Climate resilience refers to the capacity of individuals, communities, institutions, and ecosystems to anticipate, prepare for, respond to, and recover from the adverse impacts….
Intoduction

- Climate resilience is the ability of systems, communities, and ecosystems. Tto anticipate, prepare for, respond to, and recover from the adverse impacts of climate change. In the face of escalating climate challenges, including extreme weather events and shifting environmental conditions, building resilience has become paramount. It involves proactive measures such as adaptation planning, constructing resilient infrastructure. Managing natural resources sustainably, and fostering social and economic adaptability. Climate resilience is not just about weathering the storm. It is about creating robust systems that can thrive in the midst of change. By integrating diverse strategies across various sectors. It aims to fortify societies and ecosystems against the impacts of a rapidly evolving climate, promoting sustainability and safeguarding the well-being of communities worldwide.
- Climate resilience refers to the capacity of individuals, communities, institutions, and ecosystems. To anticipate, prepare for, respond to, and recover from the adverse impacts of climate change. It involves developing strategies and measures to minimize vulnerability and enhance the ability to adapt to the changing climate conditions. Climate resilience is crucial because climate change is leading to more frequent and severe weather events, such as hurricanes, floods, droughts, and heatwaves.
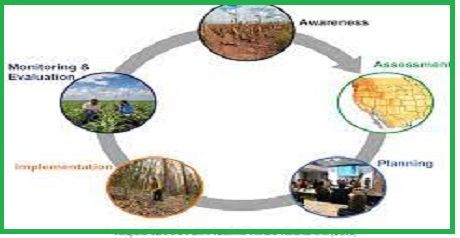
Key components of climate resilience include:
- Adaptation Planning: Developing and implementing strategies to adjust to the changing climate, considering both short-term and long-term impacts.
- Infrastructure Resilience: Designing and constructing infrastructure that can withstand extreme weather events and changing climate conditions.
- Natural Resource Management: Implementing sustainable practices for the management of natural resources, including water, land, and biodiversity. To ensure their resilience to climate change.
- Early Warning Systems: Establishing effective systems to provide timely and accurate information about impending climate-related hazards. Allowing communities to take preventive actions.
- Social and Economic Resilience: Strengthening the capacity of communities and economies to withstand and recover from climate-related shocks, including the development of diverse and robust livelihoods.
- Ecosystem Conservation: Protecting and restoring ecosystems that play a crucial role in climate regulation, such as forests, wetlands, and coastal areas.
- Education and Capacity Building: Increasing awareness and understanding of climate change impacts, as well as building the skills and knowledge needed to implement adaptive strategies.
- Governance and Policy: Developing and enforcing policies that support climate resilience at local, national, and international levels.

Efforts to enhance climate resilience require collaboration and coordination among governments, communities, businesses, and non-governmental organizations. It involves a combination of technical, social, economic, and environmental measures to build a more resilient and sustainable future in the face of a changing climate.

Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
Hiya, I’m really glad I have found this info. Nowadays bloggers publish only about gossips and net and this is actually irritating. A good web site with exciting content, this is what I need. Thank you for keeping this web site, I will be visiting it. Do you do newsletters? Can’t find it.
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me. https://www.binance.info/uk-UA/register?ref=W0BCQMF1
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?