um cassino online que e uma verdadeira explosao. Tem uma enxurrada de jogos de cassino irados, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino cheios de estilo. A equipe do cassino entrega um atendimento que e uma joia, com uma ajuda que e pura energia. As transacoes do cassino sao simples como um estalo, as vezes mais recompensas no cassino seriam um baita diferencial. No geral, FSWin Casino vale demais explorar esse cassino para quem curte apostar com estilo no cassino! Vale falar tambem o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo, o que deixa cada sessao de cassino ainda mais alucinante.
fswin promo|
80hg88.cc – Really cool site, I like how the pages flow smoothly when navigating.
44lou5 – This site has a unique design and great content.
xfj222 – The design is minimalist yet effective.
5xqvk – The layout is clean and easy to navigate.
mhcw3kct – The layout is clean and easy to navigate.
20b7f9xg.xyz – The writing is direct and helpful—no fluff, which I appreciate.
ryla6760 – The testimonials and success stories are truly inspiring.
Ich bin total fasziniert von Snatch Casino, es liefert ein aufregendes Abenteuer. Das Spielangebot ist beeindruckend, mit spannenden Sportwetten. Die Hilfe ist schnell und professionell, bietet prazise Losungen. Die Gewinne kommen schnell, gelegentlich zusatzliche Belohnungen waren top. Zusammenfassend Snatch Casino garantiert eine top Spielerfahrung fur Spieler auf der Suche nach Spa? ! Au?erdem das Design ist ansprechend und intuitiv, erleichtert die Gesamterfahrung.
гѓ—гѓгѓўг‚ігѓјгѓ‰ snatch casino 2024|
Acho incrivel Flabet Casino, parece um turbilhao de prazer. O escolha de titulos e enorme, compreendendo milhares de jogos adaptados para criptos. Os agentes sao ultra-responsivos, respondendo em um piscar de olhos. Os pagamentos sao fluidos e seguros, por vezes mais rodadas gratis seriam um plus. No geral, Flabet Casino e obrigatorio para os jogadores para os apaixonados por cassino ! Ademais o site e estiloso e rapido, o que aumenta o prazer de jogar.
wesley safadao flabet|
xmlos – I enjoy the fresh perspective this site offers.
seostream – I appreciate the depth of information provided here.
ifyss – The content is diverse and engaging.
caneguida – This site offers a unique perspective on various topics.
683tz084 – The layout is clean and easy to navigate.
iyimu – Great resource for those interested in niche subjects.
seoelitepro – I enjoy the fresh perspective this site offers.
elipso.site – I often drop by here, always something new to read.
hpwt02n0me – Pages load fast, I didn’t notice any delays or glitches.
u888vn – I found this site very helpful and easy to explore.
fcalegacy – Really appreciated the depth and clarity of the content.
rinatmat – Very user friendly, and I like the topic variety here.
comprafacilrd – Found some good reviews, seems like they deliver reliably.
htechwebservice – Nice layout, content is clear and useful for web dev folks.
wzoo – Very user-friendly site, loads fast and no clutter.
pacerproes – Definitely bookmarking this for future reference and revisits.
bslthemes – I appreciate the depth of information provided here.
3366app – A reliable source for up-to-date information.
h7721 – Solid content and presentation, I’ll be coming back.
bongda247 – I appreciate the depth of information provided here.
basingstoketransition – Clear call to action, motivates me to do more for environment.
3styler – The content is well-researched and thought-provoking.
onlineforextrading – Looks like a serious site with useful forex-trading content always.
Je suis allie avec Mafia Casino, ca eleve le jeu a un niveau de boss legendaire. La cache de jeux est un arsenal cache de plus de 5000 armes, offrant des cashbacks 15% et VIP 5 niveaux des capos comme Evolution et Pragmatic Play. Le support client est un consigliere vigilant et incessant, assurant une loyaute fidele dans le syndicate. Les transferts glissent stables et acceleres, occasionnellement davantage de pots-de-vin bonus quotidiens renforceraient l’empire. A la fin de cette conspiration, Mafia Casino devoile un plan de triomphes secrets pour les parrains de casinos virtuels ! Par surcroit le portail est une planque visuelle imprenable, simplifie la traversee des complots ludiques.
mafia casino bonus|
seodigitalelevate – Very impressed with the depth of information here, keep it up.
live-sex-cam – This place feels lively and engaging, super fun experience overall.
artvoyage – The blog posts about art travel are wonderfully written and engaging.
Ich bin total fasziniert von Snatch Casino, es ist eine dynamische Erfahrung. Es gibt eine unglaubliche Vielfalt an Spielen, mit immersiven Live-Sitzungen. Der Kundenservice ist erstklassig, antwortet in Sekundenschnelle. Die Transaktionen sind zuverlassig, obwohl die Angebote konnten gro?zugiger sein. Zum Schluss Snatch Casino ist eine au?ergewohnliche Plattform fur Casino-Fans ! Hinzu kommt die Site ist stylish und schnell, erleichtert die Gesamterfahrung.
snatch casino no deposit promo code|
nowmining – Found their calculators very accurate, makes planning easier for me.
manchunyuan8 – Navigation is straightforward, didn’t get lost at all actually.
shineonx – Definitely worth bookmarking, I want to see updates soon.
post34 – Nice site, content feels fresh and genuinely useful for daily readers.
capsaqiu – Navigation is intuitive, I didn’t struggle to find basic info.
crowltheselinks – I clicked through a few pages, layout is a bit rough but functional.
saltburn – Keep an eye on this, it might surprise once fully built out.
liveforextrading – I like the live updates, helps me stay on top of the markets.
cyrusmining – No reviews found easily, so trustworthiness is uncertain at this stage.
myzb27 – Images load smoothly, no major lag when switching pages.
wraoys – Just visited, the layout is very minimal and seems sort of placeholder.
dhpb-smile – Seems like early stage, hope they build it out gradually.
antsmarket – SSL is valid, which is a good sign—but that alone isn’t sufficient.
Букмекерская контора Vavada предлагает комфортные условия для игроков.
Ставки на спорт предлагают высокие коэффициенты.
Игроки могут делать прогнозы, используя промо и бонусы.
Панель управления проста, и быстро переходить к игре.
Для всех пользователей подготовлены бонусы, узнать больше можно бк вавада.
Сервис работает официально.
axin2 – Curious to see updates, will revisit next week for changes.
thefreemath – Found some new perspectives here, material is engaging and clear.
pomni – I like how easy it is to browse categories, feels smooth.
bbc2y – Very minimal styling so far, but that can evolve with updates.
ouyicn – If this is for promotion, ensure transparency and trust first.
karsynskrusaders – Navigation is straightforward, I didn’t struggle to find info.
Мен ар дайым Лука Модричти көргөндө чыныгы лидерликти байкайм.Эгер Лука Модрич кетсе, Реалдын орто талаасы өзгөрөт. Анын статистикасы ар бир сезон таң калтырат. Жаш өткөн сайын Модричтин тажрыйбасы баалуу болуп жатат. Легенданын бардык трофейлери бир тизмекте — ыңгайлуу окула турган: Лука Модрич трофеи. Лука Модрич Хорватия үчүн сыймык.
Футбол сүйүүчүлөрү үчүн Модрич — Реалдын жүрөгү. Лука Модричтин балалык чагы оор болсо да, ал чоң жетишкендикке жетти. Футболдо андай деңгээлге жетүү оңой эмес. Кайда барбасын, ал ар дайым легенда бойдон калат.
Je suis integre a Mafia Casino, ca forge un syndicate de defis impitoyables. Il pullule d’une legion de complots interactifs, avec des slots aux themes gangster qui font chanter les rouleaux. Le support client est un consigliere vigilant et incessant, mobilisant des canaux multiples pour une execution immediate. Les flux sont masques par des voiles crypto, occasionnellement des complots promotionnels plus frequents dynamiseraient le territoire. En apotheose mafieuse, Mafia Casino forge une legende de jeu gangster pour les mafiosi des paris crypto ! Par surcroit la circulation est instinctive comme un chuchotement, infuse une essence de mystere mafieux.
avis mafia casino en ligne|
wexfordliteraryartsfestival – The platform’s design is clean and user-friendly.
dayofthedeadatx – This could really streamline the process of art authentication.
Acho incrivel Flabet Casino, da uma energia de jogo louca. As opcoes sao vastas e variadas, compreendendo milhares de jogos adaptados para criptos. O suporte esta disponivel 24/7, garantindo ajuda instantanea. As transacoes sao confiaveis, no entanto gostaria de mais bonus variados. Para resumir, Flabet Casino vale realmente a pena para os apaixonados por cassino ! Por outro lado a navegacao e super facil, o que aumenta o prazer de jogar.
bГґnus flabet|
Ich liebe absolut Snatch Casino, es fuhlt sich wie ein Sturm des Vergnugens an. Der Katalog ist einfach gigantisch, mit immersiven Live-Sitzungen. Der Service ist von bemerkenswerter Effizienz, antwortet in Sekundenschnelle. Die Auszahlungen sind superschnell, jedoch zusatzliche Belohnungen waren top. Zusammenfassend Snatch Casino garantiert eine top Spielerfahrung fur Crypto-Liebhaber ! Au?erdem das Design ist ansprechend und intuitiv, verstarkt den Wunsch zuruckzukehren.
i snatch casino|
casteintheuk – Browsing through, I can see how this could help artists globally.
J’eprouve une loyaute infinie pour Mafia Casino, ca eleve le jeu a un niveau de boss legendaire. La cache de jeux est un arsenal cache de plus de 5000 armes, incluant des roulettes pour des tours de table. L’assistance murmure des secrets nets, chuchotant des solutions claires et rapides. Les transferts glissent stables et acceleres, bien que des complots promotionnels plus frequents dynamiseraient le territoire. En apotheose mafieuse, Mafia Casino se dresse comme un pilier pour les capos pour les parrains de casinos virtuels ! En pot-de-vin supplementaire l’interface est un repaire navigable avec ruse, ce qui propulse chaque pari a un niveau de don.
casino nice mafia|
Ich bin fasziniert von SpinBetter Casino, es erzeugt eine Spielenergie, die fesselt. Das Angebot an Spielen ist phanomenal, mit dynamischen Tischspielen. Die Hilfe ist effizient und pro, verfugbar rund um die Uhr. Die Transaktionen sind verlasslich, ab und an die Offers konnten gro?zugiger ausfallen. Zusammengefasst, SpinBetter Casino garantiert hochsten Spa? fur Online-Wetten-Fans ! Hinzu kommt die Site ist schnell und stylish, gibt den Anreiz, langer zu bleiben. Besonders toll die Sicherheit der Daten, die den Spa? verlangern.
https://spinbettercasino.de/|
https://kiteschoolhurghada.ru/
Ich bin verblufft von NV Casino, es ist ein Abenteuer, das pulsiert wie ein Herzschlag. Es wartet eine Fulle an spannenden Spielen, inklusive aufregender Sportwetten. Der Service ist rund um die Uhr verfugbar, mit praziser Unterstutzung. Die Auszahlungen sind ultraschnell, trotzdem mehr Belohnungen waren ein Hit. Zum Abschluss, NV Casino garantiert Top-Unterhaltung fur Krypto-Liebhaber ! Au?erdem die Oberflache ist intuitiv und stylish, fugt eine Prise Magie hinzu.
https://playnvcasino.de/|
I have a real passion for Wazamba Casino, it’s an adventure that throbs with excitement. The array of titles is vast, offering live dealer games that immerse you. Plus 200 free spins to start strong. Professional and helpful assistance. Payments are secure and reliable, nevertheless extra rewards would be fantastic. Broadly speaking, Wazamba Casino provides guaranteed enjoyment for those who enjoy crypto ! Moreover the site is fast and responsive, adds a layer of excitement. Notably crypto-friendly banking options, offering more ways to win.
https://wazambagr.com/|
Je suis ebloui par Bingoal Casino, c’est une plateforme qui foisonne de vigueur. Il existe une abondance de jeux envoutants, incluant des paris sportifs electrisants. Associe a des paris gratuits. Le service est operationnel 24/7, toujours pret a intervenir. Les paiements sont proteges et lisses, par moments des bonus plus diversifies seraient souhaitables. En synthese, Bingoal Casino merite une exploration approfondie pour ceux qui parient en crypto ! A mentionner l’interface est intuitive et raffinee, ce qui eleve chaque session a un niveau superieur. Egalement notable les evenements communautaires captivants, qui stimule l’engagement.
Voir l’offre|
Ich habe eine Leidenschaft fur NV Casino, es erzeugt eine Energie, die suchtig macht. Die Vielfalt der Titel ist atemberaubend, mit dynamischen Live-Sessions. Die Hilfe ist effizient und professionell, bietet klare Antworten. Die Gewinne kommen ohne Verzogerung, dennoch regelma?igere Promos waren super. Zusammengefasst, NV Casino ist ein Muss fur Gamer fur Spieler auf der Suche nach Action ! Daruber hinaus die Site ist schnell und elegant, fugt eine Prise Magie hinzu.
playnvcasino.de|
Je suis emerveille par Locowin Casino, ca offre un thrill incomparable. Le catalogue est abondant et multifacette, comprenant des jeux optimises pour les cryptos. Le bonus d’accueil est seduisant. Le suivi est impeccable, joignable a tout moment. Les retraits sont effectues rapidement, mais des offres plus genereuses ajouteraient de l’attrait. En bref, Locowin Casino est indispensable pour les joueurs pour les joueurs en quete d’excitation ! Ajoutons que la navigation est simple et plaisante, incite a prolonger l’experience. Egalement appreciable les paiements securises en crypto, propose des avantages personnalises.
DГ©marrer maintenant|
Je suis stupefait par Locowin Casino, on detecte une vibe folle. Le repertoire est opulent et multifacette, incluant des paris sportifs electrisants. Le bonus d’accueil est attractif. L’equipe d’assistance est remarquable, assurant un support premium. Les retraits sont realises promptement, mais des offres plus liberales ajouteraient de la valeur. Globalement, Locowin Casino merite une exploration approfondie pour ceux qui parient en crypto ! Ajoutons que la plateforme est esthetiquement remarquable, ajoute un confort notable. Un autre avantage cle les paiements securises en crypto, qui stimule l’engagement.
Apprendre en ligne|
J’adore l’ambiance de Casinia Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde d’elegance. Les options sont vastes comme un royaume, offrant des sessions live immersives. Plus un Bonus Crab pour demarrer. L’assistance est efficace et courtoise, offrant des reponses claires. Les paiements sont securises et fluides, parfois quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient bienvenus. Dans l’ensemble, Casinia Casino garantit du fun a chaque instant pour les amateurs de sensations fortes ! Notons aussi la navigation est simple et agreable, facilite une immersion totale. A noter egalement le programme VIP avec 5 niveaux, assure des transactions fiables.
AccГ©der maintenant|
Je suis surpris par Locowin Casino, ca transporte dans un univers envoutant. La gamme de jeux est spectaculaire, offrant des sessions live intenses. Associe a des tours gratuits sans wager. Les agents reagissent avec promptitude, assurant un support premium. Les benefices arrivent sans latence, bien que quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient apprecies. En synthese, Locowin Casino fournit une experience ineffacable pour les enthousiastes de casino en ligne ! Par ailleurs la navigation est simple et engageante, ajoute un confort notable. Un autre avantage cle les paiements securises en crypto, offre des privileges sur mesure.
Visiter le contenu|
официальный сайт ПокерОК
ПокерОК сайт
J’ai une passion debordante pour Bingoal Casino, ca plonge dans un univers envoutant. La diversite des titres est stupefiante, proposant des jeux de table immersifs. Pour un demarrage en force. L’assistance est efficace et professionnelle, joignable a tout moment. Le processus est simple et efficace, bien que des bonus plus diversifies seraient apprecies. Dans l’ensemble, Bingoal Casino est une plateforme qui impressionne pour ceux qui aiment parier en crypto ! A noter l’interface est intuitive et elegante, facilite une immersion totale. Particulierement notable les paiements securises en crypto, assure des transactions fiables.
Savoir plus|
J’ai une passion ardente pour Bingoal Casino, c’est une plateforme qui foisonne de vigueur. La gamme des titres est stupefiante, offrant des sessions live intenses. Doublement des depots jusqu’a 200 €. Le service est operationnel 24/7, toujours pret a intervenir. Les operations sont solides et veloces, cependant des offres plus liberales ajouteraient de la valeur. En synthese, Bingoal Casino est une plateforme qui excelle pour les enthousiastes de casino en ligne ! Ajoutons que l’interface est intuitive et raffinee, stimule le desir de revenir. Particulierement attractif les options de paris sportifs etendues, offre des privileges sur mesure.
En savoir sur le sujet|
tripskan Tripscan трипскан – двуязычное представление названия сервиса, предполагающее охват аудитории, говорящей как на английском, так и на русском языках. TripScan/Трипскан, вероятно, является многофункциональной платформой для путешественников, предлагающей широкий спектр услуг, включающих поиск и сравнение цен на авиабилеты и отели, планирование маршрутов, бронирование экскурсий и трансферов, а также получение информации о визовых требованиях и других аспектах подготовки к путешествию. Данный сервис стремится предоставить пользователям все необходимые инструменты для организации комфортного и безопасного путешествия в любой уголок мира.
Je suis absolument captive par Bingoal Casino, ca plonge dans un univers envoutant. La diversite des titres est stupefiante, comprenant des jeux adaptes aux cryptos. Amplifiant l’experience initiale. Les agents repondent avec celerite, avec une aide precise et rapide. Les gains arrivent sans retard, parfois plus de promos regulieres seraient un plus. En bref, Bingoal Casino garantit du plaisir a chaque instant pour les passionnes de jeux modernes ! Par ailleurs le design est moderne et fluide, facilite une immersion totale. Egalement remarquable les paiements securises en crypto, renforce le sentiment de communaute.
DГ©bloquer plus|
Ich bin beeindruckt von SpinBetter Casino, es ist eine Erfahrung, die wie ein Wirbelsturm pulsiert. Es wartet eine Fulle spannender Optionen, mit dynamischen Tischspielen. Die Agenten sind blitzschnell, mit praziser Unterstutzung. Die Zahlungen sind sicher und smooth, trotzdem regelma?igere Aktionen waren toll. Alles in allem, SpinBetter Casino ist eine Plattform, die uberzeugt fur Casino-Liebhaber ! Daruber hinaus die Navigation ist kinderleicht, gibt den Anreiz, langer zu bleiben. Hervorzuheben ist die Vielfalt an Zahlungsmethoden, die Vertrauen schaffen.
spinbettercasino.de|
J’ai une passion ardente pour Bingoal Casino, c’est une plateforme qui foisonne de vigueur. L’eventail de jeux est extraordinaire, comprenant des jeux optimises pour les cryptos. Le bonus d’inscription est seduisant. Le suivi est exemplaire, toujours pret a intervenir. Les retraits sont realises promptement, cependant des incitations additionnelles seraient un benefice. En synthese, Bingoal Casino fournit une experience ineffacable pour les joueurs a la recherche d’aventure ! De surcroit le design est contemporain et lisse, ajoute un confort notable. Un plus significatif le programme de fidelite avec des niveaux VIP, garantit des transactions securisees.
AccГ©der au site|
Je suis accro a Locowin Casino, c’est une plateforme qui bouillonne d’energie. Il y a une multitude de jeux excitants, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Accompagne de tours gratuits sans wager. Le support client est exceptionnel, toujours pret a aider. Les transactions sont fiables et rapides, neanmoins des recompenses supplementaires seraient un atout. Au final, Locowin Casino offre une experience memorable pour les amateurs de sensations fortes ! De plus le site est rapide et attrayant, donne envie de prolonger l’experience. Un autre atout majeur le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, renforce le sentiment de communaute.
Entrer maintenant|
J’ai un engouement sincere pour Locowin Casino, il delivre une experience unique. Les alternatives sont incroyablement etendues, proposant des jeux de table immersifs. Pour un lancement puissant. Le service est operationnel 24/7, proposant des reponses limpides. La procedure est aisee et efficace, de temps a autre des bonus plus diversifies seraient souhaitables. Tout compte fait, Locowin Casino merite une exploration approfondie pour ceux qui parient en crypto ! De surcroit l’interface est intuitive et raffinee, stimule le desir de revenir. Particulierement attractif les paiements securises en crypto, renforce le sens de communaute.
Visiter l’offre|
I’m totally obsessed with Astronaut Crash by 100HP Gaming, it delivers edge-of-your-seat tension. The multiplier climbs with nail-biting suspense, with customizable bet sizes from $0.10 to $150. Instant demo mode for practice. Support is lightning-fast and helpful, providing clear multiplier histories. Low fees on high-volume wins, however more bonus rounds could add variety. All things considered, Astronaut Crash stands out in 100HP’s lineup for crypto gamblers ! Plus the sound design amps the tension, simplifying bet adjustments. Standout element tournaments for competitive crashes, ensures fast and fee-free payouts.
https://astronaut-crashgame777.com/|
dodge ram trx технические характеристики купить додж – это приобрести автомобиль с брутальным дизайном и мощными двигателями, предлагающий незабываемые ощущения от вождения и привлекающий внимание своим харизматичным внешним видом.
Флойд Мейвезердин ар бир беттеши чоң шоу катары кабыл алынат. Флойд Мейвезер жеңиштеринин саны боюнча рекорд койгон. Флойд Мейвезердин акыркы беттештери жана жыйынтыктары Флойд Мейвезер рекорд бөлүмүндө жарыяланган.
Анын фамилиясы дүйнөлүк брендге айланган. Флойд Мейвезер спорт тарыхына кирген аттардын бири. Флойд Мейвезердин карьерасы көп жылдык эмгектин натыйжасы.
Флойд Мейвезер – тартиптин жана күчтүн символу.
Флойд Мейвезер ар дайым өз максатына жеткен. Анын фанаттары дүйнөнүн бардык бурчунда бар. Флойд Мейвезер ар дайым жаңы рекорддорду жарата берет.
J’aime l’atmosphere unique de Bingoal Casino, il procure une odyssee unique. L’eventail de jeux est spectaculaire, avec des slots innovants et thematises. Pour un lancement puissant. Le suivi est exemplaire, avec une assistance exacte et veloce. Les benefices arrivent sans latence, cependant quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient apprecies. En synthese, Bingoal Casino est essentiel pour les amateurs pour ceux qui parient en crypto ! A mentionner le design est contemporain et lisse, ajoute un confort notable. Un autre avantage cle les evenements communautaires captivants, offre des privileges sur mesure.
Aller lГ -bas|
hip
Ich bin beeindruckt von SpinBetter Casino, es fuhlt sich an wie ein Strudel aus Freude. Es gibt eine unglaubliche Auswahl an Spielen, mit dynamischen Tischspielen. Der Kundenservice ist ausgezeichnet, bietet klare Losungen. Die Transaktionen sind verlasslich, obwohl zusatzliche Freispiele waren ein Highlight. Zusammengefasst, SpinBetter Casino ist absolut empfehlenswert fur Adrenalin-Sucher ! Au?erdem die Plattform ist visuell ein Hit, was jede Session noch besser macht. Hervorzuheben ist die Sicherheit der Daten, die das Spielen noch angenehmer machen.
spinbettercasino.de|
J’ai une passion ardente pour Bingoal Casino, ca procure un thrill exceptionnel. Le repertoire est luxuriant et multifacette, avec des slots innovants et thematises. Doublement des depots jusqu’a 200 €. Les agents reagissent avec promptitude, avec une assistance exacte et veloce. Les operations sont solides et veloces, bien que des incitations additionnelles seraient un benefice. En fin de compte, Bingoal Casino est essentiel pour les amateurs pour les aficionados de jeux contemporains ! En outre la navigation est simple et engageante, stimule le desir de revenir. Egalement notable les options de paris sportifs etendues, qui stimule l’engagement.
Aller pour les dГ©tails|
Je suis impressionne par Casinia Casino, c’est une plateforme qui rayonne de luxe. La selection de jeux est royale, avec des slots thematiques et innovants. Plus un Bonus Crab pour demarrer. Le suivi est impeccable, avec une aide precise. Les retraits sont rapides comme l’eclair, cependant quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient bienvenus. En resume, Casinia Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs pour les passionnes de jeux modernes ! Notons aussi le site est rapide et attrayant, ajoute une touche de luxe. Un autre atout majeur le programme VIP avec 5 niveaux, renforce le sentiment de communaute.
Voir tout de suite|
Je suis epate par Locowin Casino, on ressent une vibe delirante. Le catalogue est riche et diversifie, incluant des paris sportifs palpitants. Le bonus de bienvenue est attractif. Le service est disponible 24/7, joignable a toute heure. Le processus est simple et efficace, mais des bonus plus varies seraient bienvenus. Dans l’ensemble, Locowin Casino est une plateforme qui dechire pour les fans de casino en ligne ! Ajoutons que la plateforme est visuellement top, ajoute une touche de confort. Egalement appreciable le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, qui booste l’engagement.
Profiter de l’offre|
I’m wildly enthusiastic about Astronaut Crash by 100HP Gaming, it mimics a high-altitude adrenaline surge. The rocket’s ascent builds unbearable suspense, backed by robust RNG for true randomness. Balanced volatility for steady thrills. Chats connect in a flash, eager to troubleshoot mid-flight. Deals are fortified and frictionless, still wider stake limits for pros. Taking stock, Astronaut Crash redefines crash gaming standards for multiplier maniacs ! Bonus layout supports marathon marathons, cranking the ascent hype. Key highlight practice arena with live data, facilitates low-cost transfers.
astronaut-crashgame777.com|
Ich bin komplett hin und weg von SpinBetter Casino, es bietet einen einzigartigen Kick. Das Angebot an Spielen ist phanomenal, mit dynamischen Tischspielen. Der Service ist von hoher Qualitat, bietet klare Losungen. Die Auszahlungen sind ultraschnell, gelegentlich regelma?igere Aktionen waren toll. In Kurze, SpinBetter Casino garantiert hochsten Spa? fur Spieler auf der Suche nach Action ! Hinzu kommt die Site ist schnell und stylish, gibt den Anreiz, langer zu bleiben. Ein weiterer Vorteil die Community-Events, die das Spielen noch angenehmer machen.
https://spinbettercasino.de/|
Je suis hypnotise par Casinia Casino, c’est une plateforme qui scintille de grandeur. Les options sont vastes comme un empire, offrant des sessions live captivantes. L’offre de bienvenue est somptueuse. Les agents repondent avec une rapidite fulgurante, joignable a toute heure. Les gains arrivent sans tarder, de temps a autre des bonus plus varies seraient un joyau. Dans l’ensemble, Casinia Casino est une plateforme qui trone en maitre pour les amateurs de casino en ligne ! Par ailleurs la navigation est intuitive comme un edit, incite a prolonger l’experience. A souligner aussi les tournois reguliers pour la rivalite, garantit des transactions fiables.
Commencer Г dГ©couvrir|
J’ai un faible pour Casinia Casino, ca procure un plaisir aristocratique. La variete des titres est majestueuse, avec des slots thematiques et innovants. Renforcant votre capital initial. L’assistance est efficace et courtoise, toujours pret a servir. Les gains arrivent sans delai, de temps en temps des offres plus genereuses ajouteraient du prestige. Dans l’ensemble, Casinia Casino vaut largement le detour pour les joueurs en quete d’excitation ! En prime la navigation est simple et fluide, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Un autre atout majeur les tournois reguliers pour la competition, qui booste l’engagement.
Tout trouver|
J’apprecie l’environnement de Locowin Casino, c’est une plateforme qui explose d’energie. Il y a une profusion de jeux captivants, comprenant des jeux adaptes aux cryptos. Pour un lancement puissant. Le suivi est exemplaire, assurant un support premium. Les operations sont solides et veloces, mais des bonus plus diversifies seraient souhaitables. En fin de compte, Locowin Casino est une plateforme qui excelle pour les joueurs a la recherche d’aventure ! De surcroit la plateforme est esthetiquement remarquable, ajoute un confort notable. A souligner aussi les paiements securises en crypto, garantit des transactions securisees.
Découvrir l’avis|
I’m completely enthralled with Wazamba Casino, it’s a journey that resonates with mystery. The choices are broad and multifaceted, boasting over 5,000 games from 100+ providers. Boosting your playtime. Maintaining seamless sessions. Operations are straightforward, yet offers could be more lavish. Concluding, Wazamba Casino delivers unmatched fun for crypto users ! Furthermore the layout is user-friendly and thematic, heightening game immersion. Particularly impressive secure crypto payment methods, providing ongoing rewards.
https://wazambagr.com/|
Изготовление Металлоконструкций Металлические Здания Металлические здания – это быстровозводимые и экономичные конструкции, которые широко используются в различных отраслях промышленности и строительства. Наша компания предлагает проектирование, изготовление и монтаж металлических зданий любой сложности, включая склады, производственные цеха, торговые центры, ангары и другие объекты. Мы используем высококачественный металлопрокат и современные технологии строительства, обеспечивающие прочность, надежность и долговечность зданий. Наши здания могут быть утеплены сэндвич-панелями или другими материалами, обеспечивающими комфортные условия эксплуатации в любое время года. Мы предлагаем широкий выбор архитектурных решений, позволяющих создать уникальный и привлекательный внешний вид здания. Выбирая нас, вы выбираете быстрое, надежное и экономичное решение для вашего бизнеса.
Hey there! Do you use Twitter? I’d like to follow you if that would be okay. I’m absolutely enjoying your blog and look forward to new posts.
kraken маркетплейс
telecharger 1xbet pour android melbet – paris sportif
1xbet cameroun apk parier foot en ligne
telecharger 1xbet telecharger 1xbet pour android
bs2best зеркало В курсе ли ты, что сотрясает самые глубины тёмной сети? Blacksprut — это не просто название. Это новый уровень в обеспечении анонимности, оперативности и безопасности сделок. Посети bs2best.at — там тебе откроются двери в мир, о котором другие предпочитают умалчивать. Получи доступ к информации, которую тщательно скрывают от общего внимания. Только для тех, кто понимает и разбирается. Без возможности обнаружения. Без каких-либо уступок. Только Blacksprut. Не упусти свой шанс стать одним из первых — bs2best.at уже готов принять тебя в свои ряды. Готов ли ты к тому, что узнаешь?
Ich bin abhangig von SpinBetter Casino, es ist eine Erfahrung, die wie ein Wirbelsturm pulsiert. Die Titelvielfalt ist uberwaltigend, mit innovativen Slots und fesselnden Designs. Die Hilfe ist effizient und pro, bietet klare Losungen. Der Ablauf ist unkompliziert, dennoch zusatzliche Freispiele waren ein Highlight. Alles in allem, SpinBetter Casino ist eine Plattform, die uberzeugt fur Online-Wetten-Fans ! Daruber hinaus die Plattform ist visuell ein Hit, fugt Magie hinzu. Hervorzuheben ist die Sicherheit der Daten, die das Spielen noch angenehmer machen.
https://spinbettercasino.de/|
J’ai une passion debordante pour Locowin Casino, ca offre un thrill incomparable. Les options sont incroyablement vastes, proposant des jeux de table immersifs. Accompagne de paris gratuits. Le service est disponible 24/7, avec une aide precise et rapide. Les transactions sont fiables et rapides, parfois plus de promos regulieres seraient un plus. Pour conclure, Locowin Casino merite une visite pour les passionnes de jeux modernes ! En bonus l’interface est intuitive et elegante, facilite une immersion totale. Un autre point fort les options de paris sportifs variees, renforce le sentiment de communaute.
Visiter la plateforme|
Je suis fascine par Locowin Casino, on detecte une vibe folle. Il y a une profusion de jeux captivants, avec des slots au style innovant. Doublement des depots jusqu’a 1850 €. Le service est operationnel 24/7, toujours pret a intervenir. Les operations sont solides et veloces, bien que des bonus plus diversifies seraient souhaitables. Tout compte fait, Locowin Casino merite une exploration approfondie pour les enthousiastes de casino en ligne ! A mentionner la plateforme est esthetiquement remarquable, ce qui eleve chaque session a un niveau superieur. Un autre avantage cle les evenements communautaires captivants, offre des privileges sur mesure.
Voir toutes les infos|
Je suis completement obsede par Locowin Casino, c’est une plateforme qui explose d’energie. Il y a une profusion de jeux captivants, incluant des paris sportifs electrisants. Renforcant l’experience de depart. Les agents reagissent avec promptitude, toujours pret a intervenir. Les paiements sont proteges et lisses, mais plus de promotions frequentes seraient un atout. En fin de compte, Locowin Casino est essentiel pour les amateurs pour les joueurs a la recherche d’aventure ! Par ailleurs la navigation est simple et engageante, stimule le desir de revenir. A souligner aussi le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, qui stimule l’engagement.
Aller au site|
Tenho uma paixao intensa por BETesporte Casino, sinto uma energia de estadio. A variedade de titulos e impressionante, incluindo apostas esportivas palpitantes. Fortalece seu saldo inicial. O suporte ao cliente e de elite, garantindo atendimento de alto nivel. Os ganhos chegam sem demora, no entanto mais apostas gratis seriam incriveis. Em sintese, BETesporte Casino e uma plataforma que domina o campo para amantes de apostas esportivas ! Acrescentando que a interface e fluida e energetica, aumenta o prazer de apostar. Muito atrativo os torneios regulares para rivalidade, fortalece o senso de comunidade.
Ler mais|
https://bs2tsite4.lat
Je suis completement fou de Locowin Casino, ca procure un plaisir intense. Il y a une multitude de jeux excitants, offrant des sessions live dynamiques. Accompagne de tours gratuits sans wager. L’assistance est efficace et pro, garantissant un support de qualite. Les transactions sont fiables et rapides, de temps en temps quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient cool. Pour conclure, Locowin Casino garantit du fun a chaque instant pour les joueurs en quete d’excitation ! Cerise sur le gateau le site est rapide et attrayant, ajoute une touche de confort. Particulierement interessant les options de paris sportifs variees, qui booste l’engagement.
Trouver le meilleur|
Je suis surpris par Locowin Casino, on detecte une vibe folle. Le repertoire est opulent et multifacette, incluant des paris sportifs electrisants. Associe a des tours gratuits sans wager. Le suivi est exemplaire, assurant un support premium. Les operations sont solides et veloces, de temps a autre des bonus plus diversifies seraient souhaitables. Globalement, Locowin Casino garantit du divertissement constant pour les enthousiastes de casino en ligne ! Ajoutons que la navigation est simple et engageante, facilite une immersion complete. Un autre avantage cle les paiements securises en crypto, garantit des transactions securisees.
Touchez ici|
J’aime l’atmosphere de Locowin Casino, ca transporte dans un univers envoutant. La gamme de jeux est spectaculaire, proposant des jeux de table immersifs. Doublement des depots jusqu’a 1850 €. L’aide est performante et experte, assurant un support premium. Les paiements sont proteges et lisses, par moments quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient apprecies. En synthese, Locowin Casino garantit du divertissement constant pour ceux qui parient en crypto ! En outre l’interface est intuitive et raffinee, ajoute un confort notable. Particulierement attractif les evenements communautaires captivants, renforce le sens de communaute.
Cliquer et voir|
Estou completamente apaixonado por BETesporte Casino, proporciona uma aventura eletrizante. A selecao de jogos e fenomenal, oferecendo jogos de mesa envolventes. O bonus de boas-vindas e empolgante. O servico esta disponivel 24/7, oferecendo respostas claras. Os ganhos chegam sem atraso, embora bonus mais variados seriam um golaco. No geral, BETesporte Casino e essencial para apostadores para jogadores em busca de emocao ! Vale destacar a navegacao e intuitiva e rapida, instiga a prolongar o jogo. Um diferencial importante os pagamentos seguros em cripto, assegura transacoes confiaveis.
Explorar agora|
Estou completamente vidrado por F12.Bet Casino, parece uma pista de alta octanagem cheia de adrenalina. O leque do cassino e um asfalto de delicias. incluindo jogos de mesa com um toque de velocidade. Os agentes sao rapidos como um pit crew. oferecendo respostas claras como um painel. Os pagamentos sao lisos como asfalto. porem mais giros gratis seriam supersonicos. Para encurtar, F12.Bet Casino promete uma diversao que e uma ultrapassagem para os fas de adrenalina supersonica! E mais a plataforma acelera com um visual veloz. tornando cada sessao ainda mais acelerada.
f12 bet casino|
Galera, resolvi contar como foi no 4PlayBet Casino porque me pegou de surpresa. A variedade de jogos e bem acima da media: poquer estrategico, todos bem otimizados ate no celular. O suporte foi amigavel, responderam em minutos pelo chat, algo que passa seguranca. Fiz saque em PIX e o dinheiro entrou muito rapido, ponto fortissimo. Se tivesse que criticar, diria que seria legal torneios de slots, mas isso nao estraga a experiencia. Enfim, o 4PlayBet Casino me conquistou. Vale experimentar.
baixar 4play bet|
Amo a energia de PlayPIX Casino, oferece um prazer eletrizante. A variedade de titulos e estonteante, com slots de design inovador. Eleva a experiencia de jogo. A assistencia e eficiente e amigavel, com suporte rapido e preciso. O processo e simples e elegante, de vez em quando recompensas extras seriam eletrizantes. Resumindo, PlayPIX Casino oferece uma experiencia memoravel para amantes de emocoes fortes ! Adicionalmente o site e rapido e cativante, tornando cada sessao mais vibrante. Muito atrativo o programa VIP com niveis exclusivos, fortalece o senso de comunidade.
Descobrir mais|
online broadcast
J’ai un coup de foudre pour Locowin Casino, on ressent une vibe delirante. La variete des titres est impressionnante, offrant des sessions live dynamiques. Amplifiant l’experience initiale. Les agents repondent avec rapidite, avec une aide precise et rapide. Les paiements sont securises et fluides, parfois des offres plus genereuses ajouteraient du piquant. En bref, Locowin Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs pour les joueurs en quete d’excitation ! Ajoutons que le design est moderne et fluide, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Un plus non negligeable les tournois reguliers pour la competition, assure des transactions fiables.
Essayer maintenant|
J’adore l’eclat vibrant de Casinia Casino, il offre une aventure etincelante. Les options sont vastes comme un ciel etoile, proposant des jeux de table raffines. L’offre de bienvenue est eclatante. Les agents repondent comme une etoile filante, offrant des solutions cristallines. Les paiements sont securises et fluides, mais plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient de l’eclat. Pour conclure, Casinia Casino merite une exploration eblouissante pour les joueurs en quete d’eclat ! A noter la plateforme scintille comme une etoile, ce qui rend chaque session plus eclatante. Un atout cle les paiements securises en crypto, offre des privileges continus.
Explorer davantage|
Je suis totalement seduit par Locowin Casino, ca transporte dans un monde captivant. Il y a une multitude de jeux excitants, offrant des sessions live dynamiques. Doublement des depots jusqu’a 1850 €. Le service est disponible 24/7, avec une aide precise et rapide. Les gains arrivent sans delai, cependant des recompenses supplementaires seraient un atout. En resume, Locowin Casino est une plateforme qui dechire pour les joueurs en quete d’excitation ! Notons aussi l’interface est intuitive et stylee, ajoute une touche de confort. Particulierement interessant les paiements securises en crypto, offre des recompenses continues.
DГ©couvrir la page|
Acho simplesmente fenomenal Brazino Casino, tem um ritmo de jogo que reluz como um coral. O catalogo de jogos e um oceano de prazeres. incluindo mesas com charme subaquatico. O atendimento e solido como um coral. assegurando apoio sem turbulencia aquatica. O processo e claro e sem tempestades. mas mais recompensas fariam o coracao nadar. Ao final, Brazino Casino e uma onda de adrenalina para os fas de adrenalina marinha! De bonus o visual e uma explosao de corais. tornando cada sessao ainda mais aquatica.
baixa brazino777 apk|
Estou alucinado com PlayPix Casino, e uma explosao de diversao que carrega como um buffer. O catalogo de jogos e uma tela de emocoes. incluindo jogos de mesa com um toque cibernetico. Os agentes sao rapidos como um download. disponivel por chat ou e-mail. Os ganhos chegam rapido como um render. porem mais recompensas fariam o coracao pixelar. Ao final, PlayPix Casino promete uma diversao que e um glitch para os amantes de cassinos online! Alem disso o layout e vibrante como um codigo. criando uma experiencia de cassino cibernetica.
robo roleta a playpix|
Estou alucinado com Fogo777 Casino, explode com uma vibe de cassino flamejante. As escolhas sao vibrantes como chamas. com caca-niqueis modernos que hipnotizam como fogos. O atendimento esta sempre ativo 24/7. garantindo suporte direto e sem cinzas. Os saques sao velozes como um ritual de fogo. ocasionalmente mais recompensas fariam o coracao queimar. No geral, Fogo777 Casino e um altar de emocoes para quem curte apostar com estilo flamejante! E mais o layout e vibrante como uma tocha. adicionando um toque de fogo ao cassino.
fogo777 Г© confiГЎvel|
Je suis envoute par BankOnBet Casino, il propose une aventure de casino qui accumule comme un compte en banque. La selection du casino est une pile de plaisirs. proposant des slots de casino a theme financier. The support is as solid as a vault door. garantissant un aide sans fuites. The process is clear like a balance sheet. parfois plus de tours gratuits au casino ce serait un investissement. Globalement, BankOnBet Casino c’est un casino a miser sans hesiter pour les joueurs qui aiment parier avec style au casino! Plus le design est elegant comme un vault. ajoute une touche de luxe bancaire au casino.
bankonbet kod promocyjny bez depozytu|
Fiquei impressionado com BETesporte Casino, sinto um rugido de adrenalina. A selecao de jogos e fenomenal, com sessoes ao vivo cheias de energia. O bonus de boas-vindas e empolgante. O suporte ao cliente e excepcional, garantindo atendimento de alto nivel. As transacoes sao confiaveis, embora promocoes mais frequentes dariam um toque extra. Resumindo, BETesporte Casino vale uma aposta certa para jogadores em busca de emocao ! Alem disso a plataforma e visualmente impactante, facilita uma imersao total. Outro destaque os eventos comunitarios envolventes, que impulsiona o engajamento.
Continuar lendo|
Estou completamente apaixonado por PlayPIX Casino, sinto um pulsar selvagem. A selecao de jogos e fenomenal, com sessoes ao vivo cheias de energia. 100% ate €500 + rodadas gratis. A assistencia e eficiente e amigavel, oferecendo respostas claras. Os ganhos chegam sem atraso, embora ofertas mais generosas seriam bem-vindas. Em sintese, PlayPIX Casino garante diversao constante para quem aposta com cripto ! Acrescentando que a interface e fluida e estilosa, aumenta o prazer de jogar. Um diferencial significativo os eventos comunitarios envolventes, que aumenta o engajamento.
Ver o site|
официальный сайт ПокерОК
играть на сайте ПокерОК
bs2web at В курсе ли ты, что сотрясает самые глубины тёмной сети? Blacksprut — это не просто название. Это новый уровень в обеспечении анонимности, оперативности и безопасности сделок. Посети bs2best.at — там тебе откроются двери в мир, о котором другие предпочитают умалчивать. Получи доступ к информации, которую тщательно скрывают от общего внимания. Только для тех, кто понимает и разбирается. Без возможности обнаружения. Без каких-либо уступок. Только Blacksprut. Не упусти свой шанс стать одним из первых — bs2best.at уже готов принять тебя в свои ряды. Готов ли ты к тому, что узнаешь?
новый фитнес клуб фитнес клуб москва цены
fan stream
Me encantei pelo ritmo de BR4Bet Casino, parece um festival de luzes cheio de adrenalina. As opcoes sao ricas e reluzem como luzes. oferecendo sessoes ao vivo que reluzem como chamas. Os agentes sao rapidos como um raio de farol. respondendo veloz como uma chama acesa. Os ganhos chegam rapido como uma lanterna. de vez em quando mais bonus regulares seriam radiantes. No fim das contas, BR4Bet Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os faroleiros do cassino! De lambuja a plataforma reluz com um visual brilhante. transformando cada aposta em uma aventura iluminada.
br4bet Г© confiavel|
Sou viciado no role de OshCasino, e um cassino online que detona como um vulcao. Os titulos do cassino sao um espetaculo vulcanico, oferecendo sessoes de cassino ao vivo que sao uma chama. Os agentes do cassino sao rapidos como um estalo, com uma ajuda que e puro calor. Os pagamentos do cassino sao lisos e blindados, porem mais recompensas no cassino seriam um diferencial vulcanico. No geral, OshCasino garante uma diversao de cassino que e um vulcao para quem curte apostar com estilo no cassino! E mais a plataforma do cassino detona com um visual que e puro magma, faz voce querer voltar pro cassino como uma erupcao.
code promo osh|
Ich bin verblufft von NV Casino, es fuhlt sich an wie ein Wirbel aus Freude. Es gibt eine beeindruckende Auswahl an Optionen, mit Slots im innovativen Design. Der Support ist von herausragender Qualitat, immer bereit zu helfen. Der Prozess ist unkompliziert, ab und zu regelma?igere Promos waren super. Insgesamt, NV Casino bietet unvergesslichen Spa? fur Casino-Enthusiasten ! Au?erdem die Navigation ist kinderleicht, macht die Erfahrung flussiger.
playnvcasino.de|
Estou completamente empolgado com BETesporte Casino, sinto uma energia de estadio. A variedade de titulos e impressionante, oferecendo jogos de mesa dinamicos. Com uma oferta inicial para impulsionar. O suporte ao cliente e de elite, com suporte preciso e rapido. O processo e simples e direto, embora ofertas mais generosas dariam um toque especial. No geral, BETesporte Casino garante diversao a cada rodada para entusiastas de jogos modernos ! Acrescentando que a interface e fluida e energetica, adiciona um toque de estrategia. Um diferencial importante os eventos comunitarios envolventes, proporciona vantagens personalizadas.
Descobrir agora|
UFCдеги рейтинги, рекорду жана статистикасы бир бетте чогултулуп, издөөнү жеңилдетет.
Жаңыланган постерлер жана расмий анонстар чыкканда, баракча дароо толукталат. ислам махачев бой смотреть Түз эфирге чейин анонс, кийин кыска обзор менен жыйынтык чыгарабыз. Ар бир раундга тез-тез жаңыртуу болот. Жеткиликтүү интервьюлардан цитаталарды чогултуп, мотивация жана даярдык жөнүндө баяндайбыз. Эгер ресми анонс чыкса, дата жана локация дароо жаңыланат. Беттешке чейинки форма, спарринг жана медициналык текшерүүлөр боюнча расмий шилтемелер бар.
Медиа бөлүмүндө айрым раунддардагы негизги эпизоддордун GIF/кыска видео талдоосу берилет. Кайсы раунддарда өзгөрүү болушу ыктымал экенин тенденцияларга карап белгилеп беребиз. Тарыхый моменттердин хронологиясы визуал карта түрүндө берилип, оңой кыдырып чыгасыз. Издөө функциясы боюнча ачкыч сөздөрдү киргизип, керектүү бөлүмгө тез өтүңүз.
Estou pirando total com JabiBet Casino, parece uma correnteza de diversao. A gama do cassino e simplesmente um maremoto, com slots de cassino unicos e empolgantes. O servico do cassino e confiavel e brabo, acessivel por chat ou e-mail. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como um redemoinho, mesmo assim mais recompensas no cassino seriam um diferencial brabo. Em resumo, JabiBet Casino e um cassino online que e uma onda gigante para os amantes de cassinos online! De bonus a navegacao do cassino e facil como surfar, aumenta a imersao no cassino como uma onda gigante.
jabibet app download|
Adoro o clima insano de PagolBet Casino, tem uma vibe de jogo que e pura eletricidade. Tem uma enxurrada de jogos de cassino irados, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino cheios de energia. O suporte do cassino ta sempre na ativa 24/7, dando solucoes na hora e com precisao. Os pagamentos do cassino sao lisos e blindados, mesmo assim mais bonus regulares no cassino seria top. Resumindo, PagolBet Casino oferece uma experiencia de cassino que e puro choque para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! Alem disso a plataforma do cassino detona com um visual que e puro trovao, aumenta a imersao no cassino a mil.
codigo promocional pagolbet|
Estou completamente apaixonado por BETesporte Casino, leva a um universo de apostas dinamico. O catalogo e vibrante e diversificado, suportando jogos compativeis com criptomoedas. 100% ate R$600 + apostas gratis. O acompanhamento e impecavel, acessivel a qualquer momento. O processo e simples e direto, as vezes ofertas mais generosas dariam um toque especial. Em sintese, BETesporte Casino vale uma aposta certa para quem usa cripto para jogar ! Alem disso o design e moderno e vibrante, adiciona um toque de estrategia. Igualmente impressionante os torneios regulares para rivalidade, que impulsiona o engajamento.
http://www.betesporte365.app|
https://pikman.info/ PR & Marketing Expertise: Data-Driven Marketing, Paid Search/SEM (Linkedin Ads, Facebook Ads, Google Ads, YouTube Ads, Yandex Ads, Bing Ads), Search Engine Optimization/SEO, Display, Retargeting, Social Media/SMM, Paid Media, Account Based Marketing/ABM, Digital Marketing/Strategy, Data Analytics, Customer Acquisition, Web Marketing, Business Development, Full Stack Marketing, Customer Journey, Content Marketing, A/B Split Testing, Budget Management, Conversational Marketing, Conversion Rate Optimization, Growth Marketing, Multi-Touch Attribution, Copywriting, Data Journalism, Content writing, Visual Storytelling, Brand Identity, Web Design UX/UI, Digital Media, Content Marketing, Demand Generation, Forecasting and Modeling.
social video
Acho simplesmente magnifico Richville Casino, da uma energia de cassino tao luxuosa quanto um trono. As opcoes de jogo no cassino sao ricas e reluzentes, com slots de cassino tematicos de luxo. Os agentes do cassino sao rapidos como um coche de gala, garantindo suporte de cassino direto e sem falhas. O processo do cassino e claro e sem intrigas, porem mais giros gratis no cassino seria opulento. Na real, Richville Casino promete uma diversao de cassino reluzente para os apaixonados por slots modernos de cassino! Alem disso a interface do cassino e fluida e brilha como um salao de baile, faz voce querer voltar ao cassino como um rei ao seu trono.
richville mi restaurants|
Estou pirando com RioPlay Casino, e um cassino online que samba como uma escola de carnaval. A gama do cassino e simplesmente um bloco de carnaval, com slots de cassino tematicos de festa. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e uma bateria de escola de samba, respondendo mais rapido que um batuque. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como um desfile na avenida, mas mais bonus regulares no cassino seria um arraso. Na real, RioPlay Casino vale demais sambar nesse cassino para quem curte apostar com gingado no cassino! Alem disso a navegacao do cassino e facil como um passo de carnaval, o que torna cada sessao de cassino ainda mais animada.
rioplay 2.0 download|
Galera, quero registrar aqui no 4PlayBet Casino porque superou minhas expectativas. A variedade de jogos e simplesmente incrivel: blackjack envolvente, todos funcionando perfeito. O suporte foi eficiente, responderam em minutos pelo chat, algo que vale elogio. Fiz saque em Ethereum e o dinheiro entrou na mesma hora, ponto fortissimo. Se tivesse que criticar, diria que mais brindes fariam falta, mas isso nao estraga a experiencia. Enfim, o 4PlayBet Casino tem diferencial real. Ja virou parte da minha rotina.
cassino 4play|
Fiquei impressionado com BETesporte Casino, transporta para um mundo de apostas vibrante. Ha uma multidao de jogos emocionantes, suportando jogos adaptados para criptos. 100% ate R$600 + apostas gratis. O acompanhamento e impecavel, acessivel a qualquer hora. Os ganhos chegam sem demora, de vez em quando bonus mais variados seriam um gol. Para finalizar, BETesporte Casino oferece uma experiencia inesquecivel para amantes de apostas esportivas ! Vale destacar a plataforma e visualmente impactante, aumenta o prazer de apostar. Notavel tambem o programa VIP com niveis exclusivos, que impulsiona o engajamento.
Ver os detalhes|
pop rock
Estou alucinado com PlayPix Casino, tem uma energia de jogo tao vibrante quanto um codigo binario em furia. A colecao e um codigo de entretenimento. oferecendo lives que explodem como overclock. O time do cassino e digno de um programador. com ajuda que renderiza como um glitch. Os saques sao velozes como um upload. entretanto mais bonus regulares seriam digitais. No fim das contas, PlayPix Casino garante um jogo que reluz como pixels para os apaixonados por slots modernos! De lambuja o site e uma obra-prima de estilo digital. transformando cada aposta em uma aventura pixelada.
sinais da roleta playpix|
Me encantei pelo nado de Brazino Casino, parece um abismo de adrenalina subaquatica. As escolhas sao vibrantes como um atol. com jogos adaptados para criptomoedas. O atendimento esta sempre ativo 24/7. disponivel por chat ou e-mail. Os ganhos chegam rapido como uma corrente. em alguns momentos mais bonus seriam um diferencial oceanico. Para encurtar, Brazino Casino promete uma diversao que e uma mare para os mergulhadores do cassino! Adicionalmente o design e fluido como uma onda. fazendo o cassino reluzir como um recife.
gerador de cГіdigos promocionais brazino777|
Estou completamente vidrado por SambaSlots Casino, tem uma vibe de jogo tao vibrante quanto um bloco de rua. O catalogo de jogos do cassino e uma folia total, com slots de cassino tematicos de festa. Os agentes do cassino sao rapidos como um passista, garantindo suporte de cassino direto e sem perder o ritmo. O processo do cassino e limpo e sem tropecos, porem queria mais promocoes de cassino que botam pra quebrar. No geral, SambaSlots Casino vale demais sambar nesse cassino para quem curte apostar com gingado no cassino! De lambuja o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo carioca, faz voce querer voltar ao cassino como num desfile sem fim.
la sambaslots casino code bonus 2021|
Je trouve absolument fantastique 7BitCasino, il offre une sensation de casino unique. La gamme de jeux est tout simplement impressionnante, proposant des jeux de table elegants et classiques. Le support est ultra-reactif et professionnel, joignable a toute heure. Les paiements sont fluides et securises, bien que les promotions pourraient etre plus genereuses, comme des offres de cashback plus avantageuses. En resume, 7BitCasino est un incontournable pour les passionnes de jeux numeriques ! En bonus la navigation est intuitive et rapide, ce qui intensifie le plaisir de jouer.
7bitcasino no deposit bonus codes|
официальный сайт ПокерОК
ПокерОК сайт
1xbet cameroun apk pariez sur le foot
https://bsmef.at
Estou alucinado com BR4Bet Casino, tem um ritmo de jogo que acende como uma tocha. O leque do cassino e um brilho de delicias. com jogos adaptados para criptomoedas. O atendimento e solido como um farol. com ajuda que ilumina como uma tocha. As transacoes sao faceis como um brilho. mas mais bonus seriam um diferencial reluzente. Em resumo, BR4Bet Casino e um cassino online que e um farol de diversao para os cacadores de vitorias reluzentes! Vale dizer o site e uma obra-prima de estilo radiante. criando uma experiencia de cassino reluzente.
plataforma br4bet|
Acho simplesmente intergalactico SpeiCasino, parece uma galaxia cheia de diversao estelar. As opcoes de jogo no cassino sao ricas e brilhantes como estrelas, oferecendo sessoes de cassino ao vivo que brilham como nebulosas. Os agentes do cassino sao rapidos como um cometa, dando solucoes na hora e com precisao. Os pagamentos do cassino sao lisos e blindados, as vezes as ofertas do cassino podiam ser mais generosas. Na real, SpeiCasino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! Alem disso a interface do cassino e fluida e reluz como uma aurora boreal, eleva a imersao no cassino a um nivel cosmico.
spei com|
Curto demais a vibracao de JonBet Casino, tem um ritmo de jogo que ecoa como um coral. O catalogo de jogos e uma camara de prazeres. com jogos adaptados para criptomoedas. O suporte e um eco de eficiencia. assegurando apoio sem dissonancias. Os ganhos chegam rapido como um eco. as vezes mais bonus seriam um diferencial ressonante. Na real, JonBet Casino e uma vibracao de adrenalina para os fas de adrenalina sonora! E mais o design e um espetaculo visual harmonico. tornando cada sessao ainda mais ressonante.
jonbet. bet.br|
Adoro o swing de BacanaPlay Casino, da uma energia de cassino que e pura purpurina. A gama do cassino e simplesmente um sambodromo de prazeres, com caca-niqueis de cassino modernos e contagiantes. O suporte do cassino ta sempre na ativa 24/7, dando solucoes na hora e com precisao. Os pagamentos do cassino sao lisos e blindados, de vez em quando mais recompensas no cassino seriam um diferencial festivo. Em resumo, BacanaPlay Casino vale demais sambar nesse cassino para quem curte apostar com gingado no cassino! Vale dizer tambem o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo carioca, adiciona um toque de folia ao cassino.
melhores slots bacanaplay|
Fiquei fascinado com PlayPIX Casino, proporciona uma aventura eletrizante. A selecao de jogos e fenomenal, oferecendo jogos de mesa envolventes. Com uma oferta inicial para impulsionar. O suporte ao cliente e excepcional, sempre pronto para resolver. As transacoes sao confiaveis, embora recompensas extras seriam eletrizantes. No geral, PlayPIX Casino e uma plataforma que brilha para quem aposta com cripto ! Alem disso o design e moderno e vibrante, adiciona um toque de conforto. Outro destaque os pagamentos seguros em cripto, oferece recompensas continuas.
Navegar no site|
blsp at Заинтригован, что вызывает резонанс в тёмных закоулках сети? Blacksprut — это не просто наименование, это воплощение идеала анонимности, стремительной работы и непоколебимой уверенности. Отправляйся на bs2best.at — в обитель, где раскрывают секреты, о которых предпочитают молчать. Здесь тебе станет доступно сокровенное знание, охраняемое от непосвященных. Исключительно для тех, кто понимает суть. Никаких улик. Никаких соглашений. Только Blacksprut. Не упусти драгоценную возможность стать пионером — bs2best.at распахнул врата для тех, кто ищет истину. Хватит ли тебе отваги заглянуть правде в лицо?
Amo a energia de BETesporte Casino, proporciona uma aventura cheia de emocao. O catalogo e vibrante e diversificado, oferecendo jogos de mesa dinamicos. O bonus de boas-vindas e empolgante. O suporte ao cliente e excepcional, oferecendo respostas claras. Os ganhos chegam sem atraso, contudo promocoes mais frequentes dariam um toque extra. Para finalizar, BETesporte Casino e essencial para apostadores para fas de cassino online ! Alem disso o site e veloz e envolvente, instiga a prolongar o jogo. Notavel tambem os torneios regulares para rivalidade, oferece recompensas continuas.
Saber mais|
virtual meet
Achou loucamente incrivel DazardBet Casino, tem uma vibe de jogo alucinante. A selecao de titulos do cassino e de outro mundo, com jogos de cassino perfeitos para criptomoedas. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e fora da curva, dando solucoes claras e na hora. Os saques no cassino sao rapidos como um foguete, de vez em quando mais recompensas no cassino seriam um baita diferencial. No geral, DazardBet Casino oferece uma experiencia de cassino inesquecivel para os amantes de cassinos online! De quebra a plataforma do cassino arrasa com um visual eletrizante, da um toque de classe ao cassino.
dazardbet login|
Ich bin total hingerissen von Richard Casino, es bietet ein Casino-Abenteuer, das wie ein Thron funkelt. Die Spielauswahl im Casino ist wie ein koniglicher Schatz, inklusive eleganter Casino-Tischspiele. Der Casino-Kundenservice ist wie ein koniglicher Hofstaat, mit Hilfe, die wie ein Thron majestatisch ist. Casino-Transaktionen sind simpel wie ein kaiserlicher Befehl, ab und zu mehr regelma?ige Casino-Boni waren furstlich. Alles in allem ist Richard Casino ein Online-Casino, das wie ein Palast strahlt fur Spieler, die auf majestatische Casino-Kicks stehen! Zusatzlich die Casino-Seite ist ein grafisches Meisterwerk, was jede Casino-Session noch prachtiger macht.
richard casino no deposit bonus code 2025|
Estou alucinado com SpellWin Casino, tem uma vibe de jogo tao fascinante quanto um grimorio antigo. A selecao de titulos do cassino e um caldeirao de emocoes, com slots de cassino tematicos de fantasia. O servico do cassino e confiavel e encantador, garantindo suporte de cassino direto e sem maldicoes. O processo do cassino e limpo e sem truques, de vez em quando queria mais promocoes de cassino que hipnotizam. Resumindo, SpellWin Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! Alem disso o design do cassino e um espetaculo visual encantado, adiciona um toque de encantamento ao cassino.
spellwin kasyno|
bs2web at Приготовься узнать, что взорвало тёмные глубины интернета. Blacksprut – это не просто бренд. Это новый эталон анонимности, головокружительной скорости и абсолютной надежности в онлайн-мире. Посети bs2best.at – место, где раскрывают секреты, о которых другие даже шепотом боятся говорить. Ты получишь эксклюзивный доступ к данным, которые тщательно скрывают от непосвященных. Только для тех, кто в теме и готов к большему. Ни одного следа в сети, никаких уступок – только бескомпромиссная анонимность с Blacksprut. Не упусти эту уникальную возможность – стань одним из первых, кто узнает правду. bs2best.at уже ждёт тебя. Готов ли ты увидеть то, что скрыто от большинства?
Ich bin fasziniert von SpinBetter Casino, es ist eine Erfahrung, die wie ein Wirbelsturm pulsiert. Es wartet eine Fulle spannender Optionen, mit aufregenden Sportwetten. Der Service ist von hoher Qualitat, immer parat zu assistieren. Die Transaktionen sind verlasslich, trotzdem mehr Rewards waren ein Plus. In Kurze, SpinBetter Casino ist absolut empfehlenswert fur Casino-Liebhaber ! Daruber hinaus die Navigation ist kinderleicht, gibt den Anreiz, langer zu bleiben. Ein weiterer Vorteil die Vielfalt an Zahlungsmethoden, die das Spielen noch angenehmer machen.
https://spinbettercasino.de/|
Ich bin total begeistert von Lapalingo Casino, es bietet ein Casino-Abenteuer, das wie ein Regenbogen funkelt. Die Auswahl im Casino ist ein echtes Spektakel, mit Live-Casino-Sessions, die wie ein Gewitter krachen. Der Casino-Support ist rund um die Uhr verfugbar, sorgt fur sofortigen Casino-Support, der beeindruckt. Casino-Zahlungen sind sicher und reibungslos, ab und zu mehr regelma?ige Casino-Boni waren ein Knaller. Zusammengefasst ist Lapalingo Casino ein Online-Casino, das wie ein Sturm begeistert fur Fans von Online-Casinos! Und au?erdem die Casino-Navigation ist kinderleicht wie ein Windhauch, Lust macht, immer wieder ins Casino zuruckzukehren.
lapalingo registro|
backstage connect
Tenho uma paixao ardente por PlayPIX Casino, leva a um universo de pura adrenalina. As opcoes sao amplas como um festival, oferecendo jogos de mesa envolventes. O bonus de boas-vindas e empolgante. O acompanhamento e impecavel, sempre pronto para resolver. O processo e simples e elegante, de vez em quando ofertas mais generosas seriam bem-vindas. No fim, PlayPIX Casino vale uma visita epica para entusiastas de jogos modernos ! Alem disso a navegacao e intuitiva e envolvente, adiciona um toque de conforto. Igualmente impressionante os pagamentos seguros em cripto, fortalece o senso de comunidade.
Ler mais|
This is very interesting, You are a very skilled blogger. I’ve joined your feed and look forward to seeking more of your fantastic post. Also, I’ve shared your web site in my social networks!
https://easystaffingmd.com/
Ich bin total begeistert von DrueGlueck Casino, es liefert einen einzigartigen Adrenalinkick. Die Auswahl im Casino ist einfach ein Knaller, mit modernen Casino-Slots, die fesseln. Der Casino-Kundenservice ist der Hammer, antwortet in Sekundenschnelle. Casino-Gewinne kommen wie der Blitz, ab und zu mehr regelma?ige Casino-Boni waren cool. Kurz gesagt ist DrueGlueck Casino ein Online-Casino, das alles sprengt fur die, die mit Stil im Casino wetten! Und au?erdem die Casino-Oberflache ist flussig und mega cool, das Casino-Erlebnis total intensiviert.
drueckglueck bewertung|
https://heyzine.com/flip-book/9c1f359b6d.html
J’adore l’elegance de Impressario Casino, ca transporte dans un monde gourmand. Les options sont vastes comme un menu etoile, incluant des paris sportifs distingues. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Le service est disponible 24/7, avec une aide precise. Les retraits sont fluides comme la Seine, bien que des recompenses additionnelles seraient royales. En bref, Impressario Casino vaut une visite sophistiquee pour les passionnes de jeux modernes ! De plus le site est rapide et attractif, donne envie de prolonger l’experience. Un plus les paiements securises en crypto, renforce le sentiment de communaute.
Visiter la page d’accueil|
J’ai une affection pour Impressario Casino, on ressent une ambiance delicate. La selection de jeux est somptueuse, incluant des paris sportifs distingues. Renforcant votre capital initial. L’assistance est efficace et professionnelle, offrant des reponses claires. Les retraits sont fluides comme la Seine, bien que plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du piquant. Dans l’ensemble, Impressario Casino vaut une visite sophistiquee pour les amateurs de sensations elegantes ! Par ailleurs la navigation est simple et gracieuse, facilite une immersion totale. A souligner les paiements securises en crypto, offre des recompenses continues.
Visiter la page web|
Je suis totalement envoute par BassBet Casino, ca plonge dans un monde de beats. Les options sont vastes comme un concert, proposant des jeux de table elegants. Amplifiant le plaisir de jeu. Le service est disponible 24/7, avec une aide precise. Les gains arrivent sans delai, de temps a autre quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient bien venus. Pour conclure, BassBet Casino vaut une jam session pour les joueurs en quete d’excitation ! De plus l’interface est fluide comme un solo, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Un autre atout les evenements communautaires engageants, qui booste l’engagement.
bassbetcasinologinfr.com|
J’ai une passion fluviale pour BassBet Casino, on ressent une ambiance de riviere. Le catalogue est riche et varie, proposant des jeux de table elegants. Amplifiant le plaisir de jeu. Le support est irreprochable, avec une aide precise. Les retraits sont fluides comme un delta, neanmoins plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du rythme. Pour conclure, BassBet Casino garantit un plaisir constant pour les fans de casino en ligne ! De plus le site est rapide et attractif, ajoute une touche de vitesse. Un plus les options de paris sportifs variees, propose des avantages personnalises.
bassbetcasinobonus777fr.com|
Je suis totalement envoute par Spinit Casino, on ressent une ambiance de livre. Il y a une profusion de jeux fascinants, offrant des sessions live immersives. Le bonus de bienvenue est magique. L’assistance est efficace et professionnelle, joignable a toute heure. Les retraits sont fluides comme un conte, de temps a autre des recompenses additionnelles seraient narratives. En bref, Spinit Casino vaut une lecture magique pour les passionnes de jeux modernes ! En bonus la plateforme est visuellement envoutante, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Un autre atout les paiements securises en crypto, renforce le sentiment de communaute.
https://spinitcasinologinfr.com/|
Je suis completement envoute par Olympe Casino, ca transporte dans un monde mythique. Les options sont vastes comme un pantheon, comprenant des jeux optimises pour les cryptos. Le bonus de bienvenue est divin. Le service est disponible 24/7, garantissant un support celeste. Les gains arrivent sans delai, cependant des offres plus genereuses seraient olympiennes. En bref, Olympe Casino garantit un plaisir divin pour les fans de casino en ligne ! En bonus l’interface est fluide comme un nectar, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Un atout olympien les tournois reguliers pour la competition, propose des avantages sur mesure.
https://olympefr.com/|
https://foxcoin.info/code-promo-1xbet-cote-divoire/
kraken сайт Кракен: Сущность и Альтернативы “Kraken” – это не просто платформа, это идеология, основанная на свободе слова, анонимности и обходе цензуры. Однако, стоит помнить, что в этом мире не существует абсолютной безопасности. Всегда есть риск быть разоблаченным, обманутым или столкнуться с последствиями своих действий. Перед тем как погрузиться в пучину ” кракен”, необходимо взвесить все “за” и “против”, оценить свои возможности и принять на себя ответственность за свой выбор.
трансы Екатеринбург Локальные Сообщества: Поддержка и Информация Эти каналы служат важным ресурсом для транс-сообщества. Здесь можно найти информацию о врачах, психологах, юристах и других специалистах, оказывающих поддержку транс-персонам. Каналы помогают в поиске дружелюбных мест, где можно безопасно и комфортно проводить время. Они также предоставляют платформу для обмена опытом, обсуждения проблем и просто для общения с людьми, которые понимают.
Hi there mates, how is everything, and what you would like to say on the topic of this article, in my view its genuinely amazing designed for me.
кэт казино зеркало
Je suis accro a BassBet Casino, ca plonge dans un monde de notes blues. Le catalogue est riche et varie, offrant des sessions live immersives. Renforcant votre capital initial. Le support est irreprochable, garantissant un support de qualite. Les gains arrivent sans delai, bien que des offres plus genereuses seraient blues. En bref, BassBet Casino offre une experience memorable pour les passionnes de jeux modernes ! A noter la plateforme est visuellement musicale, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Un plus les options de paris sportifs variees, qui booste l’engagement.
https://bassbetcasinologinfr.com/|
Роберт Левандовскинин статистикасы укмуштай — ал ар бир оюнда гол салат.
Роберт Левандовски денесин мыкты формада кармайт. Роберт Левандовски голдорунун саны ар жыл сайын өсүүдө. Левандовски өз өлкөсүнүн сыймыгы. Жаңылыктарды, статистиканы жана Роберт Левандовскинин акыркы интервьюларын robert-lewandowski-kg.com сайтынан көрүңүз. Левандовски Барселонада лидер болуп калды.
Левандовски спорттук тарбиянын маанисин ар дайым белгилейт. Левандовски спорттук формасын жоготпойт.
Роберт Левандовскинин чоң атасы тууралуу уламыштар айтылат. Роберт Левандовски карьерасын толук берилип өткөрөт.
J’ai un amour vibrant pour BassBet Casino, ca transporte dans un univers de beats. Il y a un flot de jeux captivants, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. Amplifiant l’excitation du jeu. Le support client est au top, garantissant un service de haute qualite. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, mais des recompenses supplementaires seraient vibrantes. Dans l’ensemble, BassBet Casino est un must pour les joueurs pour les amateurs de sensations vibrantes ! De plus l’interface est fluide comme un mix, donne envie de prolonger la fete. Un point fort les paiements securises en crypto, renforce la communaute.
bassbetcasinoappfr.com|
Je suis totalement illumine par BassBet Casino, on ressent une vibe lumineuse. Il y a un flot de jeux captivants, comprenant des jeux adaptes aux cryptos. Amplifiant l’excitation du jeu. Disponible 24/7 via chat ou email, avec une aide precise. Les gains arrivent sans attendre, mais des offres plus genereuses seraient lumineuses. Dans l’ensemble, BassBet Casino est une plateforme qui brille pour ceux qui parient avec des cryptos ! De plus la plateforme est visuellement fluorescente, donne envie de prolonger l’eclat. Particulierement cool les paiements securises en crypto, qui dynamise l’engagement.
bassbetcasinopromocodefr.com|
J’ai une passion devorante pour Monte Cryptos Casino, c’est une plateforme qui vibre comme un smart contract. Le catalogue est opulent et divers, offrant des sessions en direct immersives. Boostant votre capital initial. Disponible 24/7 via chat ou email, avec une aide rapide et fiable. Les gains arrivent sans delai, de temps a autre plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient l’experience. Pour conclure, Monte Cryptos Casino garantit un plaisir constant pour les adeptes de jeux modernes ! De plus l’interface est fluide comme un flux de donnees, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Egalement cool les evenements communautaires decentralises, qui booste l’engagement.
Lire plus loin|
Je suis charme par Impressario Casino, on ressent une ambiance delicate. La variete des titres est raffinee, proposant des jeux de table raffines. Avec des depots instantanes. Le support client est impeccable, avec une aide precise. Le processus est simple et elegant, parfois des offres plus genereuses seraient exquises. Dans l’ensemble, Impressario Casino garantit un plaisir constant pour les passionnes de jeux modernes ! En bonus la navigation est simple et gracieuse, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Particulierement interessant les evenements communautaires engageants, qui booste l’engagement.
Commencer Г lire|
Ich liebe die Atmosphare bei Snatch Casino, es verspricht ein einzigartiges Abenteuer. Das Portfolio ist vielfaltig und attraktiv, mit Spielen, die Krypto unterstutzen. Er gibt Ihnen einen Kickstart. Der Service ist absolut zuverlassig. Gewinne kommen sofort an, dennoch mehr Aktionen wurden das Erlebnis steigern. In Summe, Snatch Casino ist ein Ort, der begeistert. Au?erdem die Seite ist zugig und ansprechend, eine Note von Eleganz hinzufugt. Ein starkes Plus sind die sicheren Krypto-Transaktionen, kontinuierliche Belohnungen bieten.
https://snatch-casino.de/de-de/|
J’adore l’atmosphere mythique de Spinit Casino, c’est une plateforme qui tourbillonne comme un conte. Le catalogue est riche et varie, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Avec des depots instantanes. Le support client est enchante, joignable a toute heure. Les gains arrivent sans delai, de temps a autre des bonus plus varies seraient un chapitre. Pour conclure, Spinit Casino offre une experience memorable pour ceaux qui aiment parier en crypto ! Ajoutons que la plateforme est visuellement envoutante, ce qui rend chaque session plus enchantee. Egalement appreciable les evenements communautaires engageants, assure des transactions fiables.
spinitcasinobonusfr.com|
Je suis charme par Impressario Casino, ca transporte dans un monde gourmand. Il y a une abondance de jeux captivants, incluant des paris sportifs distingues. Amplifiant le plaisir de jeu. Les agents repondent avec courtoisie, avec une aide precise. Les gains arrivent sans delai, neanmoins quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient bien venus. Au final, Impressario Casino offre une experience memorable pour les fans de casino en ligne ! A noter la plateforme est visuellement somptueuse, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Particulierement interessant les paiements securises en crypto, qui booste l’engagement.
Entrer maintenant|
Je suis epoustoufle par BassBet Casino, ca offre un plaisir melodique. La selection de jeux est harmonieuse, offrant des sessions live immersives. Amplifiant l’excitation du jeu. Disponible 24/7 via chat ou email, joignable a tout moment. Les retraits sont fluides comme une note tenue, de temps en temps des recompenses supplementaires seraient vibrantes. Pour conclure, BassBet Casino est un must pour les joueurs pour ceux qui parient avec des cryptos ! Ajoutons que le design est moderne et soul, ajoute une touche de soul. Un point fort les tournois reguliers pour la competition, propose des avantages sur mesure.
https://bassbetcasinopromocodefr.com/|
J’ai une passion feerique pour Spinit Casino, c’est une plateforme qui tourbillonne comme un conte. La variete des titres est magique, incluant des paris sportifs dynamiques. Amplifiant le plaisir de jeu. Le service est disponible 24/7, offrant des reponses claires. Les gains arrivent sans delai, cependant des recompenses additionnelles seraient narratives. En resume, Spinit Casino garantit un plaisir constant pour les fans de casino en ligne ! Par ailleurs la navigation est simple et magique, facilite une immersion totale. Un autre atout le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, assure des transactions fiables.
https://spinitcasinobonusfr.com/|
Je suis fascine par Impressario Casino, il evoque un tapis rouge scintillant. Il y a une profusion de jeux captivants, proposant des jeux de table elegants. Boostant votre capital initial. Les agents repondent avec une classe rare, toujours pret a briller. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, bien que plus de promotions regulieres ajouteraient du prestige. Dans l’ensemble, Impressario Casino vaut une visite glamour pour les adeptes de jeux modernes ! En plus le site est rapide et envoutant, ajoute une touche de prestige. Un atout les evenements communautaires engageants, assure des transactions fiables.
Plonger dedans|
Je suis stupefait par Monte Cryptos Casino, ca offre un plaisir numerique unique. Il y a une profusion de jeux captivants, incluant des paris en direct dynamiques. Amplifiant l’experience de jeu. Disponible 24/7 via chat ou email, garantissant un service de pointe. Le processus est lisse comme un wallet, neanmoins des offres plus genereuses ajouteraient du charme. En resume, Monte Cryptos Casino est un must pour les fans de blockchain pour les adeptes de jeux modernes ! Ajoutons que l’interface est fluide comme un flux de donnees, facilite une immersion totale. Un avantage notable les tournois reguliers pour la competition, offre des recompenses continues.
Aller plus en profondeur|
Hi there Dear, are you in fact visiting this website daily, if so afterward you will definitely take fastidious experience.
https://kra42c.com
code promo 1xBet casino en ligne Ultimately, the goal is to find a “code promo pour 1xBet” or “code promo sur 1xbet” that provides a real advantage. Whether it’s a “bonus d’inscription 1xbet” or a “code promo 1xbet 131$,” smart bettors understand the power of a well-chosen promotional code. Thorough research, verification, and understanding the terms and conditions are paramount to successfully leveraging these offers.
kraken сайт Kraken сайт – это не просто веб-страница, а тщательно выстроенная экосистема, живущая по своим, порой негласным правилам. Это цифровой оазис для тех, кто ценит приватность и независимость, но одновременно и зона повышенного риска, где каждое действие должно быть обдуманным и взвешенным. Здесь встречаются анонимные продавцы и покупатели, заключаются спорные сделки, и разгораются нешуточные страсти. Чтобы не заблудиться в этом лабиринте, необходимо обладать острым умом, твердой рукой и непоколебимой верой в свою интуицию.
Greate article. Keep posting such kind of info on your blog. Im really impressed by your site.
Hey there, You have performed an incredible job. I’ll definitely digg it and individually recommend to my friends. I am sure they will be benefited from this web site.
kra42 cc
J’adore l’harmonie de Olympe Casino, ca transporte dans un monde mythique. Les options sont vastes comme un orchestre, incluant des paris sportifs epiques. Renforcant votre tresor initial. Le service est disponible 24/7, avec une aide precise. Les paiements sont securises et fluides, neanmoins des offres plus genereuses seraient olympiennes. Dans l’ensemble, Olympe Casino offre une experience legendaire pour les joueurs en quete d’epopee ! A noter le site est rapide et glorieux, ajoute une touche de mythologie. Egalement remarquable les tournois reguliers pour la competition, assure des transactions fiables.
olympefr.com|
Ich bin absolut begeistert von Cat Spins Casino, es ist ein Ort voller Energie. Das Angebot an Titeln ist riesig, mit interaktiven Live-Spielen. Mit einfachen Einzahlungen. Der Service ist rund um die Uhr verfugbar. Der Prozess ist einfach und transparent, trotzdem regelma?igere Promos wurden das Spiel aufwerten. Alles in allem, Cat Spins Casino ist ein Ort, der begeistert. Hinzu kommt ist das Design stilvoll und modern, das Spielerlebnis bereichert. Ein hervorragendes Plus die lebendigen Community-Events, ma?geschneiderte Privilegien liefern.
Einen Blick werfen|
J’adore l’energie de Sugar Casino, ca pulse comme une soiree animee. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, offrant des tables live interactives. Il amplifie le plaisir des l’entree. Le support est pro et accueillant. Les transactions sont toujours fiables, neanmoins des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. Globalement, Sugar Casino garantit un amusement continu. Notons egalement le site est rapide et engageant, facilite une immersion totale. Un avantage notable les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, qui dynamise l’engagement.
Aller Г la page|
J’adore l’energie de Ruby Slots Casino, il offre une experience dynamique. Les jeux proposes sont d’une diversite folle, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Les transactions sont fiables et efficaces, malgre tout des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. Au final, Ruby Slots Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. En extra la navigation est intuitive et lisse, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. Particulierement fun les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, cree une communaute vibrante.
Entrer sur le site|
I think everything published was very logical. However, what about this? what if you added a little content? I mean, I don’t want to tell you how to run your website, but what if you added something that makes people want more? I mean %BLOG_TITLE% is a little vanilla. You ought to look at Yahoo’s front page and watch how they write post titles to get viewers to click. You might add a related video or a pic or two to grab readers excited about everything’ve got to say. In my opinion, it could bring your blog a little bit more interesting.
https://dindiaetist.dk/melbet-na-android-2025-obzor/
Je suis captive par Olympe Casino, on ressent une energie divine. La selection de jeux est olympienne, offrant des sessions live immortelles. Renforcant votre tresor initial. Les agents repondent comme des muses, garantissant un support celeste. Le processus est simple et glorieux, bien que plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient de la gloire. Pour conclure, Olympe Casino est une plateforme qui regne sur l’Olympe pour les amateurs de sensations mythiques ! Ajoutons que la plateforme est visuellement olympienne, ajoute une touche de mythologie. Egalement remarquable les options de paris sportifs variees, offre des recompenses eternelles.
https://olympefr.com/|
Nice post. I learn something new and challenging on websites I stumbleupon on a daily basis. It’s always helpful to read content from other writers and use a little something from their web sites.
https://theschoolhouse.co.tz/2025/10/08/melbet-kazino-skachat-2025/
Ich bin ein gro?er Fan von Cat Spins Casino, es entfuhrt in eine Welt voller Nervenkitzel. Es gibt eine riesige Vielfalt an Spielen, mit stilvollen Tischspielen. 100 % bis zu 500 € plus Freispiele. Der Support ist zuverlassig und hilfsbereit. Gewinne kommen sofort an, gelegentlich mehr Promo-Vielfalt ware toll. Kurz gesagt, Cat Spins Casino ist ein absolutes Highlight. Ubrigens die Oberflache ist glatt und benutzerfreundlich, jede Session unvergesslich macht. Besonders erwahnenswert sind die sicheren Krypto-Zahlungen, exklusive Boni bieten.
Mehr entdecken|
Ich freue mich auf Cat Spins Casino, es sorgt fur pure Unterhaltung. Die Spiele sind abwechslungsreich und spannend, mit Krypto-kompatiblen Spielen. Der Bonus ist wirklich stark. Die Mitarbeiter sind schnell und kompetent. Der Prozess ist einfach und transparent, dennoch mehr Bonusvielfalt ware ein Vorteil. In Summe, Cat Spins Casino bietet ein unvergessliches Erlebnis. Au?erdem die Plattform ist visuell ansprechend, eine Prise Stil hinzufugt. Ein Hauptvorteil die breiten Sportwetten-Angebote, die die Community enger zusammenschwei?en.
Tauchen Sie ein|
Ich schatze die Spannung bei Cat Spins Casino, es ladt zu spannenden Spielen ein. Die Auswahl ist atemberaubend vielfaltig, mit Krypto-kompatiblen Spielen. Der Bonus fur Neukunden ist attraktiv. Der Service ist einwandfrei. Die Zahlungen sind sicher und sofortig, trotzdem regelma?igere Promos wurden das Spiel aufwerten. In Summe, Cat Spins Casino bietet ein einmaliges Erlebnis. Au?erdem die Plattform ist visuell ansprechend, eine vollstandige Eintauchen ermoglicht. Ein gro?artiges Plus sind die sicheren Krypto-Zahlungen, exklusive Boni bieten.
Mehr entdecken|
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Ruby Slots Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, offrant des tables live interactives. Le bonus de depart est top. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, neanmoins plus de promotions frequentes boosteraient l’experience. En bref, Ruby Slots Casino offre une experience hors du commun. A mentionner la plateforme est visuellement dynamique, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. A signaler les nombreuses options de paris sportifs, propose des avantages sur mesure.
Essayer ceci|
It’s amazing designed for me to have a website, which is useful designed for my know-how. thanks admin
номер для смс
Ich liebe die Atmosphare bei Cat Spins Casino, es bietet ein mitrei?endes Spielerlebnis. Das Angebot ist ein Paradies fur Spieler, mit Live-Sportwetten. Mit einfachen Einzahlungen. Der Support ist effizient und professionell. Transaktionen laufen reibungslos, jedoch mehr Aktionen waren ein Gewinn. Am Ende, Cat Spins Casino ist ein Ort, der begeistert. Daruber hinaus die Plattform ist visuell ansprechend, und ladt zum Verweilen ein. Ein gro?er Pluspunkt die haufigen Turniere fur mehr Spa?, reibungslose Transaktionen sichern.
Cat Spins|
Ich schatze die Energie bei Cat Spins Casino, es bietet ein mitrei?endes Spielerlebnis. Es gibt eine beeindruckende Anzahl an Titeln, mit interaktiven Live-Spielen. 100 % bis zu 500 € und Freispiele. Der Support ist professionell und schnell. Transaktionen sind zuverlassig und klar, ab und zu gro?ere Angebote waren super. In Summe, Cat Spins Casino ist ein Highlight fur Casino-Fans. Zudem die Navigation ist klar und flussig, zum Bleiben einladt. Ein wichtiger Vorteil die dynamischen Community-Events, reibungslose Transaktionen sichern.
http://www.catspinsbonus.com|
Ich freue mich sehr uber Cat Spins Casino, es entfuhrt in eine Welt voller Nervenkitzel. Es gibt eine Fulle an aufregenden Titeln, mit Krypto-freundlichen Titeln. Er bietet einen gro?artigen Vorteil. Der Service ist absolut zuverlassig. Der Prozess ist einfach und transparent, dennoch ein paar zusatzliche Freispiele waren klasse. In Summe, Cat Spins Casino bietet ein einmaliges Erlebnis. Nebenbei die Navigation ist einfach und klar, eine vollstandige Immersion ermoglicht. Ein wichtiger Vorteil die dynamischen Community-Events, ma?geschneiderte Privilegien liefern.
Cat Spins|
Je suis epate par Sugar Casino, ca pulse comme une soiree animee. Il y a une abondance de jeux excitants, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, mais plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du peps. Dans l’ensemble, Sugar Casino garantit un amusement continu. En plus le design est tendance et accrocheur, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Un avantage notable les evenements communautaires vibrants, qui motive les joueurs.
Entrer sur le site|
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Ruby Slots Casino, il cree une experience captivante. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. Il rend le debut de l’aventure palpitant. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, cependant des recompenses en plus seraient un bonus. Pour faire court, Ruby Slots Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. A souligner le site est rapide et engageant, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. Particulierement attrayant les competitions regulieres pour plus de fun, qui motive les joueurs.
Aller au site|
Je suis bluffe par Sugar Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, avec des slots aux designs captivants. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Disponible 24/7 pour toute question. Les paiements sont surs et efficaces, parfois plus de promotions frequentes boosteraient l’experience. Au final, Sugar Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. Ajoutons que la navigation est fluide et facile, booste le fun du jeu. Un avantage notable les tournois reguliers pour la competition, offre des recompenses continues.
Naviguer sur le site|
Je suis fascine par Sugar Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. Les options sont aussi vastes qu’un horizon, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Le support est efficace et amical. Le processus est simple et transparent, par moments des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. En somme, Sugar Casino merite une visite dynamique. Par ailleurs le design est style et moderne, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. A souligner les competitions regulieres pour plus de fun, offre des recompenses continues.
En savoir plus|
7k casino регистрация рабочее зеркало 7к позволяет игрокам всегда оставаться на связи, независимо от ситуации.
Ich bin vollig uberzeugt von Cat Spins Casino, es verspricht pure Spannung. Es gibt eine Fulle an aufregenden Titeln, mit Slots in modernem Look. Der Bonus fur Neukunden ist attraktiv. Der Support ist schnell und freundlich. Transaktionen laufen reibungslos, von Zeit zu Zeit mehr Aktionen wurden das Erlebnis steigern. Letztlich, Cat Spins Casino ist ein Top-Ziel fur Casino-Fans. Au?erdem die Plattform ist visuell ansprechend, zum Verweilen einladt. Ein besonders cooles Feature sind die sicheren Krypto-Transaktionen, ma?geschneiderte Privilegien liefern.
Website erkunden|
Galera, quero registrar aqui no 4PlayBet Casino porque me impressionou bastante. A variedade de jogos e de cair o queixo: slots modernos, todos funcionando perfeito. O suporte foi bem prestativo, responderam em minutos pelo chat, algo que passa seguranca. Fiz saque em PIX e o dinheiro entrou muito rapido, ponto fortissimo. Se tivesse que criticar, diria que faltam bonus extras, mas isso nao estraga a experiencia. No geral, o 4PlayBet Casino vale demais a pena. Recomendo sem medo.
4play west la|
Ich habe einen Narren gefressen an Cat Spins Casino, es schafft eine mitrei?ende Stimmung. Es gibt zahlreiche spannende Spiele, mit Spielen fur Kryptowahrungen. Mit blitzschnellen Einzahlungen. Erreichbar 24/7 per Chat oder E-Mail. Die Zahlungen sind sicher und effizient, manchmal mehr Bonusvielfalt ware ein Vorteil. Zum Schluss, Cat Spins Casino ist perfekt fur Casino-Liebhaber. Zudem die Benutzeroberflache ist flussig und intuitiv, und ladt zum Verweilen ein. Ein Hauptvorteil die lebendigen Community-Events, regelma?ige Boni bieten.
Details prГјfen|
I can’t get enough of Pinco, it’s got that winning energy. There’s a flood of exciting games, featuring traditional card games. With smooth, fast deposits. The help desk is excellent. Transactions run without a hitch, nevertheless more regular deals would energize the play. In conclusion, Pinco is a place that electrifies. What’s more navigation is effortless, adds a layer of polish. Also fantastic are the regular contests for thrill, that ensures safe transactions.
Read the details|
Je suis enthousiasme par Ruby Slots Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, offrant des sessions live immersives. 100% jusqu’a 500 € plus des tours gratuits. Le support est efficace et amical. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, cependant des offres plus genereuses seraient top. En conclusion, Ruby Slots Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. A mentionner le design est tendance et accrocheur, ajoute une touche de dynamisme. Un plus les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, cree une communaute soudee.
Visiter le site|
Je suis completement seduit par Sugar Casino, on y trouve une energie contagieuse. Les options de jeu sont incroyablement variees, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Disponible 24/7 pour toute question. Les paiements sont surs et efficaces, quelquefois des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. En somme, Sugar Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. Pour completer la plateforme est visuellement vibrante, booste le fun du jeu. Egalement excellent le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, propose des privileges personnalises.
Obtenir les dГ©tails|
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Sugar Casino, il cree une experience captivante. Il y a une abondance de jeux excitants, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Le support client est irreprochable. Les paiements sont surs et efficaces, par contre plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. Pour finir, Sugar Casino assure un divertissement non-stop. Pour completer la navigation est fluide et facile, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. Un plus le programme VIP avec des privileges speciaux, cree une communaute vibrante.
DГ©couvrir les offres|
Je suis bluffe par Sugar Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. Il offre un demarrage en fanfare. Le suivi est toujours au top. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, malgre tout des recompenses supplementaires seraient parfaites. En conclusion, Sugar Casino assure un fun constant. Pour couronner le tout le design est moderne et attrayant, facilite une immersion totale. Egalement top les competitions regulieres pour plus de fun, renforce le lien communautaire.
Lancer le site|
J’adore a fond 7BitCasino, on dirait une sensation de casino unique. La gamme de jeux est tout simplement impressionnante, incluant des slots de pointe. Le service client est remarquable, garantissant une aide immediate via chat en direct ou email. Les paiements sont fluides et securises, occasionnellement j’aimerais plus d’offres promotionnelles, ou des promotions hebdomadaires plus frequentes. Dans l’ensemble, 7BitCasino vaut pleinement le detour pour les adeptes de sensations fortes ! Ajoutons que la navigation est intuitive et rapide, ce qui intensifie le plaisir de jouer.
7bitcasino 25|
Ich bin beeindruckt von der Qualitat bei Cat Spins Casino, es ladt zu spannenden Spielen ein. Die Spielauswahl ist beeindruckend, mit Spielautomaten in kreativen Designs. Er bietet einen tollen Startvorteil. Die Mitarbeiter sind schnell und kompetent. Zahlungen sind sicher und schnell, dennoch haufigere Promos wurden begeistern. Letztlich, Cat Spins Casino garantiert dauerhaften Spielspa?. Zudem die Plattform ist optisch ansprechend, eine Note von Eleganz hinzufugt. Ein gro?artiges Plus die spannenden Community-Aktionen, die Community enger verbinden.
Seite entdecken|
Ich liebe die Atmosphare bei Cat Spins Casino, es entfuhrt in eine Welt voller Spa?. Es gibt eine enorme Vielfalt an Spielen, mit Krypto-kompatiblen Spielen. Er gibt Ihnen einen Kickstart. Der Support ist schnell und freundlich. Der Prozess ist klar und effizient, aber gro?ere Boni waren ein Highlight. Am Ende, Cat Spins Casino ist definitiv einen Besuch wert. Zusatzlich die Benutzeroberflache ist klar und flussig, das Spielerlebnis steigert. Ein Hauptvorteil die breiten Sportwetten-Angebote, die Gemeinschaft starken.
Zur Website gehen|
Ich bin fasziniert von SpinBetter Casino, es erzeugt eine Spielenergie, die fesselt. Das Angebot an Spielen ist phanomenal, mit aufregenden Sportwetten. Die Agenten sind blitzschnell, bietet klare Losungen. Die Auszahlungen sind ultraschnell, ab und an mehr abwechslungsreiche Boni waren super. Global gesehen, SpinBetter Casino garantiert hochsten Spa? fur Spieler auf der Suche nach Action ! Nicht zu vergessen die Site ist schnell und stylish, gibt den Anreiz, langer zu bleiben. Ein Pluspunkt ist die mobilen Apps, die den Einstieg erleichtern.
spinbettercasino.de|
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Ruby Slots Casino, on ressent une ambiance de fete. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Les gains sont transferes rapidement, de temps a autre des recompenses en plus seraient un bonus. Globalement, Ruby Slots Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. Pour ajouter l’interface est intuitive et fluide, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. A noter les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, cree une communaute vibrante.
DГ©couvrir le contenu|
J’adore la vibe de Sugar Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. Les jeux proposes sont d’une diversite folle, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Le service d’assistance est au point. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, par moments plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du peps. Au final, Sugar Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. Pour couronner le tout la navigation est intuitive et lisse, ajoute une touche de dynamisme. Particulierement attrayant les evenements communautaires vibrants, assure des transactions fluides.
DГ©couvrir dГЁs maintenant|
Je suis accro a Sugar Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. La gamme est variee et attrayante, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. Avec des depots instantanes. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, parfois plus de promotions frequentes boosteraient l’experience. En conclusion, Sugar Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. En extra l’interface est lisse et agreable, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. Un avantage les tournois reguliers pour la competition, offre des recompenses continues.
Cliquer pour voir|
Je suis completement seduit par Ruby Slots Casino, il cree une experience captivante. La selection de jeux est impressionnante, offrant des sessions live palpitantes. Avec des depots instantanes. Le support client est irreprochable. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, par moments plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du peps. Pour finir, Ruby Slots Casino assure un fun constant. Notons egalement la navigation est fluide et facile, facilite une immersion totale. A mettre en avant les nombreuses options de paris sportifs, propose des avantages uniques.
Voir la page d’accueil|
Ich bin total hingerissen von Cat Spins Casino, es begeistert mit Dynamik. Das Angebot ist ein Paradies fur Spieler, mit dynamischen Wettmoglichkeiten. Mit sofortigen Einzahlungen. Der Service ist absolut zuverlassig. Der Prozess ist klar und effizient, dennoch gro?ere Angebote waren super. Letztlich, Cat Spins Casino sorgt fur ununterbrochenen Spa?. Ubrigens ist das Design stilvoll und modern, eine vollstandige Eintauchen ermoglicht. Ein gro?artiges Bonus die dynamischen Community-Veranstaltungen, ma?geschneiderte Vorteile liefern.
Jetzt eintreten|
Ich bin beeindruckt von SpinBetter Casino, es ist eine Erfahrung, die wie ein Wirbelsturm pulsiert. Es gibt eine unglaubliche Auswahl an Spielen, mit immersiven Live-Sessions. Der Service ist von hoher Qualitat, bietet klare Losungen. Die Zahlungen sind sicher und smooth, trotzdem zusatzliche Freispiele waren ein Highlight. Zusammengefasst, SpinBetter Casino garantiert hochsten Spa? fur Casino-Liebhaber ! Nicht zu vergessen die Plattform ist visuell ein Hit, verstarkt die Immersion. Ein weiterer Vorteil die mobilen Apps, die den Einstieg erleichtern.
spinbettercasino.de|
J’ai une passion debordante pour Sugar Casino, ca transporte dans un univers de plaisirs. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, incluant des options de paris sportifs dynamiques. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Le support client est irreprochable. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, neanmoins des bonus plus frequents seraient un hit. Globalement, Sugar Casino garantit un plaisir constant. A mentionner la plateforme est visuellement dynamique, booste l’excitation du jeu. A souligner les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, offre des recompenses continues.
Aller voir|
Je ne me lasse pas de Sugar Casino, il cree un monde de sensations fortes. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, proposant des jeux de table classiques. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Disponible 24/7 par chat ou email. Les gains sont verses sans attendre, parfois des offres plus genereuses seraient top. En resume, Sugar Casino garantit un plaisir constant. De plus le design est tendance et accrocheur, ajoute une touche de dynamisme. Egalement top les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, renforce la communaute.
Parcourir le site|
J’adore le dynamisme de Ruby Slots Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. La bibliotheque est pleine de surprises, incluant des options de paris sportifs dynamiques. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Les gains sont transferes rapidement, par moments des offres plus genereuses rendraient l’experience meilleure. Pour faire court, Ruby Slots Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. En extra la navigation est intuitive et lisse, facilite une immersion totale. Particulierement interessant les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, cree une communaute vibrante.
Approfondir|
Ich bin total hingerissen von Cat Spins Casino, es schafft eine elektrisierende Atmosphare. Die Spiele sind abwechslungsreich und spannend, mit Live-Sportwetten. 100 % bis zu 500 € mit Freispielen. Der Service ist einwandfrei. Auszahlungen sind schnell und reibungslos, trotzdem ein paar zusatzliche Freispiele waren klasse. Zusammenfassend, Cat Spins Casino garantiert langanhaltenden Spa?. Nebenbei die Plattform ist optisch ein Highlight, jede Session unvergesslich macht. Ein hervorragendes Plus ist das VIP-Programm mit besonderen Vorteilen, das die Motivation steigert.
Zur Website gelangen|
Ich bin ganz hin und weg von Cat Spins Casino, es entfuhrt in eine Welt voller Nervenkitzel. Die Spielesammlung ist uberwaltigend, mit Krypto-freundlichen Titeln. Der Bonus ist wirklich stark. Der Support ist zuverlassig und hilfsbereit. Transaktionen sind immer sicher, in manchen Fallen waren mehr Bonusvarianten ein Plus. Im Gro?en und Ganzen, Cat Spins Casino sorgt fur ununterbrochenen Spa?. Hinzu kommt die Plattform ist visuell beeindruckend, zum Verweilen einladt. Ein klasse Bonus die breiten Sportwetten-Angebote, die Gemeinschaft starken.
Jetzt stöbern|
Ich habe einen Narren gefressen an Cat Spins Casino, es bietet eine dynamische Erfahrung. Es gibt eine enorme Vielfalt an Spielen, mit Spielautomaten in kreativen Designs. Mit einfachen Einzahlungen. Der Support ist effizient und professionell. Transaktionen sind immer sicher, allerdings mehr Promo-Vielfalt ware toll. Alles in allem, Cat Spins Casino ist ein Ort fur pure Unterhaltung. Nebenbei die Navigation ist unkompliziert, jeden Augenblick spannender macht. Ein starkes Feature ist das VIP-Programm mit tollen Privilegien, die die Community enger zusammenschwei?en.
http://www.catspinsbonus.com|
Ich bin abhangig von SpinBetter Casino, es liefert ein Abenteuer voller Energie. Der Katalog ist reichhaltig und variiert, mit aufregenden Sportwetten. Die Hilfe ist effizient und pro, bietet klare Losungen. Die Gewinne kommen prompt, trotzdem die Offers konnten gro?zugiger ausfallen. Alles in allem, SpinBetter Casino garantiert hochsten Spa? fur Online-Wetten-Fans ! Zusatzlich die Interface ist intuitiv und modern, fugt Magie hinzu. Ein Pluspunkt ist die Vielfalt an Zahlungsmethoden, die den Spa? verlangern.
https://spinbettercasino.de/|
Je suis bluffe par Sugar Casino, on y trouve une energie contagieuse. Le choix est aussi large qu’un festival, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. Avec des depots instantanes. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, par ailleurs des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. En fin de compte, Sugar Casino offre une experience inoubliable. Notons egalement l’interface est intuitive et fluide, permet une plongee totale dans le jeu. A mettre en avant les transactions crypto ultra-securisees, qui motive les joueurs.
Visiter maintenant|
Je suis totalement conquis par Ruby Slots Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. La bibliotheque est pleine de surprises, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. Il amplifie le plaisir des l’entree. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Les paiements sont surs et efficaces, quelquefois des recompenses en plus seraient un bonus. Globalement, Ruby Slots Casino assure un fun constant. A souligner l’interface est simple et engageante, ajoute une touche de dynamisme. Un avantage le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, offre des bonus exclusifs.
Continuer ici|
Ich liebe das Flair von Cat Spins Casino, es schafft eine elektrisierende Atmosphare. Es gibt eine riesige Vielfalt an Spielen, mit traditionellen Tischspielen. Er sorgt fur einen starken Einstieg. Der Support ist schnell und freundlich. Gewinne kommen ohne Verzogerung, dennoch mehr Bonusangebote waren spitze. In Summe, Cat Spins Casino ist ein absolutes Highlight. Zusatzlich die Plattform ist optisch ein Highlight, eine Prise Stil hinzufugt. Ein Hauptvorteil ist das VIP-Programm mit besonderen Vorteilen, ma?geschneiderte Vorteile liefern.
Webseite besuchen|
J’adore le dynamisme de Sugar Casino, ca transporte dans un monde d’excitation. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Le support est pro et accueillant. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, bien que des recompenses en plus seraient un bonus. En resume, Sugar Casino offre une experience hors du commun. A mentionner l’interface est lisse et agreable, incite a rester plus longtemps. Egalement excellent les paiements securises en crypto, propose des privileges personnalises.
Apprendre comment|
Galera, resolvi contar como foi no 4PlayBet Casino porque nao e so mais um cassino online. A variedade de jogos e de cair o queixo: blackjack envolvente, todos rodando lisos. O suporte foi amigavel, responderam em minutos pelo chat, algo que passa seguranca. Fiz saque em cartao e o dinheiro entrou mais ligeiro do que imaginei, ponto fortissimo. Se tivesse que criticar, diria que mais brindes fariam falta, mas isso nao estraga a experiencia. Na minha visao, o 4PlayBet Casino me conquistou. Recomendo sem medo.
4play hush|
Ich bin komplett hin und weg von SpinBetter Casino, es erzeugt eine Spielenergie, die fesselt. Der Katalog ist reichhaltig und variiert, mit Spielen, die fur Kryptos optimiert sind. Die Agenten sind blitzschnell, immer parat zu assistieren. Die Zahlungen sind sicher und smooth, gelegentlich zusatzliche Freispiele waren ein Highlight. Zum Ende, SpinBetter Casino ist ein Muss fur alle Gamer fur Spieler auf der Suche nach Action ! Zusatzlich das Design ist ansprechend und nutzerfreundlich, gibt den Anreiz, langer zu bleiben. Zusatzlich zu beachten die Community-Events, die den Spa? verlangern.
https://spinbettercasino.de/|
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Sugar Casino, ca transporte dans un univers de plaisirs. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, offrant des tables live interactives. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Le support est pro et accueillant. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, bien que des recompenses en plus seraient un bonus. Pour conclure, Sugar Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. Pour ajouter le design est style et moderne, incite a prolonger le plaisir. Particulierement interessant le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, assure des transactions fiables.
Continuer ici|
Je suis enthousiasme par Ruby Slots Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. Le bonus initial est super. Le support est fiable et reactif. Les transactions sont fiables et efficaces, neanmoins des offres plus genereuses rendraient l’experience meilleure. Au final, Ruby Slots Casino vaut une visite excitante. Par ailleurs l’interface est lisse et agreable, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Un avantage les nombreuses options de paris sportifs, propose des privileges sur mesure.
Obtenir plus|
J’ai un faible pour Sugar Casino, ca transporte dans un univers de plaisirs. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, neanmoins des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. En conclusion, Sugar Casino offre une aventure memorable. Pour completer le site est rapide et engageant, ajoute une touche de dynamisme. A noter les transactions en crypto fiables, propose des avantages uniques.
Approfondir|
Ich liebe die Atmosphare bei Cat Spins Casino, es ist ein Ort voller Energie. Es gibt eine riesige Vielfalt an Spielen, mit Krypto-kompatiblen Spielen. Er gibt Ihnen einen tollen Boost. Der Kundensupport ist erstklassig. Der Prozess ist unkompliziert, in seltenen Fallen mehr Bonusangebote waren ideal. Im Gro?en und Ganzen, Cat Spins Casino ist ein absolutes Highlight. Hinzu kommt die Plattform ist optisch ein Highlight, eine Prise Stil hinzufugt. Ein bemerkenswertes Extra sind die sicheren Krypto-Transaktionen, die die Begeisterung steigern.
Mit dem Lesen beginnen|
Ich bin total angetan von Cat Spins Casino, es schafft eine aufregende Atmosphare. Das Spieleportfolio ist unglaublich breit, mit Krypto-kompatiblen Spielen. Der Willkommensbonus ist gro?zugig. Der Kundendienst ist hervorragend. Auszahlungen sind zugig und unkompliziert, manchmal mehr Aktionen waren ein Gewinn. Insgesamt, Cat Spins Casino ist ein Muss fur Spielbegeisterte. Au?erdem ist das Design stilvoll und einladend, jeden Augenblick spannender macht. Ein gro?artiges Bonus ist das VIP-Programm mit besonderen Vorteilen, personliche Vorteile bereitstellen.
Angebote entdecken|
Ich habe einen Narren gefressen an Cat Spins Casino, es ist ein Ort, der begeistert. Das Spieleportfolio ist unglaublich breit, mit dynamischen Wettmoglichkeiten. 100 % bis zu 500 € inklusive Freispiele. Erreichbar rund um die Uhr. Der Prozess ist unkompliziert, allerdings gro?ere Boni waren ein Highlight. Im Gro?en und Ganzen, Cat Spins Casino bietet ein gro?artiges Erlebnis. Ubrigens die Plattform ist optisch ein Highlight, das Spielerlebnis bereichert. Ein bemerkenswertes Extra die lebendigen Community-Events, die die Motivation erhohen.
Website starten|
Ich bin beeindruckt von SpinBetter Casino, es erzeugt eine Spielenergie, die fesselt. Der Katalog ist reichhaltig und variiert, mit dynamischen Tischspielen. Die Agenten sind blitzschnell, mit praziser Unterstutzung. Die Zahlungen sind sicher und smooth, ab und an regelma?igere Aktionen waren toll. Zusammengefasst, SpinBetter Casino ist absolut empfehlenswert fur Casino-Liebhaber ! Au?erdem die Plattform ist visuell ein Hit, erleichtert die gesamte Erfahrung. Hervorzuheben ist die Sicherheit der Daten, die den Einstieg erleichtern.
spinbettercasino.de|
J’ai une passion debordante pour Ruby Slots Casino, ca offre une experience immersive. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, comprenant des titres adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Il donne un avantage immediat. Le service client est de qualite. Les paiements sont surs et efficaces, a l’occasion quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. Pour finir, Ruby Slots Casino vaut une visite excitante. A signaler le design est tendance et accrocheur, facilite une immersion totale. Un avantage notable le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, garantit des paiements securises.
DГ©couvrir les offres|
Je suis bluffe par Sugar Casino, ca invite a l’aventure. La selection est riche et diversifiee, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. Le bonus initial est super. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Le processus est transparent et rapide, cependant des bonus varies rendraient le tout plus fun. Pour finir, Sugar Casino merite une visite dynamique. En plus l’interface est intuitive et fluide, ajoute une vibe electrisante. Un plus les nombreuses options de paris sportifs, assure des transactions fiables.
Cliquez ici|
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Ruby Slots Casino, on y trouve une energie contagieuse. La bibliotheque de jeux est captivante, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, en revanche des offres plus importantes seraient super. Dans l’ensemble, Ruby Slots Casino assure un divertissement non-stop. Par ailleurs le site est fluide et attractif, booste le fun du jeu. Egalement excellent les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, garantit des paiements securises.
Lire plus|
Hey there this is kind of of off topic but I was wanting to know if blogs use WYSIWYG editors or if you have to manually code with HTML. I’m starting a blog soon but have no coding skills so I wanted to get advice from someone with experience. Any help would be greatly appreciated!
https://spotwin.org/melbet-skachat-prilozhenie-2025/
бонус онлайн казино 1000
J’ai une passion debordante pour Frumzi Casino, ca invite a l’aventure. La selection est riche et diversifiee, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Le processus est transparent et rapide, en revanche des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. En somme, Frumzi Casino vaut une visite excitante. En complement la navigation est simple et intuitive, apporte une energie supplementaire. A mettre en avant les tournois reguliers pour la competition, propose des avantages sur mesure.
Commencer Г naviguer|
Je suis fascine par Wild Robin Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. Les options de jeu sont incroyablement variees, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, cependant des recompenses supplementaires seraient parfaites. En somme, Wild Robin Casino est un endroit qui electrise. Par ailleurs l’interface est intuitive et fluide, incite a prolonger le plaisir. Un point cle les options de paris sportifs variees, assure des transactions fiables.
Poursuivre la lecture|
J’adore le dynamisme de Wild Robin Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, proposant des jeux de cartes elegants. Avec des depots instantanes. Le support est fiable et reactif. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, a l’occasion quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. Dans l’ensemble, Wild Robin Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. De surcroit le site est rapide et style, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. Egalement top les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, offre des bonus constants.
DГ©marrer maintenant|
J’ai une affection particuliere pour Cheri Casino, ca invite a l’aventure. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. Avec des depots fluides. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Le processus est simple et transparent, cependant des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. En resume, Cheri Casino vaut une visite excitante. A noter le design est tendance et accrocheur, apporte une touche d’excitation. Un avantage notable les options de paris sportifs variees, cree une communaute vibrante.
Explorer le site web|
J’adore la vibe de Cheri Casino, il offre une experience dynamique. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Le service client est excellent. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, a l’occasion quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. Dans l’ensemble, Cheri Casino est un immanquable pour les amateurs. Notons egalement le design est tendance et accrocheur, permet une immersion complete. Un bonus le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, garantit des paiements rapides.
Apprendre comment|
J’ai une passion debordante pour Instant Casino, on ressent une ambiance de fete. La bibliotheque de jeux est captivante, offrant des experiences de casino en direct. Il donne un avantage immediat. Disponible 24/7 par chat ou email. Les paiements sont surs et efficaces, rarement quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. En bref, Instant Casino offre une experience inoubliable. Par ailleurs le site est fluide et attractif, apporte une touche d’excitation. Particulierement cool les nombreuses options de paris sportifs, propose des privileges personnalises.
https://instantcasinobonusfr.com/|
Je suis fascine par Wild Robin Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, avec des slots aux designs captivants. Il donne un avantage immediat. Le suivi est impeccable. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, a l’occasion plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. Dans l’ensemble, Wild Robin Casino est un must pour les passionnes. En plus le design est moderne et attrayant, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. Un avantage notable les options variees pour les paris sportifs, propose des avantages sur mesure.
AccГ©der maintenant|
Je suis totalement conquis par Wild Robin Casino, ca invite a l’aventure. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. Avec des depots fluides. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, occasionnellement des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. En bref, Wild Robin Casino offre une experience inoubliable. Par ailleurs la plateforme est visuellement vibrante, booste le fun du jeu. Un point cle les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, propose des privileges sur mesure.
Approfondir|
J’ai une passion debordante pour Cheri Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, avec des slots aux designs captivants. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Le service client est excellent. Les gains sont verses sans attendre, mais encore plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. En conclusion, Cheri Casino est un immanquable pour les amateurs. En complement la navigation est simple et intuitive, permet une plongee totale dans le jeu. Egalement top les evenements communautaires engageants, qui motive les joueurs.
Voir plus|
Je suis totalement conquis par Cheri Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. La bibliotheque de jeux est captivante, comprenant des titres adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Le service est disponible 24/7. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, occasionnellement des offres plus genereuses seraient top. Pour finir, Cheri Casino vaut une visite excitante. En extra la navigation est claire et rapide, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. Un point cle le programme VIP avec des privileges speciaux, qui booste la participation.
Savoir plus|
Je suis completement seduit par Instant Casino, ca offre une experience immersive. Le catalogue est un tresor de divertissements, proposant des jeux de table classiques. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Le service client est de qualite. Les gains sont verses sans attendre, cependant plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du peps. Pour conclure, Instant Casino offre une experience hors du commun. Notons aussi l’interface est lisse et agreable, ajoute une touche de dynamisme. A noter le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, offre des bonus constants.
DГ©couvrir davantage|
Je suis totalement conquis par Frumzi Casino, on y trouve une vibe envoutante. La bibliotheque est pleine de surprises, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. Il donne un elan excitant. Le suivi est impeccable. Les gains sont transferes rapidement, parfois des offres plus genereuses rendraient l’experience meilleure. Pour faire court, Frumzi Casino garantit un plaisir constant. En plus l’interface est simple et engageante, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. Un bonus le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, propose des avantages uniques.
Voir maintenant|
Рейтинг казино онлайн Україна допомагає знайти перевірені платформи. Топ казино України обирають за надійність і швидкі виплати.
Легальні онлайн казино гарантують підтримку 24/7. Потрібен короткий список найнадійніших брендів? Перевірте кращі онлайн казино україни та умови верифікації. Кращі казино України мають позитивні відгуки гравців.
Онлайн казино в Україні працюють лише з перевіреними провайдерами. Легальні онлайн казино України діють згідно із законом. Казино онлайн Україна дає змогу грати без ризиків. Рейтинг казино онлайн Україна допомагає знайти найкращу платформу. Онлайн казино Україна з миттєвим виводом коштів — реальність.
Оформите онлайн-займ https://zaimy-87.ru без визита в офис: достаточно паспорта, проверка за минуты. Выдача на карту, кошелёк или счёт. Прозрачный договор, напоминания о платеже, безопасность данных, акции для новых клиентов. Сравните предложения и выберите выгодно.
Обновлено сегодня: https://zebraschool.com.ua
Je suis bluffe par Wild Robin Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, offrant des experiences de casino en direct. Il amplifie le plaisir des l’entree. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, neanmoins des recompenses supplementaires seraient parfaites. En bref, Wild Robin Casino assure un fun constant. Notons egalement la plateforme est visuellement vibrante, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Egalement genial le programme VIP avec des recompenses exclusives, propose des privileges sur mesure.
DГ©couvrir la page|
J’adore la vibe de Frumzi Casino, ca offre une experience immersive. Les jeux proposes sont d’une diversite folle, offrant des sessions live immersives. Il donne un elan excitant. Le service client est de qualite. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, mais encore des bonus plus frequents seraient un hit. Au final, Frumzi Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. A noter la plateforme est visuellement captivante, facilite une immersion totale. Un point fort les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, assure des transactions fiables.
Parcourir le site|
J’ai une passion debordante pour Frumzi Casino, on ressent une ambiance de fete. Les options sont aussi vastes qu’un horizon, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. Il rend le debut de l’aventure palpitant. Le service client est de qualite. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, mais des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. Pour conclure, Frumzi Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. Pour completer le site est rapide et immersif, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Un avantage les options variees pour les paris sportifs, assure des transactions fiables.
http://www.frumzicasinoappfr.com|
J’adore l’energie de Cheri Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Le support client est irreprochable. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, cependant plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. En somme, Cheri Casino assure un divertissement non-stop. Pour completer le site est rapide et style, apporte une touche d’excitation. A signaler les evenements communautaires vibrants, offre des recompenses regulieres.
Poursuivre la lecture|
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Wild Robin Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. Les options de jeu sont incroyablement variees, avec des slots aux designs captivants. Avec des depots fluides. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, occasionnellement quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient geniaux. En somme, Wild Robin Casino merite une visite dynamique. A noter l’interface est intuitive et fluide, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. Particulierement fun les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, offre des recompenses regulieres.
http://www.wildrobincasinologinfr.com|
J’adore la vibe de Instant Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, proposant des jeux de table classiques. Il donne un avantage immediat. Le support est efficace et amical. Les retraits sont simples et rapides, par ailleurs des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. En resume, Instant Casino offre une experience hors du commun. En complement le site est rapide et style, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. Un point cle les tournois reguliers pour la competition, propose des avantages uniques.
Visiter la plateforme|
Je suis fascine par Cheri Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. La gamme est variee et attrayante, offrant des experiences de casino en direct. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Les agents sont toujours la pour aider. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, parfois quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. En somme, Cheri Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. A signaler le site est rapide et immersif, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. Un point fort les evenements communautaires vibrants, offre des bonus constants.
VГ©rifier le site|
Je suis sous le charme de Frumzi Casino, il cree une experience captivante. Les options de jeu sont infinies, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. Il donne un avantage immediat. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Les transactions sont toujours fiables, par contre quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient geniaux. En conclusion, Frumzi Casino offre une experience hors du commun. Par ailleurs la navigation est fluide et facile, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. A souligner les competitions regulieres pour plus de fun, propose des avantages uniques.
DГ©couvrir|
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Instant Casino, on y trouve une vibe envoutante. La selection est riche et diversifiee, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Le support client est irreprochable. Le processus est transparent et rapide, occasionnellement quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient geniaux. En conclusion, Instant Casino merite une visite dynamique. Pour couronner le tout le site est fluide et attractif, facilite une experience immersive. Un bonus le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, offre des bonus constants.
Plonger dedans|
Je suis enthousiasme par Instant Casino, ca invite a l’aventure. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Le suivi est toujours au top. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, de temps a autre des recompenses supplementaires seraient parfaites. Pour conclure, Instant Casino offre une experience inoubliable. Pour couronner le tout la navigation est intuitive et lisse, facilite une immersion totale. A noter les options de paris sportifs variees, cree une communaute vibrante.
Voir la page d’accueil|
турниры казино
J’adore le dynamisme de Betzino Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. Il donne un elan excitant. Le service client est excellent. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, cependant plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. Pour conclure, Betzino Casino merite un detour palpitant. Pour completer la plateforme est visuellement dynamique, facilite une immersion totale. Un element fort les evenements communautaires engageants, qui stimule l’engagement.
Regarder de plus prГЁs|
наплавляемая гидроизоляция цена наплавляемая гидроизоляция цена .
наркология наркология .
карнизы с электроприводом купить карнизы с электроприводом купить .
Je suis enthousiasme par Vbet Casino, on ressent une ambiance de fete. La gamme est variee et attrayante, offrant des tables live interactives. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Le suivi est toujours au top. Le processus est simple et transparent, quelquefois des offres plus importantes seraient super. Pour conclure, Vbet Casino est un must pour les passionnes. Pour ajouter le design est tendance et accrocheur, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Egalement top les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, propose des privileges personnalises.
Entrer maintenant|
1000 рублей без депозита Мы рады приветствовать новых игроков и хотим сделать ваше знакомство с нами максимально приятным. Поэтому мы дарим вам 1000 рублей, которые вы можете использовать для игры сразу после регистрации. Никаких вложений – только азарт и возможность выиграть!
ремонт подвального помещения ремонт подвального помещения .
электрокарниз двухрядный цена https://www.elektrokarniz797.ru .
услуги гидроизоляции подвала https://gidroizolyaciya-podvala-cena.ru/ .
торкрет бетон цена торкрет бетон цена .
цена ремонта подвала https://www.gidroizolyaciya-cena-8.ru .
электрические гардины для штор https://www.elektrokarniz797.ru .
гидроизоляция подвала под ключ https://gidroizolyaciya-podvala-cena.ru/ .
карниз с приводом http://www.elektrokarniz777.ru .
умный дом жалюзи интеграция http://elektricheskie-zhalyuzi97.ru .
Je suis emerveille par Betzino Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, proposant des jeux de table classiques. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Les transactions sont fiables et efficaces, de temps en temps quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. En fin de compte, Betzino Casino merite une visite dynamique. En plus le site est rapide et style, ajoute une touche de dynamisme. Un point cle les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, renforce la communaute.
Entrer|
J’adore le dynamisme de Betzino Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. La bibliotheque est pleine de surprises, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Le bonus initial est super. Le support client est irreprochable. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, de temps a autre plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. Pour conclure, Betzino Casino merite un detour palpitant. En complement le site est rapide et engageant, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. Un avantage les competitions regulieres pour plus de fun, renforce le lien communautaire.
Voir le site|
Je suis accro a Vbet Casino, ca offre une experience immersive. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, offrant des sessions live immersives. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Les retraits sont simples et rapides, a l’occasion quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. En resume, Vbet Casino vaut une visite excitante. A mentionner la navigation est fluide et facile, ajoute une touche de dynamisme. Egalement genial les tournois reguliers pour la competition, garantit des paiements securises.
Visiter maintenant|
электрокарниз купить электрокарниз купить .
жалюзи с электроприводом купить жалюзи с электроприводом купить .
карниз электро elektrokarniz777.ru .
J’ai un faible pour Betzino Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. Les jeux proposes sont d’une diversite folle, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. Il amplifie le plaisir des l’entree. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, malgre tout des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. Dans l’ensemble, Betzino Casino assure un divertissement non-stop. En extra le design est moderne et attrayant, facilite une experience immersive. Un atout les tournois reguliers pour la competition, cree une communaute soudee.
http://www.betzinocasinobonusfr.com|
Je suis completement seduit par Betway Casino, il cree une experience captivante. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Disponible 24/7 par chat ou email. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, par ailleurs plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. En conclusion, Betway Casino garantit un plaisir constant. A souligner la plateforme est visuellement captivante, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Un point cle le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, propose des privileges sur mesure.
Visiter le site|
Je suis fascine par Betway Casino, ca invite a l’aventure. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. Il amplifie le plaisir des l’entree. Le service est disponible 24/7. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, de temps a autre quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. En conclusion, Betway Casino merite une visite dynamique. De surcroit la plateforme est visuellement vibrante, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. Un atout le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, qui motive les joueurs.
Ouvrir maintenant|
Je suis captive par Belgium Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. Avec des depots instantanes. Le support est fiable et reactif. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, mais plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du peps. Pour faire court, Belgium Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. A mentionner l’interface est intuitive et fluide, permet une immersion complete. Un avantage notable les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, qui dynamise l’engagement.
Parcourir maintenant|
Je suis captive par Belgium Casino, ca invite a l’aventure. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. Le bonus de depart est top. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Les gains arrivent sans delai, neanmoins plus de promotions frequentes boosteraient l’experience. En resume, Belgium Casino est un must pour les passionnes. Par ailleurs le site est rapide et immersif, permet une immersion complete. Particulierement attrayant les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, assure des transactions fiables.
Voir la page d’accueil|
Je suis accro a Betway Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. Les options sont aussi vastes qu’un horizon, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Les paiements sont surs et efficaces, de temps en temps quelques free spins en plus seraient bienvenus. En somme, Betway Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. Par ailleurs le site est rapide et style, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. Egalement top les options de paris sportifs variees, garantit des paiements rapides.
VГ©rifier ceci|
Je suis fascine par Betify Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. Les jeux proposes sont d’une diversite folle, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Le support est pro et accueillant. Les transactions sont toujours fiables, parfois des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. Pour finir, Betify Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. Notons egalement le site est rapide et engageant, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. Egalement excellent les transactions en crypto fiables, qui motive les joueurs.
Aller voir|
Je suis fascine par Gamdom Casino, ca offre une experience immersive. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. Il donne un elan excitant. Le service client est excellent. Les paiements sont surs et efficaces, cependant des offres plus genereuses rendraient l’experience meilleure. Pour conclure, Gamdom Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. Ajoutons aussi le design est moderne et energique, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. A noter le programme VIP avec des recompenses exclusives, cree une communaute soudee.
Visiter en ligne|
Pinco-da idman və kazino bir yerdədir. Yeni oyunçular üçün pulsuz bonuslar burada pinco qeydiyyat. Pinco-da qeydiyyat etmək asandır.
Pinco betdə əmsallar çox cəlbedicidir.
J’ai une passion debordante pour Betify Casino, on y trouve une vibe envoutante. La gamme est variee et attrayante, offrant des tables live interactives. Il donne un elan excitant. Disponible 24/7 pour toute question. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, par ailleurs des bonus plus frequents seraient un hit. Globalement, Betify Casino garantit un plaisir constant. Pour couronner le tout le design est moderne et attrayant, permet une immersion complete. Un element fort les transactions en crypto fiables, propose des privileges sur mesure.
Rejoindre maintenant|
согласование перепланировки нежилого помещения в нежилом здании https://pereplanirovka-nezhilogo-pomeshcheniya16.ru .
поставка медицинского оборудования поставка медицинского оборудования .
купить рулонные шторы москва купить рулонные шторы москва .
1xbwt giri? https://www.1xbet-giris-5.com .
купить электрические рулонные шторы https://avtomaticheskie-rulonnye-shtory1.ru/ .
1xbet giri? adresi 1xbet giri? adresi .
1xbet spor bahislerinin adresi 1xbet spor bahislerinin adresi .
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Belgium Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. La bibliotheque est pleine de surprises, proposant des jeux de table classiques. Le bonus de depart est top. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Les retraits sont simples et rapides, cependant des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. Globalement, Belgium Casino offre une experience hors du commun. De surcroit la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, apporte une energie supplementaire. Un avantage notable les evenements communautaires vibrants, qui booste la participation.
DГ©couvrir le contenu|
J’ai une affection particuliere pour Gamdom Casino, ca invite a l’aventure. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, proposant des jeux de table classiques. Avec des depots fluides. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Les gains arrivent sans delai, en revanche plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. En bref, Gamdom Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. En bonus la navigation est intuitive et lisse, apporte une touche d’excitation. Un point fort les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, offre des recompenses continues.
VГ©rifier le site|
Je suis sous le charme de Betway Casino, ca transporte dans un univers de plaisirs. Les options sont aussi vastes qu’un horizon, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. Le bonus initial est super. Le service client est excellent. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, occasionnellement plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. Globalement, Betway Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. Par ailleurs le site est rapide et style, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Egalement excellent les evenements communautaires vibrants, assure des transactions fluides.
Parcourir le site|
перепланировка в нежилом помещении https://www.pereplanirovka-nezhilogo-pomeshcheniya17.ru .
перепланировка нежилого помещения в москве http://www.pereplanirovka-nezhilogo-pomeshcheniya18.ru .
смартвэй официальный сайт смвэй http://www.sajt-smart-way.ru .
кожаные жалюзи с электроприводом avtomaticheskie-zhalyuzi.ru .
net seo http://www.optimizaciya-i-seo-prodvizhenie-sajtov-moskva.ru .
сколько стоит перепланировка квартиры в бти [url=http://www.skolko-stoit-uzakonit-pereplanirovku-1.ru]сколько стоит перепланировка квартиры в бти[/url] .
перепланировка нежилого помещения в нежилом здании перепланировка нежилого помещения в нежилом здании .
бамбуковые электрожалюзи http://www.avtomaticheskie-zhalyuzi.ru .
компании по продвижению сайта http://www.reiting-kompanii-po-prodvizheniyu-sajtov.ru/ .
Усі деталі за посиланням: https://prezza.com.ua/transport.html
компании занимающиеся продвижением сайтов компании занимающиеся продвижением сайтов .
Je suis bluffe par Belgium Casino, ca invite a l’aventure. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Le service est disponible 24/7. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, par contre des recompenses en plus seraient un bonus. En resume, Belgium Casino est un endroit qui electrise. Pour ajouter le design est moderne et energique, ce qui rend chaque moment plus vibrant. Egalement excellent le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, offre des recompenses continues.
Explorer plus|
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Betify Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, proposant des jeux de table classiques. Il propulse votre jeu des le debut. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Le processus est clair et efficace, neanmoins des offres plus importantes seraient super. Pour faire court, Betify Casino offre une aventure memorable. A souligner le design est style et moderne, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. Un bonus le programme VIP avec des privileges speciaux, garantit des paiements securises.
https://betifycasino365fr.com/|
J’adore l’energie de Betify Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. Les options de jeu sont infinies, proposant des jeux de cartes elegants. Il offre un demarrage en fanfare. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Le processus est transparent et rapide, en revanche des recompenses supplementaires seraient parfaites. Pour conclure, Betify Casino est une plateforme qui pulse. Par ailleurs le design est tendance et accrocheur, permet une plongee totale dans le jeu. Egalement top les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, offre des recompenses regulieres.
Voir maintenant|
ganabet casino https://ganabet-online.com .
стоимость оформления перепланировки квартиры стоимость оформления перепланировки квартиры .
newsky slot login http://www.newsky-online.com .
Töltsd le az apk verziót, és élvezd a Casino Royale játékokat bárhol. Nyerj nagyot a Casino Royale online platformon – gyors, egyszerű, biztonságos. Fedezd fel a legjobb ajánlatokat a venice hotel casino royale játékai között. Nyerj hatalmas összegeket a Casino Royale élő játékain.
A Casino Royale játékai között megtalálod a legjobb rulett és póker asztalokat. A Casino Royale wallpaper 4K a legjobb háttér a telefonodra. A legjobb casino royale online játékok most elérhetők Magyarországon. A játékosok véleménye alapján ez az egyik legjobb oldal. A Casino Royale játékainál fontos a stratégia és a türelem. A legújabb élő fogadások és kaszinó játékok egy helyen. Kiváló ügyfélszolgálat és bónusz lehetőségek várnak.
J’adore l’energie de Betway Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. Le bonus de depart est top. Le support est efficace et amical. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, quelquefois des recompenses en plus seraient un bonus. En fin de compte, Betway Casino merite un detour palpitant. A souligner le site est rapide et immersif, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. A souligner les competitions regulieres pour plus de fun, propose des privileges sur mesure.
Explorer le site|
Je suis fascine par Betway Casino, ca transporte dans un univers de plaisirs. La selection est riche et diversifiee, offrant des sessions live palpitantes. Avec des depots instantanes. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Le processus est clair et efficace, cependant des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. En bref, Betway Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. De surcroit la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. A souligner les tournois reguliers pour la competition, renforce la communaute.
VГ©rifier le site|
J’ai un faible pour Gamdom Casino, il offre une experience dynamique. Les options de jeu sont incroyablement variees, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. Il rend le debut de l’aventure palpitant. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, malgre tout des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. Dans l’ensemble, Gamdom Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs. Ajoutons aussi la navigation est fluide et facile, facilite une experience immersive. Egalement super les evenements communautaires engageants, assure des transactions fiables.
Voir le site|
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Belgium Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. 100% jusqu’a 500 € plus des tours gratuits. Le support est fiable et reactif. Le processus est simple et transparent, quelquefois des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. En bref, Belgium Casino est une plateforme qui pulse. A noter le design est moderne et energique, apporte une energie supplementaire. A signaler les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, offre des recompenses regulieres.
VГ©rifier le site|
J’adore le dynamisme de Betify Casino, on ressent une ambiance de fete. Les jeux proposes sont d’une diversite folle, avec des slots aux designs captivants. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Disponible 24/7 pour toute question. Le processus est transparent et rapide, a l’occasion plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. Globalement, Betify Casino vaut une visite excitante. Pour completer la plateforme est visuellement vibrante, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. Egalement top le programme VIP avec des privileges speciaux, cree une communaute vibrante.
Obtenir plus|
Je suis totalement conquis par Belgium Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. Les options de jeu sont incroyablement variees, offrant des tables live interactives. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Les retraits sont simples et rapides, neanmoins quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. Dans l’ensemble, Belgium Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. Ajoutons que le design est moderne et energique, permet une plongee totale dans le jeu. A souligner le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, propose des avantages sur mesure.
Savoir plus|
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Azur Casino, ca offre une experience immersive. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, neanmoins des offres plus genereuses seraient top. Dans l’ensemble, Azur Casino est un must pour les passionnes. Par ailleurs le design est tendance et accrocheur, ajoute une touche de dynamisme. Un avantage les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, qui stimule l’engagement.
Explorer le site|
Je suis completement seduit par 1xBet Casino, on ressent une ambiance de fete. Le catalogue est un tresor de divertissements, offrant des sessions live immersives. Il donne un avantage immediat. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, quelquefois des bonus varies rendraient le tout plus fun. Pour finir, 1xBet Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. A noter la navigation est fluide et facile, incite a rester plus longtemps. Egalement genial le programme VIP avec des privileges speciaux, renforce le lien communautaire.
Continuer ici|
J’ai une affection particuliere pour Lucky 31 Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. La selection est riche et diversifiee, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Le support est efficace et amical. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, par ailleurs des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. Au final, Lucky 31 Casino offre une aventure memorable. Ajoutons aussi le site est fluide et attractif, incite a rester plus longtemps. A souligner les evenements communautaires vibrants, garantit des paiements rapides.
http://www.lucky31casino365fr.com|
J’adore la vibe de Action Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. La selection est riche et diversifiee, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. Il donne un avantage immediat. Le support est pro et accueillant. Le processus est transparent et rapide, occasionnellement des offres plus genereuses seraient top. En resume, Action Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. D’ailleurs le design est style et moderne, ajoute une vibe electrisante. Un avantage notable les evenements communautaires vibrants, propose des privileges personnalises.
Plongez-y|
Pretty section of content. I just stumbled upon your website and in accession capital to assert that I get in fact enjoyed account your blog posts. Any way I will be subscribing to your feeds and even I achievement you access consistently rapidly.
https://sa-kat.de/2025/10/26/melbet-obzor-2025-2/
casino ganabet l?nea https://www.ganabet-online.com .
сколько стоит согласование перепланировки квартиры сколько стоит согласование перепланировки квартиры .
J’ai une passion debordante pour Azur Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. Le catalogue est un tresor de divertissements, offrant des experiences de casino en direct. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Disponible 24/7 pour toute question. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, mais encore des recompenses en plus seraient un bonus. Dans l’ensemble, Azur Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. A noter la plateforme est visuellement vibrante, incite a rester plus longtemps. Un point cle le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, offre des bonus exclusifs.
Passer à l’action|
Thanks for the good writeup. It actually used to be a amusement account it. Look complicated to more added agreeable from you! However, how can we be in contact?
https://tigaan.com/uncategorized/melbet-bukmekerskaya-obzor-2025/
узаконить перепланировку цена узаконить перепланировку цена .
Официальный сайт Kraken https://kra44-cc.at безопасная платформа для анонимных операций в darknet. Полный доступ к рынку через актуальные зеркала и onion ссылки.
перепланировка квартиры цена перепланировка квартиры цена .
Je suis accro a Azur Casino, il cree une experience captivante. La gamme est variee et attrayante, offrant des sessions live palpitantes. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Le support est pro et accueillant. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, a l’occasion des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. Pour finir, Azur Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. Ajoutons que la plateforme est visuellement dynamique, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. Un atout les options variees pour les paris sportifs, renforce la communaute.
Entrer maintenant|
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour 1xBet Casino, il offre une experience dynamique. Le choix est aussi large qu’un festival, avec des slots aux designs captivants. Il amplifie le plaisir des l’entree. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, neanmoins quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. Pour faire court, 1xBet Casino est une plateforme qui pulse. Par ailleurs le design est tendance et accrocheur, booste le fun du jeu. Un plus les evenements communautaires engageants, garantit des paiements rapides.
Tout apprendre|
Je suis totalement conquis par Lucky 31 Casino, ca pulse comme une soiree animee. Les options de jeu sont infinies, comprenant des titres adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Il rend le debut de l’aventure palpitant. Le suivi est toujours au top. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, parfois des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. Pour conclure, Lucky 31 Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. Pour ajouter le site est rapide et immersif, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Un element fort les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, qui booste la participation.
Commencer Г explorer|
J’adore le dynamisme de 1xBet Casino, ca invite a l’aventure. Les options de jeu sont infinies, proposant des jeux de cartes elegants. Il amplifie le plaisir des l’entree. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Le processus est simple et transparent, cependant des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. Au final, 1xBet Casino merite une visite dynamique. Par ailleurs la plateforme est visuellement captivante, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. Un point cle les options variees pour les paris sportifs, cree une communaute vibrante.
Voir la page|
Je suis totalement conquis par 1xBet Casino, ca invite a l’aventure. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, bien que plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du peps. Pour conclure, 1xBet Casino est un immanquable pour les amateurs. A noter la navigation est simple et intuitive, apporte une energie supplementaire. Egalement super les evenements communautaires vibrants, renforce le lien communautaire.
DГ©couvrir les faits|
valor casino login valor casino login .
surewin-casino surewin-online.com .
beep beep casino bonus code http://beepbeepcasino-online.com .
good day 4 play casino no deposit bonus good day 4 play casino no deposit bonus .
newsky88 newsky-online.com .
J’ai un faible pour Azur Casino, on ressent une ambiance de fete. Les jeux proposes sont d’une diversite folle, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. Il offre un demarrage en fanfare. Le support est fiable et reactif. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, toutefois des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. Au final, Azur Casino vaut une visite excitante. A noter le design est moderne et energique, apporte une energie supplementaire. Un point cle les transactions en crypto fiables, qui booste la participation.
Essayer maintenant|
valor bet casino app download http://valorslots.com/ .
цена ремонта с перепланировкой http://www.uzakonit-pereplanirovku-cena.ru/ .
перепланировки квартир https://www.soglasovanie-pereplanirovki-1.ru .
surewin casino malaysia http://www.surewin-online.com/ .
beepbeep casino https://beepbeepcasino-online.com .
ganabet bono $400 casino https://www.ganabet-online.com .
valor slots valor slots .
good day 4 play good day 4 play .
newsky88 slot https://newsky-online.com .
казино beep beep https://beepbeepcasino-online.com/ .
surewin casino https://surewin-online.com/ .
J’ai une affection particuliere pour Lucky 31 Casino, ca offre une experience immersive. On trouve une profusion de jeux palpitants, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. Avec des transactions rapides. Le support est pro et accueillant. Les retraits sont simples et rapides, a l’occasion des recompenses supplementaires seraient parfaites. Pour conclure, Lucky 31 Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. A mentionner le design est moderne et energique, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. Un avantage notable les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, garantit des paiements securises.
Ouvrir le site|
Je suis accro a Azur Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, offrant des sessions live palpitantes. Avec des depots fluides. Les agents sont toujours la pour aider. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, de temps en temps des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. Pour finir, Azur Casino est un immanquable pour les amateurs. Par ailleurs la navigation est intuitive et lisse, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Particulierement attrayant les competitions regulieres pour plus de fun, propose des privileges sur mesure.
Voir plus|
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Action Casino, ca invite a l’aventure. Les jeux proposes sont d’une diversite folle, offrant des experiences de casino en direct. Il propulse votre jeu des le debut. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Le processus est simple et transparent, par moments des offres plus genereuses seraient top. En resume, Action Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. D’ailleurs le design est tendance et accrocheur, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Egalement genial les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, offre des bonus exclusifs.
Lire plus|
Je suis sous le charme de Azur Casino, on ressent une ambiance de fete. La selection de jeux est impressionnante, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. Avec des depots instantanes. Le service client est excellent. Les gains arrivent sans delai, neanmoins des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. Pour conclure, Azur Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. Pour ajouter l’interface est simple et engageante, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. Un plus les tournois reguliers pour la competition, garantit des paiements rapides.
DГ©couvrir|
J’ai une affection particuliere pour Lucky 31 Casino, ca transporte dans un monde d’excitation. Le choix est aussi large qu’un festival, offrant des experiences de casino en direct. Il offre un demarrage en fanfare. Disponible 24/7 par chat ou email. Les transactions sont fiables et efficaces, bien que des offres plus genereuses rendraient l’experience meilleure. Pour finir, Lucky 31 Casino assure un fun constant. D’ailleurs le site est fluide et attractif, incite a prolonger le plaisir. Un point fort le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, offre des bonus constants.
Aller à l’intérieur|
J’ai un faible pour 1xBet Casino, ca offre une experience immersive. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, offrant des experiences de casino en direct. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Le suivi est toujours au top. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, en revanche des offres plus genereuses rendraient l’experience meilleure. Pour finir, 1xBet Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. En complement le site est rapide et engageant, apporte une touche d’excitation. A mettre en avant le programme VIP avec des privileges speciaux, propose des privileges personnalises.
DГ©couvrir les faits|
Je suis bluffe par Action Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. La bibliotheque est pleine de surprises, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Le support est efficace et amical. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, occasionnellement quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. En conclusion, Action Casino offre une aventure memorable. Pour ajouter le design est tendance et accrocheur, incite a rester plus longtemps. Particulierement fun les competitions regulieres pour plus de fun, qui stimule l’engagement.
Voir la page d’accueil|
J’adore l’energie de Lucky 31 Casino, ca invite a l’aventure. Les options sont aussi vastes qu’un horizon, comprenant des titres adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Il donne un elan excitant. Le service est disponible 24/7. Le processus est clair et efficace, cependant quelques free spins en plus seraient bienvenus. Pour conclure, Lucky 31 Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. A souligner la plateforme est visuellement captivante, incite a rester plus longtemps. Un atout les evenements communautaires engageants, qui stimule l’engagement.
Voir plus|
Immediate Olux se distingue comme une plateforme d’investissement en crypto-monnaies de pointe, qui exploite la puissance de l’intelligence artificielle pour proposer a ses membres des avantages concurrentiels decisifs.
Son IA etudie les marches financiers en temps reel, repere les opportunites et met en ?uvre des strategies complexes avec une precision et une vitesse inaccessibles aux traders humains, optimisant ainsi les perspectives de gain.
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Action Casino, ca transporte dans un univers de plaisirs. Les options de jeu sont incroyablement variees, comprenant des titres adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Il amplifie le plaisir des l’entree. Le service client est de qualite. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, de temps a autre plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. En conclusion, Action Casino vaut une visite excitante. Par ailleurs la navigation est claire et rapide, permet une immersion complete. Particulierement interessant les evenements communautaires dynamiques, offre des bonus constants.
Obtenir des infos|
Clarte Nexive se distingue comme une plateforme de placement crypto de pointe, qui met a profit la puissance de l’intelligence artificielle pour offrir a ses utilisateurs des atouts competitifs majeurs.
Son IA scrute les marches en temps reel, identifie les opportunites et met en ?uvre des strategies complexes avec une exactitude et une rapidite inatteignables pour les traders humains, augmentant de ce fait les perspectives de gain.
goliath casino review https://www.goliath-casino.com .
кухни на заказ санкт петербург кухни на заказ санкт петербург .
кухня на заказ спб https://kuhni-spb-12.ru/ .
Юридические переводы от бюро Перевод и Право Юридические переводы от бюро Перевод и Право .
устный перевод стоимость teletype.in/@alexd78/D1bRUvZKB7G .
Je suis enthousiasme par Azur Casino, ca transporte dans un monde d’excitation. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Le suivi est toujours au top. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, par contre des offres plus genereuses seraient top. En resume, Azur Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. En complement le design est moderne et attrayant, ajoute une vibe electrisante. Un plus les transactions crypto ultra-securisees, offre des bonus constants.
Explorer la page|
Je suis totalement conquis par Lucky 31 Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. On trouve une profusion de jeux palpitants, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. Le bonus initial est super. Les agents sont toujours la pour aider. Les gains sont transferes rapidement, par ailleurs des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. Globalement, Lucky 31 Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. En complement la plateforme est visuellement vibrante, permet une plongee totale dans le jeu. Un atout les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, cree une communaute soudee.
http://www.casinolucky31fr.com|
Je suis captive par 1xBet Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Les retraits sont simples et rapides, en revanche quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. Globalement, 1xBet Casino offre une aventure memorable. En complement la plateforme est visuellement dynamique, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. Un plus les evenements communautaires dynamiques, offre des recompenses continues.
Naviguer sur le site|
Je suis captive par Lucky 31 Casino, ca pulse comme une soiree animee. La selection est riche et diversifiee, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. Il amplifie le plaisir des l’entree. Le support est efficace et amical. Les transactions sont fiables et efficaces, rarement des recompenses supplementaires seraient parfaites. Au final, Lucky 31 Casino est un must pour les passionnes. En plus le site est rapide et immersif, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Un element fort le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, propose des avantages uniques.
https://lucky31casino366fr.com/|
J’adore l’energie de 1xBet Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, comprenant des titres adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Disponible 24/7 pour toute question. Les paiements sont surs et efficaces, bien que quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. En conclusion, 1xBet Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. Ajoutons aussi l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, facilite une experience immersive. Un avantage notable les options de paris sportifs variees, qui motive les joueurs.
Aller en ligne|
goliath casino app goliath-casino.com .
icebet casino logowanie https://icebet-online.com .
Je suis bluffe par Action Casino, il cree une experience captivante. On trouve une profusion de jeux palpitants, comprenant des titres adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Le processus est transparent et rapide, parfois des offres plus genereuses rendraient l’experience meilleure. Au final, Action Casino assure un fun constant. Pour couronner le tout la navigation est intuitive et lisse, booste l’excitation du jeu. A signaler les tournois reguliers pour la competition, qui dynamise l’engagement.
Plongez-y|
Je suis sous le charme de Azur Casino, ca transporte dans un monde d’excitation. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, parfois quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient geniaux. En fin de compte, Azur Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. En extra la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, permet une immersion complete. A souligner les transactions en crypto fiables, assure des transactions fluides.
Visiter la page web|
синхронный перевод услуги dzen.ru/a/aRDuRn3LkCngCegS .
юридический перевод заказать юридический перевод заказать .
устный перевод в москве teletype.in/@alexd78/D1bRUvZKB7G .
синхронный переводчик стоимость dzen.ru/a/aRDuRn3LkCngCegS .
aviator money http://www.aviator-game-cash.com .
aviator money http://www.aviator-game-winner.com .
aviation game aviation game .
it перевод цена telegra.ph/Oshibka-lokalizacii-pochemu-vash-IT-produkt-ne-ponimayut-za-granicej-11-09 .
топ -10 бюро переводов в мск teletype.in/@alexd78/iF-xjHhC3iA .
синхронный перевод заказать dzen.ru/a/aRDuRn3LkCngCegS .
Je suis emerveille par Pokerstars Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. Les options sont aussi vastes qu’un horizon, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. Il donne un elan excitant. Disponible 24/7 par chat ou email. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, quelquefois quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. Au final, Pokerstars Casino est un immanquable pour les amateurs. De plus l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. Un avantage les transactions en crypto fiables, renforce la communaute.
VГ©rifier ceci|
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Casinozer Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. Les options de jeu sont incroyablement variees, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Les transactions sont toujours fiables, de temps en temps des bonus varies rendraient le tout plus fun. En conclusion, Casinozer Casino est une plateforme qui pulse. Pour completer l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. Particulierement fun les competitions regulieres pour plus de fun, propose des avantages sur mesure.
DГ©couvrir dГЁs maintenant|
Je suis totalement conquis par Pokerstars Casino, on y trouve une vibe envoutante. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Les gains sont transferes rapidement, neanmoins des recompenses supplementaires seraient parfaites. En bref, Pokerstars Casino garantit un plaisir constant. En plus l’interface est lisse et agreable, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. A mettre en avant les transactions crypto ultra-securisees, renforce la communaute.
Emmenez-moi lГ -bas|
Je suis emerveille par Mystake Casino, ca offre une experience immersive. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, offrant des tables live interactives. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Les retraits sont simples et rapides, quelquefois plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du peps. Pour finir, Mystake Casino vaut une visite excitante. A noter l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. A mettre en avant les evenements communautaires engageants, propose des avantages uniques.
Essayer maintenant|
топ бюро переводов teletype.in/@alexd78/iF-xjHhC3iA .
IT перевод в бюро переводов Перевод и Право telegra.ph/Oshibka-lokalizacii-pochemu-vash-IT-produkt-ne-ponimayut-za-granicej-11-09 .
plane crash real money game https://aviator-game-deposit.com .
????? ??? http://www.aviator-game-predict.com .
электрические карнизы купить https://www.prokarniz36.ru .
Je suis completement seduit par Stake Casino, ca offre une experience immersive. La bibliotheque est pleine de surprises, incluant des options de paris sportifs dynamiques. Avec des depots instantanes. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, neanmoins des recompenses en plus seraient un bonus. En bref, Stake Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. En complement la navigation est intuitive et lisse, booste l’excitation du jeu. Un point fort les nombreuses options de paris sportifs, offre des recompenses continues.
Obtenir plus|
J’adore le dynamisme de Pokerstars Casino, on ressent une ambiance de fete. La bibliotheque de jeux est captivante, incluant des options de paris sportifs dynamiques. Il propulse votre jeu des le debut. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, cependant des offres plus genereuses rendraient l’experience meilleure. En resume, Pokerstars Casino assure un fun constant. Ajoutons que le site est rapide et immersif, facilite une experience immersive. Egalement excellent les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, offre des recompenses regulieres.
Jeter un coup d’œil|
Je suis enthousiasme par Pokerstars Casino, ca offre une experience immersive. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, avec des slots aux designs captivants. Il propulse votre jeu des le debut. Le suivi est toujours au top. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, de temps en temps des offres plus genereuses rendraient l’experience meilleure. Globalement, Pokerstars Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. Par ailleurs l’interface est lisse et agreable, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. Un atout les evenements communautaires vibrants, propose des privileges sur mesure.
Lire les dГ©tails|
Je suis emerveille par Stake Casino, ca pulse comme une soiree animee. Les options sont aussi vastes qu’un horizon, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Les retraits sont simples et rapides, cependant plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. En conclusion, Stake Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. Notons egalement l’interface est simple et engageante, facilite une immersion totale. Un avantage notable les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, cree une communaute vibrante.
Voir les dГ©tails|
Je suis captive par Casinozer Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Le suivi est impeccable. Le processus est transparent et rapide, cependant des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. Pour faire court, Casinozer Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. A noter l’interface est intuitive et fluide, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. Egalement excellent les options de paris sportifs variees, offre des recompenses regulieres.
Voir le site|
Je suis epate par Mystake Casino, il cree une experience captivante. Le choix est aussi large qu’un festival, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Le service est disponible 24/7. Les gains sont verses sans attendre, mais des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. En conclusion, Mystake Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs. Par ailleurs la navigation est fluide et facile, incite a prolonger le plaisir. Egalement super les transactions en crypto fiables, propose des avantages uniques.
Aller sur le site|
Je suis totalement conquis par Casinozer Casino, il cree un monde de sensations fortes. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. Il rend le debut de l’aventure palpitant. Le service est disponible 24/7. Le processus est simple et transparent, par contre des offres plus genereuses rendraient l’experience meilleure. Pour conclure, Casinozer Casino est une plateforme qui pulse. Pour completer l’interface est lisse et agreable, permet une immersion complete. Un element fort les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, propose des avantages sur mesure.
Visiter maintenant|
карниз для штор с электроприводом http://provorota.su .
электронный карниз для штор электронный карниз для штор .
Je suis epate par Pokerstars Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. Le bonus de depart est top. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, mais encore des bonus plus frequents seraient un hit. Pour faire court, Pokerstars Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. A souligner le design est tendance et accrocheur, permet une immersion complete. Un point fort les evenements communautaires engageants, qui motive les joueurs.
Aller sur le site web|
электронный карниз для штор электронный карниз для штор .
электрокранизы https://www.elektrokarnizy77.ru .
электрические гардины для штор http://www.elektrokarniz-dlya-shtor15.ru .
электрокранизы https://elektrokarniz-dlya-shtor11.ru/ .
электрокарниз купить в москве электрокарниз купить в москве .
Je suis sous le charme de Pokerstars Casino, on y trouve une vibe envoutante. Le choix est aussi large qu’un festival, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Le service client est de qualite. Les retraits sont simples et rapides, a l’occasion des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. Pour finir, Pokerstars Casino assure un divertissement non-stop. D’ailleurs l’interface est simple et engageante, ce qui rend chaque moment plus vibrant. Egalement super les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, offre des bonus constants.
http://www.pokerstarscasino365fr.com|
Je suis accro a Stake Casino, il cree une experience captivante. Les options sont aussi vastes qu’un horizon, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Le processus est simple et transparent, de temps en temps des recompenses supplementaires seraient parfaites. Pour finir, Stake Casino est une plateforme qui pulse. En plus la plateforme est visuellement vibrante, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Particulierement attrayant le programme VIP avec des recompenses exclusives, propose des avantages sur mesure.
http://www.casinostakefr.com|
A Malina Casino ingyenes pörgetései kezdőknek is elég jó indulást adnak.
A Malina gyakori kérdések rész hasznos, ha új vagy a fogadásban. Az online casino Malina jó kombináció sport és kaszinó játékokkal.
A Malina Casino arvostelu sok pozitív tapasztalatot említ. Mobilon sokkal kényelmesebb játszani, én is így használom → malina casino app. A Malina Casino reviews nagyon sok pozitív visszajelzést tartalmaz.
A Malina Casino no deposit bonus sok sportfogadónak jó indulás. A Malina Casino erfahrungen főleg a sportfogadást dicséri. A Malina Casino 20 free spins kezdésnek ideális. A Malina Casino promo kódok változóak, érdemes figyelni.
J’ai une passion debordante pour Pokerstars Casino, ca invite a l’aventure. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Le suivi est impeccable. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, cependant plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. En conclusion, Pokerstars Casino est une plateforme qui pulse. Ajoutons aussi l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. Un bonus les transactions en crypto fiables, propose des avantages sur mesure.
Aller voir|
J’ai un faible pour Stake Casino, il cree un monde de sensations fortes. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, avec des slots aux designs captivants. Il donne un avantage immediat. Disponible 24/7 par chat ou email. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, de temps a autre plus de promotions frequentes boosteraient l’experience. En bref, Stake Casino offre une experience inoubliable. Pour completer la plateforme est visuellement captivante, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. Egalement excellent les tournois reguliers pour la competition, propose des privileges personnalises.
Parcourir maintenant|
Je suis fascine par Mystake Casino, ca transporte dans un monde d’excitation. Le choix est aussi large qu’un festival, proposant des jeux de table classiques. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Disponible 24/7 pour toute question. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, bien que quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. En bref, Mystake Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs. A noter le site est fluide et attractif, booste l’excitation du jeu. Un element fort le programme VIP avec des recompenses exclusives, assure des transactions fiables.
DГ©couvrir davantage|
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Casinozer Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. Avec des transactions rapides. Le service est disponible 24/7. Le processus est simple et transparent, parfois des recompenses supplementaires seraient parfaites. En conclusion, Casinozer Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. De plus l’interface est simple et engageante, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. Particulierement attrayant les paiements securises en crypto, garantit des paiements securises.
http://www.casinozercasino365fr.com|
J’ai une affection particuliere pour Mystake Casino, ca transporte dans un monde d’excitation. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, proposant des jeux de table classiques. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Les agents sont toujours la pour aider. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, bien que plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. En resume, Mystake Casino assure un fun constant. En extra la plateforme est visuellement vibrante, ajoute une vibe electrisante. Particulierement fun le programme VIP avec des recompenses exclusives, assure des transactions fluides.
DГ©couvrir les offres|
Je suis fascine par Casinozer Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. Les options sont aussi vastes qu’un horizon, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Les transactions sont toujours fiables, en revanche des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. En resume, Casinozer Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. En extra la plateforme est visuellement dynamique, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. A mettre en avant les options de paris sportifs variees, cree une communaute vibrante.
Ouvrir maintenant|
Срочно переведём документы – сертифицированный перевод документов для визы. Бюро переводов в Самаре. Работаем 10 лет. Документы, нотариальное заверение, срочно. Гарантия конфиденциальности.
Наследственные документы точно – перевод документов на русский нотариально заверенные. Перевод доверенностей. Самарское бюро. Нотариальное заверение. Срочно и качественно. Юридическая точность. Конфиденциально.
Je suis captive par Pokerstars Casino, ca offre une experience immersive. Les options sont aussi vastes qu’un horizon, proposant des jeux de cartes elegants. 100% jusqu’a 500 € plus des tours gratuits. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, cependant des recompenses supplementaires seraient parfaites. Pour faire court, Pokerstars Casino assure un fun constant. Notons aussi l’interface est lisse et agreable, facilite une experience immersive. Egalement genial les evenements communautaires engageants, propose des privileges personnalises.
Visiter maintenant|
Je suis captive par Coolzino Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. Le bonus de depart est top. Le service d’assistance est au point. Les gains arrivent sans delai, neanmoins des bonus varies rendraient le tout plus fun. En fin de compte, Coolzino Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. En plus la plateforme est visuellement vibrante, apporte une touche d’excitation. Egalement excellent les transactions en crypto fiables, qui motive les joueurs.
Lancer le site|
J’ai une affection particuliere pour MonteCryptos Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. Les jeux proposes sont d’une diversite folle, offrant des experiences de casino en direct. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, neanmoins des recompenses en plus seraient un bonus. Globalement, MonteCryptos Casino merite une visite dynamique. D’ailleurs la navigation est fluide et facile, facilite une immersion totale. Particulierement fun les transactions en crypto fiables, assure des transactions fiables.
Explorer plus|
J’adore la vibe de MonteCryptos Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. La selection de jeux est impressionnante, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, en revanche des bonus plus frequents seraient un hit. Au final, MonteCryptos Casino offre une aventure memorable. De plus le site est fluide et attractif, permet une plongee totale dans le jeu. Particulierement fun les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, offre des bonus constants.
DГ©couvrir les faits|
Je suis epate par Lucky8 Casino, il offre une experience dynamique. Les options de jeu sont infinies, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. Il propulse votre jeu des le debut. Le support est efficace et amical. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, malgre tout des bonus varies rendraient le tout plus fun. En conclusion, Lucky8 Casino vaut une visite excitante. En plus la navigation est claire et rapide, facilite une immersion totale. Un avantage les evenements communautaires engageants, renforce le lien communautaire.
Voir la page d’accueil|
Je ne me lasse pas de NetBet Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. La gamme est variee et attrayante, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. Avec des depots instantanes. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, de temps en temps des offres plus genereuses seraient top. Pour conclure, NetBet Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. En extra le design est tendance et accrocheur, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Un bonus les evenements communautaires vibrants, propose des avantages sur mesure.
Lire plus|
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de NetBet Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. 100% jusqu’a 500 € plus des tours gratuits. Le suivi est toujours au top. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, mais encore des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. Pour faire court, NetBet Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. A souligner la plateforme est visuellement vibrante, apporte une energie supplementaire. Un atout les transactions crypto ultra-securisees, cree une communaute soudee.
Passer à l’action|
birxbet giri? https://1xbet-12.com/ .
I believe everything wrote was very logical. However, what about this? suppose you were to write a killer headline? I ain’t saying your content is not solid., but suppose you added something to maybe grab people’s attention? I mean %BLOG_TITLE% is a little vanilla. You might glance at Yahoo’s home page and see how they create news headlines to grab viewers interested. You might try adding a video or a picture or two to get readers interested about everything’ve written. In my opinion, it might make your website a little bit more interesting.
Find Female Escorts Rio
What’s up friends, pleasant paragraph and fastidious urging commented here, I am really enjoying by these.
https://rockradio.com.ua/korpus-fary-hyundai-i30-1-ho-pokolinnya.html
курсовые заказ http://www.kupit-kursovuyu-6.ru .
кухни на заказ в спб недорого кухни на заказ в спб недорого .
Recommended reading: https://blaga.en.cx/guestbook/messages.aspx?page=1&fmode=gb&topic=379118&anchor#7972739
ремонт квартир сайты москва http://www.rejting-remontnyh-kompanij-moskvy.com .
jahaj udane wala game aviator-game-predict.com .
ремонт квартир москва качественно http://luchshie-remontnye-kompanii-moskvy.com/ .
What’s up, its good piece of writing concerning media print, we all be familiar with media is a enormous source of information.
biggest escort directory Rio
mt5 download for pc mt5 download for pc .
экспертиза протечки квартиры http://ekspertiza-zaliva-kvartiry-3.ru/ .
электрические жалюзи на окна электрические жалюзи на окна .
установление причины залива http://www.ekspertiza-zaliva-kvartiry-1.ru/ .
заказать филлеры оптом http://www.filler-kupit1.ru .
сколько стоит экспертиза после залива http://ekspertiza-zaliva-kvartiry-5.ru .
курсовые заказ курсовые заказ .
филлер цена http://www.filler-kupit.ru .
заказать курсовую работу спб http://www.kupit-kursovuyu-6.ru .
заказать качественную курсовую заказать качественную курсовую .
купить курсовую сайт купить курсовую сайт .
сайт для заказа курсовых работ http://kupit-kursovuyu-7.ru .
куплю курсовую работу куплю курсовую работу .
наркология клиника наркология клиника .
карнизы с электроприводом купить prokarniz36.ru .
электрокарниз двухрядный цена http://www.elektrokarniz-dlya-shtor499.ru/ .
карниз электроприводом штор купить http://www.elektrokarniz-dlya-shtor11.ru .
наркологический центр москва наркологический центр москва .
двойные рулонные шторы с электроприводом https://rulonnye-shtory-s-elektroprivodom177.ru .
умные шторы умные шторы .
аренда погрузчик экскаватор arenda-ekskavatora-pogruzchika-5.ru .
подвал дома ремонт gidroizolyacziya-podvala-iznutri-czena.ru .
обмазочная гидроизоляция цена обмазочная гидроизоляция цена .
усиление проема металлом усиление проема металлом .
инъекционная гидроизоляция своими руками инъекционная гидроизоляция своими руками .
экскаватор погрузчик jcb аренда https://www.arenda-ekskavatora-pogruzchika-6.ru .
покупка курсовых работ kupit-kursovuyu-21.ru .
гидроизоляция цена за метр gidroizolyacziya-czena.ru .
усиление проёмов композитными материалами http://www.usilenie-proemov1.ru .
стоимость аренды экскаватора погрузчика за час стоимость аренды экскаватора погрузчика за час .
Excellent blog you have here but I was wondering if you knew of any forums that cover the same topics discussed here? I’d really like to be a part of group where I can get feedback from other experienced individuals that share the same interest. If you have any recommendations, please let me know. Bless you!
凯伦皮里第一季高清完整版,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
Pass completion, accuracy rates and distribution statistics tracked
爱一帆海外版,专为华人打造的高清视频平台,支持全球加速观看。
Simply wanna remark on few general things, The website pattern is perfect, the written content is rattling superb : D.
范德沃克第二季高清完整版AI深度学习内容匹配,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
塔尔萨之王第二季高清完整版,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
中職粉絲必備的官方認證資訊平台,24小時不間斷提供官方中職新聞、球員數據分析,以及專業的比賽預測。
Bundesliga livescore today, German football with Bayern Munich and Dortmund updates
Best New Online Casino Australia 2025 Fresh Bonuses Waiting
ifvod平台,专为海外华人设计,提供高清视频和直播服务。
iyftv海外华人首选,智能AI观看体验优化,提供最新华语剧集、美剧、日剧等高清在线观看。
官方授权的ifuntv海外华人首选,第一时间提供最新华语剧集、美剧、日剧等高清在线观看。
范德沃克第二季高清完整官方版,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。